Investigation of Component Interactions During the Hydrothermal Process Using a Mixed-Model Cellulose/Hemicellulose/Lignin/Protein and Real Cotton Stalk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Intercomponent Blending Process
2.2.2. Hydrothermal Liquefaction
2.2.3. Characterization of Hydrothermal Bio-Oil
3. Results and Discussion
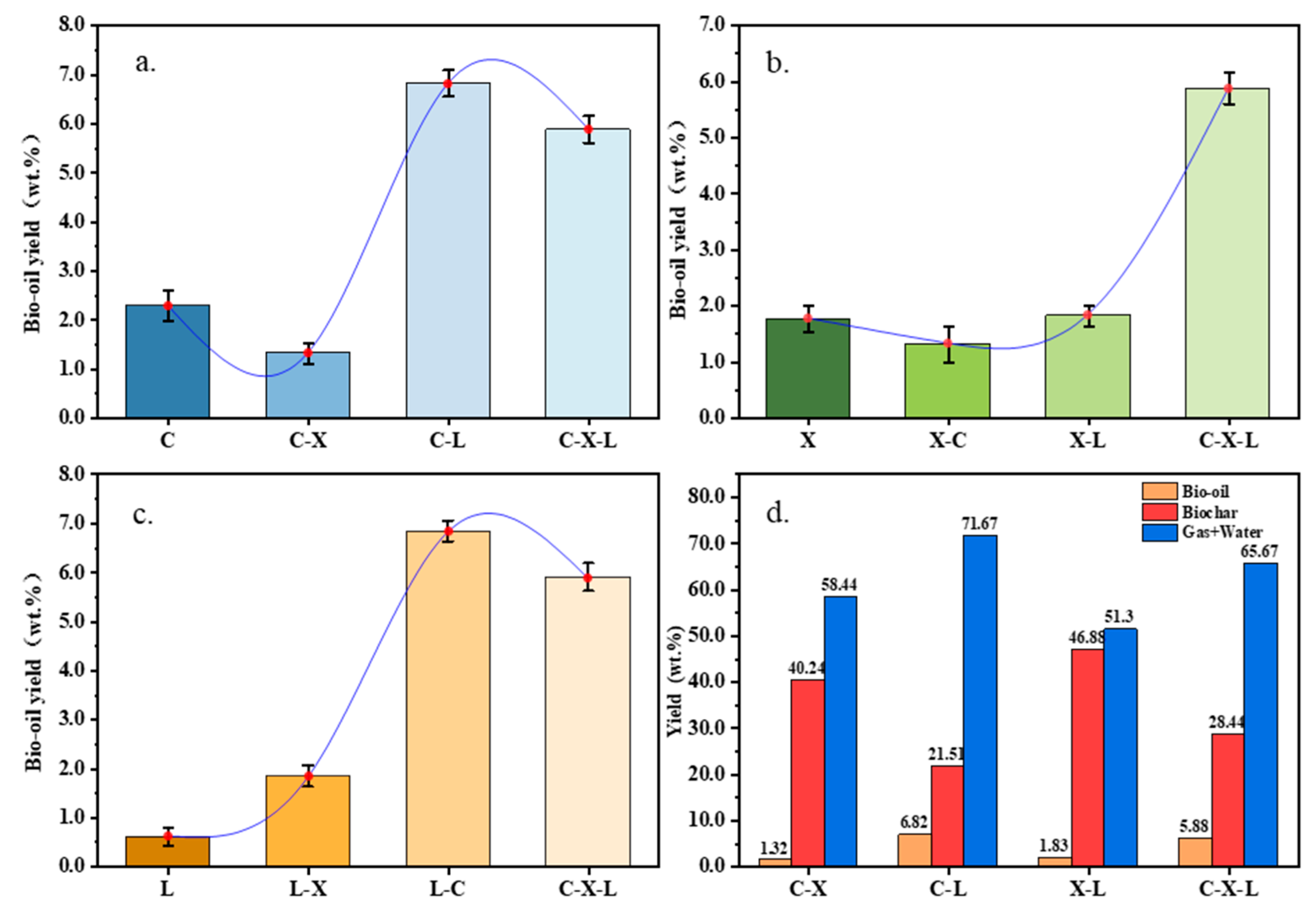
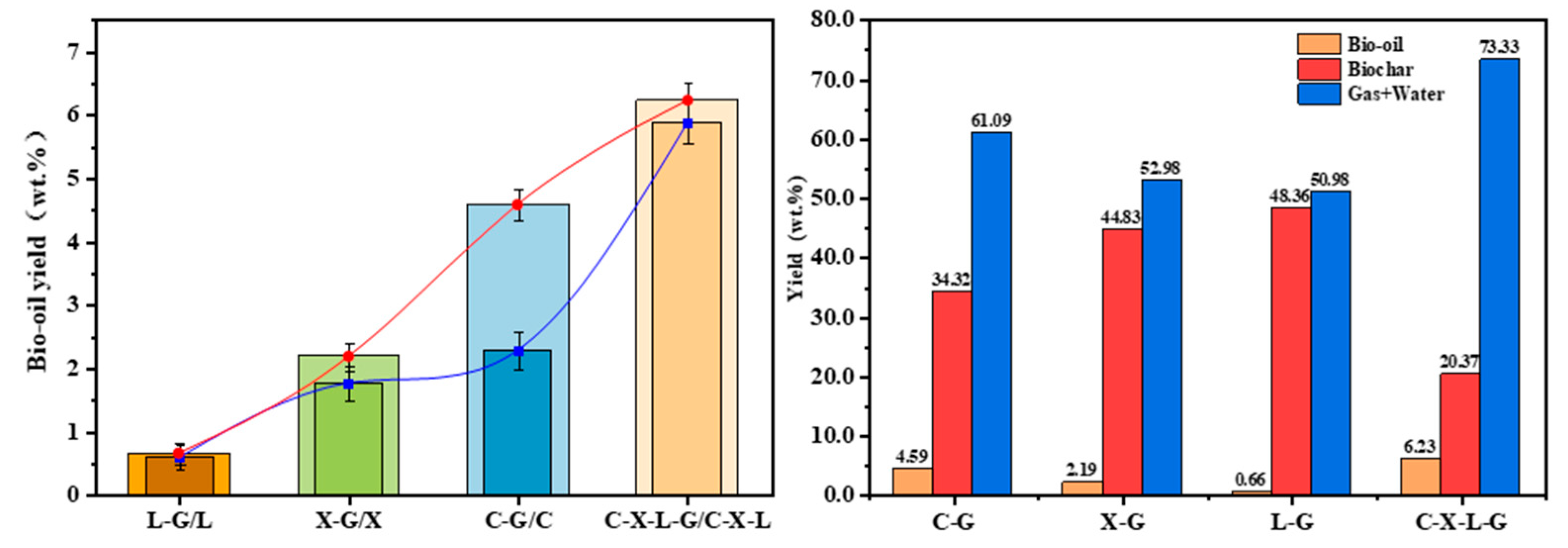
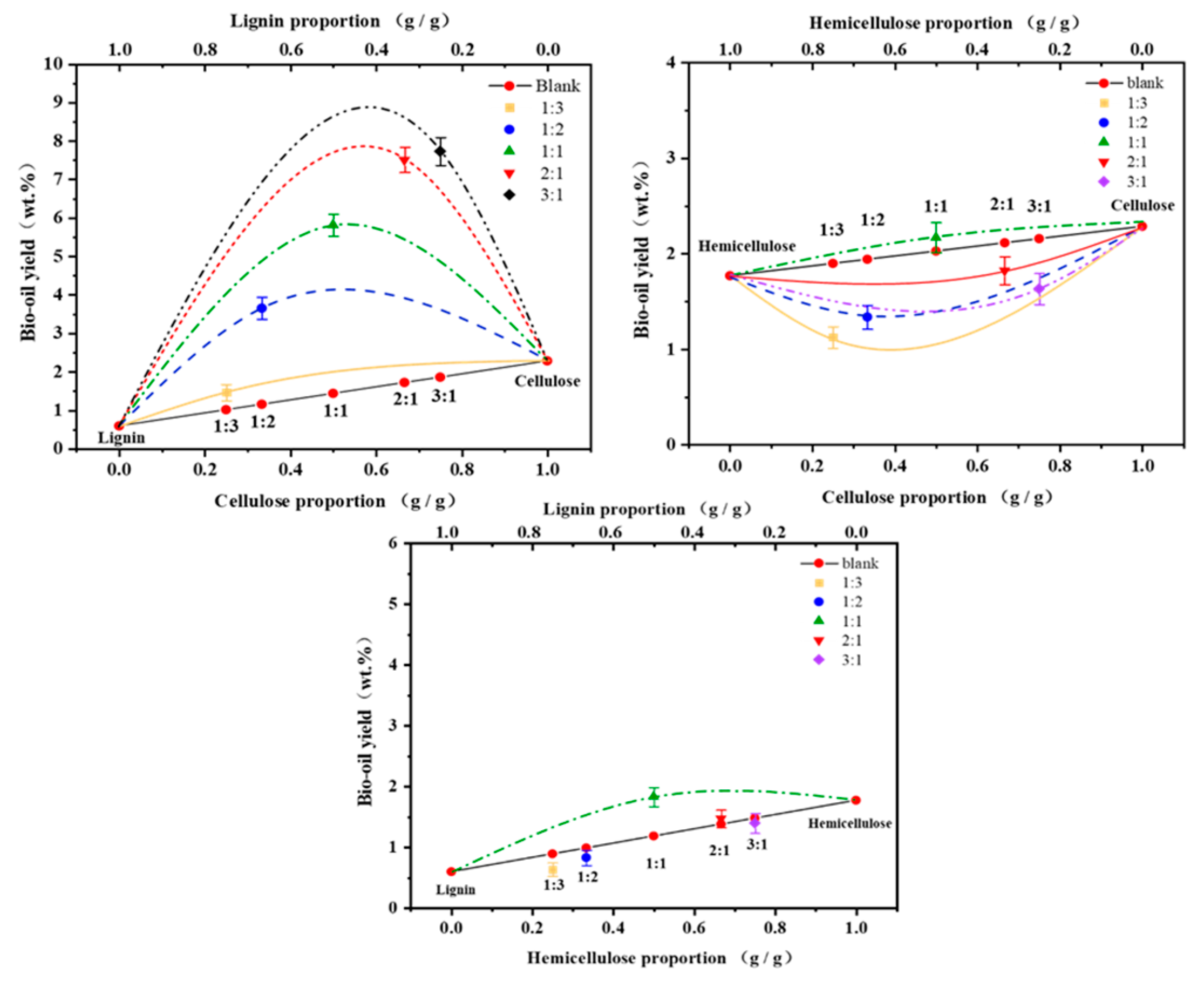
3.1. Distribution of Bio-Oil Products
3.1.1. Interaction Between Single Components in Cotton Stalk
3.1.2. Effect of Single Component Content on Binary Interaction
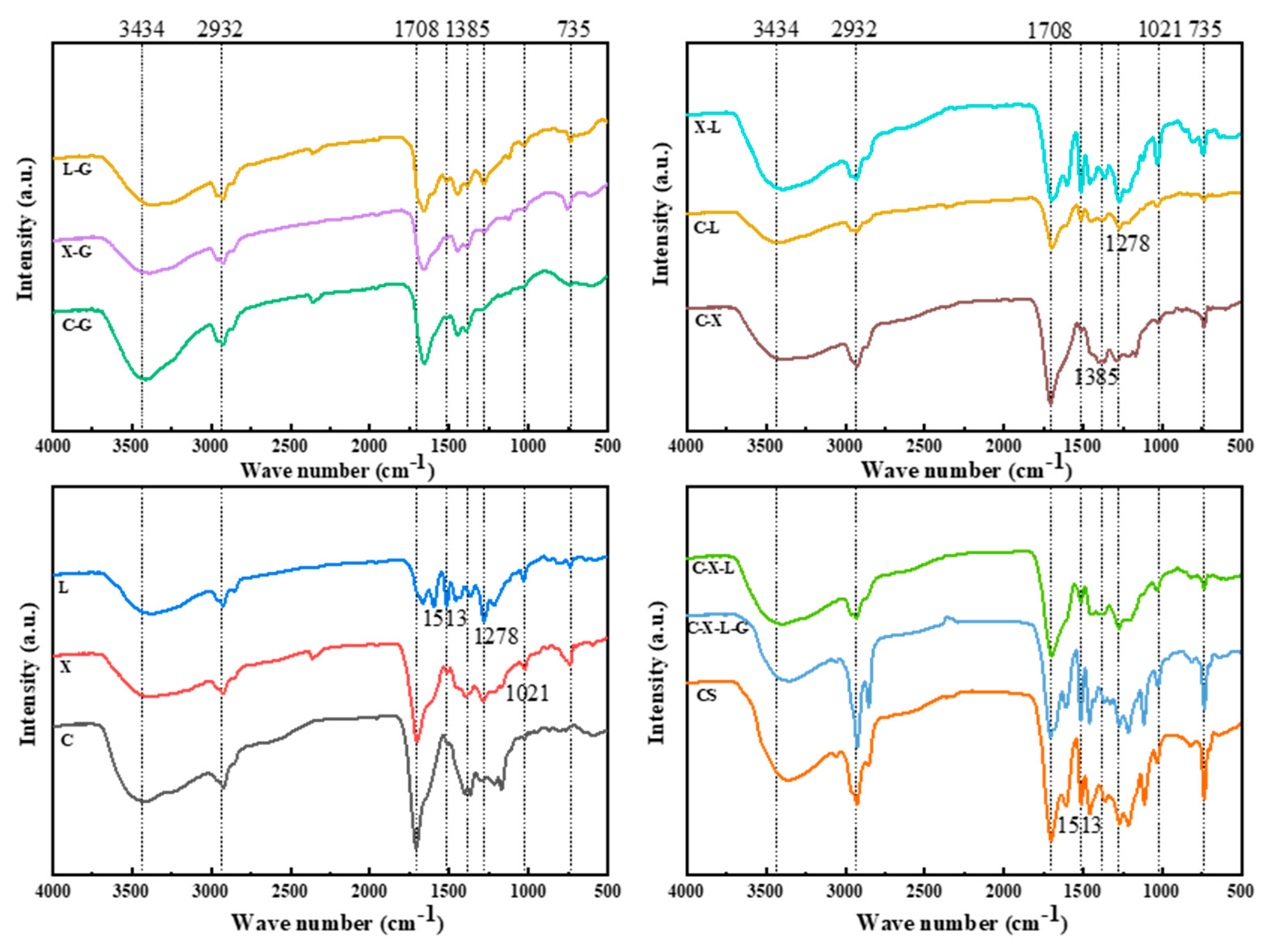
3.2. Characterization of Biomass Oil
3.2.1. FTIR
3.2.2. Elemental Analysis
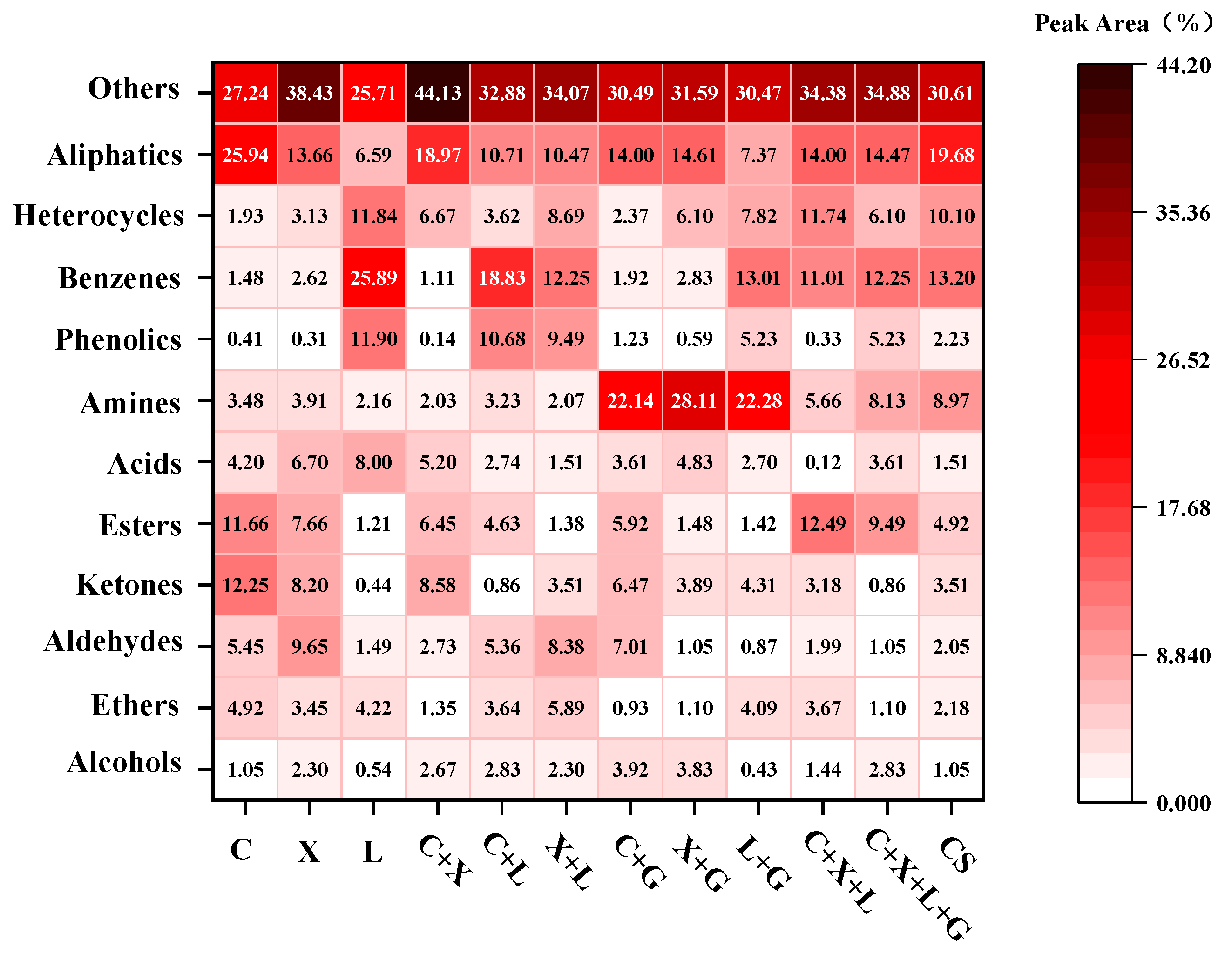
3.2.3. GC-MS Analysis of Bio-Oil
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Chong, L.; Du, J.; Tahir, N.; Awasthi, M.K. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Bio-Oil Production: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Gholizadeh, M. Progress of the Applications of Bio-Oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Saka, S. Cellulose–Hemicellulose and Cellulose–Lignin Interactions in Wood Pyrolysis at Gasification Temperature. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 80, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Choi, Y.; Yoo, C.G.; Kim, T.H.; Brown, R.C.; Shanks, B.H. Cellulose–Hemicellulose and Cellulose–Lignin Interactions During Fast Pyrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicianni, P.; Cardone, G.; Sorrentino, G.; Ragucci, R. Hemicellulose, Cellulose and Lignin Interactions on Arundo donax Steam Assisted Pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 110, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhong, F.; Liang, X.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Q.; Niu, W.; Meng, H. Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Conversion of Crop Straw: Enhancing the Properties of Liquid Product and Hydrochar by Varying Temperature and Medium. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 290, 117192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Ding, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, C.; Chen, B.; Song, A.; Zhu, D.; Li, H.; et al. Catalytic Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Chinese Herb Residue for the Production of High-Quality Bio-Oil. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 11205–11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Tu, Z.; Hu, J.; Wu, F. Renewable Fuel and Value-Added Chemicals Potential of Reed Straw Waste (RSW) by Pyrolysis: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, Products Characterization, and Biochar Application for Malachite Green Removal. Renew. Energy 2024, 229, 120724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan Subramanya, S.; Savage, P.E. Identifying and Modeling Interactions Between Biomass Components During Hydrothermal Liquefaction in Sub-, Near-, and Supercritical Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13874–13882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Ming, H.; Hu, H.; Dou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hu, Z. Investigation of Cotton Stalk-Derived Hydrothermal Bio-Oil: Effects of Mineral Acid/Base and Oxide Additions. Energies 2024, 17, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Yu, X.; Wang, H.; Ming, H.; Ge, S.; Liu, F.; Peng, H.; Sonne, C.; Zhang, L. Life Cycle Assessment of Bio-Oil Prepared from Low-Temperature Hydrothermal Oxide-Catalyzed Cotton Stalk. Energy 2023, 208, 128554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Guo, X.; Ge, S. Influence of Typical Pretreatment on Cotton Stalk Conversion Activity and Bio-Oil Property During Low Temperature (180–220 °C) Hydrothermal Process. Fuel 2022, 328, 125250–125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Caprariis, B.; Bavasso, I.; Bracciale, M.P.; Damizia, M.; De Filippis, P.; Scarsella, M. Enhanced Bio-Crude Yield and Quality by Reductive Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Oak Wood Biomass: Effect of Iron Addition. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 139, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Norouzi, O.; Salaudeen, S.; Acharya, B.; Dutta, A. Prediction of Hydrothermal Carbonization with Respect to the Biomass Components and Severity Factor. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 9916–9924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Cellulose–Hemicellulose Interactions During Fast Pyrolysis with Different Temperatures and Mixing Methods. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Hornung, U.; Dahmen, N.; Kruse, A. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Protein-Containing Biomass: Study of Model Compounds for Maillard Reactions. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2018, 8, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hu, M.; Du, G.; Tian, S.; He, Z.; Liu, B.; Ma, W. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Sewage Sludge by Microwave Pretreatment. Energy Fuels 2019, 34, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, M. Fractionation of Bio-Oil Produced from Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Microalgae by Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, J.; He, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Hu, X. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Cellulose in Ammonia/Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Yu, Y.; Gao, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, H. Formation of Anhydro-Sugars in the Primary Volatiles and Solid Residues from Cellulose Fast Pyrolysis in a Wire-Mesh Reactor. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 5204–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Yi, W.M.; Wang, N.N. Bio-Oil Production from Cotton Stalk. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Tan, Z. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Cellulose to Bio-Oil Under Acidic, Neutral and Alkaline Conditions. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapini, T.; Dos Santos, M.S.N.; Bonatto, C.; Wancura, J.H.; Mulinari, J.; Camargo, A.F.; Klanovicz, N.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V.; Fongaro, G.; et al. Hydrothermal Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Hemicellulose Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, B.; Feng, H. Effects of the Aqueous Phase Recycling on Bio-Oil Yield in Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Spirulina platensis, α-Cellulose, and Lignin. Energy 2019, 179, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Cellulose–Lignin Interactions During Fast Pyrolysis with Different Temperatures and Mixing Methods. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 90, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xin, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Effect of Volatiles Interaction During Pyrolysis of Cellulose, Hemicellulose, and Lignin at Different Temperatures. Fuel 2019, 248, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushimi, C.; Katayama, S.; Tasaka, K.; Suzuki, M.; Tsutsumi, A. Elucidation of the Interaction Among Cellulose, Xylan, and Lignin in Steam Gasification of Woody Biomass. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, M. Formation of Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals During Thermochemical Processes and Their Correlations with Unintentional Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6529–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


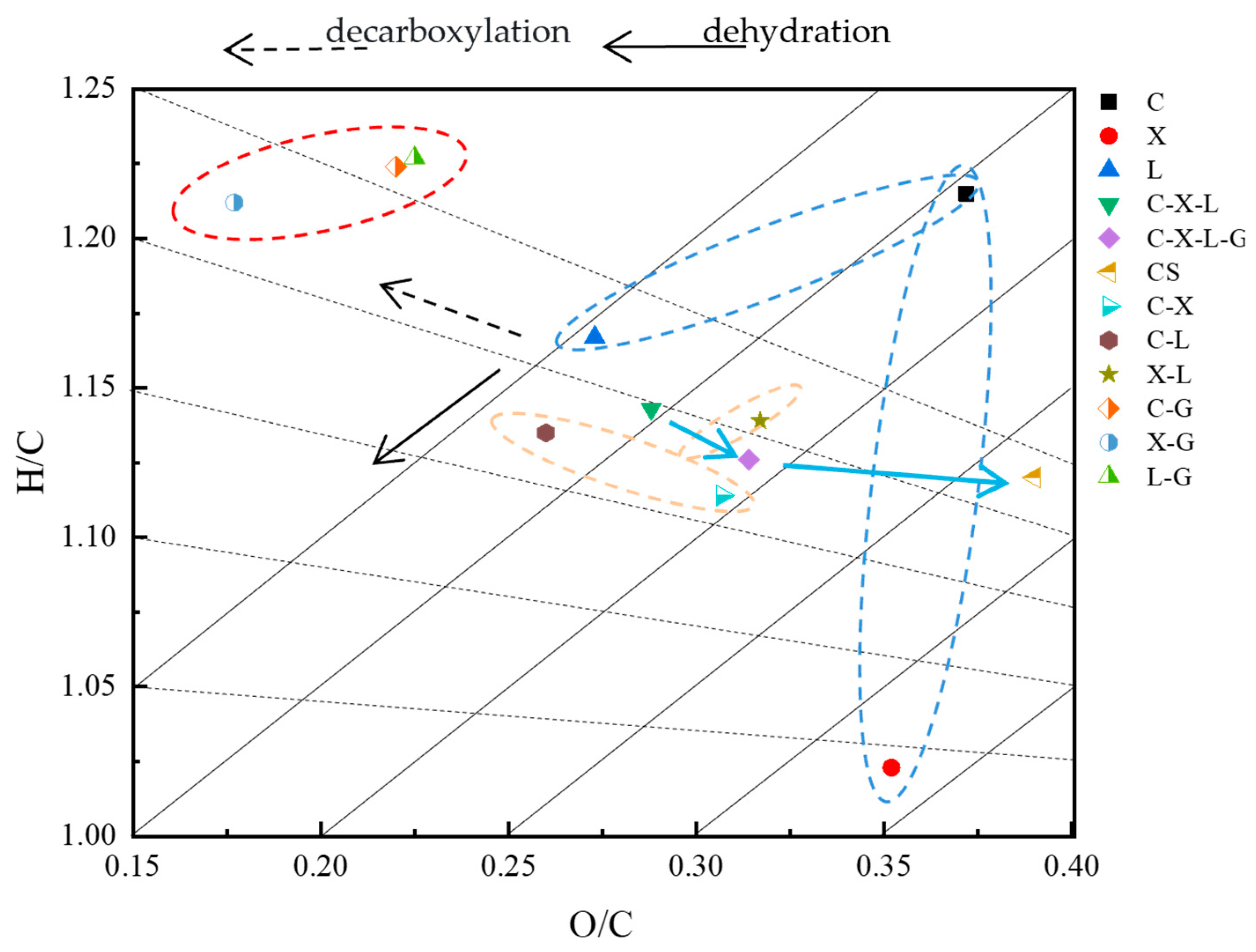

| Samples | C (wt.%) | N (wt.%) | H (wt.%) | S (wt.%) | O (wt.%) | H/C | O/C | HHV (MJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellulose | 62.51 | 0.06 | 6.374 | 0.073 | 30.983 | 1.215 | 0.372 | 24.707 |
| hemicellulose | 64.19 | 0.03 | 5.511 | 0.208 | 30.061 | 1.023 | 0.352 | 24.220 |
| lignin | 64.60 | 0.37 | 6.325 | 5.227 | 23.478 | 1.167 | 0.273 | 27.173 |
| cellulose + hemicellulose | 66.04 | 0.33 | 6.341 | 0.276 | 27.013 | 1.144 | 0.307 | 26.581 |
| cellulose + lignin | 66.48 | 0.34 | 6.331 | 3.784 | 23.065 | 1.135 | 0.260 | 27.753 |
| hemicellulose + lignin | 64.04 | 0.14 | 6.123 | 2.682 | 27.015 | 1.139 | 0.317 | 25.822 |
| cellulose + glycine | 63.99 | 10.32 | 6.575 | 0.394 | 18.721 | 1.224 | 0.220 | 27.713 |
| hemicellulose + glycine | 66.49 | 10.62 | 6.760 | 0.425 | 15.705 | 1.212 | 0.177 | 29.364 |
| lignin + glycine | 64.45 | 7.93 | 6.634 | 1.705 | 19.281 | 1.227 | 0.225 | 27.978 |
| mixed component | 65.32 | 0.17 | 6.263 | 3.152 | 25.095 | 1.143 | 0.288 | 26.842 |
| mixed component + glycine | 63.72 | 0.53 | 6.021 | 3.076 | 26.653 | 1.126 | 0.314 | 25.381 |
| cotton stalk | 61.52 | 0.62 | 5.734 | 0.262 | 31.864 | 1.120 | 0.390 | 23.320 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Zuo, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. Investigation of Component Interactions During the Hydrothermal Process Using a Mixed-Model Cellulose/Hemicellulose/Lignin/Protein and Real Cotton Stalk. Energies 2025, 18, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051290
Guo S, Zuo J, Yang X, Wang H, Cheng L, Zhang L. Investigation of Component Interactions During the Hydrothermal Process Using a Mixed-Model Cellulose/Hemicellulose/Lignin/Protein and Real Cotton Stalk. Energies. 2025; 18(5):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051290
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shengjun, Jiachen Zuo, Xiao Yang, Hui Wang, Lihua Cheng, and Libo Zhang. 2025. "Investigation of Component Interactions During the Hydrothermal Process Using a Mixed-Model Cellulose/Hemicellulose/Lignin/Protein and Real Cotton Stalk" Energies 18, no. 5: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051290
APA StyleGuo, S., Zuo, J., Yang, X., Wang, H., Cheng, L., & Zhang, L. (2025). Investigation of Component Interactions During the Hydrothermal Process Using a Mixed-Model Cellulose/Hemicellulose/Lignin/Protein and Real Cotton Stalk. Energies, 18(5), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051290




