Dimensionless Maps for the Validity of Analytical Ground Heat Transfer Models for GSHP Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ILS—Infinite Line Source Model
3. ICS—Infinite Cylindrical Source Model
4. FLS—Finite Line Source Model
5. FCS—Finite Cylindrical Source Model
6. Summary List of the Proposed Dimensionless Criteria
- The ILS model is practically equivalent to the ICS one when:
- The ILS model is practically equivalent to the FLS one when:
- The ICS model is practically equivalent to the FCS one when:
- The FLS model is practically equivalent to the FCS one when:
7. Superposition Techniques
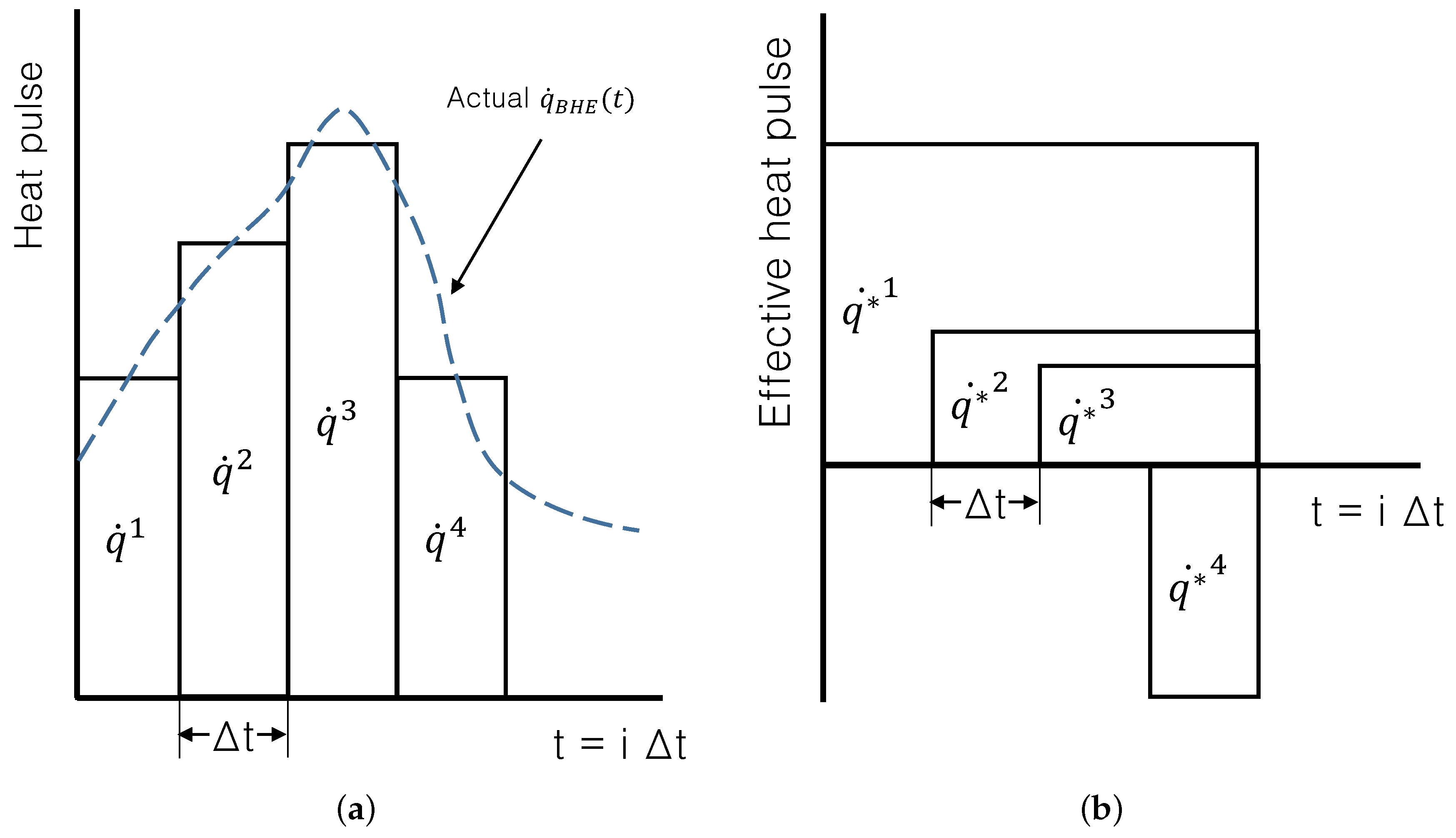
7.1. Time Superposition Technique
7.2. Space Superposition Technique
8. Illustrative Examples
8.1. Example #1
8.2. Example #2
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
Acronyms
| ASHRAE | American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers |
| BHE | Borehole heat exchanger |
| COP | Coefficient of performance of the heat pump in heating mode |
| EER | Coefficient of performance of the heat pump in cooling mode |
| FCS | Finite cylindrical source model |
| FLS | Finite line source model |
| GHE | Ground heat exchanger |
| GSHP | Ground-source heat pump system |
| ICS | Infinite cylindrical source model |
| ILS | Infinite line source model |
Symbols
| D | BHE installation depth |
Exponential integral function | |
Fourier number referred to the radial coordinate | |
Fourier number referred to the borehole radius | |
Fourier number referred to the borehole depth | |
| G | “G-function” or dimensionless soil temperature |
Borehole depth, | |
Boreholes number | |
Thermal power, | |
| R | Dimensionless radial coordinate |
BHE aspect ratio | |
Borehole thermal resistance, m·K·W−1 | |
| T | Temperature, or °C |
| Z | Dimensionless axial coordinate |
Gauss error function | |
Linear heat flux, W·m−1 | |
| r | Radius, m |
Borehole radius, | |
| t | Time, |
Borehole characteristic time, | |
Position vector, | |
| z | Axial coordinate, |
Greek Letters
| α | Thermal diffusivity, m2·s−1 |
| β | Auxiliary integration variable |
| λ | Thermal conductivity, W·m−1·K−1 |
| γ | Euler’s constant |
| Θ | Dimensionless temperature |
Subscripts
| b | Borehole |
| g | Ground source |
| f | Circulating fluid within BHE ducts |
| s | Steady state |
Superscripts
| ¯ | Mean value |
| 0 | Initial time |
| n | Current time step |
| i | Generic time step |
References
- Sarbu, I.; Sebarchievici, C. General review of ground-source heat pump systems for heating and cooling of buildings. Energy Build. 2014, 70, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.D.; Moura, P.; Vaz, G.C.; de Almeida, A.T. Ground source heat pumps as high efficient solutions for building space conditioning and for integration in smart grids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, W.; Conti, P.; Schito, E.; Testi, D. On sustainable and efficient design of ground-source heat pump systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 655, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P. A novel evaluation criterion for GSHP systems based on operative performances. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th International Youth Conference on Energy (IYCE), Pisa, Italy, 27–30 May 2015; pp. 1–8.
- Atam, E.; Helsen, L. Ground-coupled heat pumps: Part 1—Literature review and research challenges in modeling and optimal control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 54, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atam, E.; Helsen, L. Ground-coupled heat pumps: Part 2—Literature review and research challenges in optimal design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 54, 1668–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, F.; Gosselin, L. New methodology to design ground coupled heat pump systems based on total cost minimization. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 62, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comparison, J.D.S.; Cullin, J.R.; Spitler, J.D. Comparison of simulation-based design procedures for hybrid ground source heat pump systems. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on System Simulation in Buildings, Liege, Belgium, 13–15 December 2010.
- Sayyaadi, H.; Amlashi, E.H.; Amidpour, M. Multi-objective optimization of a vertical ground source heat pump using evolutionary algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavy, M.; Nguyen, H.V.; Leong, W.H.; Dworkin, S.B. A methodology and computerized approach for optimizing hybrid ground source heat pump system design. Renew. Energy 2013, 57, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Reiter, S.; Rigo, P. A review on simulation-based optimization methods applied to building performance analysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarosa, C.; Conti, P.; Franco, A.; Grassi, W.; Testi, D. Analysis of thermodynamic losses in ground source heat pumps and their influence on overall system performance. J. Phys. Confer. Ser. 2014, 547, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khoury, R. Computational Modeling of Shallow Geothermal Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Volume 4, p. 245. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.J.; Roux, J.J.; Bernier, M.A.; Cauret, O. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of vertical ground heat exchangers: Domain decomposition and state model reduction. HVAC R Res. 2011, 17, 912–927. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, P.; Testi, D.; Grassi, W. Revised heat transfer modeling of double-U vertical ground-coupled heat exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 106, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batini, N.; Rotta Loria, A.F.; Conti, P.; Testi, D.; Grassi, W.; Laloui, L. Energy and geotechnical behaviour of energy piles for different design solutions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 86, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, M.; Conti, P. Numerical simulation of geothermal resources: A critical overlook. In Proceedings of the European Geothermal Congress 2013, Pisa, Italy, 3–7 June 2013.
- Lamarche, L. Short-term behavior of classical analytic solutions for the design of ground-source heat pumps. Renew. Energy 2013, 57, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geothermal Energy. In ASHRAE Handbook—HVAC Applications; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011; Chapter 34; p. 34.
- Colangelo, G.; Romano, D.; de Risi, A.; Starace, G.; Laforgia, D. A Matlab-Simulink tool for ground source heat pumps simulation. La Termotec. 2012, 3, 63–72. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Lai, A.C. Review of analytical models for heat transfer by vertical ground heat exchangers (GHEs): A perspective of time and space scales. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskilson, P. Thermal Analysis of Heat Extraction Boreholes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lund, Lund, Sweden, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ingersoll, L.R.; Zobel, O.J.; Ingersoll, A.C. Heat Conduction with Engineering, Geological and Other Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1954; p. 325. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, M.; Bernier, M.; Marchio, D. Validity ranges of three analytical solutions to heat transfer in the vicinity of single boreholes. Geothermics 2009, 38, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelvin, T.W. Mathematical and Physical Papers; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1882. [Google Scholar]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jeager, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh, S.P.; Rafferty, K. Design of Geothermal Systems for Commercial and Institutional Buildings; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE): Atlanta, GA, USA, 1997; p. 167. [Google Scholar]
- Man, Y.; Yang, H.; Diao, N.; Liu, J.; Fang, Z. A new model and analytical solutions for borehole and pile ground heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2593–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoin, A. Stockage Intersaisonnier de Chaleur Dans le sol par Batterie D’échangeurs Baionnette Verticaux: Modèle de préDimensionnement. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne, Reims, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.Y.; Diao, N.R.; Fang, Z.H. A finite line-source model for boreholes in geothermal heat exchangers. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2002, 31, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, J.; Javed, S. An analytical method to calculate borehole fluid temperatures for time-scales from minutes to decades. ASHRAE Trans. 2011, 117, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Lai, A.C. Heat-source solutions to heat conduction in anisotropic media with application to pile and borehole ground heat exchangers. Appl. Energy 2012, 96, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozisik, M.N. Heat Conduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Multiphysics® v. 5.2. COMSOL AB. Available online: http//:www.comsol.com (accessed on 26 October 2016).






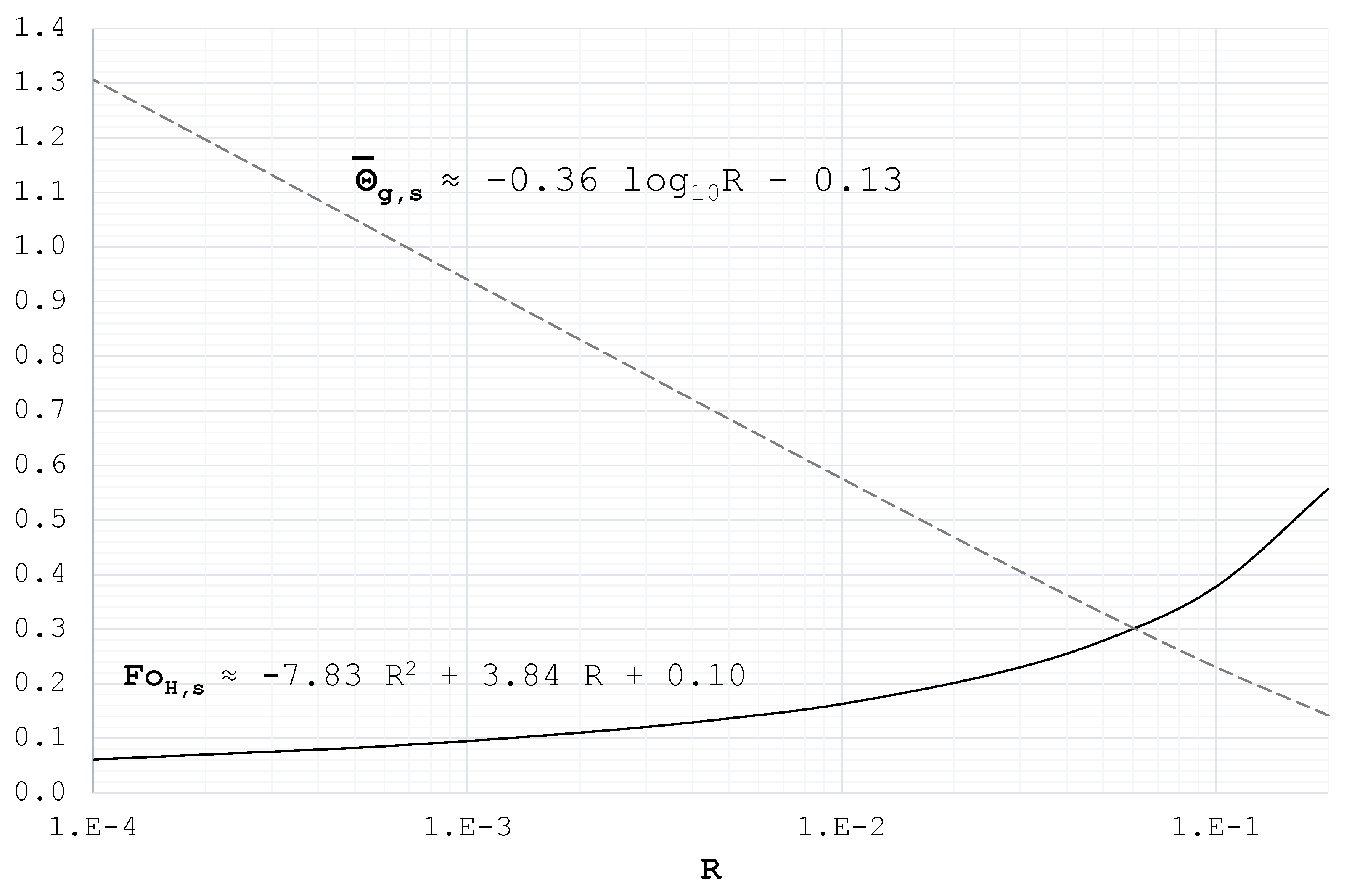





| Geometry | Purely-Conductive Media | Saturated Porous Media | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infinite axial extension | ILS Infinite line source | ICS Infinite cylindrical source | MILS Moving infinite line source | MICS Moving infinite cylindrical source (not yet developed) |
| Finite axial extension | FLS Finite line source | FCS Finite cylindrical source | MFLS Moving finite line source | MFCS Moving finite cylindrical source (not yet developed) |
| Parameter | Configuration #1 | Configuration #2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ground thermal conductivity, | W·m−1·K−1 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Ground thermal diffusivity, | m2·s−1 | 4.8 × 10−7 | 4.8 × 10−7 |
| Borehole radius, | m | 0.075 | 0.075 |
| Borehole depth, | m | 100 | 60 |
| r | 0.075 | 5 | 10 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| ILS | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| ICS | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| FLS | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.10 |
| FCS | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.10 |
| r | 0.075 | 5 | 10 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years | 1 Day | 1 Week | 1 Month | 1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| ILS | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| ICS | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 0.69 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| FLS | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| FCS | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conti, P. Dimensionless Maps for the Validity of Analytical Ground Heat Transfer Models for GSHP Applications. Energies 2016, 9, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110890
Conti P. Dimensionless Maps for the Validity of Analytical Ground Heat Transfer Models for GSHP Applications. Energies. 2016; 9(11):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110890
Chicago/Turabian StyleConti, Paolo. 2016. "Dimensionless Maps for the Validity of Analytical Ground Heat Transfer Models for GSHP Applications" Energies 9, no. 11: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110890
APA StyleConti, P. (2016). Dimensionless Maps for the Validity of Analytical Ground Heat Transfer Models for GSHP Applications. Energies, 9(11), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9110890






