Investigation on the Reaction Energy, Dynamic Mechanical Behaviors, and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al with Different TiH2 Percentages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Material Fabrication
2.2. Measurement of Reaction Energy
2.3. Dynamic Compression Tests
2.4. Drop-Weight Tests
3. Results and Discussion
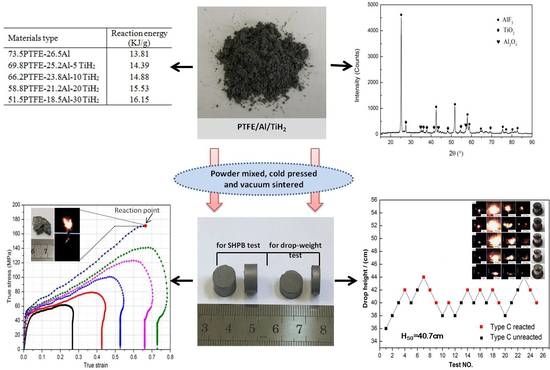
3.1. Reaction Energy
3.2. Dynamic Compression Properties
3.3. Impact Sensitivity and Reaction Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With an increase of TiH2 content, the reaction energy of PTFE/Al/TiH2 under an oxygen atmosphere obviously increases. Especially, the reaction heat of type E composites reaches up to 16.15 MJ/kg, which is 3.7 times than that of TNT.
- (2)
- All the five types of composites show strain hardening and strain rate hardening effects; the yield strength and hardening modulus increases with the increase of strain rates. A relatively low mass ratio of TiH2 granules help to improve the materials’ compressive strength, and the maximum even reaches 173.2 MPa with a 5% TiH2 percentage, which is 10.1% higher than that of PTFE/Al. Excessive TiH2 granules would lead to a decrease of the material’s strength. SEM images of the recovered samples indicate that the fracture of the PTFE matrix, and interface debonding between the reinforcing granules and PTFE matrix are the main mechanisms for material failure.
- (3)
- With the increase of TiH2 content from 5% up to 30%, the material’s impact sensitivity shows a decreasing trend. Compared with PTFE/Al, the addition of TiH2 (less than 20%) would enhance the impact sensitivity of the materials, while excessive TiH2 (more than 30%) would significantly reduce the material’s sensitivity.
- (4)
- The material’s reaction degree is sensitive to the mass ratio of TiH2. At a certain drop height of 90cm, the reaction degree of the materials becomes stronger first and then weaker with an increase of TiH2 content, which would be the most violent at a 5% content of TiH2. In addition, special sparks fly off from the reaction zone of the four composites with the TiH2 particles, but not from the PTFE/Al reaction zone. The recovered sample residues indicate that the reaction proceeds more and more incompletely with an increased TiH2 mass fraction, and a shear-induced initiation mechanism is applicable to these types of reactive materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, R.J.; Mock, W.J.; Carney, J.; Holt, W.H.; Pangilinan, G.I.; Gamache, R.M.; Boteler, J.M.; Bohl, D.G.; Drotar, J.; Lawrence, G.W. Reactive Materials Studies. Shock Compression Condens. Matter 2005, 845, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Z.W.; Yu, W. Impact-induced initiation and energy release behavior of reactive materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 074904. [Google Scholar]
- Glavier, L.; Taton, G.; Ducéré, J.M.; Baijot, V.; Pinon, S.; Calais, T.; Estève, A.; Rouhani, M.D.; Rossi, C. Nanoenergetics as pressure generator for nontoxic impact primers: Comparison of Al/Bi2O3, Al/CuO, Al/MoO3 nanothermites and Al/PTFE. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgoborodov, A.Y.; Makhov, M.N.; Kolbanev, I.V.; Streletskii, A.N.; Fortov, V.E. Detonation in an aluminum-Teflon mixture. JETP Lett. 2005, 81, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobosyan, M.A.; Martirosyan, K.S. Consolidation of lunar regolith simulant by Activated thermite reactions. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2014, 28, 04014105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, H.X.; Mao, Y.M.; Wu, S.Z. An initiation phenomenon of Al-PTFE under quasi-static compression. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 637, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, S.Z.; Wang, H.X.; Tao, Z.M.; Fang, X. A crack-induced initiation mechanism of Al-PTFE under quasi-static compression and the investigation of influencing factors. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casem, D.T. Mechanical Response of an Al-PTFE Composite to Uniaxial Compression over a Range of Strain Rates and Temperatures; Army Research Lab.: Aderdeen, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, R.G. Energy Release Characteristics of Impact-Initiated Energetic Materials; Materials Research Society: Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mcgregor, N.M.; Sutherland, G.T. Plate Impact Experiments on a Porous Teflon-Aluminum Mixture. Shock Compress. Condens. Matter 2003, 706, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, C.; Dong, Y.X.; Maimaitituersun, W.; Ren, Y.M.; Feng, S.S. Experimental Study on impact-induced initiation thresholds of polytetrafluoroethylene/aluminum composite. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielson, D.B.; Tanner, R.L.; Lund, G.K. High Strength Reactive Materials and Methods of Making. U.S. Patent 2007/7307117 B2, 11 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Walley, S.M.; Hunt, R.J.A.; Proud, W.G.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Meyers, M.A. High-strain, high-strain-rate flow and failure in PTFE/Al/W granular composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, L.; Shi, A.S.; Zhang, Y.G.; He, Y.; Guan, Z.W. Experimental study of the compression properties of Al/W/PTFE granular composites under elevated strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 581, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Yang, S.Q.; Zhang, W. The mechanical behaviors of polytetrafluorethylene/Al/W energetic composites. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 285401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Maimaitituersun, W.; Dong, Y.X.; Chao, T. A study on the mechanical properties and impact-induced initiation characteristics of brittle PTFE/Al/W reactive materials. Materials 2017, 10, 452. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, H.F. Damage effects of aluminum plate by reactive material projectile impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 104, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.X.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Lan, J.; Li, S.K.; He, C.; Xue, X.Y. Effects of multi-component co-addition on reaction characteristics and impact damage properties of reactive material. Mater. Des. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walley, S.M.; Field, J.E.; Biers, R.A.; Proud, W.G.; Williamson, D.M.; Jardine, A.P. The use of glass anvils in drop-weight studies of energetic materials. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2015, 40, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.X.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, X.B. Investigation on reaction energy, mechanical behavior and impact insensitivity of W/PTFE/Al composites with different W percentage. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xuan, F.Z.; Xiao, B.; He, L.; Gao, Y. Improved adhesion between nickel-titanium SMA and polymer matrix via acid treatment and nano-silica particles coating. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2018, 27, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Fang, X.; Wang, H.X.; Dong, W.; Li, Y.C. The effect of crystallinity on compressive properties of Al-PTFE. Polymers 2016, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Jiang, C.L.; Niu, H.H. Experimental study on impact-induced reaction characteristics of PTFE/Ti composites enhanced by W particles. Materials 2017, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhou, L.M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liang, W.Y. Effect of fiber surface modification on the lifetime of glass fiber reinforced polymerized cyclic butylene terephthalate composites in hygrothermal conditions. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F. Research of raise solid propellant burning rate by using titanium hydride. Winged Missiles J. 1997, 6, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, D.; Quebral, A.; Baroody, E.; Sanborn, W. Investigation of the thermal degradation of the aged pyrotechnic titanium hydride/potassium perchlorate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 85, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W. Air Explosion Characteristics of a Novel TiH2/RDX Composite Explosive. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2015, 51, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Meng, X.R.; Feng, C.T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, S.S.; Ma, H.H.; Shen, Z.W. The effect of the hydrogen containing material TiH2 on the detonation characteristics of emulsion explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.S.; Fang, X.; Gao, Z.R.; Wang, H.X.; Huang, J.Y.; Yao, M.; Li, Y.C. Mechanical and reaction properties of Al/TiH2/PTFE under quasi-static compression. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, W.R.; Baber, B.B.; Ku, P.M. New test techniques for evaluating the compatibility of materials with liquid oxygen under impact. Tribol. Trans. 1968, 11, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J. Properties of Heterogeneous Energetic Materials under High Strain, High Strain Rate Deformation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 59–109. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, S.Z.; Mao, Y.M.; Wang, H.X. Reactions of Al-PTFE under impact and quasi-static compression. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Type | Mass Fraction (wt %) | TMD (g cm−3) | Density (g cm−3) | Relative Density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | Al | TiH2 | ||||
| A | 73.5 | 26.5 | 0 | 2.31 | 2.20 | 95.2% |
| B | 69.8 | 25.2 | 5 | 2.36 | 2.24 | 94.9% |
| C | 66.2 | 23.8 | 10 | 2.41 | 2.33 | 96.7% |
| D | 58.8 | 21.2 | 20 | 2.52 | 2.42 | 96.0% |
| E | 51.5 | 18.5 | 30 | 2.63 | 2.51 | 95.4% |
| Type | Reaction Energy (MJ/kg) |
|---|---|
| A | 13.81 |
| B | 14.39 |
| C | 14.88 |
| D | 15.53 |
| E | 16.15 |
| Type | Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardening Modulus (MPa) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Critical Failure Strain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 49.6 | 189.3 | 157.3 | 0.58 |
| B | 52.3 | 192.4 | 173.2 | 0.66 |
| C | 58.8 | 172.1 | 156.5 | 0.65 |
| D | 63.3 | 164.3 | 156.1 | 0.59 |
| E | 65.7 | 144.7 | 142.8 | 0.57 |
| Type | Characteristic Drop Height (cm) |
|---|---|
| A | 46.4 |
| B | 36.6 |
| C | 40.7 |
| D | 45.0 |
| E | 66.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, J.; Zhong, M.; Chen, L.; Yao, M. Investigation on the Reaction Energy, Dynamic Mechanical Behaviors, and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al with Different TiH2 Percentages. Materials 2018, 11, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102008
Yu Z, Fang X, Li Y, Wu J, Wu S, Zhang J, Ren J, Zhong M, Chen L, Yao M. Investigation on the Reaction Energy, Dynamic Mechanical Behaviors, and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al with Different TiH2 Percentages. Materials. 2018; 11(10):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102008
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhongshen, Xiang Fang, Yuchun Li, Jiaxiang Wu, Shuangzhang Wu, Jun Zhang, Junkai Ren, Mingshou Zhong, Liping Chen, and Miao Yao. 2018. "Investigation on the Reaction Energy, Dynamic Mechanical Behaviors, and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al with Different TiH2 Percentages" Materials 11, no. 10: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102008
APA StyleYu, Z., Fang, X., Li, Y., Wu, J., Wu, S., Zhang, J., Ren, J., Zhong, M., Chen, L., & Yao, M. (2018). Investigation on the Reaction Energy, Dynamic Mechanical Behaviors, and Impact-Induced Reaction Characteristics of PTFE/Al with Different TiH2 Percentages. Materials, 11(10), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11102008