Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model and Numerical Procedure
3. The Case Study
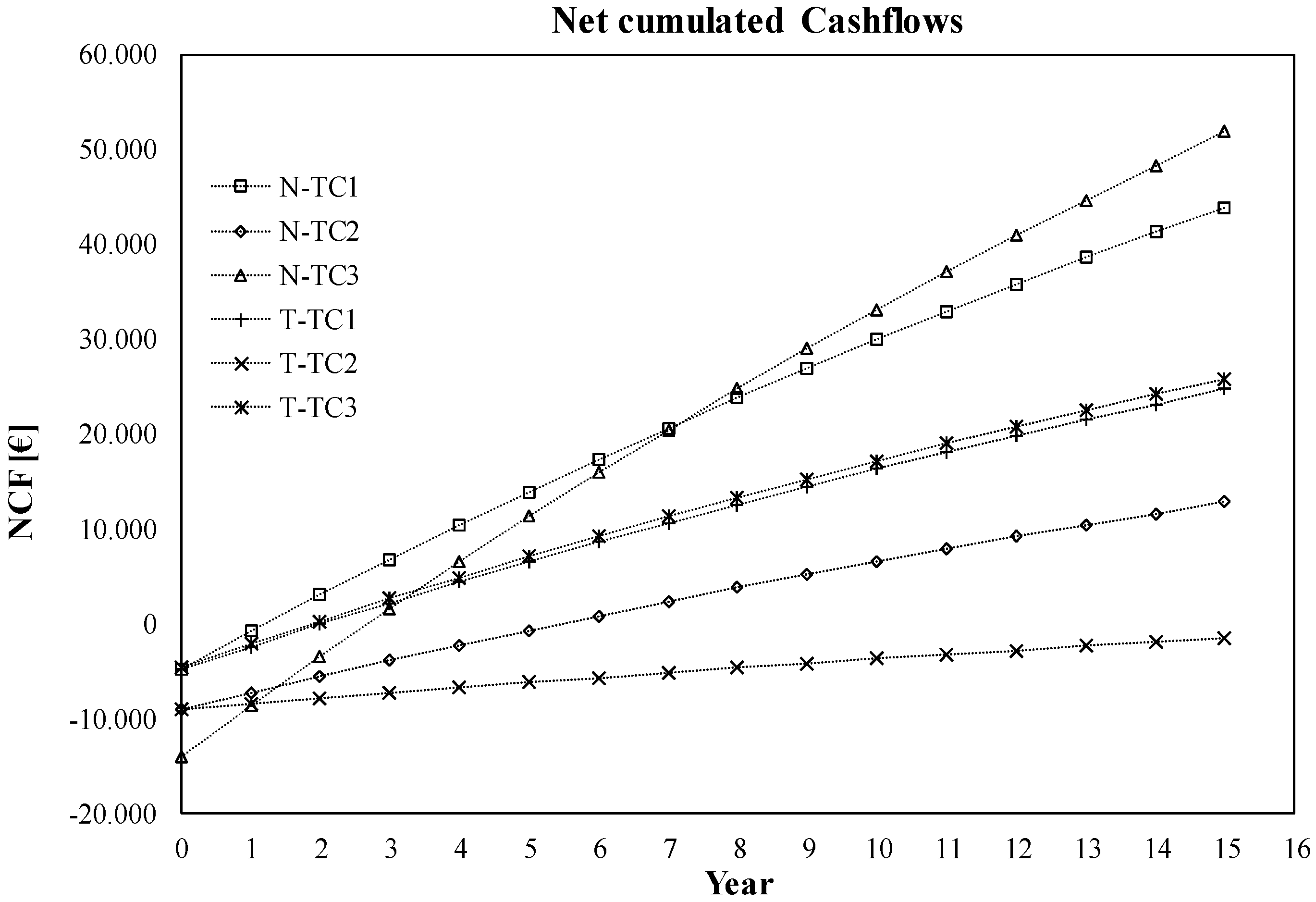
4. Economic Analysis
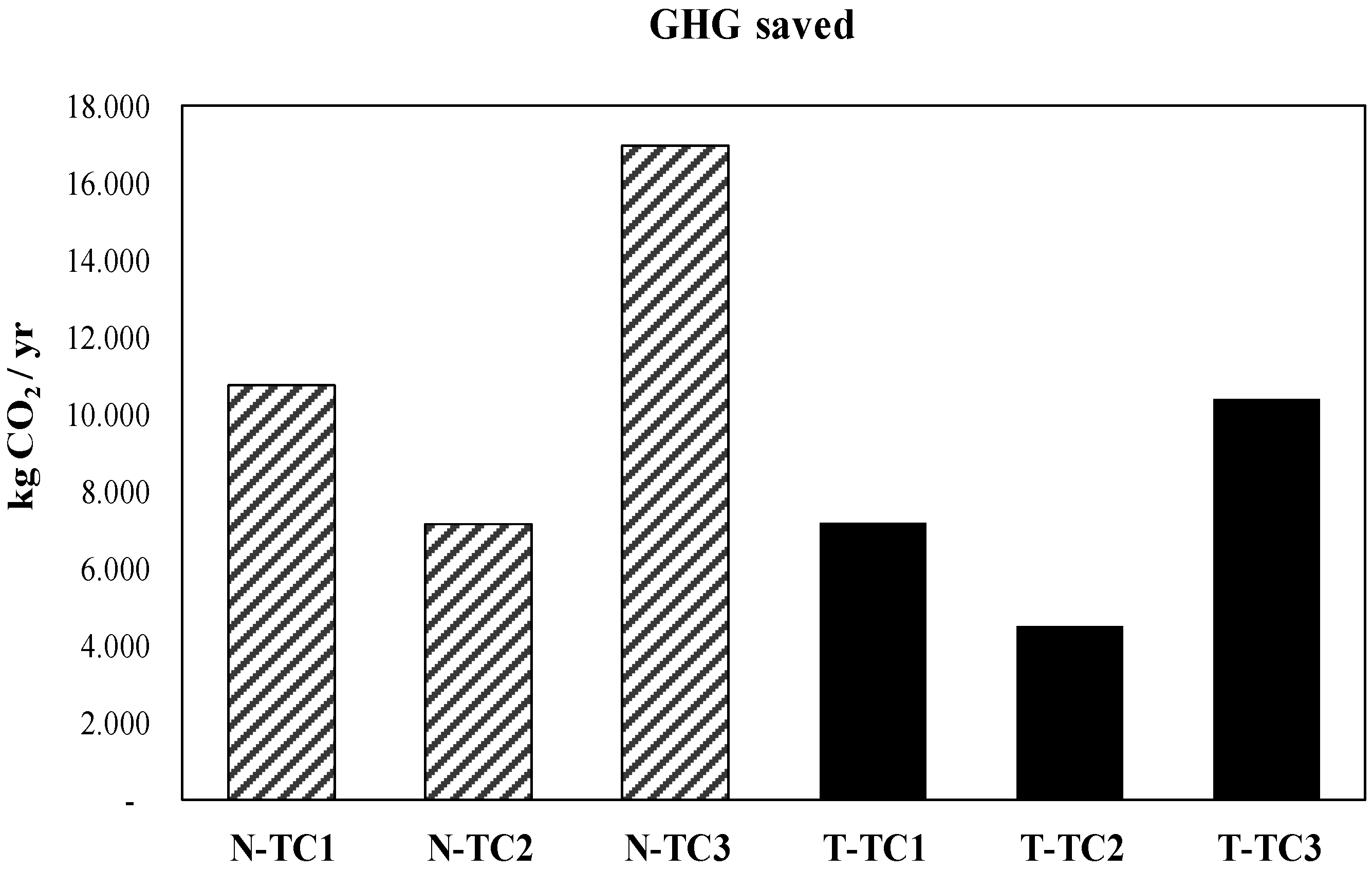
5. Environmental Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Pipe No. | Start Node | End Node | Diameter D (mm) | Length Li (m) | Roughnees ks (mm) | Discharge Q (l/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 300 | 200 | 0.003 | 36.33 |
| 2 | 2 | 3 | 150 | 110 | 0.003 | 11.37 |
| 3 | 3 | 4 | 150 | 170 | 0.003 | 7.64 |
| 4 | 4 | 5 | 80 | 32 | 0.003 | 0.97 |
| 5 | 6 | 5 | 80 | 180 | 0.003 | 0.88 |
| 6 | 3 | 6 | 80 | 32 | 0.003 | 2.73 |
| 7 | 7 | 2 | 150 | 90 | 0.003 | 18.96 |
| 8 | 8 | 7 | 150 | 110 | 0.003 | 9.41 |
| 9 | 9 | 8 | 150 | 300 | 0.003 | 8.85 |
| 10 | 10 | 9 | 150 | 44 | 0.003 | 8.29 |
| 11 | 10 | 11 | 80 | 100 | 0.003 | 2.69 |
| 12 | 11 | 12 | 80 | 20 | 0.003 | 2.69 |
| 13 | 12 | 13 | 80 | 110 | 0.003 | 1.51 |
| 14 | 13 | 14 | 80 | 140 | 0.003 | 0.1 |
| 15 | 15 | 14 | 80 | 110 | 0.003 | 4.55 |
| 16 | 15 | 7 | 150 | 44 | 0.003 | 9.03 |
| 17 | 15 | 16 | 80 | 184 | 0.003 | 3.23 |
| 18 | 17 | 16 | 80 | 110 | 0.003 | 0.43 |
| 19 | 13 | 16 | 80 | 110 | 0.003 | 1.79 |
| 20 | 17 | 12 | 80 | 80 | 0.003 | 1.22 |
| 21 | 10 | 17 | 80 | 90 | 0.003 | 2.88 |
| 22 | 18 | 10 | 150 | 120 | 0.003 | 1.93 |
| 23 | 20 | 21 | 200 | 100 | 0.003 | 45.79 |
| 24 | 21 | 22 | 200 | 220 | 0.003 | 36.25 |
| 25 | 22 | 23 | 200 | 100 | 0.003 | 36.25 |
| 26 | 23 | 24 | 200 | 80 | 0.003 | 36.25 |
| 27 | 24 | 25 | 200 | 60 | 0.003 | 36.25 |
| 28 | 25 | 19 | 200 | 170 | 0.003 | 27.98 |
| 29 | 19 | 18 | 150 | 102 | 0.003 | 8.38 |
| 30 | 25 | 26 | 100 | 34 | 0.003 | 8.27 |
| 31 | 27 | 26 | 100 | 58 | 0.003 | 4.84 |
| 32 | 28 | 27 | 100 | 128 | 0.003 | 2.15 |
| 33 | 29 | 28 | 100 | 51 | 0.003 | 0.8 |
| 34 | 29 | 30 | 100 | 64 | 0.003 | 0.11 |
| 35 | 30 | 31 | 100 | 30 | 0.003 | 1.11 |
| 36 | 31 | 32 | 80 | 76 | 0.003 | 1.11 |
| 37 | 32 | 33 | 80 | 85 | 0.003 | 0.27 |
| 38 | 33 | 34 | 80 | 70 | 0.003 | 0.09 |
| 39 | 34 | 35 | 80 | 42 | 0.003 | 0.3 |
| 40 | 36 | 19 | 200 | 38 | 0.003 | 19.6 |
| 41 | 36 | 37 | 80 | 88 | 0.003 | 0.48 |
| 42 | 37 | 26 | 80 | 84 | 0.003 | 2.16 |
| 43 | 32 | 27 | 80 | 51 | 0.003 | 1.29 |
| 44 | 37 | 33 | 80 | 84 | 0.003 | 1.06 |
| 45 | 35 | 38 | 150 | 25 | 0.003 | 17.59 |
| 46 | 38 | 39 | 150 | 82 | 0.003 | 17.59 |
| 47 | 40 | 39 | 100 | 60 | 0.003 | 6.83 |
| 48 | 41 | 40 | 100 | 20 | 0.003 | 4.87 |
| 49 | 42 | 41 | 100 | 154 | 0.003 | 4.87 |
| 50 | 43 | 42 | 100 | 90 | 0.003 | 2.39 |
| 51 | 43 | 44 | 100 | 170 | 0.003 | 1.55 |
| 52 | 45 | 44 | 100 | 74 | 0.003 | 3.27 |
| 53 | 45 | 46 | 100 | 56 | 0.003 | 7.38 |
| 54 | 46 | 39 | 100 | 74 | 0.003 | 7.38 |
| 55 | 45 | 47 | 100 | 112 | 0.003 | 2.81 |
| 56 | 47 | 48 | 100 | 54 | 0.003 | 2.81 |
| 57 | 48 | 49 | 100 | 74 | 0.003 | 1.06 |
| 58 | 44 | 49 | 100 | 170 | 0.003 | 1.87 |
| 59 | 49 | 50 | 100 | 24 | 0.003 | 2.93 |
| 60 | 50 | 51 | 100 | 128 | 0.003 | 1.26 |
| 61 | 52 | 51 | 100 | 92 | 0.003 | 0.36 |
| 62 | 53 | 52 | 100 | 106 | 0.003 | 1.63 |
| 63 | 50 | 53 | 100 | 94 | 0.003 | 0.96 |
| 64 | 54 | 53 | 100 | 86 | 0.003 | 5.41 |
| 65 | 54 | 43 | 100 | 195 | 0.003 | 2.63 |
| 66 | 54 | 55 | 110 | 50 | 0.003 | 9.54 |
| 67 | 55 | 56 | 110 | 114 | 0.003 | 9.54 |
| 68 | 56 | 57 | 110 | 255 | 0.003 | 9.54 |
| 69 | 57 | 21 | 110 | 110 | 0.003 | 9.54 |
| 70 | 35 | 36 | 200 | 24 | 0.003 | 19.55 |
| Node ID | Node Elevation z (m) | Water Head H (m) | Demand q (l/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 190 | 190 | 0 |
| 2 | 141.5 | 189.75 | 1.4 |
| 3 | 143 | 189.23 | 1 |
| 4 | 145.4 | 188.87 | 4.32 |
| 5 | 150.5 | 188.84 | 0.2 |
| 6 | 147 | 188.99 | 0.2 |
| 7 | 137.2 | 188.58 | 0.52 |
| 8 | 135.25 | 188.22 | 0.56 |
| 9 | 126.1 | 187.36 | 0.56 |
| 10 | 128.45 | 187.25 | 4.65 |
| 11 | 134.8 | 186.49 | 0 |
| 12 | 134.9 | 186.34 | 2.4 |
| 13 | 148 | 186.07 | 3.2 |
| 14 | 158.3 | 186.07 | 4.65 |
| 15 | 138.5 | 188.45 | 1.25 |
| 16 | 137 | 186.44 | 1.87 |
| 17 | 132 | 186.47 | 1.23 |
| 18 | 132.5 | 187.27 | 6.45 |
| 19 | 135 | 187.53 | 0 |
| 20 | 195 | 195 | 0 |
| 21 | 186 | 193.35 | 45.79 |
| 22 | 181 | 191.07 | 0 |
| 23 | 154.5 | 190.03 | 0 |
| 24 | 156 | 189.2 | 0 |
| 25 | 156 | 188.58 | 0 |
| 26 | 156 | 187.85 | 1.27 |
| 27 | 154 | 187.42 | 1.39 |
| 28 | 172 | 187.23 | 1.35 |
| 29 | 166 | 187.21 | 0.91 |
| 30 | 158 | 187.22 | 1 |
| 31 | 154 | 187.23 | 0 |
| 32 | 150 | 187.33 | 0.46 |
| 33 | 143.1 | 187.33 | 0.87 |
| 34 | 139.5 | 187.34 | 0.21 |
| 35 | 135 | 187.34 | 1.67 |
| 36 | 135 | 187.41 | 0.53 |
| 37 | 146 | 187.44 | 0.62 |
| 38 | 134 | 187.06 | 0 |
| 39 | 131 | 186.14 | 3.38 |
| 40 | 136 | 185.25 | 1.96 |
| 41 | 136 | 185.1 | 0 |
| 42 | 156 | 183.94 | 2.48 |
| 43 | 159 | 183.78 | 3.47 |
| 44 | 134.5 | 183.65 | 2.95 |
| 45 | 129.5 | 183.9 | 1.3 |
| 46 | 130 | 184.86 | 0 |
| 47 | 132.5 | 183.62 | 0 |
| 48 | 133.5 | 183.48 | 1.75 |
| 49 | 143 | 183.45 | 0 |
| 50 | 143 | 183.39 | 2.63 |
| 51 | 142.5 | 183.32 | 1.62 |
| 52 | 149 | 183.33 | 1.27 |
| 53 | 150 | 183.42 | 2.82 |
| 54 | 164 | 184.21 | 1.5 |
| 55 | 165 | 185.08 | 0 |
| 56 | 168 | 187.05 | 0 |
| 57 | 183 | 191.45 | 0 |
References
- Barry, J.A. WATERGY: Energy and Water Efficiency in Municipal Water Supply and Wastewater Treatment Cost-Effective Savings of Water and Energy; The Alliance to Save Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tucciarelli, T.; Criminisi, A.; Termini, D. Leak analysis in pipeline systems by means of optimal valve regulation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walski, T.; Bezts, W.; Posluzny, E.; Weir, M.; Withman, B. Modeling leakage reduction through pressure control. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2006, 98, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, L.; Ramos, H.; Coelho, S. Pressure control for leakage minimisation in water distribution systems management. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazif, S.; Karamouz, M.; Tabesh, M.; Moridi, A. Pressure management model for urban water distribution networks. Water Res. Manag. 2010, 24, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapallaz, J.; Eichenberger, P.; Fischer, G. Manual on Pumps Used as Turbines; Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Braunschweig, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, H.; Borga, A. Pumps as turbines: An unconventional solution to energy production. Urban Water 1999, 1, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, H.; Kumar, V.A.; Yadav, S. Experimental investigation of centrifugal pump working as turbine for small hydropower systems. Energy Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Giugni, M.; Fontana, N.; Portolano, D. Energy saving policy in water distribution networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ’09), Valencia, Spain, 15–17 April 2009.
- Milici, B.; De Marchis, M. Statistics of inertial particle deviation from fluid particle trajectories in horizontal rough wall turbulent channel flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2016, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; del Giudice, G.; Fecarotta, O.; Ramos, H. PAT design strategy for energy recovery in water distribution networks by electrical regulation. Energies 2013, 6, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.V.; Patel, R.N. Investigations on pump running in turbine mode: A review of the state-of-the-art. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 841–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, H.; Kumar, V.A. Reverse running pumps analytical, experimental and computational study: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.A. Pump as turbines for low cost microhydropower. Renew. Energy 1999, 9, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Nourbakhsh, A. Experimental study of characteristic curves of centrifugal pumps working as turbines in different specific speeds. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2008, 32, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Nourbakhsh, A. Theoretical, numerical and experimental investigation of centrifugal pumps in reverse operation. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2008, 32, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Nestmann, F. Internal hydraulic analysis of impeller rounding in centrifugal pumps as turbines. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2011, 35, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Derakhshan, S.; Kong, F.Y. Theoretical, numerical and experimental prediction of pump as turbine performance. Renew. Energy 2012, 48, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; del Giudice, G.; Fecarotta, O.; Ramos, H. Energy production in water distribution networks: A PAT design strategy. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3947–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaga, M. Pump as turbine—A pico-hydro alternative in Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; Fecarotta, O.; Sinagra, M.; Tucciarelli, T. Cost-benefit analysis for hydropower production in water distribution networks by pump as turbine. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puleo, V.; Fontanazza, C.M.; Notaro, V.; De Marchis, M.; Freni, G.; la Loggia, G. Pumps as turbines (PATs) in water distribution networks affected by intermittent service. J. Hydroinform. 2014, 16, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, N.; Giugni, G.; Portolano, D. Losses reduction and energy production in water-distribution networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2012, 138, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motwani, K.H.; Jain, S.V.; Patel, R.N. Cost analysis of pump as turbine for pico hydropower plants—A case study. Proc. Eng. 2013, 51, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Fontanazza, C.M.; Freni, G.; la Loggia, G.; Napoli, E.; Notaro, V. Analysis of the impact of intermittent distribution by modelling the network-filling process. J. Hydroinform. 2011, 13, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freni, G.; De Marchis, M.; Napoli, E. Implementation of pressure reduction valves in a dynamic water network model. J. Hydroinform. 2014, 16, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marchis, M.; Milici, B.; Freni, G. Pressure-discharge law of local tanks connected to a water distribution network: Experimental and mathematical results. Water 2015, 7, 4701–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Freni, G. Pump as turbine implementation in a dynamic numerical model: Cost analysis for energy recovery in water distribution network. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Milici, B.; Napoli, E. Numerical observations of turbulence structure modification in channel flow over 2D and 3D rough walls. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 56, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Milici, B.; Sardina, G.; Napoli, E. Interaction between turbulent structures and particles in roughened channel. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 78, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítkovský, J.P.; Bergant, A.; Simpson, A.R.; Lambert, M.F. Systematic evaluation of one-dimensional unsteady friction models in simple pipelines. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Fontanazza, C.M.; Freni, G.; la Loggia, G.; Napoli, E.; Notaro, V. A model of the filling process of an intermittent distribution network. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartano, V.; Morreale, G.; Sinagra, M.; Tucciarelli, T. Numerical and experimental investigation of a cross-flow water turbine. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marchis, M. Large eddy simulations of roughened channel flows: Estimation of the energy losses using the slope of the roughness. Comput. Fluids 2016, 140, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvuglia, A.; Messineo, A. Using recurrent artificial neural networks to forecast household electricity consumption. Energy Procedia 2012, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, R.; Messineo, A.; Millan, M.; Volpe, M.; Kandiyoti, R. Assessment of olive wastes as energy source: Pyrolysis, torrefaction and the key role of H loss in thermal breakdown. Energy 2015, 82, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Volpe, R.; Panno, D.; Messineo, A. Upgrade of citrus waste as a biofuel via slow pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, A.; Esposito, A.; Messineo, A.; Orlando, C.; Tumino, D. 3D CFD analysis of vertical axis wind turbine. Energies 2015, 8, 3013–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M.; Fontanazza, C.; Freni, G.; Notaro, V.; Puleo, V. Experimental evidence of leaks in elastic pipes. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Scenario | Dimp (mm) | QBEP (m3/s) | HBEP (m) | PBEP (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC1 | 200 | 0.029 | 9.00 | 1600 |
| TC2 | 300 | 0.015 | 15.00 | 3.00 |
| Scenario | Pinst (kW) | ADEP (kWh/Day) | AYEP (kWh/Year) | EGE (€) | CWC (€) | MC (€/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-TC1 | 1.60 | 60.00 | 21,900.00 | 3800.00 | 1100.00 | 750.00 |
| N-TC2 | 3.00 | 40.00 | 14,600.00 | 7100.00 | 2100.00 | 1400.00 |
| N-TC3 | 4.60 | 95.00 | 34,700.00 | 10,800.00 | 3200.00 | 2100.00 |
| T-TC1 | 1.60 | 40.00 | 14,600.00 | 3800.00 | 1100.00 | 750.00 |
| T-TC2 | 3.00 | 25.00 | 9100.00 | 7100.00 | 2100.00 | 1400.00 |
| T-TC3 | 4.60 | 58.00 | 21,200.00 | 10,800.00 | 3200.00 | 2100.00 |
| Indicator | N-TC1 | N-TC2 | N-TC3 | T-TC1 | T-TC2 | T-TC3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 (€) | 4900 | 9200 | 14,000 | 4900 | 9200 | 4600 |
| NPV (€) | 43,900 | 12,700 | 51,800 | 24,700 | −1600 | 25,700 |
| PI (%) | 896 | 260 | 1058 | 504 | −34 | 526 |
| PbT (Years) | 1.24 | 5.50 | 2.70 | 2.07 | >12 | 1.91 |
| ROI (%) | 83.0 | 20.0 | 39.0 | 51.0 | 7.0 | 55.0 |
| IRR (%) | 83.0 | 18.0 | 39.0 | 50.5 | 0.5 | 55.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Marchis, M.; Milici, B.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A. Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis. Energies 2016, 9, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110877
De Marchis M, Milici B, Volpe R, Messineo A. Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis. Energies. 2016; 9(11):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110877
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Marchis, Mauro, Barbara Milici, Roberto Volpe, and Antonio Messineo. 2016. "Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis" Energies 9, no. 11: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110877
APA StyleDe Marchis, M., Milici, B., Volpe, R., & Messineo, A. (2016). Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis. Energies, 9(11), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110877









