Review of Pre-Ignition Research in Methanol Engines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Application of Methanol Fuel in Engines
2.1. Spark-Ignition Methanol Engines
2.2. Dual-Fuel Methanol Combustion Systems
2.3. Compression-Ignition Methanol Engines
3. Issues with Methanol as an Engine Fuel
4. Pre-Ignition and Knocking in Methanol Engines
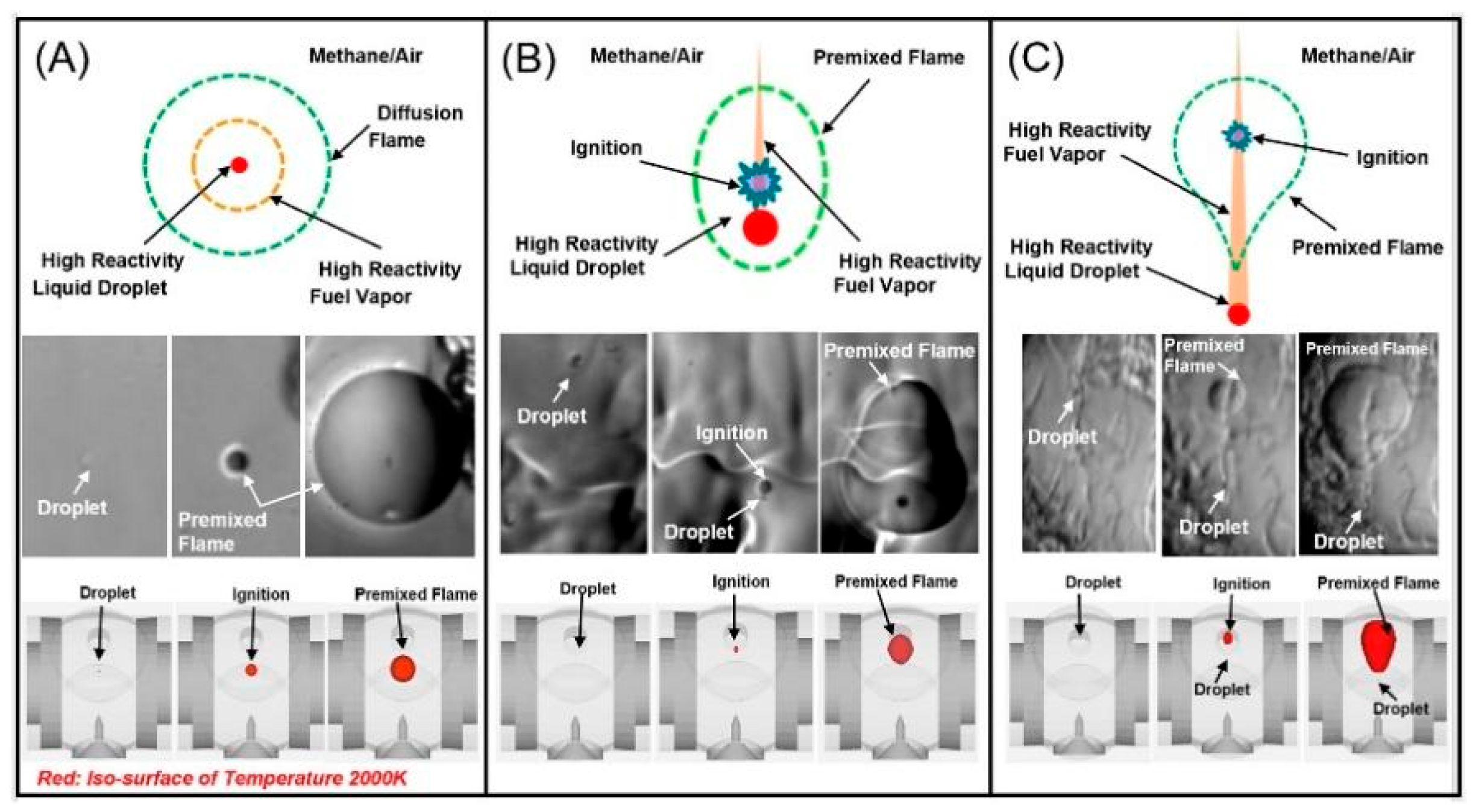
4.1. Manifestations of Pre-Ignition in Methanol Engines
4.2. Mechanisms and Sources of Pre-Ignition
4.2.1. Sustained Pre-Ignition
4.2.2. Sporadic Pre-Ignition
4.3. Knocking Behavior of Methanol
4.3.1. End-Gas Auto-Ignition-Induced Knocking
4.3.2. Deflagration-Based Knocking
5. Factors Influencing Methanol Pre-Ignition and Mitigation Methods
5.1. Sustained Pre-Ignition
5.2. Sporadic Pre-Ignition
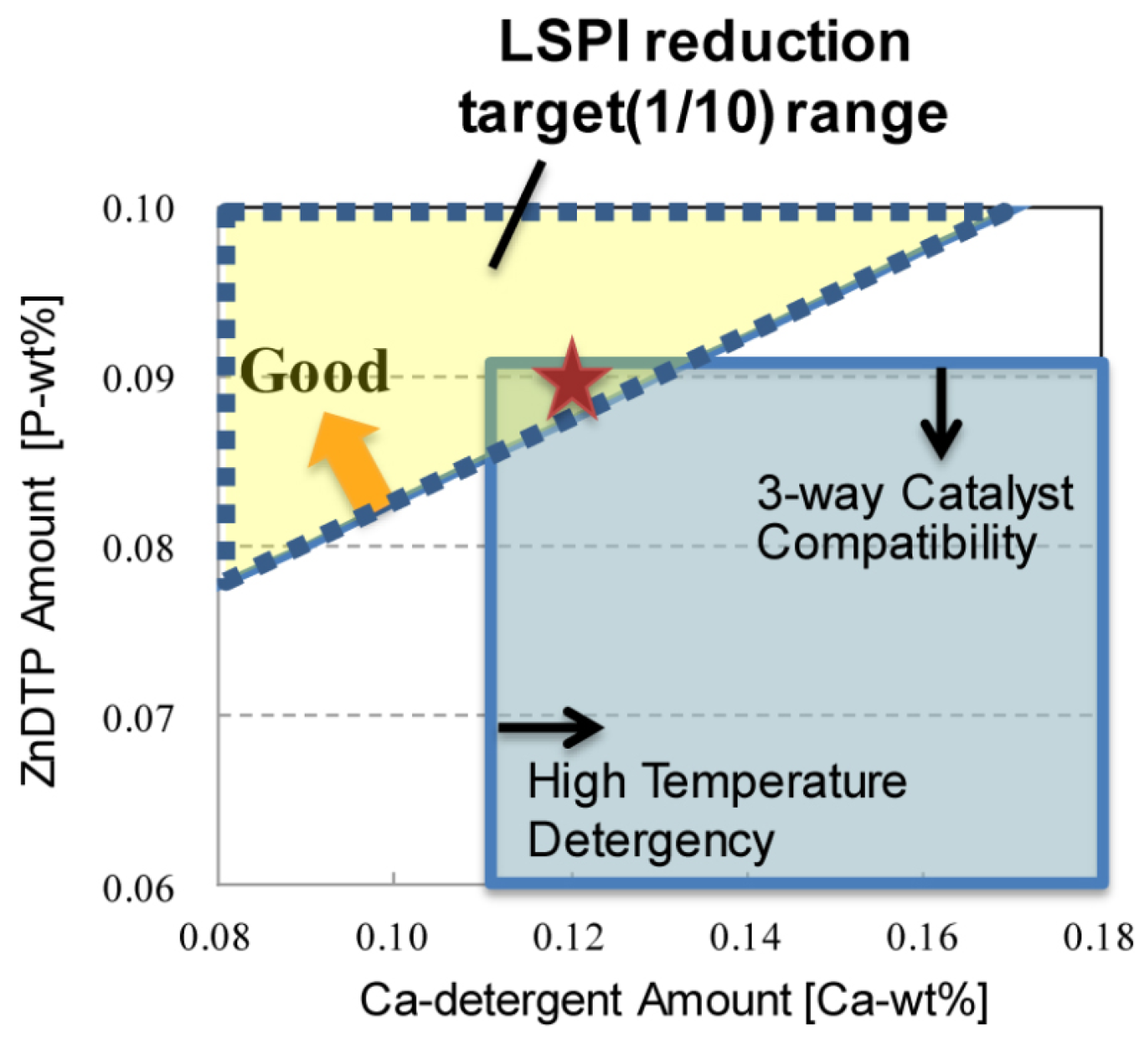
5.2.1. Influence of Engine Oil
- Base Oil
- Additives
- Engine Oil Droplet Size
5.2.2. Influence of Floating Particles in the Combustion Chamber
5.2.3. Influence of Engine Design Parameters and Operating Conditions
- Compression Ratio
- Piston Design
- Spark Plugs
- Thermodynamic Conditions
- Spray Wall Impingement and Injection Strategies
6. Current Challenges in Methanol Pre-Ignition Research
6.1. Limitations in In-Cylinder Combustion Testing Techniques
6.2. Limitations in Numerical Simulation Accuracy
6.3. Unclear Mechanisms of Methanol–Oil Interaction
7. Summary and Outlook
- Enhancing optical diagnostics for methanol engine combustion, enabling comprehensive analysis of ignition source types, locations, and flame propagation to deepen understanding of methanol pre-ignition processes;
- Incorporating Large Eddy Simulation (LES) and more detailed chemical kinetic models into numerical simulations to improve predictions of pre-ignition and knock with greater precision;
- Advancing research on the chemical reaction dynamics of engine oil in methanol environments to understand the theoretical basis for oil-induced pre-ignition and guide the development of pre-ignition-resistant oil formulations;
- Leveraging artificial intelligence to analyze pre-ignition patterns by extracting key features from extensive experimental data, enabling real-time monitoring and intelligent predictions of engine operating states;
- Employing novel methods to suppress mixture reactivity, such as water injection, which has proven effective in reducing cylinder temperatures and minimizing hotspots. Precise control of water injection timing, quantity, and location can mitigate rapid flame propagation, reducing pre-ignition and knocking risks. Additionally, ammonia, a low-carbon fuel with a high octane rating, shows promise for reducing methanol reactivity due to its high solubility in methanol;
- Utilizing in-cylinder direct injection and diffusion combustion techniques. Direct injection combined with multiple injections can enhance methanol atomization, reduce wall impingement, and lower the likelihood of oil dilution. Diffusion combustion, avoiding premixed flames altogether, is one of the most effective strategies for pre-ignition suppression.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China-SAE. Energy-Saving and New Energy Automobile Technology Roadmap 2.0; China-SAE: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Yao, A. Review on methanol as fuel for engines and its future prospect. J. Automot. Saf. Energy 2023, 14, 521–535. [Google Scholar]
- Verhelst, S.; Turner, J.W.G.; Sileghem, L.; Vancoillie, J. Methanol as a fuel for internal combustion engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 43–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.X.; Wang, Q.N.; Li, X.P.; Su, Y.; Hong, W. Influence of Ignition Timings and EGR on Performance and Emissions of a Spark-Ignition Methanol Engine with High Compression Ratio. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 953–954, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güdden, A.; Pischinger, S.; Geiger, J.; Heuser, B.; Müther, M. An experimental study on methanol as a fuel in large bore high speed engine applications—Port fuel injected spark ignited combustion. Fuel 2021, 303, 121292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, C.-M.; Su, Y.; Dou, H.-L.; Liu, X.-J. Effect of injection and ignition timings on performance and emissions from a spark-ignition engine fueled with methanol. Fuel 2010, 89, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Lin, K.Y.; Li, B.Z.; Song, R.Z.; Gong, Y.F. Experimental Study on the Stratified and Homogeneous Charge of a Direct-Injection Spark Ignition Methanol Engine. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2011, 225, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.; Liu, F. Numerical study of effect of injection and ignition timings on combustion and unregulated emissions of DISI methanol engine during cold start. Renew. Energy 2017, 112, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, J.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W.; Yu, X.; Li, W. Combustion and emissions characteristics of methanol/gasoline CISI engines under different injection modes. Fuel 2023, 333, 126506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, B.; Ren, R.; An, D.; Hong, W. Experimental Study on Combustion and Emission Characteristics of a Lean Burn Engine Fueled with Methanol/Gasoline. Chin. Intern. Combust. Engine Eng. 2018, 39, 48–52, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.C.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, A.; Bose, A. Methanol and petrol blended alternate fuel for future sustainable engine: A performance and emission analysis. Measurement 2020, 155, 107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cuty Clemente, E.R.; Hu, T.; Wei, Y. Study of spark ignition engine fueled with methanol/gasoline fuel blends. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, K. Effect of excess air/fuel ratio and methanol addition on the performance, emissions, and combustion characteristics of a natural gas/methanol dual-fuel engine. Fuel 2019, 255, 115799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Yuan, X.; Duan, Q.; Yang, B.; Zeng, K. Experimental investigation on performance and combustion characteristics of spark-ignition dual-fuel engine fueled with methanol/natural gas. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 150, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, F. Evaluation on combustion and lean-burn limit of a medium compression ratio hydrogen/methanol dual-injection spark-ignition engine under methanol late-injection. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, A.; Yao, C. Effects of diesel injection pressure on the performance and emissions of a HD common-rail diesel engine fueled with diesel/methanol dual fuel. Fuel 2015, 140, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yao, C.; Wang, Q.; Pan, W.; Han, G. Combustion and emission characteristics of a turbocharged diesel engine using high premixed ratio of methanol and diesel fuel. Fuel 2015, 140, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Denbratt, I. Experimental investigation into the combustion characteristics of a methanol-Diesel heavy duty engine operated in RCCI mode. Fuel 2018, 226, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Duan, Q.; Kou, H.; Zeng, K. Parametric study on effects of methanol injection timing and methanol substitution percentage on combustion and emissions of methanol/diesel dual-fuel direct injection engine at full load. Fuel 2020, 279, 118424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönn, K.; Swarts, A.; Kalaskar, V.; Alger, T.; Tripathi, R.; Keskiväli, J.; Kaario, O.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; Reitz, R.; Larmi, M. Low-speed pre-ignition and super-knock in boosted spark-ignition engines: A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 95, 101064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Investigation of methanol ignition phenomena using a rapid compression machine. Combust. Flame 2020, 211, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.R.; Blanco, J.A.; Swain, M.N. Abnormal Combustion in a Methanol Fueled Engine. SAE Trans. 1989, 98, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Yao, A.; Yao, C. The Detonation Phenomenon of High Compression Ratio Methanol Engines. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2017, 23, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Y. Study of knock in a high compression ratio spark-ignition methanol engine by multi-dimensional simulation. Energy 2013, 50, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suijs, W.; De Graeve, R.; Verhelst, S. An exploratory study of knock intensity in a large-bore heavy-duty methanol engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 302, 118089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Reitz, R.D. Knocking combustion in spark-ignition engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 61, 78–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DECHEMA, e.V. Society for Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology. In DECHEMA Corrosion Handbook; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dahnz, C.; Han, K.-M.; Spicher, U.; Magar, M.; Schießl, R.; Maas, U. Investigations on pre-ignition in highly supercharged SI engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2010, 3, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuka, T.; Kano, M.; Mori, K.; Werner, W.; Schulte, S. Study of HSPI/LSPI from Spark Plugs on Turbocharged Gasoline Engines. In Proceedings of the Knocking in Gasoline Engines, 5th International Conference, Berlin, Germany, 12–13 December 2017; Günther, M., Sens, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switherland, 2018; pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Niu, C.; Li, M.; Li, X. Study on Pre-ignition Control Technology of Methanol Engine. In Proceedings of the 2024 World Congress on Internal Combustion Engine, Tianjin, China, 19–23 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Auto-ignition and knocking characteristics of methanol. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Internal Combustion Engines, Wuxin, China, 20 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.J.; Emerson, D.R.; Bradley, D. Modes of reaction front propagation from hot spots. Combust. Flame 2003, 133, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Shuai, S.; Law, C.K. Analysis of pre-ignition to super-knock: Hotspot-induced deflagration to detonation. Fuel 2015, 144, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willand, J.; Daniel, M.; Montefrancesco, E.; Geringer, B.; Hofmann, P.; Kieberger, M. Limits on downsizing in spark ignition engines due to pre-ignition. MTZ Worldw. 2009, 70, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.; Alger, T. Lubricant Reactivity Effects on Gasoline Spark Ignition Engine Knock. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2012, 5, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Hirano, S.; Yamashita, M. Investigation of Engine Oil Effect on Abnormal Combustion in Turbocharged Direct Injection—Spark Ignition Engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2012, 5, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Yamashita, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Kato, K. Investigation of Engine Oil Effect on Abnormal Combustion in Turbocharged Direct Injection—Spark Ignition Engines (Part 2); SAE Technical Paper 2013-01-2569; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gschiel, K.; Wilfling, K.; Schneider, M. Development of a method to investigate the influence of engine oil and its additives on combustion anomalies in hydrogen engines. Automot. Engine Technol. 2024, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Teraji, A.; Noda, T. Mechanism Analysis on LSPI Occurrence in Boosted S. I. Engines; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-1867; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bhoite, S.; Windom, B.; Singh, J.; Montgomery, D.; Marchese, A.J. A study of ignition and combustion of liquid hydrocarbon droplets in premixed fuel/air mixtures in a rapid compression machine. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 2533–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, T.; Heiss, M.; Bobicic, N.; Holly, W.; Pritze, S. A Comprehensive Simulation Approach to Irregular Combustion; SAE Techincal Paper 2014-01-1214; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dingle, S.F.; Cairns, A.; Zhao, H.; Williams, J.; Williams, O.; Ali, R. Lubricant Induced Pre-Ignition in an Optical SI Engine; SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-1222; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Welling, O.; Moss, J.; Williams, J.; Collings, N. Measuring the Impact of Engine Oils and Fuels on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in Downsized Engines. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülser, T.; Grünefeld, G.; Brands, T.; Günther, M.; Pischinger, S. Optical Investigation on the Origin of Pre-Ignition in a Highly Boosted SI Engine Using Bio-Fuels; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Inoue, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Abnormal Combustion in a Highly Boosted SI Engine—The Occurrence of Super Knock; SAE Technical Paper 2012-01-1141; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Kou, H.; Zeng, K. Experimental study of knock combustion and direct injection on knock suppression in a high compression ratio methanol engine. Fuel 2022, 311, 122505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Takei, K.; Yoshida, K.; Shoji, H.; Yamazaki, A. Effect of EGR-Induced Hot Residual Gas on Combustion when Operating a Two-Stroke Engine on Alcohol Fuels; International Fuels & Lubricants Meeting & Exposition, 2000/10/16/; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Uddeen, K.; Tang, Q.; Shi, H.; Almatrafi, F.; Magnotti, G.; Turner, J. A Comparative Study of Knock Formation in Gasoline and Methanol Combustion Using a Multiple Spark Ignition Approach: An Optical Investigation; SAE Technical Paper 2024-01-2105; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, T. Knock of Low-Speed Two-Stroke Marine Dual-Fuel Engine with Low Injection Pressure of Natural Gas. J. Propuls. Technol. 2021, 42, 2522–2530. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, E.; Strickland, T.; Abboud, R.; MacDonald, J.; Lee, S.; Lopez Pintor, D. Deflagration-Based Knock of Methanol SI Combustion and Its Implications for Combustion Noise; SAE Technical Paper 2024-01-2819; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, B.; Tan, Y.; Gao, Y. High frequency combustion instability in liquid rocket engines: Review. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2024, 45, 113–139. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, E.; Abboud, R.; Strickland, T.; Kim, N.; Lopez Pintor, D.; Sjöberg, M. Effect of Dibutyl Ether—Methanol Blend Ratios on Deflagration-Based and Autoignition-Based Knock in Spark-Ignition Engines. Fuel 2024, 376, 132670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welling, O.; Collings, N.; Williams, J.; Moss, J. Impact of Lubricant Composition on Low-speed Pre-Ignition; SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-1213; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, A.; Burns, R.; Dougherty, R.; Deckman, D.; Patel, M. Investigation of Engine Oil Base Stock Effects on Low Speed Pre-Ignition in a Turbocharged Direct Injection SI Engine. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2016, 9, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Kuboyama, T.; Yamada, T.; Suzuki, M. Investigation of Lubricating Oil Properties Effect on Low Speed Pre-Ignition; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-1870; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, K.A.; Dingwell, L.; Yang, K.; Lam, W.Y.; Styer, J.P. Engine Oil Additive Impacts on Low Speed Pre-Ignition. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2016, 9, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Yamashita, M.; Hirano, S.; Kato, K.; Watanabe, I.; Ito, K. Engine Oil Development for Preventing Pre-Ignition in Turbocharged Gasoline Engine. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Noda, T.; Hirabe, M.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Kusaka, J.; Daisho, Y. An Investigation on the Ignition Characteristics of Lubricant Component Containing Fuel Droplets Using Rapid Compression and Expansion Machine. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2016, 9, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassai, M.; Torii, K.; Shiraishi, T.; Noda, T.; Goh, T.K.; Wilbrand, K.; Wakefield, S.; Healy, A.; Doyle, D.; Cracknell, R.; et al. Research on the Effect of Lubricant Oil and Fuel Properties on LSPI Occurrence in Boosted S. I. Engines; SAE Technical Paper 2016-01-2292; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kocsis, M.C.; Briggs, T.; Anderson, G. The Impact of Lubricant Volatility, Viscosity and Detergent Chemistry on Low Speed Pre-Ignition Behavior. SAE Int. J. Engines 2017, 10, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Xiang, S.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, P.; He, X.; Gupta, A.; Shao, H.; Wang, Y. Effect of Oil and Gasoline Properties on Pre-Ignition and Super-Knock in a Thermal Research Engine (TRE) and an Optical Rapid Compression Machine (RCM); SAE Technical Paper 2016-01-0720; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, K.; Shimizu, K.; Hayakawa, N.; Miyasaka, T.; Iijima, A.; Shoji, H.; Utaka, T.; Tamura, K.; Kamano, H. Influence of Ca−, Mg− and Na-Based Engine Oil Additives on Abnormal Combustion in a Spark-Ignition Engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2015, 9, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Miura, K.; Hayakawa, N.; Ishino, T.; Iijima, A.; Shoji, H.; Tamura, K.; Utaka, T.; Kamano, H. A Study on the Effect of a Calcium-Based Engine Oil Additive on Abnormal SI Engine Combustion. SAE Int. J. Engines 2014, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, K.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Kuboyama, T.; Imai, Y.; Yamada, T.; Hatamura, K. Investigation and Improvement of LSPI Phenomena and Study of Combustion Strategy in Highly Boosted SI Combustion in Low Speed Range; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-0756; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tsunoda, D.; Xie, M.; Kuboyama, T.; Morikawa, K. Numerical Simulation to Understand the Cause and Sequence of LSPI Phenomena and Suggestion of CaO Mechanism in Highly Boosted SI Combustion in Low Speed Range; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-0755; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, A.; Boese, D.; Young, A.W. Controlling Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in Modern Automotive Equipment Part 3: Identification of Key Additive Component Types and Other Lubricant Composition Effects on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, K.; Kato, T.; Ogano, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Kato, K.; Kaneko, T. Engine Oil Formulation Technology to Prevent Pre-ignition in Turbocharged Direct Injection Spark Ignition Engines; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-2027; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, N.; Miura, K.; Miyasaka, T.; Ishino, T.; Iijima, A.; Shoji, H.; Tamura, K.; Utaka, T.; Kamano, H. A Study on the Effect of Zn- and Mo-Based Engine Oil Additives on Abnormal SI Engine Combustion using In-Cylinder Combustion Visualization. SAE Int. J. Engines 2014, 8, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormos, B.; Garcia-Oliver, J.M.; Bastidas, S.; Domínguez, B.; Oliva, F.; Cárdenas, D. Investigation on low-speed pre-ignition from the quantification and identification of engine oil droplets release under ambient pressure conditions. Measurement 2020, 163, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtomo, M.; Miyagawa, H.; Koike, M.; Yokoo, N.; Nakata, K. Pre-Ignition of Gasoline-Air Mixture Triggered by a Lubricant Oil Droplet. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2014, 7, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y. Investigation on Ignition of a Single Lubricating Oil Droplet in Premixed Combustible Mixture at Engine-Relevant Conditions; SAE Technical Paper 2019-01-0298; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, S.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Simulation for Oil Droplet Evaporation Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions. Trans. CSICE 2019, 37, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. The Effect of Oil Intrusion on Super Knock in Gasoline Engine; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi, G.T.; Bradley, D. Pre-ignition and ‘super-knock’ in turbo-charged spark-ignition engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2012, 13, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenel, P.; Seyfried, P.; Kleeberg, H.; Tomazic, D. Systematic Approach to Analyze and Characterize Pre-Ignition Events in Turbocharged Direct-Injected Gasoline engines; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Miyashita, S.; Izumi, Y.; Hayakawa, Y. Study of low-speed pre-ignition in boosted spark ignition engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2014, 7, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Liu, H.; Long, Y.; Wang, J.-X. Experimental Study on Pre-Ignition and Super-Knock in Gasoline Engine Combustion with Carbon Particle at Elevated Temperatures and Pressures; SAE Technical Paper 2015-01-0752; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zahdeh, A.; Rothenberger, P.; Nguyen, W.; Anbarasu, M.; Schmuck-Soldan, S.; Schaefer, J.; Goebel, T. Fundamental approach to investigate pre-ignition in boosted SI engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 246–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.; Alger, T.; Westmoreland, B.; Rothmaier, A. The Effects of Piston Crevices and Injection Strategy on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in Boosted SI Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, T.; Kitajima, S.; Fujii, I. Pre-Ignition Phenomena of Methanol Fuel (M85) by the Post-Ignition Technique; SAE Technical Paper 892061; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Ota, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kudo, S. Analysis of Pre-ignition of Methanol Engine. Effect of Surface Reaction upon Spark Plug Electrode. Proceedings. JSAE Annu. Congr. 1992, 921, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Menrad, H.; Haselhorst, M.; Erwig, W. Pre-Ignition and Knock Behavior of AIcohol Fuels; SAE Technical Paper 821210; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ping, Y.; Yin, Q. Experimental Study on Preignition and Mega knock in Turbocharged DI Gasoline Engine. Chin. Intern. Combust. Engine Eng. 2012, 33, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Amann, M.; Mehta, D.; Alger, T. Engine Operating Condition and Gasoline Fuel Composition Effects on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in High-Performance Spark Ignited Gasoline Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccardi, J.-M.; Escudié, D. Overview of the main mechanisms triggering low-speed pre-ignition in spark-ignition engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2014, 16, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahnz, C.; Spicher, U. Irregular combustion in supercharged spark ignition engines—Pre-ignition and other phenomena. Int. J. Engine Res. 2010, 11, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shu, G.; Liang, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z. Super Knock and Preliminary Investigation of Its Influences on Turbocharged GDI Engine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Intern. Combust. Engines 2011, 29, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, D. Suppression Strategies for Super-Knock of Turbo-Charged GDI Engines. Trans. CSICE 2014, 32, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Song, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Li, D.-S.; Chen, T. Investigation on Pre-ignition and Super-Knock in Highly Boosted Gasoline Direct Injection Engines; SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-1212; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Suppression of super-knock in TC-GDI engine using two-stage injection in intake stroke (TSII). Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 57, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, J. Investigation on Pre-Ignition Suppression of Turbo-Charged GDI Engine. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2012, 18, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Amann, M.; Alger, T.; Mehta, D. The Effect of EGR on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in Boosted SI Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2011, 4, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaveev, S.; Magar, M.; Kubach, H.; Schiessl, R.; Spicher, U.; Maas, U. Premature Flame Initiation in a Turbocharged DISI Engine—Numerical and Experimental Investigations. SAE Int. J. Engines 2013, 6, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Hofmann, P.; Geringer, B.; Williams, J.; Moss, J. Influence of Different Fuel Properties and Gasoline—Ethanol Blends on Low-Speed Pre-Ignition in Turbocharged Direct Injection Spark Ignition Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Parameter | Methanol (CH3OH) | Gasoline (C5-12) 1 | Methane (CH4) | Ethanol (C2H5OH) | Hydrogen (H2) | Ammonia (NH3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Density (kg/m³) | 791 | 740 | 423 | 789 | 39 | 680 |
| Boiling Point (°C) | 64.7 | 30–225 | −161.5 | 78.4 | −252.9 | −33.3 |
| Lower Heating Value (MJ/kg) | 19.9 | 44.5 | 50 | 26.7 | 120 | 18.6 |
| Latent Heat of Vaporization (kJ/kg) | 1169 | 290–315 | 510 | 846 | 446 | 1370 |
| Laminar Flame Speed (m/s) | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 0.07 |
| Auto-Ignition Temperature (°C) | 385 | 247–280 | 537 | 365 | 585 | 651 |
| Octane Number | 109 | 92–97 | 120 | 108.6 | 93.7 | >130 |
| Air–Fuel Ratio | 6.5 | 14.7 | 17.2 | 9 | 34.6 | 6.1 |
| Flammability Limits (Volume %) | 6–36.5 | 1.4–7.6 | 4.4–17 | 3–19 | 4–75 | 15–28 |
| Minimum Ignition Energy (mJ) | 0.14 | 0.8 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhai, C.; Zeng, X.; Shi, K.; Wu, X.; Ma, T.; Qi, Y. Review of Pre-Ignition Research in Methanol Engines. Energies 2025, 18, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18010133
Li Z, Zhai C, Zeng X, Shi K, Wu X, Ma T, Qi Y. Review of Pre-Ignition Research in Methanol Engines. Energies. 2025; 18(1):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18010133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhijie, Changhui Zhai, Xiaoxiao Zeng, Kui Shi, Xinbo Wu, Tianwei Ma, and Yunliang Qi. 2025. "Review of Pre-Ignition Research in Methanol Engines" Energies 18, no. 1: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18010133
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhai, C., Zeng, X., Shi, K., Wu, X., Ma, T., & Qi, Y. (2025). Review of Pre-Ignition Research in Methanol Engines. Energies, 18(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18010133





