Hysteresis Characteristic in the Hump Region of a Pump-Turbine Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Pump-Turbine Specification
2.2. Test Rig
3. Performance Measurements and Analysis
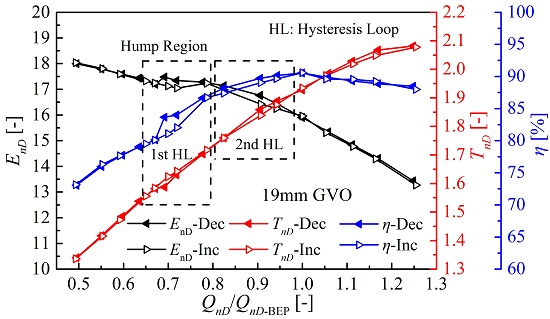
3.1. Performance Measurements
3.2. Analysis of Energy Drop
4. Experiments and Analysis of Pressure Fluctuations
4.1. Analysis of Pressure Fluctuations
4.2. Analysis of Low-Frequency Vortices
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GVO | Guide vane opening |
| BEP | Best efficiency point |
| BPF | Blade passing frequency |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| HILEM | Harbin Institute of Large Electrical Machinery |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission |
| QBEP | Discharge at the best efficiency point under the 19 mm GVO |
| nq | Specific speed of the pump-turbine in pump mode, , min−1 |
| ωs | pump dimensionless specific speed , s−1 |
| H | Pump head at the best efficiency point, m |
| Q | Pump volume discharge at the best efficiency point, m3·s−1 |
| T | Hydraulic torque, N·m |
| g | Gravitational acceleration, m·s−2 |
| ρ | Density of the water, kg·m−3 |
| D1 | Runner inlet diameter in pump mode, m |
| D2 | Runner outlet diameter in pump mode, m |
| B0 | Guide vane height, m |
| D0 | Guide vane distribution diameter, m |
| n | Rotational speed of the runner, rpm |
| n0 | Rotational speed of the runner, s−1 |
| p | Instantaneous pressure, pa |
| Time averaged pressure of 10s for every position, pa | |
| U2 | Circumferential velocity at the tip of the blades at the runner outlet, m·s−1 |
| fn | Rotational frequency, Hz |
| f0 | Minimum frequency resolution, 0.0006fn, Hz |
| f1 | The first dominant frequency, Hz |
| Δθ1 | Phase difference between RG1 and RG2, ° |
| Δθ2 | Phase difference between GV1 and GV2, ° |
| EnD | Energy coefficient, |
| QnD | Discharge coefficient, |
| TnD | Torque coefficient, |
| u | Circumferential velocity, m·s−1 |
| Cu | Component of the absolute velocity in the circumferential direction, m·s−1 |
| Δcu·u | Euler momentum (the change of velocity momentum), m2·s−2 |
Subscripts
| 1 | Runner inlet |
| 2 | Runner outlet |
| net | Net |
| gross | Gross |
| loss | Hydraulic losses |
References
- Erne, S.; Edinger, G.; Doujak, E.; Bauer, C. Numerical and experimental investigation on unsteady inflow conditions of a pump-turbine at low load. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 4th Joint US-European Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting and 12th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–7 August 2014.
- Liu, J.T.; Liu, S.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Jiao, L.; Wang, L.Q.; Sun, Y.K. Numerical investigation of the hump characteristic of a pump–turbine based on an improved cavitation model. Comput. Fluids 2012, 68, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Xiang, G.M.; Gong, R.Z.; Wei, X.Z.; Liu, Z.S. Unsteady simulation and analysis for hump characteristics of a pump turbine model. Renew. Energ. 2015, 77, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Pravesi, G.; Yuan, S.; Cavazzini, G.; Ardizzon, G. Experimental characterization of a pump-turbine in pump mode at hump instability region. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ješe, U.; Fortes-Patella, R.; Dular, M. Numerical study of pump-turbine instabilities under pumping mode off- design conditions. In Proceedings of the ASME-JSME-KSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference 2015, Seoul, Korea, 26–31 July 2015.
- Braun, O.; Kueny, J.L.; Avellan, F. Numerical analysis of flow phenomena related to the unstable energy-discharge characteristic of a pump-turbine in pump mode. In Proceedings of the 2005 ASME Fluid Engineering Division Summer Meeting and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 19–23 June 2005.
- Kaupert, K.A.; Holbein, P.; Staubli, T. A first analysis of flow field hysteresis in a pump impeller. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 1996, 118, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupert, K.A.; Staubli, T. The unsteady pressure field in a high specific speed centrifugal pump impeller—Part I: Influence of the volute. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 1999, 121, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupert, K.A.; Staubli, T. The unsteady pressure field in a high specific speed centrifugal pump impeller—Part II: Transient hysteresis in the characteristic. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 1999, 121, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, M.; Tanaka, K.; Miyagawa, K.; Okubo, T. Numerical simulation of hysteresis on head/discharge characteristics of a centrifugal pump. In Proceedings of the ASME FEDSM 4th ASME_JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 July 2003.
- Ran, H.J.; Luo, X.W.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.Y. Experimental study of the pressure fluctuations in a pump turbine at large partial flow conditions. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.J.; Luo, X.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Farhat, M. Hysteresis phenomena in hydraulic measurement. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 15, 062048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ješe, U. Numerical Study of Pump-Turbine Instabilities under Pumping Mode off-Design Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Zhao, J.L.; Gong, R.Z.; Wei, X.Z.; Qin, D.Q. Optimization of testing system and experiment research for pump turbine model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 52023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Hydraulic Turbines, STORAGE Pumps and Pump-Turbines—Model Acceptance Tests; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Gong, R.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Fu, W.W.; Wei, X.Z.; Liu, Z.S. Fluid flow analysis of drooping phenomena in pump mode for a given guide vane setting of a pump-turbine model. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A (Appl. Phys. Eng.) 2015, 16, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Han, L.; Wang, H.J.; Gong, R.Z.; Wei, X.Z.; Qin, D.Q. Flow characteristics prediction in pump mode of a pump turbine using large eddy simulation. Proc. IMechE E J. Process. Mech. Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, C.; Staubli, T.; Ledergerber, N. Unstable characteristic and rotating stall in turbine brake operation of pump-turbines. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2011, 133, 41101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific speed | nq | 36.1 min−1 | pump mode |
| Runner inlet diameter | D1 | 0.250 m | pump mode |
| Runner outlet diameter | D2 | 0.450 m | pump mode |
| Guide vane height | B0 | 0.04373 m | |
| Guide vane disribution diameter | D0 | 0.54117 m | |
| Optium GVO | GVOBEP | 25 mm | Pump mode |
| Investigated GVO | 19 mm | Pump mode |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Nielsen, T.K.; Qin, D.; Wei, X. Hysteresis Characteristic in the Hump Region of a Pump-Turbine Model. Energies 2016, 9, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9080620
Li D, Wang H, Chen J, Nielsen TK, Qin D, Wei X. Hysteresis Characteristic in the Hump Region of a Pump-Turbine Model. Energies. 2016; 9(8):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9080620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Deyou, Hongjie Wang, Jinxia Chen, Torbjørn K. Nielsen, Daqing Qin, and Xianzhu Wei. 2016. "Hysteresis Characteristic in the Hump Region of a Pump-Turbine Model" Energies 9, no. 8: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9080620
APA StyleLi, D., Wang, H., Chen, J., Nielsen, T. K., Qin, D., & Wei, X. (2016). Hysteresis Characteristic in the Hump Region of a Pump-Turbine Model. Energies, 9(8), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9080620