Regression Models Using Fully Discharged Voltage and Internal Resistance for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Reliability and Life Analysis of Lithium-Ion Batteries
1.2. Aging Parameters of the Battery
2. Test Methodology
2.1. Reliability Testing
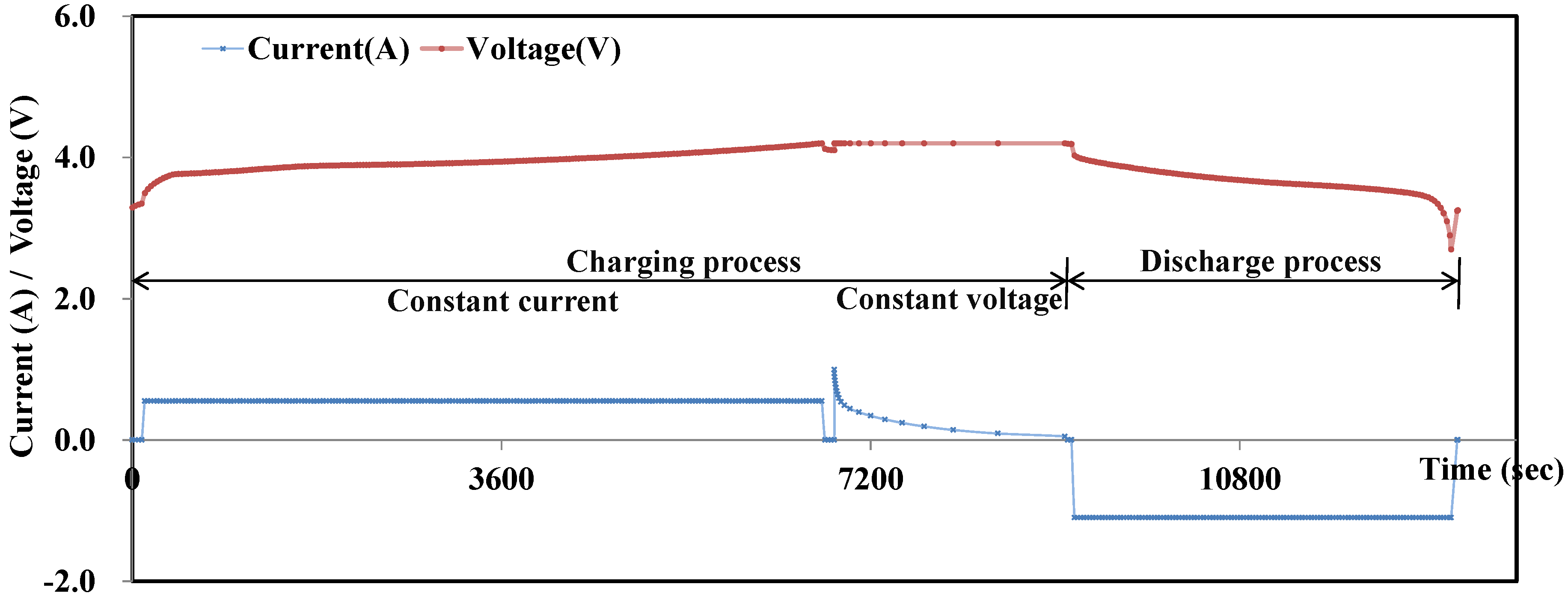

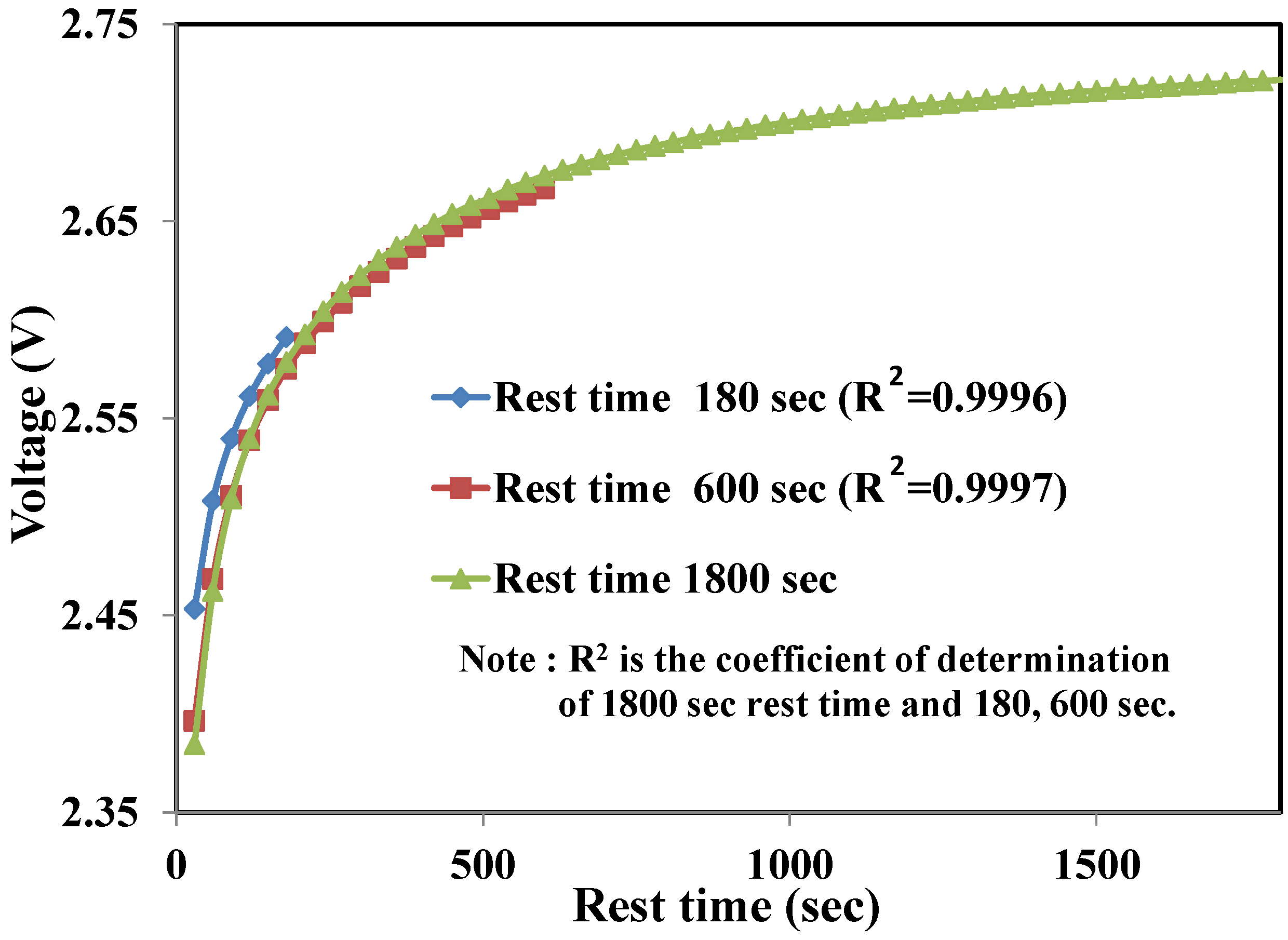
2.2. State of Health
2.3. Particle Swarm Optimizer (PSO)
2.4. Monte Carlo (MC) Method
3. Test Results
3.1. The Correlations of N, Vdis, R and SOH




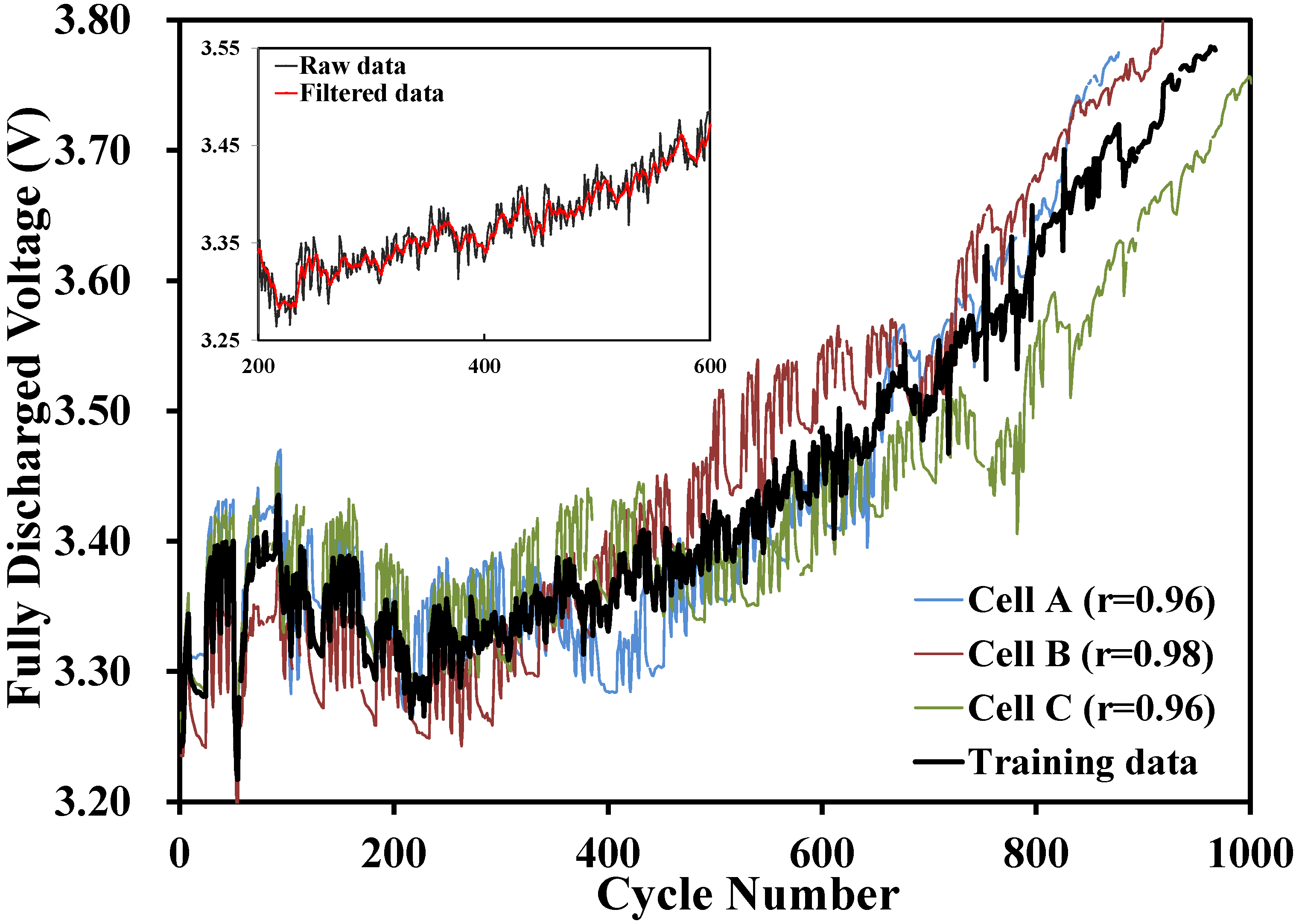
3.2. Degradation of SOH
3.2.1. (A) Cycle Number and SOH Degradation
3.2.2. (B) New SOH degradation model via Vdis and R
| Relationships | Model II | Model III |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | α1: −0.4546; α2: −13.5975 α3: 3.6551 | β1: 4.7603; β2: −0.2189 β3: −0.6383; β4: 8.5675 |
| Avg. error (%) | 1.66 | 1.59 |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.988 |
| RMSE | 0.022 | 0.021 |


4. Discussion
4.1. Battery Cycle Life Prediction

4.2. Battery Cycle Life Prediction with Model Updating
| Type | State | R2 | RMSE | Cycle life prediction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle | Error (%) | ||||
| Model I | Open | 0.956 | 0.0660 | 500 | 76 (13.2) |
| Model II | Open | 0.977 | 0.0342 | 577 | 1 (0.2) |
| Adaptive | 0.986 | 0.0350 | 577 | 1 (0.2) | |
| Model III | Open | 0.980 | 0.0322 | 599 | 23 (4.0) |
| Adaptive | 0.988 | 0.0280 | 599 | 23 (4.0) | |
4.3. Comparison of Models with Existing Literature

| Research | Xing et al. [38] | This study (Eq. 2) | This study (Eq. 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery type | Lithium-ion | LiCoO2 | LiCoO2 |
| Capacity (Ah) | 1.35 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Equation | |||
| Condition | LSA & PF | LSA | PSO & Monte Carlo |
| Variable | Cycle number | Cycle number | Vdis, R |
| R2 | 0.96~0.98 | 0.950 | 0.98 |
| Performance | 102 cycles earlier | 76 cycles late | 1 cycle late |
| Research | He et al. [37] | Xing et al. [38] | This study (Eq. 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery type | Lithium-ion | Lithium-ion | LiCoO2 |
| Capacity (Ah) | 1.1 | 1.35 | 1.1 |
| Equation | |||
| Condition | DST & Monte Carlo | LSA & PF | PSO & Monte Carlo |
| Variable | Cycle number | Cycle number | Vdis, R |
| R2 | -- | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Performance | 7 cycles | 3 cycles earlier | 23 cycles late |
5. Conclusions
- The SOH curves decayed slowly with N in the beginning, then dropped sharply as SOH approached the failure threshold, as observed from reliability test.
- SOH is highly correlated to Vdis and R, as indicated from the test data, so that Vdis and R are suitable parameters for SOH modeling. Using Vdis and R as aging parameters rather than the commonly used N further proved to have better cycle life prediction as referred to R2 and RMSE values.
- The PSO algorithm yielded optimal model coefficients and partially because of PSO was used, the selection of model type, polynomial or exponential, showed less significance. Both of the derived models accurately generated results resembling the real SOH curves of tested batteries.
- Regarding the discrimination between polynomial and exponential model, the present study showed in the polynomial model using Vdis and R as model parameters is superior to using N, but in the exponential model using N yielded better life predictions.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mierlo, J.V.; Maggetto, G.; Burgwal, E.V.D.; Gense, R. Driving style and traffic measures influences vehicle emissions and fuel consumptions. J. Automob. Eng. 2003, 218, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierlo, J.V.; Vereecken, L.; Maggetto, G.; Favrel, V.; Meyer, S.; Hecq, W. How to define clean vehicles? Environmental impact rating of vehicles. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2003, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, A.; Miller, M. Performance characteristics of lithium-ion batteries of various chemistries for plug-in hybrid vehicles. In Proceedings of the EVS24 International Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Symposium, Stavanger, Norway, 13–16 May 2009.
- Omar, N.; Daowd, M.; Verbrugge, B.; Mulder, G.; van den Bossche, J.; van Mierlo, J.; Dhaens, M.; Pauwels, S.; Leemans, F. Assessment of performance characteristics of lithium-ion batteries for PHEV vehicles applications based on a newly test methodology. In Proceedings of the EVS 25, Shenzhen, China, 5–9 November 2010.
- Silva, C.; Ross, M.; Farias, T. Evaluation of energy consumption, emissions and cost of plug-in hybrid vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N. Assessment of Rechargeable Energy Storage Systems for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussel, Belgium, September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, Y. Lithium ion secondary batteries; past 10 years and future. J. Power Sources 2001, 100, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.; Daowd, M.; Hegazy, O.; Bossche, P.V.D.; Coosemans, T.; Mierlo, J.V. Electrical double-layer capacitors in hybrid topologies—Assessment and evaluation of their performance. Energies 2012, 5, 4533–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.; Daowd, M.; Mulder, G.; Timmermans, J.M.; van den Bossche, P.; van Mierlo, P.; Pauwels, S. Assessment of performance of lithium iron phosphate oxide, nickel manganese cobalt oxide and nickel cobalt aluminum oxide based cells for using in plug-in battery electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 6–9 September 2011.
- Omar, N.; Mierlo, J.V.; Mulders, F.V.; Bossche, P.V.D. Assessment of behaviour of super capacitor-battery system in heavy hybrid lift truck vehicles. J. Asian Electr. Veh. 2009, 7, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Williard, N.; Osterman, M.; Pecht, M. Prognostics of Lithium-ion Batteries using Extended Kalman Filtering. In Proceedings of the IMAPS Advanced Technology Workshop on High Reliability Microelectronics for Military Applications, Linthicum Heights, MD, USA, 17–19 May 2011.
- Bhangu, B.S.; Bentley, P.; Stone, D.A.; Bingham, C.M. Nonlinear observers for predicting state-of-charge and state-of-health of lead-acid batteries for hybrid-electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 54, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, J.D. Electrochemical cell prognostics using online impedance measurements and model-based data fusion techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 8–15 March 2003.
- Zhang, J.; Lee, J. A review on prognostics and health monitoring of Li-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 6007–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K.; Poll, S.; Christophersen, J. An integrated approach to battery health monitoring using bayesian regression and state estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Autotestcon, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–20 September 2007.
- Piller, S.; Perrin, M.; Jossen, A. Methods for state-of-charge determination and their applications. J. Power Sources 2001, 96, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Nam, O.; Cho, B.H. Li-ion battery SOC estimation method based on the reduced order extended Kalman filtering. J. Power Sources 2007, 174, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Zhao, L.; Su, X.; Ma, P. Prognostics of lithium-Ion batteries based on battery performance analysis and flexible support vector regression. Energies 2014, 7, 6492–6508. [Google Scholar]
- Widodo, A.; Shim, M.C.; Caesarendra, W.; Yang, B.S. Intelligent prognostics for battery health monitoring based on sample entropy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 11763–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K.; Christophersen, J. Comparison of prognostic algorithms for estimating remaining useful life of batteries. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2009, 31, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williard, N.; He, W.; Pecht, M. Model based Battery Management System for Condition based Maintenance. In Proceedings of the MFPT 2012 Proceedings: The Prognostics and Health Management Solutions Conference, Dayton, OH, USA, 24–26 April 2012.
- Chen, C.; Pecht, M. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries using model-based and data-driven methods. In Proceedings of the 2012 Prognostics & System Health Management Conference, Beijing, China, 23–25 May 2012.
- He, W.; Williard, N.; Chen, C.; Pecht, M. State of charge estimation for electric vehicle batteries using unscented kalman filtering. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Xie, L.; Cui, H.J.; Liang, W.; Pecht, M. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery with unscented particle filter technique. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bole, B.; Daigle, M.; Gorospe, G. Online prediction of battery discharge and estimation of parasitic loads for an electric aircraft. In Proceedings of the Second European Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, Nantes, France, 8–10 July 2014.
- Daigle, M.; Kulkarni, C. A battery health monitoring framework for planetary rovers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 1–8 March 2014.
- Bole, B.; Kulkarni, C.S.; Daigle, M. Adaptation of an electrochemistry-based li-ion battery model to account for deterioration observed under randomized use. In Proceedings of Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 29 September–2 October 2014.
- Arulampalam, M.S.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Ma, J.; He, D. Lithium-ion battery life prognostic health management system using particle filtering framework. J. Risk Reliab. 2011, 225, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Orchard, M.E.; Hevia-Koch, P.; Zhang, B.; Tang, L. Risk measures for particle-filtering-based state-of-charge prognosis in lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5260–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, L.; DeCastro, J.; Roemer, M.; Goebel, K. Autonomous vehicle battery state-of-charge prognostics enhanced mission planning. Int. J. Progn. Health Manag. 2014, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pattipati, B.; Pattipati, K.; Christopherson, J.P.; Namburu, S.M.; Prokhorov, D.V.; Liu, Q. Automotive battery management systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Autotestcon, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 8–11 September 2008.
- Qian, K.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Y.; Allan, M. Temperature effect on electric vehicle battery cycle life in vehicle-to-grid applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution, Nanjing, China, 13–16 September 2010.
- Salkind, J.; Fennie, C.; Singh, P.; Atwater, T.; Reisner, D.E. Determination of state-of-charge and state-of-health of batteries by fuzzy logic methodology. J. Power Sources 1999, 80, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.G.; Peng, Y.; Xie, W.; Liao, H. Satellite lithium-ion battery remaining cycle life prediction with novel indirect health indicator extraction. Energies 2013, 6, 3654–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micea, M.V.; Ungurean, L.; Carstoiu, G.N.; Groza, V. Online state-of-health assessment for battery management systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Williard, N.; Osterman, M.; Pecht, M. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster–Shafer theory and the Bayesian Monte Carlo method. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10314–10321. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Ma, E.W.M.; Tsui, K.L.; Pecht, M. A case study on battery life prediction using particle filtering. In Proceedings of Prognostics & System Health Management Conference, Beijing, China, 23–25 May 2012.
- Amine, K.; Chen, C.H.; Liu, J.; Hammond, M.; Jansen, A.; Dees, D.; Bloom, I.; Vissers, D.; Henriksen, G. Factors responsible for impedance rise in high power lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 97–98, 684–687. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, J.; Novák, P.; Wagner, M.R.; Veit, C.; Möller, K.-C.; Besenhard, J.O.; Winter, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Vogler, C.; Hammouche, A. Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 147, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.P.; Bitzer, M.; Imre, Á.W.; Guzzella, L. Model-based distinction and quantification of capacity loss and rate capability fade in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7634–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pang, J.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y.; Pecht, M. Prognostics for state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on combination Gaussian process functional regression. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Liaw, B.Y. Identify capacity fading mechanism in a commercial LiFePO4 cell. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazi, Y. Semisupervised PSO-SVM regression for biophysical parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinaki, M.; Marinakis, Y.; Stavroulakis, G.E. Vibration control of beams with piezoelectric sensors and actuators using particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 6872–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-C.; Fung, R.-F. Using the modified PSO method to identify a Scott-Russell mechanism actuated by a piezoelectric element. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Ma, E.W.M.; Tsui, K.L.; Pecht, M. Battery management systems in electric and hybrid vehicles. Energies 2011, 4, 1840–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, K.-H.; Liang, J.-W.; Chang, W.; Huang, S.-C. Regression Models Using Fully Discharged Voltage and Internal Resistance for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies 2015, 8, 2889-2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042889
Tseng K-H, Liang J-W, Chang W, Huang S-C. Regression Models Using Fully Discharged Voltage and Internal Resistance for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies. 2015; 8(4):2889-2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042889
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Kuo-Hsin, Jin-Wei Liang, Wunching Chang, and Shyh-Chin Huang. 2015. "Regression Models Using Fully Discharged Voltage and Internal Resistance for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries" Energies 8, no. 4: 2889-2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042889
APA StyleTseng, K.-H., Liang, J.-W., Chang, W., & Huang, S.-C. (2015). Regression Models Using Fully Discharged Voltage and Internal Resistance for State of Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies, 8(4), 2889-2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8042889






