Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Cellulose Esters and Their Compatibility with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
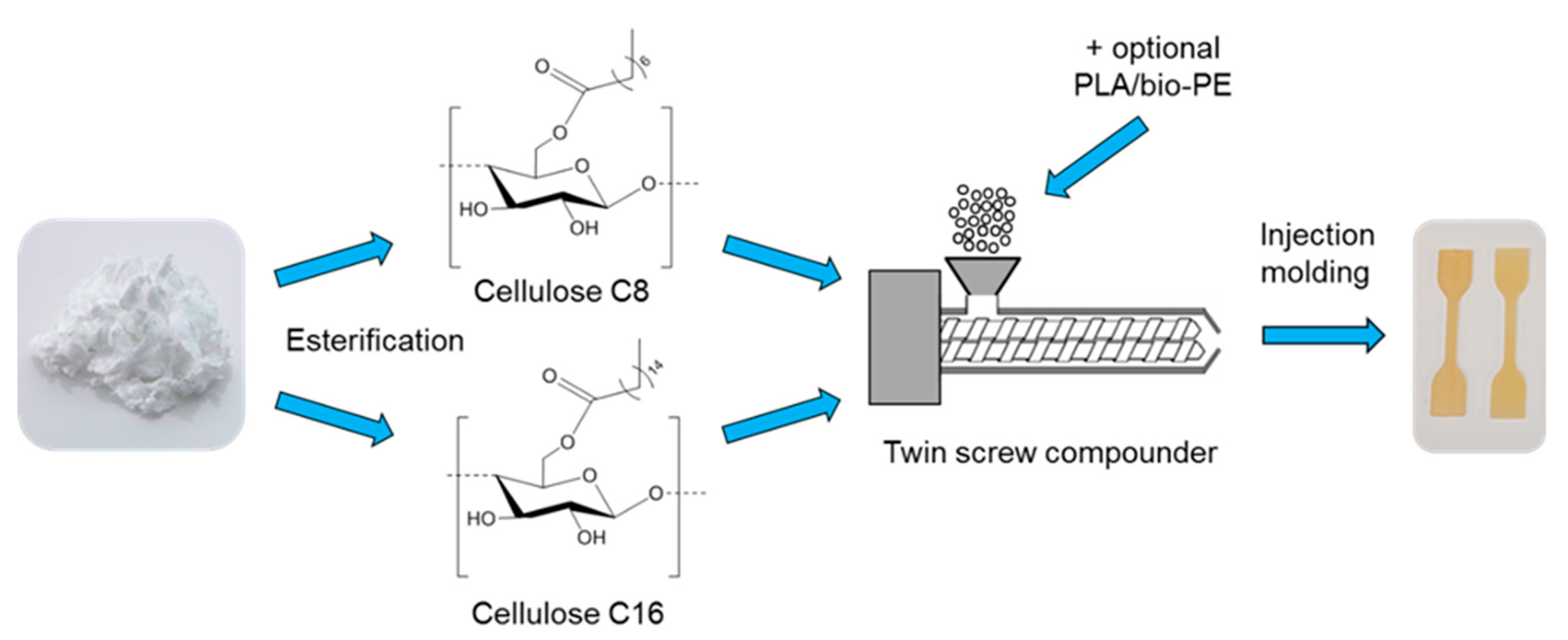
2.2.1. Preparation of Cellulose Esters
2.2.2. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (ssNMR)
2.2.3. Compounding
2.2.4. Injection Molding
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.6. Density
2.2.7. Tensile Strength Testing
2.2.8. Impact Strength Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Cellulose Esters
3.2. Injection Molding of Cellulose Esters
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Injection-Molded Cellulose Esters
3.4. The Compatibility of Cellulose Esters with PLA and Bio-PE
3.5. Mechanical Properties of Injection-Molded Cellulose Ester PE/PLA Blends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babu, R.P.; O’Connor, K.; Seeram, R. Current progress on bio-based polymers and their future trends. Prog. Biomater. 2013, 2, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, K.J.; Buchanan, C.M.; Debenham, J.S.; Rundquist, P.A.; Seiler, B.D.; Shelton, M.C.; Tindall, D. Advances in cellulose ester performance and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1605–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Philipp, B.; Heinze, T.; Heinze, U.; Wagenknecht, W. Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.-P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating Biopolymer and Sustainable Raw Material. Angew. Chemie. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Semsarilar, M.; Guthrie, J.T.; Perrier, S. Cellulose modification by polymer grafting: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willberg-Keyriläinen, P.; Talja, R.; Asikainen, S.; Harlin, A.; Ropponen, J. The effect of cellulose molar mass on the properties of palmitate esters. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willberg-Keyriläinen, P.; Vartiainen, J.; Harlin, A.; Ropponen, J. The effect of side-chain length of cellulose fatty acid esters on their thermal, barrier and mechanical properties. Cellulose 2017, 24, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havimo, M.; Jalomäki, J.; Granström, M.; Rissanen, A.; Iivanainen, T.; Kemell, M.; Heikkilä, M.; Sipi, M.; Kilpeläinen, I. Mechanical strength and water resistance of paperboard coated with long chain cellulose esters. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2011, 24, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Wibowo, A.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Development of renewable resource-based cellulose acetate bioplastic: Effect of process engineering on the performance of cellulosic plastics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2003, 43, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, A.C.; Misra, M.; Park, H.M.; Drzal, L.T.; Schalek, R.; Mohanty, A.K. Biodegradable nanocomposites from cellulose acetate: Mechanical, morphological, and thermal properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.R.; Diwan, P.V. Permeability studies of cellulose acetate free films for transdermal use: Influence of plasticizers. Pharm. Acta. Helv. 1997, 72, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöllänen, M.; Suvanto, M.; Pakkanen, T.T. Cellulose reinforced high density polyethylene composites—Morphology, Mechanical and thermal expansion properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, G.F.; Agrawal, P.; Araújo, E.M.; de Mélo, T.J.A. Polylactide/Biopolyethylene Bioblends. Polímeros 2012, 22, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, S.; Wikström, L.; Immonen, K.; Anttila, U.; Retulainen, E. Cellulose kraft pulp reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) composites: effect of fibre moisture content. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2016, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA composites: From production to properties. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksman, K.; Skrifvars, M.; Selin, J.-F. Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippola, M.; Immonen, K.; Miettinen, A.; Laukkanen, A.; Andesson, T.; Peltola, H.; Harlin, A.; Holmberg, K. Predicting stiffness and strength of birch pulp: Polylactic acid composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Itry, R.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A. Improvement of thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends by reactive extrusion with functionalized epoxy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1898–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Gong, R.H.; Hogg, P.J. Poly (lactic acid) fibre reinforced biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 62, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liu, S.; Jiang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, J.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. Effects of modifications of bamboo cellulose fibers on the improved mechanical properties of cellulose reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 62, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartrand, A.; Lavoie, J.M.; Huneault, M.A. Surface modification of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and its application in LDPE-based composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 44348, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasuriya, P.W.; Ye, L.; Mai, Y.-W.; Wu, J. Mechanical Properties of Wood Flake-Polyethylene Composites. II. Interface Modification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 2505–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Huang, Y.; Guangmin, C. Influence of Modified Wood Fibers on the Mechanical Properties of Wood Fiber-Reinforced Polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, H.; Li, M.; Huang, S.; Mei, C.; Wu, Q. Enhancing mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) through its in-situ crosslinking with maleic anhydride-modified cellulose nanocrystals from cottonseed hulls. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2018, 112, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, L.; Lee, S.; Mei, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q. The influence of grafted cellulose nanofibers and postextrusion annealing treatment on selected properties of poly(lactic acid) filaments for 3D printing. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdrobis, A.; Darie, R.N.; Totolin, M.; Cazacu, G.; Vasile, C. Low density polyethylene composites containing cellulose pulp fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashori, A. Wood–plastic composites as promising green-composites for automotive industries! Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbery, J.; Houston, D. Natural-fiber-reinforced polymer composites in automotive applications. JOM 2006, 58, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.A.; Medina, J.A.; Reinecke, H. New Thermoplastic Materials Reinforced with Cellulose Based Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 3466–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Smitthipong, W.; Kongtud, W.; Tantatherdtam, R. Polyethylene green composites reinforced with cellulose fibers (coir and palm fibers): Effect of fiber surface treatment and fiber content. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrakhiz, F.Z.; El Achaby, M.; Malha, M.; Bensalah, M.O.; Fassi-Fehri, O.; Bouhfid, R.; Benmoussa, K.; Qaiss, A. Mechanical and thermal properties of natural fibers reinforced polymer composites: Doum/low density polyethylene. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, L.G.; Panigrahi, S. Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber-reinforced composites: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Sreekala, M.S.; Thomas, S. A Review on Interface Modification and Characterization of Natural Fiber Reinforced Plastic Composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1471–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, S.; Heinze, T. Efficient Approach to Design Stable Water-Dispersible Nanoparticles of Hydrophobic Cellulose Esters. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Gray, G.R. Analysis of the positions of substitution of acetate and propionate groups in cellulose acetate–propionate by the reductive-cleavage method. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 313, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, L.A.; Marques, E.L.; Zepon, K.M.; Pereira, J.R.; Pamato, S.; de Oliveira, M.T.; Danielski, L.G.; Petronilho, F.C. Cellulose acetate butyrate/poly(caprolactonetriol) blends: Miscibility, mechanical properties, and in vivo inflammatory response. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 29, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rynkowska, E.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Kujawa, J.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Wolan, A.; Kujawski, W. The Effect of Reactive Ionic Liquid or Plasticizer Incorporation on the Physicochemical and Transport Properties of Cellulose Acetate Propionate-Based Membranes. Polymers 2018, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, M.D.S.R.; da Silva Laurentino, L.; Canuto, K.M.; Mendes, L.G.; Martins, C.M.; Silva, S.M.F.; Furtado, R.F.; Kim, S.; Biswas, A.; Cheng, H.N. Physical and mechanical testing of essential oil-embedded cellulose ester films. Polym. Test 2016, 49, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, M.E.A.; Nitta, K.H.; Yamaguchi, M. Mechanical properties of plasticized cellulose ester films at room and high temperatures. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 2354–2358. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Miyashita, Y.; Kimura, N.; Suzuki, H. Blends of poly(ε-caprolactone) with cellulose alkyl esters: effect of the alkyl side-chain length and degree of substitution on miscibility. Cellulose 1997, 4, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, R.; Teramoto, Y.; Nishio, Y. Crystallization Behavior of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Grafted onto Cellulose Alkyl Esters: Effects of Copolymer Composition and Intercomponent Miscibility. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, D.; Yao, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. “Nucleation density reduction” effect of biodegradable cellulose acetate butyrate on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). Mater. Lett. 2014, 128, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, B.-U.; Min, K.-D.; Son, Y. Investigation of the nanostructure, thermal stability, and mechanical properties of polylactic acid/cellulose acetate butyrate/clay nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2015, 150, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, G. Formation and morphology of cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB)/polyolefin and CAB/polyester in situ microfibrillar and lamellar hybrid blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3587–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyosov, A.A. Wood-Plastic Composites; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, D.R. Polymer Blends: Phase Behavior and Property Relationships. In Multicomponent Polymer Materials; Paul, D.R., Sperling, L.H., Eds.; Advances in Chemistry Series 211; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Balasuriya, P.; Ye, L.; Mai, Y.-W. Mechanical properties of wood flake–polyethylene composites. Part I: Effects of processing methods and matrix melt flow behaviour. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2001, 32, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, A.K.; Rao, R.U.; Suman, K.N.S.; Rambabu, V. Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable PLA/PCL Polymeric Blends. Procedia. Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.S.; Drzal, L.T.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Wood-fiber-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites: Evaluation of the physicomechanical and morphological properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 4856–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | Compounding Temperature (°C) | Density (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| C16 100% | 130 | 0.99 |
| C8 100% | 130 | 1.05 |
| PLA 100% | 180 | 1.25 |
| PE 100% | 180 | 0.94 |
| C16/C8 75%:25% | 130 | 1.00 |
| C16/C8 50%:50% | 130 | 1.02 |
| C16/C8 25%:75% | 130 | 1.03 |
| C16/PLA 75%:25% | 180 | 1.05 |
| C16/PLA 50%:50% | 180 | 1.12 |
| C16/PLA 25%:75% | 180 | 1.18 |
| C8/PLA 75%:25% | 180 | 1.10 |
| C8/PLA 50%:50% | 180 | 1.15 |
| C8/PLA 25%:75% | 180 | 1.19 |
| C16/PE 75%:25% | 180 | 0.98 |
| C16/PE 50%:50% | 180 | 0.97 |
| C16/PE 25%:75% | 180 | 0.95 |
| C8/PE 75%:25% | 180 | 1.02 |
| C8/PE 50%:50% | 180 | 0.99 |
| C8/PE 25%:75% | 180 | 0.96 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Willberg-Keyriläinen, P.; Orelma, H.; Ropponen, J. Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Cellulose Esters and Their Compatibility with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene. Materials 2018, 11, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122358
Willberg-Keyriläinen P, Orelma H, Ropponen J. Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Cellulose Esters and Their Compatibility with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122358
Chicago/Turabian StyleWillberg-Keyriläinen, Pia, Hannes Orelma, and Jarmo Ropponen. 2018. "Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Cellulose Esters and Their Compatibility with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene" Materials 11, no. 12: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122358
APA StyleWillberg-Keyriläinen, P., Orelma, H., & Ropponen, J. (2018). Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Cellulose Esters and Their Compatibility with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene. Materials, 11(12), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122358




