Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Membranes’ Matrix
3. Structure of Inorganic Membranes
4. Types of Inorganic Membranes
4.1. Ceramic Membrane
4.1.1. Preparation of Ceramic Membranes
4.1.2. Applications of Ceramic Membranes
4.2. Silica Membrane
4.2.1. Preparation of Silica Membrane
≡Si–OR + HO-Si≡ ↔ ≡Si–O-Si≡ + ROH (Alcohol condensation)
≡Si–OH + HO-Si≡ ↔ ≡Si–O-Si≡ + H2O (Water condensation)
4.2.2. Applications of Silica Membrane
4.3. Zeolite Membrane
4.3.1. Preparation of Zeolite Membrane
4.3.2. Applications of Zeolite Membrane
4.4. Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMM)
4.4.1. Preparation of MMM
4.4.2. Applications of MMM
4.5. Dynamic Membrane
4.6. Liquid Membrane
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N. A comprehensive review on surface modified polymer membranes for biofouling mitigation. Desalination 2015, 356, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P. Next-generation pervaporation membranes: Recent trends, challenges and perspectives. In Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation; Basile, A., Khayet, A.F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 107–141. [Google Scholar]
- Benfer, S.; Popp, U.; Richter, H.; Siewert, C.; Tomandl, G. Development and characterization of ceramic nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 22–23, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faibish, R.S.; Cohen, Y. Fouling and rejection behavior of ceramic and polymer-modified ceramic membranes for ultrafiltration of oil-in-water emulsions and microemulsions. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 191, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nair, B.N.; Taguchi, H.; Itoh, N. Development of tubular substrates, silica based membranes and membrane modules for hydrogen separation at high temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 267, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenoff, T.M.; Dong, J. Highly Selective Zeolite Membranes; Valentin, V., Svetlana, M., Michael, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, S.-L.; Tye, C.-T.; Bhatia, S. Membrane separation process—Pervaporation through zeolite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. The use of nanoparticles in polymeric and ceramic membrane structures: Review of manufacturing procedures and performance improvement for water treatment. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, S.; Gómez, D.; Álvarez, J.R. Industrial Applications of Porous Ceramic Membranes (Pressure-Driven Processes). Membr. Sci. Technol. 2008, 13, 177–216. [Google Scholar]
- Verweij, H. Inorganic membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; David, L. A review on the latest development of carbon membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 193, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-G.; Nair, S. Membranes from nanoporous 1D and 2D materials: A review of opportunities, developments, and challenges. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 104, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Johnson, D.J.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes: Surface modification for minimizing (bio)colloidal fouling. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Elam, J.W.; Darling, S.B. Membrane materials for water purification: Design, development, and application. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.; Goh, P.; Lau, W.; Misdan, N.; Ismail, A. Nanomaterials for biofouling and scaling mitigation of thin film composite membrane: A review. Desalination 2016, 393, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N.; Hashaikeh, R. Electrically conductive polymeric membranes for fouling prevention and detection: A review. Desalination 2016, 391, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.P.; Bordado, J.C. Smart composite reverse-osmosis membranes for energy generation and water desalination processes A2-. In Smart Composite Coatings and Membranes; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Buonomenna, M.G. Smart composite membranes for advanced wastewater treatments A2-. In Smart Composite Coatings and Membranes; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 371–419. [Google Scholar]
- Mohshim, D.F.; Mukhtar, H.B.; Man, Z.; Nasir, R. Latest Development on Membrane Fabrication for Natural Gas Purification: A Review. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.W.; Koros, W.J. Carbon molecular sieve gas separation membranes-I. Preparation and characterization based on polyimide precursors. Carbon 1994, 32, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morooka, S.; Kusakabe, K. Microporous Inorganic Membranes for Gas Separation. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, T.; Wessling, M. When Do Sorption-Induced Relaxations in Glassy Polymers Set in? Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4992–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, J.D.; Paul, D.R.; Koros, W.J. Natural gas permeation in polyimide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.J.; Trimm, D.L. Carbon molecular sieves used in gas separation membranes. Carbon 1983, 21, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Pervaporation. In Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 379–416. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander Stern, S. Polymers for gas separations: The next decade. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 94, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M.; Liu, Q.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Comparison of transport properties of rubbery and glassy polymers and the relevance to the upper bound relationship. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, T.A.; Fuertes, A.B. Carbon molecular sieve gas separation membranes based on poly(vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride). Carbon 2000, 38, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Mahajan, R. Pushing the limits on possibilities for large scale gas separation: Which strategies? J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 175, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saufi, S.M.; Ismail, A.F. Fabrication of carbon membranes for gas separation—A review. Carbon 2004, 42, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBain, J.W. The Sorption of Gases and Vapours by Solids. J. Phys. Chem. 1932, 37, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, R.R. Inorganic Membranes Synthesis, Characteristics and Applications; Springer Science + Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gwak, J.; Ayral, A.; Rouessac, V.; Cot, L.; Grenier, J.C.; Jang, E.S.; Choy, J.H. Synthesis and characterization of porous inorganic membranes exhibiting superconducting properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 84, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, N.; Tong, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, M.; Caro, J. Covalent synthesis of dense zeolite LTA membranes on various 3-chloropropyltrimethoxysilane functionalized supports. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Meulenberg, W.A.; Buchkremer, H.P. Manufacturing strategies for asymmetric ceramic membranes for efficient separation of oxygen from air. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koops, G.H. Preparation and Characterization of Micro- and Ultrafiltration Membranes. Encyclopedia of Desalination and Water Resource, 2002. Available online: http://www.desware.net/Sample-Chapters/D05/D09-028.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2017).
- Hsieh, H.P. (Ed.) Materials and preparation of inorganic membranes. In Membrane Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Chapter 3; pp. 23–92. [Google Scholar]
- Soria, R. Overview on industrial membranes. Catal. Today 1995, 25, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henis, J.M.S.; Tripodi, M.K. Composite hollow fiber membranes for gas separation: The resistance model approach. J. Membr. Sci. 1981, 8, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chung, T.S.; Li, D.F.; Cao, C.; Kulprathipanja, S. Fabrication of Matrimid/polyethersulfone dual-layer hollow fiber membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chung, T.S.; Wang, R. Morphological aspects and structure control of dual-layer asymmetric hollow fiber membranes formed by a simultaneous co-extrusion approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Chung, T.S.; Pramoda, K.P. Fabrication of dual-layer polyethersulfone (PES) hollow fiber membranes with an ultrathin dense-selective layer for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Wang, R.; Li, D.F.; Chng, M.L. Chemical Cross-Linking Modification of Polyimide/Poly(ether sulfone) Dual-Layer Hollow-Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagō, S.; Mizutani, Y. Microporous polypropylene hollow fibers with double layers. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, K.; Kita, H.; Okamoto, K.; Hoshino, H.; Yoshinaga, T.; Kusuki, Y. Preparation of composite hollow fiber membranes of poly(ethylene oxide)-containing polyimide and their CO2/N2 separation properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 146, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, S.; Lin, C.X.C.; Ding, L.; Thambimuthu, K.; Diniz da Costa, J.C. Ceramic membranes for gas processing in coal gasification. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Shankar, S.; Shah, P.R.; Kumar, S. A comprehensive model for catalytic membrane reactor. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2006, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.G. Recent research in catalytic inorganic membrane reactors. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2003, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tim Van Gestel, W.A.M.; Buchkremer, H.P. Manufacturing of microporous ceramic membranes for environmental applications. In Proceedings of the Innovation for Sustainable Production, Bruges, Belgium, 21–24 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K. Preparation of Ceramic Membranes. In Ceramic Membranes for Separation and Reaction; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 21–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zürcher, S.; Graule, T. Influence of dispersant structure on the rheological properties of highly-concentrated zirconia dispersions. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.H.; Kim, I.C.; Min, B.R.; Lee, K.H. Preparation and characterization of ultrathin alumina hollow fiber microfiltration membrane. Desalination 2006, 193, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaf, A.J. Fundamentals of membrane top-layer synthesis and processing. In Membrane Science and Technology; Burggraaf, A.J., Cot, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Chapter 8; pp. 259–329. [Google Scholar]
- Falamaki, C.; Beyhaghi, M. Slip casting process for the manufacture of tubular alumina microfiltration membranes. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2009, 27, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.K.; Tsai, D.S. Preparation and analysis of a silicon carbide composite membrane. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.L.O.; Vasconcelos, D.C.L.; Nunes, E.H.M.; Caldeira, L.; Costa, V.C.; Musse, A.P.; Hatimondi, S.A.; Nascimento, J.F.; Grava, W.; Vasconcelos, W.L. Processing, structural characterization and performance of alumina supports used in ceramic membranes. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Cheng, J.G.; Liu, X.Q.; Meng, G.Y.; Ding, Y.W. Preparation and Sintering of Macroporous Ceramic Membrane Support from Titania Sol-Coated Alumina Powder. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, X.; Su, W. Fabrication of dense YSZ electrolyte membranes by a modified dry-pressing using nanocrystalline powders. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1627–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering; Newnes: Boston, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Maiti, H.S. Tape-cast ceramic membranes for microfiltration application. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 5221–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Maiti, H.S. Ceramic membrane by tape casting and sol–gel coating for microfiltration and ultrafiltration application. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2009, 70, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, K.; Lidén, E. Preparation of alumina membranes by tape casting and dip coating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, J.; Avci, C.G.; Günay, V.; Terpstra, R.A.; van Eijk, J.P.G.M. Preparation and characterization of microporous ceramic hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 112, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpstra, R.A.; Bonekamp, B.C.; Veringa, H.J. Preparation, characterization and some properties of tubular alpha alumina ceramic membranes for microfiltration and as a support for ultrafiltration and gas separation membranes. Desalination 1988, 70, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallada, R.; Menéndez, M. Inorganic Membranes Synthesis, Characterization and Applications: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury, B.F.K.; Li, K. A morphological study of ceramic hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, B.F.K.; Wu, Z.; Li, K. A morphological study of ceramic hollow fibre membranes: A perspective on multifunctional catalytic membrane reactors. Catal. Today 2010, 156, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonaphapdeelert, S.; Li, K. Preparation and characterization of hydrophobic ceramic hollow fibre membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 291, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Li, H. Preparation and characterization of alumina hollow fiber membranes. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2009, 3, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, N.; Meng, B.; Tan, X.; Li, K. Preparation and Oxygen Permeation Properties of Highly Asymmetric La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−α Perovskite Hollow-Fiber Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Chen, O.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Ceramic asymmetric hollow fibre membranes—One step fabrication process. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, K.; Hughes, R. Preparation of porous aluminium oxide (Al2O3) hollow fibre membranes by a combined phase-inversion and sintering method. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiten-Olieman, M.W.J.; Raaijmakers, M.J.T.; Winnubst, L.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, A.; Benes, N.E. Porous stainless steel hollow fibers with shrinkage-controlled small radial dimensions. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Tan, X.; Ma, Z. A phase inversion/sintering process to fabricate nickel/yttria-stabilized zirconia hollow fibers as the anode support for micro-tubular solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, D.; Lin, B.; Dong, Y.; Meng, G.; Liu, X. Asymmetric porous cordierite hollow fiber membrane for microfiltration. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 487, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, D.M.; Antov, M.G.; Peričin, D.M.; Höflinger, W.; Tekić, M.N. The possibility for improvement of ceramic membrane ultrafiltration of an enzyme solution. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 33, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, J. Ceramic membranes: A robust filtration alternative. Filtr. Sep. 2005, 42, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, R.; Bhave, R.; Jung, G. Applications and benefits of ceramic membranes. Membr. Technol. 2003, 2003, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daufin, G.; Escudier, J.P.; Carrère, H.; Bérot, S.; Fillaudeau, L.; Decloux, M. Recent and Emerging Applications of Membrane Processes in the Food and Dairy Industry. Food Bioprod. Process. 2001, 79, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, B.; Fukumoto, L.R.; Koseoglu, S.S. Membrane Processing of Fruit Juices and Beverages: A Review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 109–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheryan, M.; Rajagopalan, N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 151, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska-Nowak, K.M. Application of ceramic membranes for the separation of dye particles. Desalination 2010, 254, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Capannelli, C.; del Borghi, A.; Colombino, M.; Conio, O. Water treatment for drinking purpose: Ceramic microfiltration application. Desalination 2001, 141, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Fane, A.G.; Ho, W.W.; Matsuura, T. Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh Kumar, S.; Madhu, G.M.; Roy, S. Fouling behaviour, regeneration options and on-line control of biomass-based power plant effluents using microporous ceramic membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Sinha, R.; Krishnan, E.; Patterson, C. Ceramic Filter for Small System Drinking Water Treatment: Evaluation of Membrane Pore Size and Importance of Integrity Monitoring. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, B.Z.; Gao, N.Y.; Fan, J.C. Effect of coagulation pretreatment on fouling of an ultrafiltration membrane. Desalination 2007, 204, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, B.S.; Davies, S.H.R.; Chen, K.C.; Jaglowski, D.R.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J. Effects of ozonation on the permeate flux of nanocrystalline ceramic membranes. Water Res. 2005, 39, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, J. In situ ozonation to control ceramic membrane fouling in drinking water treatment. Desalination 2013, 328, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, J. The rising pressure of global water shortages. Nature 2015, 517, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairom, N.H.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Effect of various zinc oxide nanoparticles in membrane photocatalytic reactor for Congo red dye treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 137, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alem, A.; Sarpoolaky, H.; Keshmiri, M. Sol–gel preparation of titania multilayer membrane for photocatalytic applications. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.S.; Lim, T.M.; Chiang, K.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting the performance of a low-pressure submerged membrane photocatalytic reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 130, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S. Photocatalytic membrane reactors (PMRs) in water and wastewater treatment. A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissen, S.; Xi, W.; Weidemeyer, A.; Vogelpohl, A.; Bousselmi, L.; Ghrab, A.; Nnabi, A. Comparison of suspended and fixed photocatalytic reactor systems. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2000, 44, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Augugliaro, V.; Litter, M.; Palmisano, L.; Soria, J. The combination of heterogeneous photocatalysis with chemical and physical operations: A tool for improving the photoprocess performance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2006, 7, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Y.; Irawan, A.; Ku, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of Acid Red 4 using a titanium dioxide membrane supported on a porous ceramic tube. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Meng, G.Y. Preparation of asymmetric pure titania ceramic membranes with dual functions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellobono, I.R.; Morazzoni, F.; Bianchi, R.; Mangone, E.S.; Stanescu, R.; Costache, C.; Tozzi, P.M. Solar energy driven photocatalytic membrane modules for water reuse in agricultural and food industries. Pre-industrial experience using s-triazines as model molecules. Int. J. Photoenergy 2005, 7, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shan, W.; Davies, S.H.R.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J.; Tarabara, V.V. Interactions of Aqueous NOM with Nanoscale TiO2: Implications for Ceramic Membrane Filtration-Ozonation Hybrid Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5488–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Bai, H.; Sun, D.D. Concurrent filtration and solar photocatalytic disinfection/degradation using high-performance Ag/TiO2 nanofiber membrane. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabelas, A.; Plakas, K.; Sarasidis, V.; Patsios, S. The effect of humic acids on the removal of atrazine from water in a continuous photocatalytic membrane reactor. Glob. NEST J. 2014, 16, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, M.A.; Varghese, S.; Nair, S.S. Photocatalytic water treatment by titanium dioxide: Recent updates. Catalysts 2012, 2, 572–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romão, J.; Barata, D.; Habibovic, P.; Mul, G.; Baltrusaitis, J. High throughput analysis of photocatalytic water purification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7612–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashaghi, K.S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Czermak, P. Ceramic ultra-and nanofiltration membranes for oilfield produced water treatment: A mini review. Open Environ. J. 2007, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Flynn, J.; Cook, R.; Casaday, A. Removal of oil, grease, and suspended solids from produced water with ceramic crossflow microfiltration. SPE Prod. Eng. 1991, 6, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Willershausen, D.; Ashaghi, K.S.; Engel, L.; Placido, L.; Mund, P.; Bolduan, P.; Czermak, P. Investigations on the use of different ceramic membranes for efficient oil-field produced water treatment. Desalination 2010, 250, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lee, R. Purification of produced water by ceramic membranes: Material screening, process design and economics. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 3455–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, S.R.H.; Sebzari, M.R.; Hemati, M.; Rekabdar, F.; Mohammadi, T. Ceramic membrane performance in microfiltration of oily wastewater. Desalination 2011, 265, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyhani, A.; Meighani, H.M. Optimal operating conditions of micro-and ultra-filtration systems for produced-water purification: Taguchi method and economic investigation. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 19642–19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschenfelder, S.E.; Louvisse, A.M.; Borges, C.P.; Meabe, E.; Izquierdo, J.; Campos, J.C. Evaluation of ceramic membranes for oilfield produced water treatment aiming reinjection in offshore units. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 131, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; Schlicher, R.; Long, J.; Yu, J.; Lehman, S.; Jacangelo, J.G. Recovery optimization of membrane processes for treatment of produced water with high silica content. Desal. Water Treat. 2011, 36, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silalahi, S.H.; Leiknes, T. High frequency back-pulsing for fouling development control in ceramic microfiltration for treatment of produced water. Desal. Water Treat. 2011, 28, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeger, F.; Delhaye, T.; Fuchs, W. The use of ceramic microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes for particle removal from anaerobic digester effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.H.; Tardieu, E.; Qian, Y.; Wen, X.H. Ultrafiltration membrane bioreactor for urban wastewater reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 177, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zeng, J.; Tay, J. A submerged tubular ceramic membrane bioreactor for high strength wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tewari, P.; Singh, R.; Batra, V.; Balakrishnan, M. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) for wastewater treatment: Filtration performance evaluation of low cost polymeric and ceramic membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Comparison of fouling characteristics in different pore-sized submerged ceramic membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5907–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Jing, W.; Xing, W.; Xu, N. Experiment and calculation of filtration processes in an external-loop airlift ceramic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerneaux, S.; Strużyńska, I.; Kujawski, W.M.; Persin, M.; Larbot, A. Comparison of various membrane distillation methods for desalination using hydrophobic ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbot, A.; Gazagnes, L.; Krajewski, S.; Bukowska, M.; Kujawski, W. Water desalination using ceramic membrane distillation. Desalination 2004, 168, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, S.R.; Kujawski, W.; Bukowska, M.; Picard, C.; Larbot, A. Application of fluoroalkylsilanes (FAS) grafted ceramic membranes in membrane distillation process of NaCl solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.K.; Rhadfi, T.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A.; Khraisheh, M.; Hilal, N. Reducing flux decline and fouling of direct contact membrane distillation by utilizing thermal brine from MSF desalination plant. Desalination 2016, 379, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Sondhi, K.; Majumdar, S.; Sarkar, S. Development of hydrophobic clay–alumina based capillary membrane for desalination of brine by membrane distillation. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.W.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.S. β-Sialon ceramic hollow fiber membranes with high strength and low thermal conductivity for membrane distillation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, B.; Koseoglu, H.; Yigit, N.; Sayilgan, E.; Beyhan, M.; Kitis, M. The removal of disinfection by-product precursors from water with ceramic membranes. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofs, B.; Ogier, J.; Vries, D.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Cornelissen, E.R. Comparison of ceramic and polymeric membrane permeability and fouling using surface water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoquart, C.; Servais, P.; Bérubé, P.R.; Barbeau, B. Hybrid membrane processes using activated carbon treatment for drinking water: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 411, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Tarabara, V.V.; Masten, S.J. Effect of ozone dosage and hydrodynamic conditions on the permeate flux in a hybrid ozonation–ceramic ultrafiltration system treating natural waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiksdal, L.; Leiknes, T. The effect of coagulation with MF/UF membrane filtration for the removal of virus in drinking water. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Hacarlioglu, P.; Oyama, S.T. The Effect of Pressure in Membrane Reactors: Trade-Off in Permeability and Equilibrium Conversion in the Catalytic Reforming of CH4 with CO2 at High Pressure. Top. Catal. 2004, 29, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Nishi, Y.; Utsumi, T.S.K.; Nakamura, R. Preparation of Thin Li4SiO4 Membranes by Using a CVD Method. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Ono, K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sugawara, T.; Nakao, S.I. Preparation of a stable silica membrane by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition method. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, S.; Hacarlioglu, P. The boundary between simple and complex descriptions of membrane reactors: The transition between 1-D and 2-D analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredesen, R.; Jordal, K.; Bolland, O. High-temperature membranes in power generation with CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 1129–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Gallucci, F. Membranes for Membrane Reactors; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kesmez, Ö.; Burunkaya, E.; Kiraz, N.; Çamurlu, H.E.; Asiltürk, M.; Arpaç, E. Effect of acid, water and alcohol ratios on sol-gel preparation of antireflective amorphous SiO2 coatings. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 3130–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiter, R. Hydrothermal stability of silica-based membranes. In Proceedings of Sol-Gel Conference; Energy Reasearch Center of the Netherland Porto de Galinhas: Porto de Galinhas, Brasil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, S.J.; Oyama, S.T.; de Souza, K.R.; Noronha, F.B. Review of silica membranes for hydrogen separation prepared by chemical vapor deposition. Inorg. Polym. Compos. Membr. Struct. Funct. Correl. Membr. Sci. Technol. Ser. 2011, 14, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, M.; Aida, H.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sugawara, T.; Nakao, S.i.; Yamazaki, S.; Inada, T.; Iwamoto, Y. Steam stability of a silica membrane prepared by counterdiffusion chemical vapor deposition. Desalination 2006, 193, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livage, J.; Sanchez, C. Sol-gel chemistry. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 145, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, A.B.; Klein, L.C. Transparent inorganic/organic copolymers by the sol-gel process: Copolymers of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), vinyl triethoxysilane (VTES) and (meth) acrylate monomers. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1995, 4, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estella, J.; Echeverría, J.C.; Laguna, M.; Garrido, J.J. Silica xerogels of tailored porosity as support matrix for optical chemical sensors. Simultaneous effect of pH, ethanol: TEOS and water: TEOS molar ratios, and synthesis temperature on gelation time, and textural and structural properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labropoulos, A.I.; Romanos, G.E.; Karanikolos, G.N.; Katsaros, F.K.; Kakizis, N.K.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Comparative study of the rate and locality of silica deposition during the CVD treatment of porous membranes with TEOS and TMOS. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H. Preparation of Composite Microporous Silica Membranes Using TEOS and 1, 2-Bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane as Precursors for Gas Separation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Hoang, M.; Ng, D.; Doherty, C.; Hill, A.; Gray, S. Effect of heat treatment on pervaporation separation of aqueous salt solution using hybrid PVA/MA/TEOS membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 127, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanc, P.; Larbot, A.; Palmeri, J.; Lopez, M.; Cot, L. Hafnia ceramic nanofiltration membranes. Part I: Preparation and characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 149, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Brinker, C.J.; Smith, D.M. Pore structure evolution in silica gel during aging/drying I. Temporal and thermal aging. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 142, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, R.S.A.; Hekkink, J.H.A.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A.J. Formation and characterization of supported microporous ceramic membranes prepared by sol-gel modification techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 99, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, R.S.A.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A.J. Analysis and theory of gas transport in microporous sol-gel derived ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 104, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoudjil, N.; Lamrani, N.; Larbot, A. Silica porous membranes synthesis and characterization. Desal. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elma, M.; Yacou, C.; Wang, D.K.; Smart, S.; da Costa, J.C.D. Microporous silica based membranes for desalination. Water 2012, 4, 629–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B.N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Okubo, T.; Suematsu, H.; Keizer, K.; Nakao, S.I. Sol-gel synthesis of molecular sieving silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 135, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhorn, R.J.R.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A.J. Gas transport and separation with ceramic membranes. Part II. Synthesis and separation properties of microporous membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 66, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sea, B.K.; Kusakabe, K.; Morooka, S. Pore size control and gas permeation kinetics of silica membranes by pyrolysis of phenyl-substituted ethoxysilanes with cross-flow through a porous support wall. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 130, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Oyama, S.T. Gas permeation characteristics of a hydrogen selective supported silica membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Yoshino, Y.; Nomura, M.; Nair, B.N.; Nakao, S.I. A hybrid processing method for high performance hydrogen-selective silica membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Zhang, L.; Oyama, S.T.; Niu, S.; Saraf, R.F. Synthesis, characterization, and gas permeation properties of a hydrogen permeable silica membrane supported on porous alumina. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 231, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, L. Physics and applications of dip coating and spin coating. In MRS Proceedings; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kanellopoulos, N.K. Recent Advances in Gas Separation by Microporous Ceramic Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Okubo, T.; Inoue, H. Introduction of specific gas reactivity to porous glass membranes by treatment with tetraethoxysilane. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 42, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavalas, G.R.; Megiris, C.E.; Nam, S.W. Deposition of H2-permselective SiO2 films. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Gavalas, G.R. Preparation of H2 Permselective Silica Membranes by Alternating Reactant Vapor Deposition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapatsis, M.; Gavalas, G.R.; Xomeritakis, G. Chemical vapor deposition membranes. In Membrane Science and Technology; Kanellopoulos, N.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlhorn, R.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A. Gas and surface diffusion in modified γ-alumina systems. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 46, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morooka, S.; Yan, S.; Kusakabe, K.; Akiyama, Y. Formation of hydrogen-permselective SiO2 membrane in macropores of α-alumina support tube by thermal decomposition of TEOS. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Maeda, H.; Kusakabe, K.; Morooka, S.; Akiyama, Y. Hydrogen-Permselective SiO2 Membrane Formed in Pores of Alumina Support Tube by Chemical Vapor Deposition with Tetraethylorthosilicate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 33, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiter, R.; Rietkerk, M.D.; Bonekamp, B.C.; van Veen, H.M.; Kessler, V.G.; Vente, J.F. Sol–gel routes for microporous zirconia and titania membranes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 48, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favennec, L.; Jousseaume, V.; Rouessac, V.; Fusalba, F.; Durand, J.; Passemard, G. Porous extreme low κ (ELκ) dielectrics using a PECVD porogen approach. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2004, 7, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, M.; Mee, S.; da Costa, J.D. Performance of porous inorganic membranes in non-osmotic desalination. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3998–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Fraser, T.; Myat, D.; Smart, S.; Zhang, J.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Liubinas, A.; Duke, M. A pervaporation study of ammonia solutions using molecular sieve silica membranes. Membranes 2014, 4, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elma, M.; Yacou, C.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Wang, D.K. Performance and long term stability of mesoporous silica membranes for desalination. Membranes 2013, 3, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessler, S.; Jordan, L.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Lu, G.Q. Performance of hydrophobic and hydrophilic silica membrane reactors for the water gas shift reaction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, M.C.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Do, D.D.; Gray, P.G.; Lu, G.Q. Hydrothermally Robust Molecular Sieve Silica for Wet Gas Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessler, S.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Lu, G. Hydrophobicity of templated silica xerogels for molecular sieving applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2001, 1, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xomeritakis, G.; Naik, S.; Braunbarth, C.M.; Cornelius, C.J.; Pardey, R.; Brinker, C.J. Organic-templated silica membranes: I. Gas and vapor transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 215, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, M.C.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Lu, G.Q.; Petch, M.; Gray, P. Carbonised template molecular sieve silica membranes in fuel processing systems: Permeation, hydrostability and regeneration. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, S.; Duke, M.C.; da Costa, J.C.D. Carbonised template silica membranes for desalination. Desalination 2009, 236, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladewig, B.P.; Tan, Y.H.; Lin, C.X.C.; Ladewig, K.; da Costa, J.C.D.; Smart, S. Preparation, characterization and performance of templated silica membranes in non-osmotic desalination. Materials 2011, 4, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, R.M.; Maier, W.F.; Verweij, H. Hydrophobic silica membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 158, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaniello, J.; Engelen, C.W.R.; Haije, W.G.; Pex, P.P.A.C.; Vente, J.F. Long-term pervaporation performance of microporous methylated silica membranes. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 834–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, J.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Tsuru, T. Development of Robust Organosilica Membranes for Reverse Osmosis. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13996–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battersby, S.; Smart, S.; Ladewig, B.; Liu, S.; Duke, M.C.; Rudolph, V.; Costa, J.C.D.D. Hydrothermal stability of cobalt silica membranes in a water gas shift membrane reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuhara, Y.H.; Mori, H.; Saito, T.; Iwamoto, Y. High-Temperature Hydrogen Adsorption Properties of Precursor-Derived Nickel Nanoparticle-Dispersed Amorphous Silica. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezashi, M.; Asaeda, M. Hydrogen permeation characteristics and stability of Ni-doped silica membranes in steam at high temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, D.; Liu, S.; Ladewig, B.P.; da Costa, J.C.D. Cobalt-doped silica membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.X.C.; Ding, L.P.; Smart, S.; da Costa, J.C.D. Cobalt oxide silica membranes for desalination. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, A.K.; Manawi, Y.M.; Rhadfi, T.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Khraisheh, M.; Benyahia, F. Synoptic analysis of direct contact membrane distillation performance in Qatar: A case study. Desalination 2015, 360, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, T.; Igi, R.; Kanezashi, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Fujisaki, S.; iwamoto, Y. Permeation properties of hydrogen and water vapor through porous silica membranes at high temperatures. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Santoro, S.; Galiano, F.; Basile, A. Pervaporation membranes: Preparation, characterization, and application. In Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation; Basile, A., Khayet, A.F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 19–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Pendergast, M.T.M.; Ghosh, A.K. Nanotechnology-Based Membranes for Water Purification, in Nanotechnology Applications for Clean Water, 2nd ed.; Savage, A.S.S.D., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2014; Chapter 9; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar]
- Buonomenna, M.G. Nano-enhanced reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2013, 314, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas, A.; Mallada, R.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Menéndez, M.; Santamaría, J. Preparation of mordenite membranes for pervaporation of water-ethanol mixtures. Desalination 2002, 148, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Tsutsumi, K. Adsorption characteristics of synthesized mordenite membranes. Adsorption 1997, 3, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, W.J.; van den Broeke, L.J.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J.A. Temperature dependence of one-component permeation through a silicalite-1 membrane. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Kalipcilar, H.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D. Pervaporation of organic/water mixtures through B-ZSM-5 zeolite membranes on monolith supports. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 215, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, J.; Sterte, J.; Anthonis, M.; Bons, A.J.; Carstensen, B.; Corcoran, N.; Cox, D.; Deckman, H.; de Gijnst, W.; de Moor, P.P. High-flux MFI membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 52, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Kusakabe, K.; Morooka, S. Gas permeation properties of A-type zeolite membrane formed on porous substrate by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 141, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, J.; Schoeman, B.; Sterte, J. Ultrathin oriented zeolite LTA films. Chem. Commun. 1997, 13, 1193–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, K.; Kuroda, T.; Uchino, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Morooka, S. Gas permeation properties of ion-exchanged faujasite-type zeolite membranes. AIChE J. 1999, 45, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tuan, V.A.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D. X-type zeolite membranes: Preparation, characterization, and pervaporation performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 53, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalipcilar, H.; Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Synthesis and Separation Performance of SSZ-13 Zeolite Membranes on Tubular Supports. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshusta, J.C.; Tuan, V.A.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D. Synthesis and Permeation Properties of SAPO-34 Tubular Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 3924–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, Y.H.; Tsai, T.G.; Sung, S.L.; Shih, H.C.; Wu, C.N.; Chao, K.J. Synthesis and characterization of zeolite (MFI) membrane on anodic alumina. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1996, 92, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, V.A.; Li, S.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Preparation and pervaporation properties of a MEL-type zeolite membrane. Chem. Commun. 2001, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Ueyama, K.; Matsukata, M. Synthesis of FER membrane on an alumina support and its separation properties. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Chon, S.K.I.H., Sun, U.Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 2195–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y. Dehydration of TFEA/water mixture through hydrophilic zeolite membrane by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 291, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronas, J.; Santamaria, J. State-of-the-Art in Zeolite Membrane Reactors. Top. Catal. 2004, 29, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroglu, M.; Gurkaynak, M. Fabrication and characterization of silica modified polyimide–zeolite mixed matrix membranes for gas separation properties. Polym. Bull. 2011, 66, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, B.; Smyrl, W.H.; Cussler, E.L. Polymer-zeolite composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Qu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.H.; Chen, H.L.; Gao, C.J. Preparation and characterization of surface-modified zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes for desalination. Desal. Water Treat. 2011, 34, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Hong, Z.; Milne, N.; Doherty, C.M.; Zou, L.; Lin, Y.S.; Hill, A.J.; Gu, X.; Duke, M. Desalination of seawater ion complexes by MFI-type zeolite membranes: Temperature and long term stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çulfaz, P.Z.; Çulfaz, A.; Kalıpçılar, H. Preparation of MFI type zeolite membranes in a flow system with circulation of the synthesis solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Lin, Y.; Yang, W. Synthesis and properties of A-type zeolite membranes by secondary growth method with vacuum seeding. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motuzas, J.; Julbe, A.; Noble, R.; van der Lee, A.; Beresnevicius, Z. Rapid synthesis of oriented silicalite-1 membranes by microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zah, J.; Krieg, H.M.; Breytenbach, J.C. Layer development and growth history of polycrystalline zeolite A membranes synthesised from a clear solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 93, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, A.; Gora, L.; Jansen, J.; Makkee, M.; Maschmeyer, T. Zeolite A membranes synthesized on a UV-irradiated TiO 2 coated metal support: The high pervaporation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 224, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeary, E.; Jansen, J.; Kapteijn, F. Zeolite based films, membranes and membrane reactors: Progress and prospects. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 90, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bekkum, H.; Geus, E.; Kouwenhoven, H. Supported zeolite systems and applications. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1994, 85, 509–542. [Google Scholar]
- Coronas, J.; Santamaría, J. Separations using zeolite membranes. Sep. Purif. Methods 1999, 28, 127–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemimoghadam, M.; Mohammadi, T. Preparation of NaA zeolite membranes for separation of water/UDMH mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 47, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigami, Y.; Kondo, M.; Abe, J.; Kita, H.; Okamoto, K. The first large-scale pervaporation plant using tubular-type module with zeolite NaA membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 25, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, S.; Arruebo, M.; Coronas, J.N.; Menéndez, M.; Santamaría, J. Preparation of MFI type tubular membranes by steam-assisted crystallization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 50, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsufuji, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsukata, M.; Ueyama, K. Separation of butane and xylene isomers with MFI-type zeolitic membrane synthesized by a vapor-phase transport method. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 178, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Ueyama, K.; Matsukata, M. A defect-free mordenite membrane synthesized by vapour-phase transport method. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 19, 1967–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, J.J.; Budd, P.M. Separation of alcohol/water mixtures by pervaporation through zeolite A membranes. Microporous Mater. 1997, 12, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Kita, H.; Okamoto, K.I. A novel method for the synthesis of high performance silicalite membranes. Chem. Commun. 2000, 19, 1889–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, A.R. Industrial Catalysis: By Jens Hagen Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Weinheim, Germany (2005). 507 pages. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 84, 619. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.; Bonilla, G.; Diaz, I.; Nery, J.G.; Sujaoti, K.; Amat, M.A.; Kokkoli, E.; Terasaki, O.; Thompson, R.W.; Tsapatsis, M. Microstructural optimization of a zeolite membrane for organic vapor separation. Science 2003, 300, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bein, T. Synthesis and Applications of Molecular Sieve Layers and Membranes. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.S.T.; Chao, K.J. Membranes and films of zeolite and zeolite-like materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2001, 62, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukata, M.; Kikuchi, E. Zeolitic Membranes: Synthesis, Properties, and Prospects. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 70, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Bao, Y.; Song, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Lin, L. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxy-sodalite zeolite membrane. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 75, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Tsutsumi, K. Synthesis of A-type zeolite membrane using a plate heater and its formation mechanism. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 37, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, L.C.; Kuck, J.A.; Tsapatsis, M. Deposition of oriented zeolite A films: In situ and secondary growth. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 152, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Gu, X. Scle-up of NaA zeolite membranes on α-Al2O3 hollow fibers by a secondary growth method with vacuum seeding. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Shan, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. Preparation of zeolite MFI membranes on defective macroporous alumina supports by a novel wetting–rubbing seeding method: Role of wetting agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiscareno-Lechuga, F.; Tellez, C.; Menendez, M.; Santamarí, J. A novel device for preparing zeolite—A membranes under a centrifugal force field. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 212, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y. Pervaporation of an aqueous ethanol solution through hydrophilic zeolite membranes. Desalination 2006, 193, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, C.; Gu, X. Preparation of T-type zeolite membranes using a dip-coating seeding suspension containing colloidal SiO2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Chen, H.; Chang, R.; Li, L. Synthesis and characterization of high performance NaA zeolite-polyimide composite membranes on a ceramic hollow fiber by dip-coating deposition. Desalination 2011, 273, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Yang, W. Enhancement of NaA zeolite membrane properties through organic cation addition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Synthesis and pervaporation properties of NaA zeolite membranes prepared with vacuum-assisted method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 56, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera-Titus, M.; Mallada, R.; Llorens, J.; Cunill, F.; Santamaría, J. Preparation of inner-side tubular zeolite NaA membranes in a semi-continuous synthesis system. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.; Voigt, I.; Fischer, G.; Puhlfürß, P. Preparation of zeolite membranes on the inner surface of ceramic tubes and capillaries. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera-Titus, M.; Llorens, J.; Cunill, F.; Mallada, R.; Santamaría, J. Preparation of zeolite NaA membranes on the inner side of tubular supports by means of a controlled seeding technique. Catal. Today 2005, 104, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, N. Continuous synthesis of zeolite NaA in a microchannel reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 116, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A.; Dabir, B.; Fathizadeh, M. Preparation and characterization of nano-NaX zeolite by microwave assisted hydrothermal method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobek, M.; Motuzas, J.; van Loon, M.; Dirrix, R.W.J.; Terpstra, R.A.; Julbe, A. Coupling microwave-assisted and classical heating methods for scaling-up MFI zeolite membrane synthesis. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.S.; Thian, T.C.; Bhatia, S. Synthesis, characterization and pervaporation properties of microwave synthesized zeolite A membrane. Desalination 2011, 277, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of a&b-oriented zeolite T membranes and their pervaporation properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Yang, W. Hydrothermal synthesis of NaA zeolite membrane together with microwave heating and conventional heating. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 5129–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Proverbio, E. Microwave assisted crystallization of zeolite A from dense gels. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 247, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Hydrothermal stability of LTA zeolite membranes in pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, J.; Noack, M.; Kölsch, P.; Schäfer, R. Zeolite membranes—State of their development and perspective. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 38, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S. Microporous and dense inorganic membranes: Current status and prospective. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 25, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, A.; Millani, M.R.; Kheirkhah, M. Synthesis and characterization of a NaA zeolite membrane and its applications for desalination of radioactive solutions. Desalination 2008, 225, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, J.; Nenoff, T.M.; Lee, R. Desalination by reverse osmosis using MFI zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemimoghadam, M. New nanopore zeolite membranes for water treatment. Desalination 2010, 251, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, L.; McPherson, B.; Lee, R. Removal of organics from produced water by reverse osmosis using MFI-type zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, M.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A. Effect of added NaX nano-zeolite into polyamide as a top thin layer of membrane on water flux and salt rejection in a reverse osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Oh, K.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Yeo, J.G.; Sharma, P. Pervaporative seawater desalination using NaA zeolite membrane: Mechanisms of high water flux and high salt rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jian, X. Effect of NaA zeolite particle addition on poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) composite ultrafiltration (UF) membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnakorn, D.; Rirksomboon, T.; Aungkavattana, P.; Kuanchertchoo, N.; Atong, D.; Kulprathipanja, S.; Wongkasemjit, S. Performance of sodium A zeolite membranes synthesized via microwave and autoclave techniques for water–ethanol separation: Recycle-continuous pervaporation process. Desalination 2011, 269, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, P.; Tanchuk, B.; Bastida, E.; An, W.; Kuznicki, S.M. Water desalination and de-oiling with natural zeolite membranes—Potential application for purification of SAGD process water. Desalination 2012, 286, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Yan, Y.; Subramani, A.; Huang, X.; Hurwitz, G.; Ghosh, A.K.; Jawor, A. Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: A new concept for reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 294, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, F.T.; Sun, L.; Olujić, Ž.; Jansens, P.J.; Kapteijn, F. Influence of the support layer on the flux limitation in pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 223, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoof, V.; Dotremont, C.; Buekenhoudt, A. Performance of Mitsui NaA type zeolite membranes for the dehydration of organic solvents in comparison with commercial polymeric pervaporation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas, A.; Mallada, R.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Menéndez, M.; Santamaría, J. The use of post-synthetic treatments to improve the pervaporation performance of mordenite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H.; Fuchida, K.; Horita, T.; Asamura, H.; Okamoto, K. Preparation of Faujasite membranes and their permeation properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 25, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Nakane, T. Synthesis of industrial scale NaY zeolite membranes and ethanol permeating performance in pervaporation and vapor permeation up to 130 °C and 570 kPa. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, P.; Tanchuk, B.; Gupta, A.; An, W.; Kuznicki, S.M. Pervaporative desalination of water using natural zeolite membranes. Desalination 2012, 285, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Lizon, T.; Edwards, E.; Lobiundo, G.; Santos, L.F.d. Dehydration of water/t-butanol mixtures by pervaporation: Comparative study of commercially available polymeric, microporous silica and zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Lizon, T.; Ho, Y.S.; Santos, L.F.d. Comparative study of commercially available polymeric and microporous silica membranes for the dehydration of IPA/water mixtures by pervaporation/vapour permeation. Desalination 2002, 149, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, H.M.; van Delft, Y.C.; Engelen, C.W.R.; Pex, P.P.A.C. Dewatering of organics by pervaporation with silica membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 22–23, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, A.W.; van Male, P.; Vorstman, M.A.G.; Keurentjes, J.T.F. Description of dehydration performance of amorphous silica pervaporation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 193, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, T.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Li, J.; Long, Y.; Ping, Z. Cordierite-supported ZSM-5 membrane: Preparation and pervaporation properties in the dehydration of water–alcohol mixture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, W. Preparation of silicalite-1 membrane by solution-filling method and its alcohol extraction properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, W.; Marszalek, J.; Ciolkowska, A. Renewable energy source—Dehydrated ethanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 135, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tuan, V.A.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D. Separation of 1,3-propanediol from glycerol and glucose using a ZSM-5 zeolite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 191, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Ejiri, S.; Yamada, K.; Kawakami, Y.; Yanagishita, H. Separation of acetic acid-water mixtures by pervaporation through silicalite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 123, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, C.L.; Tuan, V.A.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Separation of C6 isomers by vapor permeation and pervaporation through ZSM-5 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 176, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsufuji, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsukata, M.; Ueyama, K. Synthesis and permeation studies of ferrierite/alumina composite membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 38, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrufet, M.A.; Burnett, D.B.; Mareth, B. Modeling and operation of oil removal and desalting oilfield brines with modular units. In SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, C.P.; Kamil, N.H.A.; Junaidi, M.U.M.; Kamal, S.N.M.; Ahmad, A.L. The potential of SAPO-44 zeolite filler in fouling mitigation of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daer, S.; Kharraz, J.; Giwa, A.; Hasan, S.W. Recent applications of nanomaterials in water desalination: A critical review and future opportunities. Desalination 2015, 367, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M.; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kickelbick, G. Concepts for the incorporation of inorganic building blocks into organic polymers on a nanoscale. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Mao, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Bao, Y.; Yu, M. Ultrathin, molecular-sieving graphene oxide membranes for selective hydrogen separation. Science 2013, 342, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Silica nanoparticles as carriers of antifouling ligands for PVDF ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 433, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Development of a hydrophilic PES ultrafiltration membrane containing SiO2@N-Halamine nanoparticles with both organic antifouling and antibacterial properties. Desalination 2013, 326, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ji, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.R. Coordination-Driven In Situ Self-Assembly Strategy for the Preparation of Metal–Organic Framework Hybrid Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9775–9779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.; Zhu, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Gao, C. Preparation of monodispersed spherical mesoporous nanosilica–polyamide thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes via interfacial polymerization. Desalination 2013, 309, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Chun, J.H.; Chun, B.H.; Kim, S.H. Fabrication and characterization of the chlorine-tolerant disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/hyperbranched aromatic polyamide-grafted silica composite reverse osmosis membrane. Desal. Water Treat. 2012, 43, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, R.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L. In situ formation of Ag nanoparticles in PVDF ultrafiltration membrane to mitigate organic and bacterial fouling. Desalination 2013, 324, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisola, G.M.; Park, J.S.; Beltran, A.B.; Chung, W.J. Silver nanoparticles in a polyether-block-polyamide copolymer towards antimicrobial and antifouling membranes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- María Arsuaga, J.; Sotto, A.; del Rosario, G.; Martínez, A.; Molina, S.; Teli, S.B.; de Abajo, J. Influence of the type, size, and distribution of metal oxide particles on the properties of nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanareeswaran, G.; Thanikaivelan, P. Fabrication of cellulose acetate–zirconia hybrid membranes for ultrafiltration applications: Performance, structure and fouling analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 74, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of ZrO2/PES hybrid ultrafiltration membrane with uniform ZrO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 332, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.A.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Zularisam, A.W.; Lau, W.J.; Yuliwati, E.; Abdullah, M.S. Morphological and separation performance study of polysulfone/titanium dioxide (PSF/TiO2) ultrafiltration membranes for humic acid removal. Desalination 2011, 273, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Resosudarmo, A.; Holmes, R.L.; Li, H.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effect of modified TiO2 nanoparticles on the polyethersulfone ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 2012, 287, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lu, S.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J. Novel polysulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membrane prepared with TiO2-g-HEMA and its antifouling characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Enhancing chlorine resistances and anti-biofouling properties of commercial aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes by grafting 3-allyl-5, 5-dimethylhydantoin and N, N′-Methylenebis (acrylamide). Desalination 2013, 309, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwak, S.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Park, T.H. Design of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane as an approach to solve biofouling problem. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Leo, C.P.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2013, 308, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; He, Y. Polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane blended with nano-ZnO particle for photo-catalysis self-cleaning. Desalination 2014, 332, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, V.B.; Thétiot, F.; Ritz, S.; Pütz, S.; Choritz, L.; Lappas, A.; Förch, R.; Landfester, K.; Jonas, U. Antibacterial Surface Coatings from Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Embedded in Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel Surface Layers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2376–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Hyeon, D.H.; Chun, J.H.; Chun, B.H.; Kim, S.H. Nanocomposite poly(arylene ether sulfone) reverse osmosis membrane containing functional zeolite nanoparticles for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X. High permeability and salt rejection reverse osmosis by a zeolite nano-membrane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 6817–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellino, T.; Morse, A.; Tran, P.; Song, L.; Hamood, A.; Reid, T.; Moseley, T. Attachment of organo-selenium to polyamide composite reverse osmosis membranes to inhibit biofilm formation of S. aureus and E. coli. Desalination 2013, 309, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroña, G.N.B.; Lim, J.; Choi, M.; Jung, B. Interfacial polymerization of polyamide-aluminosilicate SWNT nanocomposite membranes for reverse osmosis. Desalination 2013, 325, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Improving the performance of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by incorporation of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Lee, J. Macroporous PVDF/TiO2 membranes with three-dimensionally interconnected pore structures produced by directional melt crystallization. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, T.; Shi, J.; Teng, K.; Wang, W.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Qian, X.; Li, C.; Fan, J. Photocatalytic antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on synergy of graphene oxide and TiO2 for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Vatanpour, V. Preparation and characterization of emulsion poly (vinyl chloride)(EPVC)/TiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandashtani, M.B.; Ashtiani, F.Z.; Karimi, M.; Fouladitajar, A. A novel approach to fabricate high performance nano-SiO2 embedded PES membranes for microfiltration of oil-in-water emulsion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshan, N.; Pakizeh, M. The effect of functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles on the morphology and triazines separation properties of cellulose acetate membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Lang, W.Z.; Miao, W.; Yan, X.; Guo, Y.J. Preparation and properties of PVDF/SiO2@ GO nanohybrid membranes via thermally induced phase separation method. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 511, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N.; Daraei, P. Enhancement in copper ion removal by PPy@ Al2O3 polymeric nanocomposite membrane. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Dass, L.A.; Ghasemi, M.; Alhoshan, M. Synthesis and optimization of PES-Fe3O4 mixed matrix nanocomposite membrane: Application studies in water purification. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, P.; Madaeni, S.S.; Ghaemi, N.; Salehi, E.; Khadivi, M.A.; Moradian, R.; Astinchap, B. Novel polyethersulfone nanocomposite membrane prepared by PANI/Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced performance for Cu(II) removal from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Moghadassi, A.; Hosseini, S.; Shabani, S.; Gholami, F. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl chloride based nanocomposite nanofiltration-membrane modified by iron oxide nanoparticles for lead removal from water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximous, N.; Nakhla, G.; Wan, W.; Wong, K. Effect of the metal oxide particle distributions on modified PES membranes characteristics and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatova, A.; Kim, E.S.; Sun, X.; Hwang, G.; Liu, Y.; El-Din, M.G. Fabrication of porous polymeric nanocomposite membranes with enhanced anti-fouling properties: Effect of casting composition. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ye, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Gao, C.; Shen, C.; Meng, Q. Antimicrobial polysulfone blended ultrafiltration membranes prepared with Ag/Cu2O hybrid nanowires. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 509, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.R.; Kim, H.J.; Joshi, M.K.; Pant, B.; Park, C.H.; Kim, J.I.; Hui, K.; Kim, C.S. One-step fabrication of multifunctional composite polyurethane spider-web-like nanofibrous membrane for water purification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.; Groth, A.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Enhanced abrasion resistant PVDF/nanoclay hollow fibre composite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M.; Mollahosseini, A.; Rajaeian, B. Structural and performance properties of UV-assisted TiO2 deposited nano-composite PVDF/SPES membranes. Desalination 2012, 285, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Rahimpour, A. Interfacially polymerized thin film nanofiltration membranes on TiO2 coated polysulfone substrate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication and properties of ultrafiltration membranes composed of polysulfone and poly(1-vinylpyrrolidone) grafted silica nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Huang, X. A novel ZnO nanoparticle blended polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for anti-irreversible fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H. Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix PES membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Development of novel SiO2–GO nanohybrid/polysulfone membrane with enhanced performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.P.; Min, B.R. Polyamide thin-film nanofiltration membranes containing TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2008, 219, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Patel, R.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.R. Silver nanoparticles immobilized on thin film composite polyamide membrane: Characterization, nanofiltration, antifouling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lannoy, C.F.; Jassby, D.; Gloe, K.; Gordon, A.D.; Wiesner, M.R. Aquatic biofouling prevention by electrically charged nanocomposite polymer thin film membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Hsiao, B.S. High flux low pressure thin film nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes based on nanofibrous substrates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Rahimpour, A. Synthesis of novel thin film nanocomposite (TFN) forward osmosis membranes using functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 435, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, N.; Asar, B.; Dizge, N.; Koyuncu, I. Investigation of characterization and biofouling properties of PES membrane containing selenium and copper nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F.; Nxumalo, E.; Krause, R.; Hoek, E.; Mamba, B. Application of polysulfone/cyclodextrin mixed-matrix membranes in the removal of natural organic matter from water. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2014, 67, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, D.G. Bulk synthesis, optimization, and characterization of highly dispersible polypyrrole nanoparticles toward protein separation using nanocomposite membranes. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Deng, B. Polymer-matrix nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ozturk, I.; Roest, K.; van Lier, J.B. A review on dynamic membrane filtration: Materials, applications and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, T.; Lu, X.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J. Hydrophilic Fe2O3 dynamic membrane mitigating fouling of support ceramic membrane in ultrafiltration of oil/water emulsion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Qiao, B.; Li, G.C.; Yang, Q.Y. Improving performance of dynamic membrane assisted by electrocoagulation for treatment of oily wastewater: Effect of electrolytic conditions. Desalination 2015, 363, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeison, D.; Díaz, I.; van Lier, J.B. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Are membranes really necessary? Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, F.; Tong, J.; Zang, L. Formation of dynamic membrane in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso, Y.; Jung, Y.J.; Park, M.S.; Wang, W.; Shimase, M.; Yamada, T.; Min, K.S. Coupling of sequencing batch reactor and mesh filtration: Operational parameters and wastewater treatment performance. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4887–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutten, I.M. Handbook of Nonwoven Filter Media; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Pu, W.; Zhang, J. Formation mechanism and structure of dynamic membrane in the dynamic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, R.Y.; Huang, C.; Chang, M.C.; Shao, H.; Shiau, B.L.; Hu, Y.J. Application of TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation and non-woven membrane filtration hybrid system for degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Desalination 2009, 245, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ma, Z.F.; Yang, Q.Y. Formation and performance of Kaolin/MnO2 bi-layer composite dynamic membrane for oily wastewater treatment: Effect of solution conditions. Desalination 2011, 270, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, M.C.; Lee, C.J.; Chou, K.S. Formation of dextran-Zr dynamic membrane and study on concentration of protein hemoglobin solution. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 162, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvoruchko, A.P.; Atamanenko, I.D.; Yurlova, L.Y. Concentration/purification of Co(II) ions by reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration combined with sorption on clay mineral montmorillonite and cation-exchange resin KU-2-8n. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.J.; Cheng, Y.H. The Role of Dynamic Membrane in Cross-Flow Microfiltration of Macromolecules. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Preparation and application of titanium dioxide dynamic membranes in microfiltration of oil-in-water emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chiang, B. Formation and characteristics of zirconium ultrafiltration dynamic membranes of various pore sizes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 143, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Z. Pollutant removal mechanisms in a bio-diatomite dynamic membrane reactor for micro-polluted surface water purification. Desalination 2012, 293, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, F. A photo-catalysis and rotating nano-CaCO3 dynamic membrane system with Fe-ZnIn2S4 efficiently removes halogenated compounds in water. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2013, 138, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wong, F.S.; Fane, A.; Xu, N. Formation of Mg(OH)2 dynamic membranes for oily water separation: Effects of operating conditions. Desalination 2006, 191, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowsky, A.E.; Kraus, K.A.; Phillips, H.O.; Johnson, J.S.; Shor, A.J. Hyperfiltration Studies. IV. Salt Rejection by Dynamically Formed Hydrous Oxide Membranes1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 5744–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, D.; Tanny, G.B. The formation mechanism of dynamic hydrous Zr(IV) oxide membranes on microporous supports. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 1978, 64, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, M.; Senō, M.; Takahashi, H.; Yamabe, T. Reverse osmosis by dynamic membranes. Desalination 1977, 22, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanny, G.B.; Johnson, J.S. The structure of hydrous Zr(IV) oxide–polyacrylate membranes: Poly(acrylic acid) deposition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, G.R.; Buckley, C.A.; Cox, J.M.; Kirk, A.; Macmillan, C.D.; Simpson, M.J. Dynamic membrane ultrafiltration and hyperfiltration for the treatment of industrial effluents for water reuse. Desalination 1983, 47, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraratananon, R.; Uttapap, D.; Tangamornsuksun, C. Self-forming dynamic membrane for ultrafiltration of pineapple juice. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 129, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishihara, S.; Tamaki, H.; Fujii, S.; Komoto, M. Clarification of technical sugar solutions through a dynamic membrane formed on a porous ceramic tube. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 41, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malack, M.H. Anderson, G.K. Formation of dynamic membranes with crossflow microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 112, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.J.M.M.; Ahmadun, F.R.; Mohamed, T.A.; Muyibi, S.A.; Pescod, M.B. Performance of flexible membrane using kaolin dynamic membrane in treating domestic wastewater. Desalination 2002, 147, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wong, F.S.; Fane, A.G.; Xu, N. Formation of dynamic membranes for oily water separation by crossflow filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Banks, C.; Heaven, S. Development of a coarse membrane bioreactor for two-stage anaerobic digestion of biodegradable municipal solid waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alguacil, F.J.; Villegas, M.A. Liquid membranes and the treatment of metal-bearing wastewaters. Rev. De Metal. 2002, 38, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudry, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Malik, M.T. Supported liquid membrane technique applicability for removal of chromium from tannery wastes. Waste Manag. 1998, 17, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gyves, J.; Miguel, E.R.d. Metal Ion Separations by Supported Liquid Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 2182–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocherginsky, N.; Yang, Q.; Seelam, L. Recent advances in supported liquid membrane technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J.; Alonso, M.; Sastre, A.M. Copper separation from nitrate/nitric acid media using Acorga M5640 extractant: Part II. Supported liquid membrane study. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, D.S.; Muthukumar, M.; Mohan, D. Extraction of zinc(II) using liquid membrane and performance optimization using response surface methodology. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2004, 63, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Jeong, J.; Chung, K.S.; Kobayashi, M. Active facilitated transport and separation of Co in Co–Ni sulfate solution by hollow fiber supported liquid membrane containing HEH (EHP). Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocherginsky, N. Facilitated Transport of Alkali Metal Cations through Supported Liquid Membranes with Fatty Acids. In Chemical Separations with Liquid Membranes; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Alguacil, F.J.; Coedo, A.; Dorado, M.; Padilla, I. Phosphine oxide mediate transport: Modelling of mass transfer in supported liquid membrane transport of gold(III) using Cyanex 923. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 3115–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Valiente, M. Studies on the mechanism of transport of lanthanide ions through supported liquid membranes containing di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (D2EHPA) as a carrier. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 155, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Future Directions of Membrane Gas Separation Technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














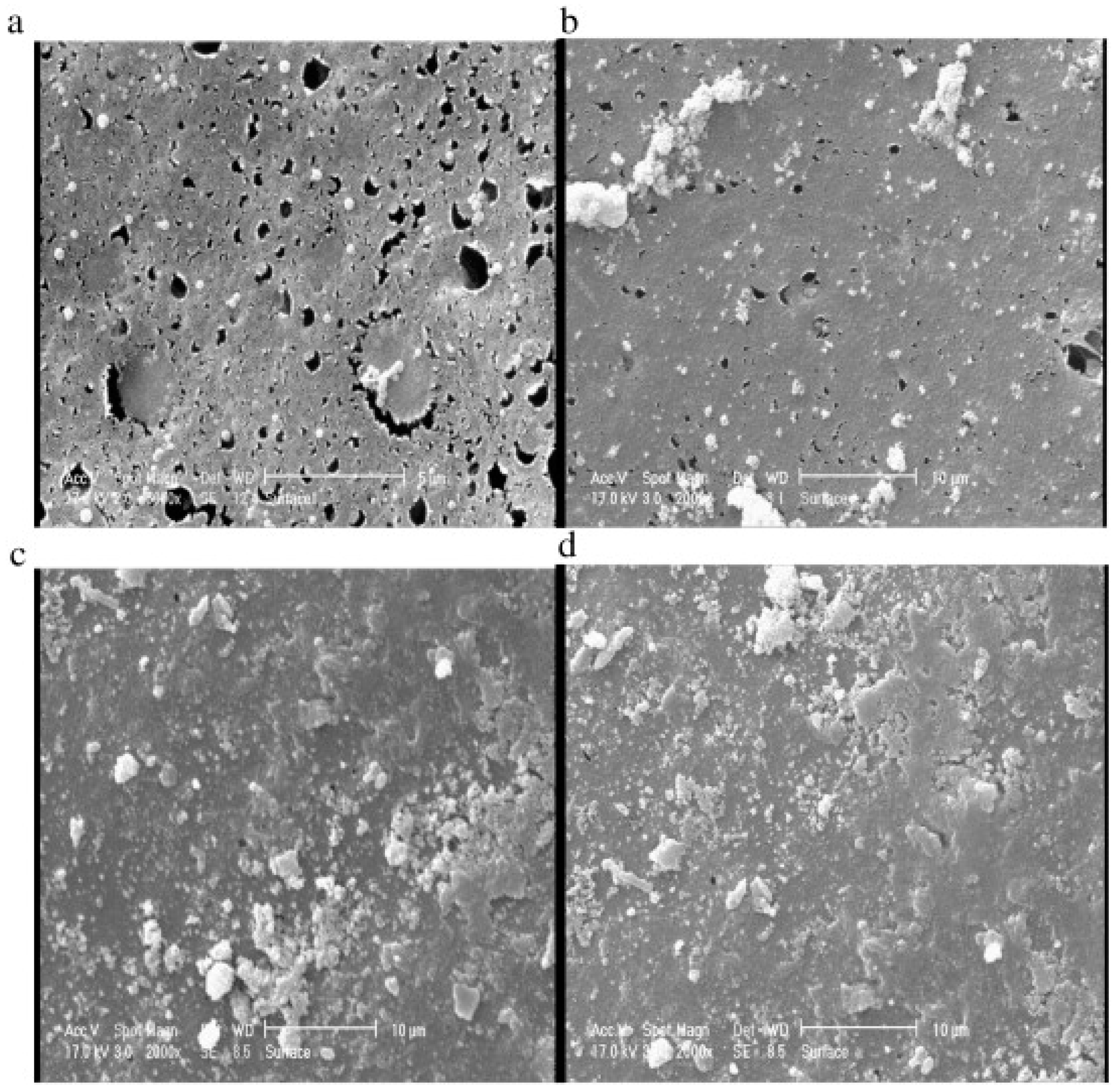



| Properties | Polymeric Membranes | Inorganic Membranes |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Rubbery or glassy type membranes based on the operating temperature [22] | Inorganic materials i.e., glass, ceramic, silica, etc. [11] |
| Characteristic | Rigid in glassy form and flexible in rubbery state [23] | Chemically and thermally stable, mechanically robust, operational under harsh feed condition [11] |
| Advantages | Cost-effectiveness, good selectivity , easy processability [1] | Withstand harsh chemical cleaning, ability to be sterilized and autoclaved, high temperature (up to 500 °C) and wear resistance, well-defined and stable pore structure, high chemical stability, long life time [11,21] |
| Disadvantages | Fouling, chemically nonresistant, limited operating temperature and pressure, short life time [24,25] | Fragile, rigid [26] |
| Porous Membrane | Pore Size Diameter, nm | Applications | Permeation Mechanism | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microporous | <2 | Gas separation + NF | Molecular sieving | Low pore size diameter with a potential use in molecular sieve separation |
| Mesoporous | 2–50 | NF + UF and gas separation | Knudsen diffusion | High permeability and low selectivity. Used in the synthesis of composite membranes. |
| Macroporous | >50 | UF/MF | Poisseuille flow | High permeability as a support in the synthesis of composite membranes, or as a distributor of reagents |
| Ceramic Membrane Material | Application Type | Flux | Removal Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | MF/UF | 118–125 LMH | 99% (oil and turbidity) and 100% (TSS) | [113] |
| ZrO | UF | 600 LMH | 90% (oil and turbidity) and 100% (TSS) | [114] |
| Al-ZrO | NF | 190–250 LMH | 95% (TDS) | [115] |
| α-Al2O3 | MF | 250 | 95% (oil) | [116] |
| Al2O3/TiO2 | MF/UF | 3.4 to 3300 LMH | 99.5% (oil) and 49% (TOC) | [110] |
| Ceramic Material | Temperature Difference (°C) | Flux (kg/m2h) | Rejection % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 65 | 13.44 | 92.3 | [123] |
| 85 | 57.74 | 99.8 | ||
| Clay Alumina | 20 | 5.48 | 99.1 | [127] |
| 60 | 98.66 | 99.96 | ||
| ZrO2 | 55 | 15.7 | 100 | [124] |
| 85 | 82.7 | 100 | ||
| Al2O3 | 58 | 18.2 | 100 | [124] |
| 90 | 129.5 | 100 | ||
| B-Sialon | 50 | 100 LMD | 99 | [128] |
| 80 | 290 LMD | 99 |
| Membrane Type | Operating Condition | Feed Concentration | Water Flux (kg/m2h) | Rejection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonized silica membranes | 20 C, 7 bar, 5 h | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 2.1–1.9 | 99.5% | [173] |
| 20 C, 1 bar | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 3.2–1.4 | 89% | [181] | |
| 20 C, 1 bar | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 2.8–1.6 | 89% | [181] | |
| 20 C, 1 bar | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 3–2 | 94% | [181] | |
| 20 C, 1 bar, 12 h | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 1.5 | 95% | [182] | |
| 20 C, 1 bar, 12 h | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 6.3–4.9 | 92% | [182] | |
| Silica membranes with incorporated metal oxide | 20 C, 1 bar, 570 h | 0.3–15 wt % | 0.4–0.3 | 99.8% | [190] |
| 50 C, 1 bar, 570 h | 0.3–15 wt % | 0.9–0.35 | 99.7% | [190] | |
| 75 C, 1 bar, 570 h | 0.3–15 wt % | 1.8–0.55 | 99.7% | [190] | |
| Methylated silica membrane | 30 C, 1 bar | 0.2 | 3 | 99% | [192] |
| 90 C, 1 bar | 0.2 | 3.4 | 99.9% | [192] | |
| 20 C, 1 bar, 5 h | 0.3–3.5 wt % | 4.7–2.5 | 88.3% | [173] |
| Filler | Polymeric Support | Application | Synthesis Method | Advantage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | PVDF | - | Directional melt crystallization | Improved the hydrophilicity | [319] |
| GO/TiO2 | PVDF | UF | Solution casting and phase inversion method | Improved photo-catalytic activity | [320] |
| TiO2 | PVC | UF | Non-solvent induced phase separation method | Improved the hydrophilicity | [321] |
| TiO2 | PES | UF | Phase inversion method | Improved the hydrophilicity | [302] |
| SiO2 | PES | MF | Combination of vapor induced phase separation and non-solvent induced phase separation | Improved the hydrophilicity | [322] |
| SiO2 | CA | UF | Phase inversion | Improved the hydrophilicity | [323] |
| SiO2/GO | PVDF | UF | Thermally induced phase separation method | Improved the hydrophilicity | [324] |
| Al2O3 | PPY | UF | Phase inversion | Improved adsorption capacity | [325] |
| Al2O3 | PES | MBR | Phase inversion | Improved the hydrophilicity | [325] |
| Fe3O4 | PVA; PES; PVC | UF/MF | Phase inversion | Magnetic property; improved Hydrophilicity | [326,327,328] |
| ZrO2 | PES | MBR | Phase inversion | Improved the hydrophilicity | [329] |
| Ag | PVP | UF | Phase inversion | Antimicrobial functionality | [330] |
| Ag-Cu2O | PSF | UF | Phase inversion | Enhanced antibacterial properties | [331] |
| Ag | PU | UF | Electrospinning | Antimicrobial functionality | [332] |
| Clay | PVDF | UF | Phase inversion | Mechanical property; Hydrophilicity | [333] |
| Support Material | Application Type | Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| mesh | MBR | Municipal wastewater treatment | [353] |
| woven fabric | MBR | Wastewater treatment | [356] |
| non-woven fabric | UF | Degradation of 4-chlorophenol | [357] |
| ceramic tube | MF | Oily wastewater treatment | [358] |
| ceramic membranes | UF | Oil-water emulsion separation | [350] |
| stainless steel tube | UF | Concentration of protein hemoglobin | [359] |
| reverse osmosis (RO) membrane | RO | Concentration/purification of Co(II) ion | [360] |
| MF membrane | MF | Rejection of macromolecules | [361] |
| UF membrane | RO | Concentration/purification of Co(II) ion | [360] |
| Porous carbon | MF | Oil-water emulsion separation | [362] |
| Dynamic Material | Support Material | Application Type | Treatment | Flux | Removal Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZrOCl | Ceramic | UF | Glucose removal | 16–34 LMH | 1.6–5.8 (glucose removal) | [363] |
| Fe2O3 | Ceramic | UF | Oil-water emulsion separation | 97.8 (COD removal) | [350] | |
| Kaolin clay | Ceramic | MF | Oil removal | 400 LMH | 96% (oil removal) | [351] |
| MnO2 | Ceramic | UF | Oil removal | 1000 LMH | - | [358] |
| TiO2 | Porous carbon | MF | Oil-water emulsion separation | 240 LMH | 98% (oil removal) | [362] |
| Diatomite | Stainless steel mesh | MBR | Surface water treatment | 92 LMH | 95% (turbidity) | [364] |
| CaCO3 | non-woven fabric | PMR | Treatment of halogenated compounds in water | - | 72% (removal of 2,4,6-Tribromophenol). And 75% (removal of 2,4-Dichlorophenol) | [365] |
| Kaolin–MnO2 | Al2O3 porous ceramic | MF | Oil removal | 120.1–153.2 LMH | 98.2–99.9 (Oil removal) | [358] |
| Mg(OH)2 | Al2O3 ceramic tubes | MF | Wastewater treatment | 1 LMH | 98 (TOC removal) | [366] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kayvani Fard, A.; McKay, G.; Buekenhoudt, A.; Al Sulaiti, H.; Motmans, F.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M. Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination. Materials 2018, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010074
Kayvani Fard A, McKay G, Buekenhoudt A, Al Sulaiti H, Motmans F, Khraisheh M, Atieh M. Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination. Materials. 2018; 11(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010074
Chicago/Turabian StyleKayvani Fard, Ahmad, Gordon McKay, Anita Buekenhoudt, Huda Al Sulaiti, Filip Motmans, Marwan Khraisheh, and Muataz Atieh. 2018. "Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination" Materials 11, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010074
APA StyleKayvani Fard, A., McKay, G., Buekenhoudt, A., Al Sulaiti, H., Motmans, F., Khraisheh, M., & Atieh, M. (2018). Inorganic Membranes: Preparation and Application for Water Treatment and Desalination. Materials, 11(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11010074





