Design Mechanism and Property of the Novel Fluorescent Probes for the Identification of Microthrix Parvicella In Situ
Abstract
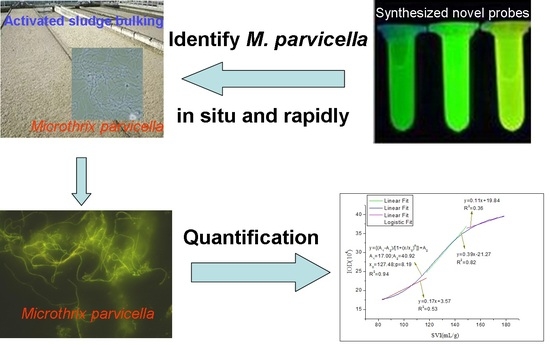
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Activated Sludge Samples
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Spectral Properties
2.3.1. Absorption and Fluorescence Measurements
2.3.2. Fluorescence Qzantum Yields
2.4. Photostability
2.5. The Labeling of M. parvicella
2.6. Images Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 1H NHM of the Fluorescent Probes
3.2. Spectral Properties of Fluorescent Probe A and Probe B in Different Solvents
3.3. The Spectral Characteristics and Structure-Function Relationship of Organic Fluorescent Probes
3.4. Photostability
3.5. The Labeling of M. Parvicella
3.5.1. Determination of the Optimal Identification Concentration
3.5.2. Labeling Effect
3.5.3. Biological Stability of the Probe
3.6. Quantification of the Fluorescence Intensity and SVI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schuler, A.J.; Jassby, D. Filament content threshold for activated sludge bulking: Artifact or reality? Water Res. 2007, 41, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo dos Santos, L.; Ferreira, V.; Neto, M.M.; Pereira, M.A.; Mota, M.; Nicolau, A. Study of 16 Portuguese activated sludge systems based on filamentous bacteria populations and their relationships with environmental parameters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5307–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Z. Filamentous and non-filamentous bulking of activated sludge encountered under nutrients limitation or deficiency conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanysacker, L.; Denis, C.; Roels, J.; Verhaeghe, K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Development and evaluation of a TaqMan duplex real-time PCR quantification method for reliable enumeration of Candidatus Microthrix. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 97, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilén, B.M.; Lumley, D.; Mattsson, A.; Mino, T. Relationship between floc composition and flocculation and settling properties studied at a full scale activated sludge plant. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4404–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.M.; Pagilla, K.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Filamentous bulking sludge-a critical review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qi, R.; Liu, M.; Li, Q.; Bao, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Tandoi, V.; Yang, M. The potential role of 'Candidatus Microthrix parvicella' in phosphorus removal during sludge bulking in two full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2014, 70, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoni, P.; Davoli, D.; Gibin, G. Survey of filamentous microorganisms from bulking and foaming activated-sludge plants in Italy. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, D.H.; Buijsen, H.J.J.V. Microscopic Sludge Investigation Manual; Technische Universiteit Eindhoven: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wágner, D.S.; Ramin, E.; Szabo, P.; Dechesne, A.; Plósz, B.G. Microthrix parvicella abundance associates with activated sludge settling velocity and rheology-Quantifying and modelling filamentous bulking. Water Res. 2015, 78, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De los Reyes, F.L.; Rothauszky, D.; Raskin, L. Microbial community structures in foaming and nonfoaming full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Water Environ. Res. 2002, 74, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.C.; Mesquita, D.P.; Amaral, A.L.; Alves, M.M.; Ferreira, E.C. Quantitative image analysis for the characterization of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5887–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhart, R.; Bradford, D.; Seviour, R.J.; Amann, R.; Blackall, L.L. Development and use of fluorescent in situ hybridization probes for the detection and identification of “ microthrix parvicella ” in activated sludge. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 20, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.L.; Köchling, T. Molecular biology techniques used in wastewater treatment: An overview. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Horn, M.; Daims, H. Fluorescent in situ hybridisation for the identification characterization of prokaryotes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.L.; Mikkelsen, L.H.; Nielsen, P.H. In situ detection of cell surface hydrophobicity of probe-defined bacteria in activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Roslev, P.; Dueholm, T.E.; Nielsen, J.L. Microthrix parvicella, a specialized lipid consumer in anaerobic-aerobic activated sludge plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesselsoe, M.; Nielsen, J.L.; Roslev, P.; Nielsen, P.H. Isotope labeling and microautoradiography of active heterotrophic bacteria on the basis of assimilation of 14CO2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, T.; Gallegos, E.L.D.L.; Schönsee, C.D.; Hesse, T.; Jochmann, M.; Wingender, J.; Denecke, M. Evaluating the influence of wastewater composition on the growth of Microthrix parvicella by GCxGC/qMS and real-time PCR. Water Res. 2016, 88, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Kristiansen, R.; Albertsen, M.; Karst, S.M.; Rossetti, S.; Nielsen, J.L.; Tandoi, V.; Seviour, R.J.; Nielsen, P.H. Metabolic model for the filamentous 'Candidatus Microthrix parvicella' based on genomic and metagenomic analyses. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Hao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L. Study on the synthesis and spectra of a novel kind of carbozole benzothiazole indole styryl cyanine dye with a carbazole bridged chain. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, A.; Karpagam, S. Synthesis, photophysical and electrochemical properties of carbazole-containing 2, 6-quinoline-based conjugated polymer. Polym. Bullet 2016, 73, 2741–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, D.; Li, R.; Tang, Y.; Fei, X.; Zhou, J. Spectra, stability and labeling of 1-(5-carboxypentyl)-4-(2-(N-ethyl-carbazole-3-yl) vinyl) pyridinium bromide with a large Stokes shift. Luminescence 2015, 31, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Ran, L.; Lin, D.; Gu, Y.; Lu, Y. Spectra, stability and labeling of a novel carbazole derivative as a fluorescent turn-on dna probe. J. Fluoresc. 2015, 25, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, X. Study on synthesis and spectrum of novel styryl cyanine dyes with a carbazole bridged chain. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magde, D.; Wong, R.; Seybold, P.G. Fluorescence quantum yields and their relation to lifetimes of rhodamine 6G and fluorescein in nine solvents: Improved absolute standards for quantum yields. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daims, H.; Lücker, S.; Wagner, M. Daime, a novel image analysis program for microbial ecology and biofilm research. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Fei, X.; Jiao, X.; Lin, D.; Zhang, B.; Cao, L. Synthesis and characterization of the fluorescent probes for the labeling of Microthrix parvicella. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2883–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, N.; Das, K.; Nath, D.N.; Bhattacharyya, K. Twisted charge transfer processes of nile red in homogeneous solutions and in faujasite zeolite. Langmuir 1994, 10, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Yong, L.; Guo, F.; Zhang, W.; Tian, M.; Yu, X. Fluorescent imaging of acidic compartments in living cells with a high selective novel one-photon ratiometric and two-photon acidic pH probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowiez, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Plenum press: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.; Sun, W.; Cao, L.; Jiao, X.; Lin, D.; Jia, G. Design and preparation of quantum dots fluorescent probes for in situ identification of Microthrix parvicella in bulking sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noutsopoulos, C.; Mamais, D.; Andreadakis, A.; Stams, A. A hypothesis on Microthrix parvicella proliferation in biological nutrient removal activated sludge systems with selector tanks. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Parameters | DCM | EtOH | MeOH | DMF | DMSO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipole moment | 1.20 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 3.86 | 3.96 | |
| Dielectric constant | 8.9 | 24.5 | 32.7 | 36.7 | 47.2 | |
| A | λmax/nm | 468 | 447 | 440 | 434 | 434 |
| ε/104 mol·L−1·cm−1 | 3.29 | 3.44 | 3.35 | 3.50 | 3.42 | |
| λem/nm | 569 | 565 | 566 | 568 | 568 | |
| fluorescence intensity | 189.41 | 273.59 | 218.62 | 228.71 | 207.52 | |
| Stokes shift/nm | 101 | 118 | 126 | 134 | 134 | |
| B | λmax/nm | 466 | 453 | 448 | 440 | 439 |
| ε/104 mol·L−1·cm−1 | 3.15 | 3.32 | 3.59 | 4.07 | 3.86 | |
| λem/nm | 573 | 573 | 573 | 574 | 573 | |
| fluorescence intensity | 13.97 | 17.43 | 12.59 | 6.78 | 14.91 | |
| Stokes shift/nm | 107 | 120 | 125 | 134 | 134 |
| Probes Sructure | λmax/nm | ε/104 mol·L−1·cm−1 | λem/nm | Fluorescence Intensity | Stokes Shift */nm | Quantum Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The series 1 A1: R3=CH3(CH2)7 A2: R4=CH3(CH2)11 A3: R5=CH3(CH2)15 A: R1 =CH3(CH2)17 B:  | A1 | 445 | 4.48 | 563 | 275.1 | 118 | 0.1086 |
| A2 | 446 | 4.29 | 564 | 296.2 | 118 | 0.1051 | |
| A3 | 445 | 3.35 | 564 | 249.2 | 119 | 0.1036 | |
| A | 447 | 3.44 | 565 | 273.59 | 118 | 0.1058 | |
| B | 453 | 3.32 | 573 | 17.43 | 120 | 0.1043 | |
The series 2 [28] 3a:Y1= R3 3b:Y2= R4 3c:Y3= R5 3d:Y4= R1 | 3a | 502 | 1.00 | 620 | 24.54 | 118 | 0.0127 |
| 3b | 502 | 3.83 | 621 | 35.98 | 119 | 0.0140 | |
| 3c | 502 | 2.45 | 620 | 27.06 | 118 | 0.0127 | |
| 3d | 502 | 3.55 | 620 | 34.74 | 118 | 0.0125 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, X.; Fei, X.; Li, S.; Lin, D.; Ma, H.; Zhang, B. Design Mechanism and Property of the Novel Fluorescent Probes for the Identification of Microthrix Parvicella In Situ. Materials 2017, 10, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070804
Jiao X, Fei X, Li S, Lin D, Ma H, Zhang B. Design Mechanism and Property of the Novel Fluorescent Probes for the Identification of Microthrix Parvicella In Situ. Materials. 2017; 10(7):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070804
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Xiumei, Xuening Fei, Songya Li, Dayong Lin, Huaji Ma, and Baolian Zhang. 2017. "Design Mechanism and Property of the Novel Fluorescent Probes for the Identification of Microthrix Parvicella In Situ" Materials 10, no. 7: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070804
APA StyleJiao, X., Fei, X., Li, S., Lin, D., Ma, H., & Zhang, B. (2017). Design Mechanism and Property of the Novel Fluorescent Probes for the Identification of Microthrix Parvicella In Situ. Materials, 10(7), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070804