On Space-Time Resolution of Inflow Representations for Wind Turbine Loads Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stochastic Simulation: Inflow and Turbine Loads
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Hub height (m) | 90 |
| Rotor diameter (m) | 126 |
| Hub-height wind speed (m/s) | 12, 15, 18 |
| Base inflow sampling rate (Hz) | 32 |
| Low-pass cut-off frequency (Hz) | 16, 8, 4, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125 |
| Grid (y × z) | 13 × 13, 11 × 11, 9 × 9 |
| Surface roughness (m) | 0.1 |
2.1. Filtering of Inflow Turbulence

2.2. Power Spectral Density Functions for Turbine Loads

2.3. Turbine Load Statistics
| Grid, filtering | FBM (kN-m) | FBM (kN-m) | TBM (kN-m) | TBM (kN-m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-min extreme | EFL | 10-min extreme | EFL | |
| 13 × 13, 32 Hz | 12,979 | 5,656 | 82,295 | 12,585 |
| 9 × 9, 1 Hz | 12,789 | 5,369 | 80,901 | 12,719 |
2.4. Wavelet Analyses of Turbine Loads

2.5. Summary on Spatio-Temporal Filtering of Inflow in Stochastic Simulation
3. Inflow Generation using Large-Eddy Simulation
3.1. Background on Large-Eddy Simulation
3.2. Large-Eddy Simulation Code
3.3. LES and Stochastic Simulation of Inflow Turbulence
| Parameters | Phase I Simulation | Phase II Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Domain size | 800 m × 800 m × 1260 m | 800 m × 800 m × 1260 m |
| Grid points | 40 × 40 × 64 | 60 × 60 × 96 |
| Spatial resolution | 20 m × 20 m × 20 m | 13.3 m × 13.3 m × 13.3 m |
| Time step | 0.2 s | 0.1 s |
| Run time | 720 min | 30 min |


3.4. Fractal Interpolation of LES-Generated Time Series

4. Extreme and Fatigue Loads based on LES and Stochastic Simulations
4.1. Turbine Load Statistics
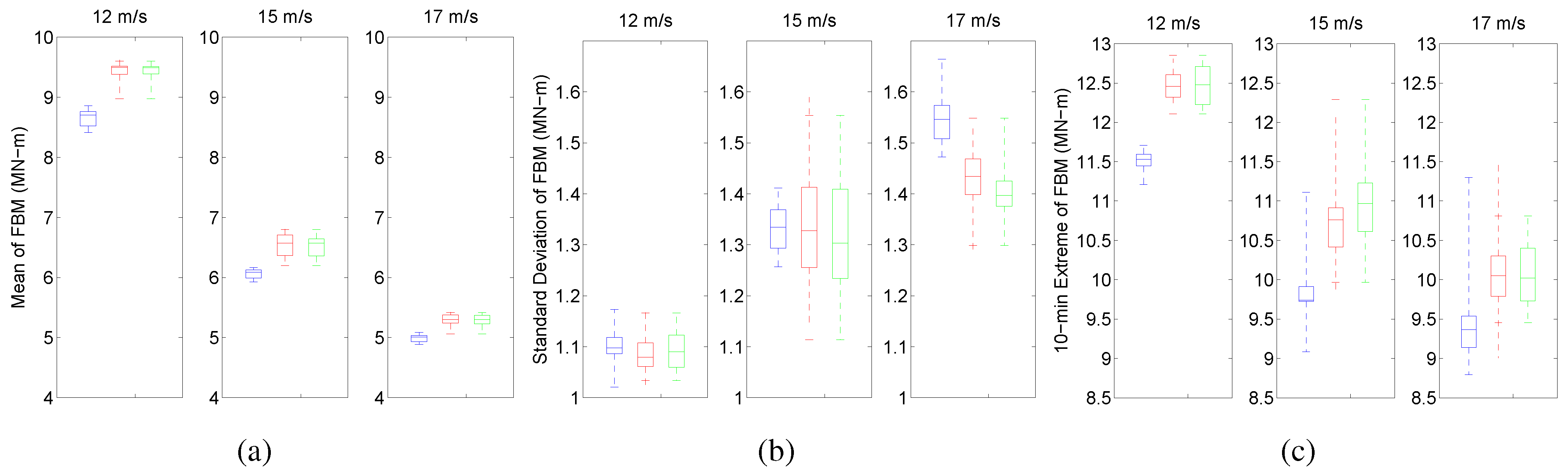
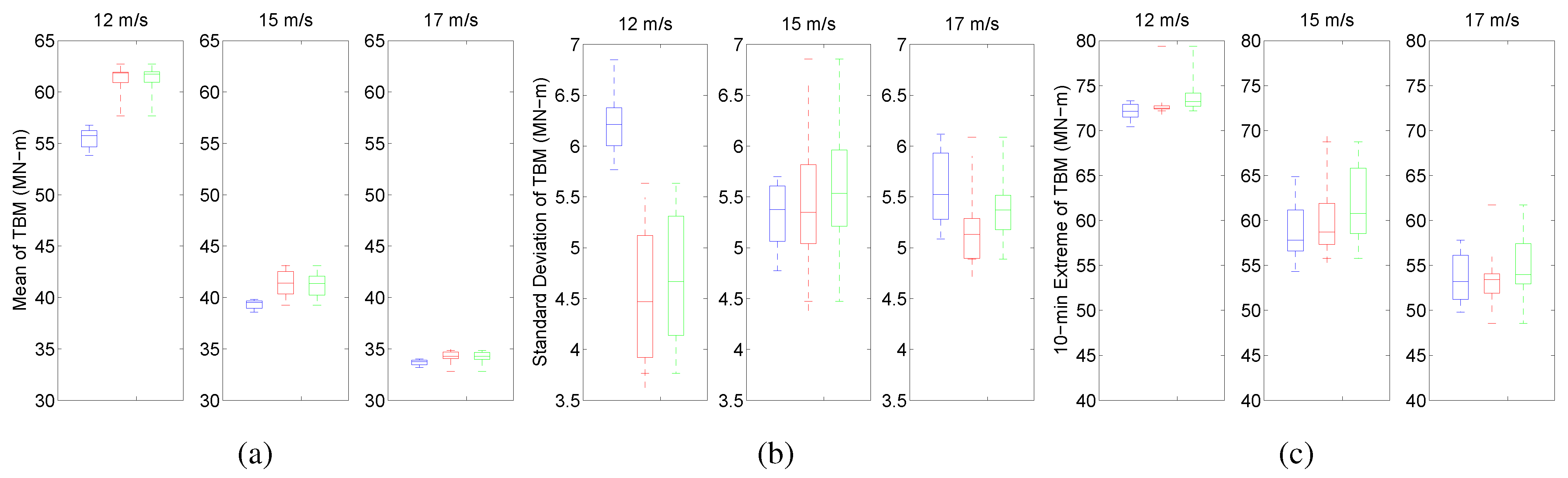
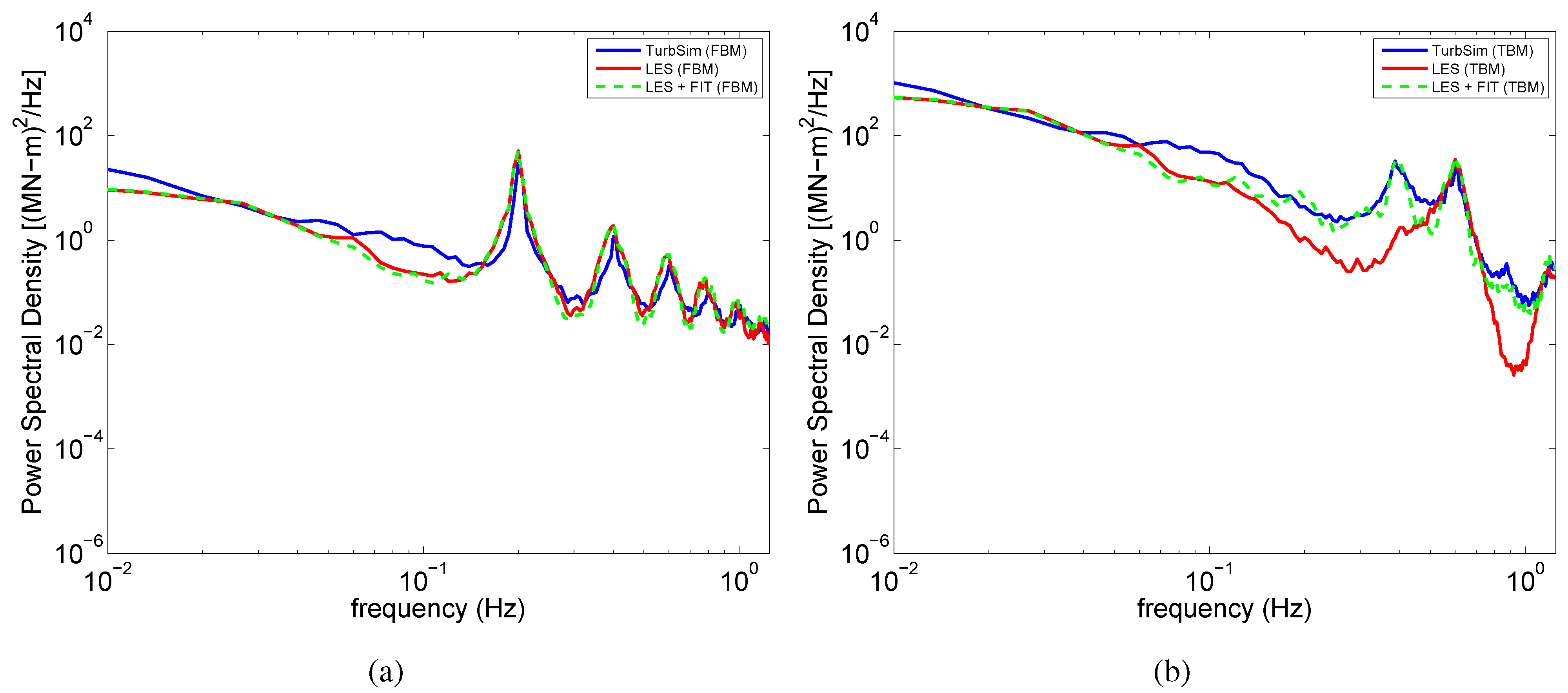
4.2. Power Spectral Density Functions of Turbine Loads
4.3. Fatigue Load Estimation

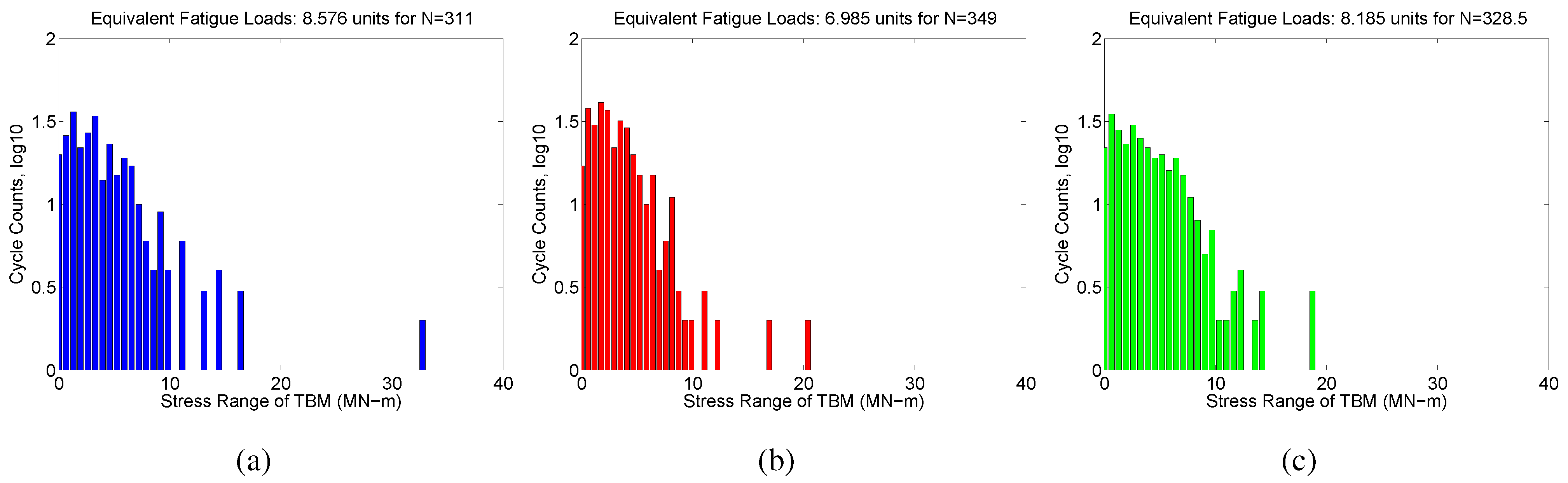
4.4. Load Probability Distributions

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Wind Turbines—Part 1: Design Requirements, 3rd ed.; IEC-61400-1; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Veers, P. Three-Dimensional Wind Simulation; Technical Report SAND88-0152; Sandia National Laboratory: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mücke, T.; Kleinhans, D.; Peinke, J. Atmospheric turbulence and its influence on the alternating loads on wind turbines. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, B. TurbSim User’s Guide: Version 1.50; Technical Report NREL/TP-500-46198; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaimal, J.C.; Wyngaard, J.C.; Izumi, Y.; Coté, O.R. Spectral characteristics of surface-layer turbulence. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1972, 98, 563–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.; Butterfield, S.; Musial, W.; Scott, G. Definition of a 5 MW Reference Wind Turbine for Offshore System Development; Technical Report NREL/TP-500-38060; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman, J.; Buhl, M. FAST User’s Guide; Technical Report NREL/EL-500-38230; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M. Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines, 2nd ed.; Earthscan Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fogle, J.; Agarwal, P.; Manuel, L. Towards an improved understanding of statistical extrapolation for wind turbine extreme loads. Wind Energy 2008, 11, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Osgood, R.; Bialasiewicz, J.; Jakubowski, A. Using wavelet analysis to assess turbulence/rotor interactions. Wind Energy 2000, 3, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sagaut, P. Large Eddy Simulations for Incompressible Flows; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–426. [Google Scholar]
- Geurts, B.J. Elements of Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation; Edwards: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–329. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Vinuesa, J.F.; Swift, A. Dynamic LES modeling of a diurnal cycle. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwstadt, F.T.M.; Mason, P.J.; Moeng, C.H.; Schumann, U. Large-eddy simulation of the convective boundary layer: A comparison of four computer codes. In Turbulent Shear Flows 8; Durst, F., Friedrich, R., Launder, B.E., Schmidt, F.W., Schumann, U., Whitelaw, J.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; pp. 343–367. [Google Scholar]
- Andrén, A.; Brown, A.R.; Graf, J.; Mason, P.J.; Moeng, C.H.; Nieuwstadt, F.T.M.; Schumann, U. Large-eddy simulation of a neutrally stratified boundary layer: A comparison of four computer codes. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 1457–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, R.J.; Macvean, M.K.; Coauthors. An Intercomparison of large-eddy simulations of the stable boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 118, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Ohya, Y. Micro-siting technique for wind turbine generators by using large-eddy simulation. J. Wind Energy Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 2121–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaf, M.; Meneveau, C.; Meyers, J. Large eddy simulation study of fully developed wind-turbine array boundary layers. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 015110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, A.; Sørensen, N.N. Hybrid RANS/LES applied to complex terrain. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, A.; Sørensen, N.N.; Berg, J.; Mann, J.; Réthoré, P.E. The bolund experiment, Part II: Blind comparison of microscale flow models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 141, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Porté-Agel, F. Large-Eddy Simulation of Wind-Turbine Wakes: Evaluation of Turbine Parametrisations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 138, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Porté-Agel, F. Large-eddy simulation of stably stratified atmospheric boundary layer turbulence: A scale-dependent dynamic modeling approach. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2074–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Porté-Agel, F.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Vinuesa, J.F.; Pahlow, M. Revisiting the local scaling hypothesis in stably stratified atmospheric boundary layer turbulence: An integration of field and laboratory measurements with large-eddy simulations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.C.; Basu, S.; Letchford, C.W. Comparison of dynamic subgrid-scale models for simulations of neutrally buoyant shear-driven atmospheric boundary layer flows. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2007, 7, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, J.F.; Basu, S.; Galmarini, S. The diurnal evolution of 222Rn and its progeny in the atmospheric boundary layer during the Wangara experiment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5003–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Holtslag, A.A.M.; Bosveld, F.C. GABLS3 LES Intercomparison Study. In Proceedings of ECMWF/GABLS Workshop on “Diurnal Cycles and the Stable Atmospheric Boundary Layer”; UK, 7–10 November 2011, European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF): Reading, UK; World Climate Research Programme (WCRP): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; F. Porté-Agel, F. Synthetic turbulence, fractal interpolation, and large-eddy simulation. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 026310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tukey, J. Extrapolatory Data Analysis; Addison-Wesley: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials Standards. Standard Practices for Cycle Counting in Fatigue Analysis; E1049-85; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, P. Structural Reliability of Offshore Wind Turbines. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sim, C.; Basu, S.; Manuel, L. On Space-Time Resolution of Inflow Representations for Wind Turbine Loads Analysis. Energies 2012, 5, 2071-2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5072071
Sim C, Basu S, Manuel L. On Space-Time Resolution of Inflow Representations for Wind Turbine Loads Analysis. Energies. 2012; 5(7):2071-2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5072071
Chicago/Turabian StyleSim, Chungwook, Sukanta Basu, and Lance Manuel. 2012. "On Space-Time Resolution of Inflow Representations for Wind Turbine Loads Analysis" Energies 5, no. 7: 2071-2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5072071
APA StyleSim, C., Basu, S., & Manuel, L. (2012). On Space-Time Resolution of Inflow Representations for Wind Turbine Loads Analysis. Energies, 5(7), 2071-2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5072071






