Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Modified with Al–3B
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
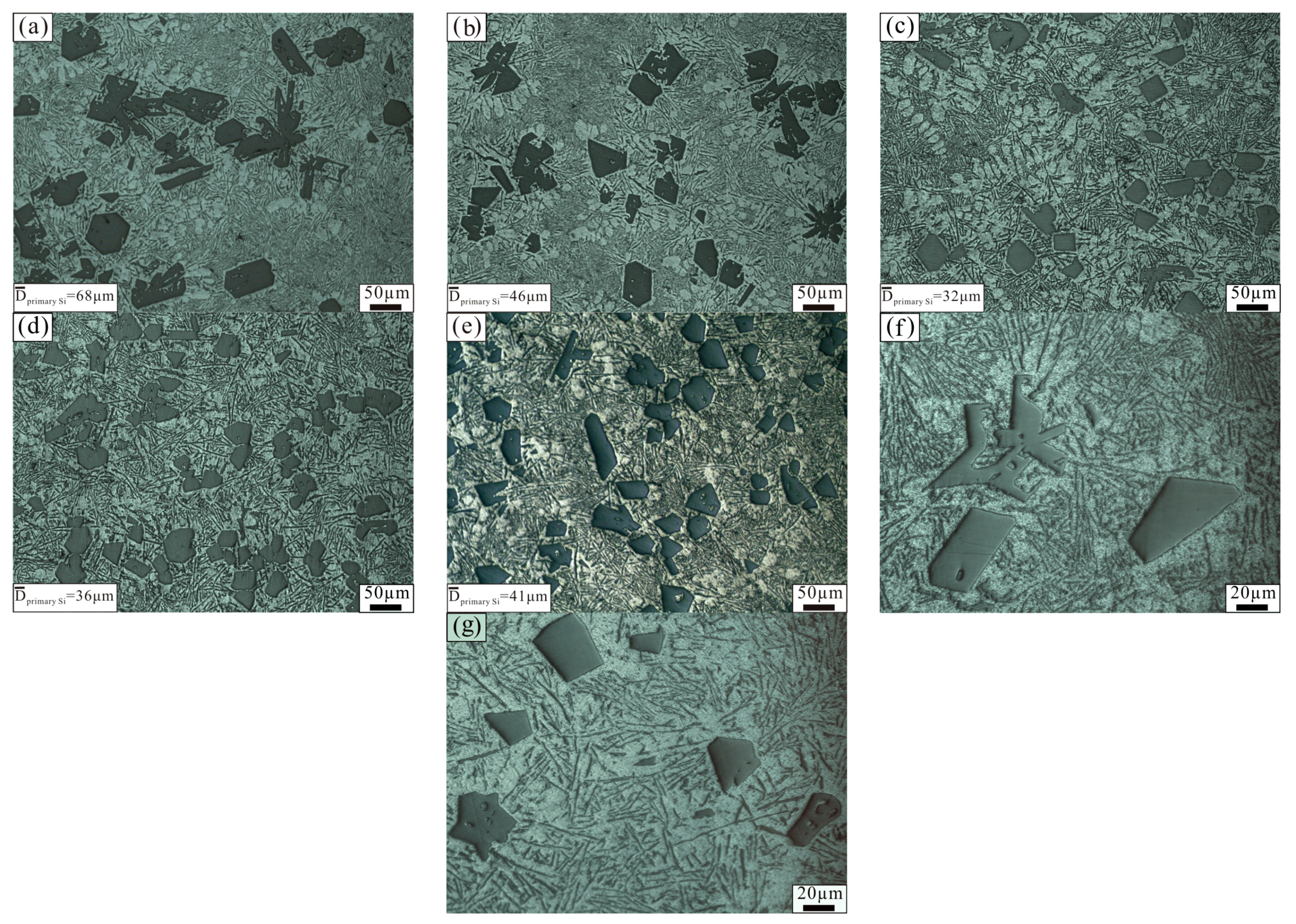
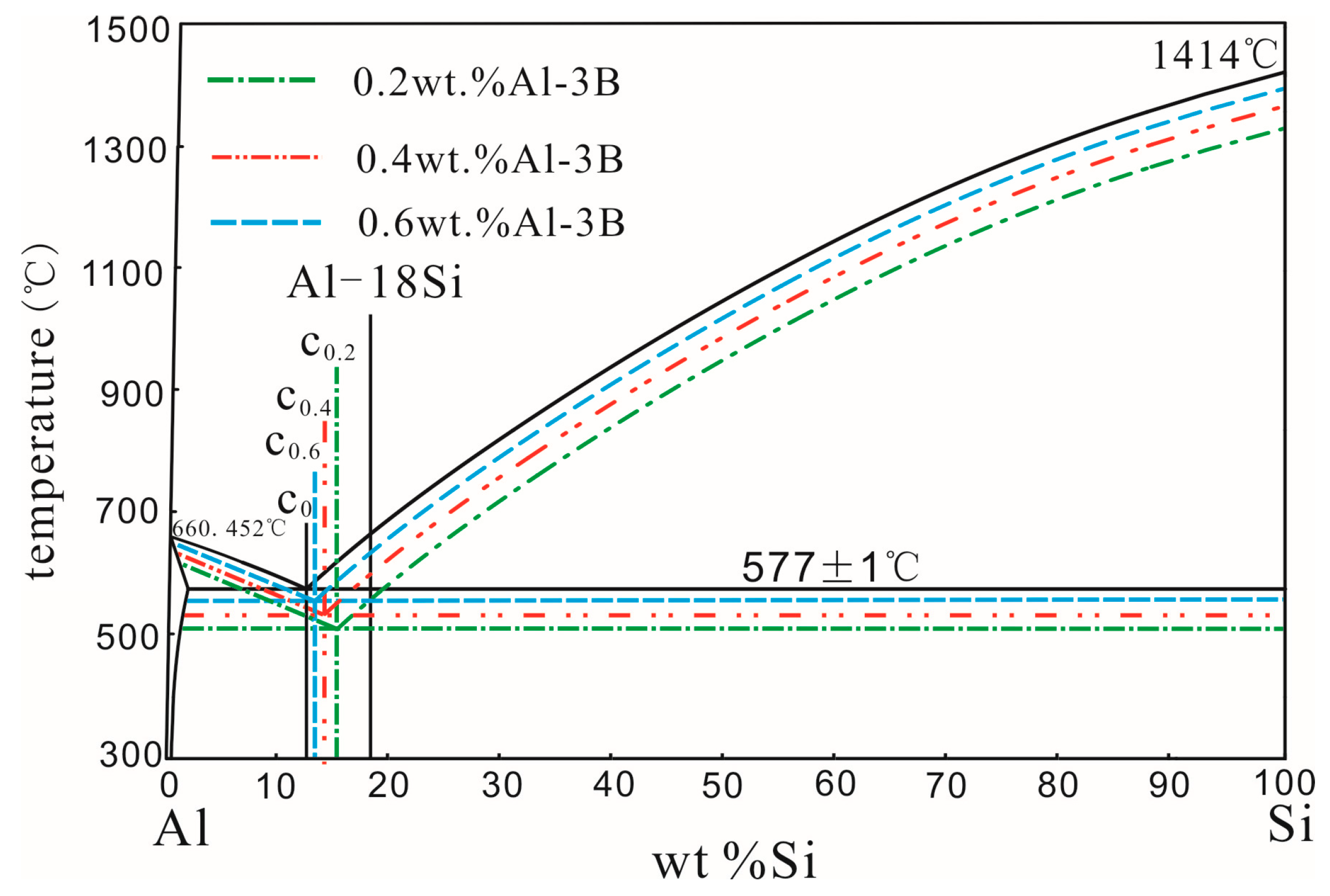
3.1. Effect of Added Amount of Al–3B on Al–18Si Alloy Microstructure
3.2. The Effect of Temperature on an Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Microstructure
3.3. The Mechanical Properties of an Hypereutectic Al–18%Si Alloy
4. Conclusions
- The size and area fraction of the primary Si in the Al–18Si alloy first decreased, and then increased as Al–3B was continuously added. When Al–18Si alloy was modified with 0.2 wt % Al–3B, the size and area fraction of the primary Si was the least.
- The size of the primary Si in the modified Al–18Si alloy hardly changed as the temperature increased from 750 °C to 800 °C. As the temperature increased to 850 °C, the primary Si was obviously refined. As the modification temperature increased, the fraction of primary Si in the modified Al–18Si alloy gradually decreased.
- After modification at 850 °C with 0.2 wt % Al–3B, the tensile strength and elongation of the modified Al–18Si alloy increased by 25% and 81%, respectively. The tensile fracture of modified Al–18Si alloy exhibited partial ductile fracture characteristics, but there were more areas of ductile characteristics compared with that of the unmodified Al–18Si alloy.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Elmadagli, M.; Gertsmana, V.Y.; Lo, J.; Alpas, A.T. FIB and TEM characterization of subsurfaces of an Al–Si alloy (A390) subjected to sliding wear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 421, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmadagli, M.; Perry, T.; Alpas, A.T. A parametric study of the relationship between microstructure and wear resistance of Al–Si alloys. Wear 2007, 262, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranos, P.; Kirkwood, D.H.; Atkinson, H.V.; Rheinlander, J.T.; Bentzen, J.J.; Toft, P.T.; Debel, C.P.; Laslaz, G.; Maenner, L.; Blais, S.M.; et al. Thixoforming of an automotive part in A390 hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 135, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Effect of Composite Modification on Microstructure and Properties of Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy; Jilin University: Jilin, China, 11 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mahato, A.; Xia, S.; Perry, T.; Sachdev, A.; Biswas, S.K. Role of silicon in resisting subsurface plastic deformation in tribology of aluminium–silicon alloys. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuzek, M. Aluminum–Silicon Casting Alloys: Atlas of Microfractographs; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, S.; An, P.; Mao, Y. Preparation of Semi–Solid Slurry of Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy by Ultrasonic Vibration. Solid State Phenom. 2008, 141–143, 767–771. Available online: https://www.scientific.net/SSP.141–143.767 (accessed on 7 July 2008).
- Li, R.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, B. Effect of Squeeze Casting on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–xSi Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.C.; Jie, J.C.; Sun, J.L.; Wang, T.M.; Cao, Z.Q.; Li, T.J. Effect of Si content on separation and purification of the primary Si phase from hypereutectic Al–Si alloy using rotating magnetic field. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.K.; Shen, N.F.; Shi, G.X. Effect of Melt Pretreatment on the Microstructures and Their Properties in Hypereutectic Al–Si Alloy. J. Zhengzhou Univ. Technol. 1999, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-S.; Lee, B.-T.; Lee, C.R.; Chun, B.-S. Microstructure of rapidly solidified Al–20Si alloy powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304–306, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Liu, X.F.; Sun, Q.Q.; Jiang, K. Effect of rapid solidification on the microstructure and refining performance of an Al–Si–P master alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5504–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tu, X.; Fukuda, Y.; Kanno, T.; Nakae, H. Modification mechanism of hypereutectic Al–Si alloy with P–Na addition. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2003, 13, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xia, T.; Lan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fan, L.; Li, P. Effect of rare earth cerium addition on the microstructure and tensile properties of hypereutectic Al–20%Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 562, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Su, X.; Wu, C. Effect of reverse modification of Al–5Ti–B master alloy on hypoeutectic ZnAl4Y alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 38, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.C.; Xu, C.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Yang, Y.F. Estimation of the shifting distance of the eutectic point in hypereutectic Al–Si alloys by the lever rule. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-16a. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Kang, H.; Fan, G.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Jie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Jian, X.; Wang, T. Grain refinement of hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys with B. Acta Mater. 2016, 120, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, C.; Li, Y. Grain refining mechanism of Al–3B master alloy on hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Hernández, F.C.; Sokolowski, J.H. Identification of Silicon Agglomerates in Quenched Al–Si Hypereutectic Alloys from Liquid State. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 7, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, F.R.; Sokolowski, J.H. Thermal analysis and microscopical characterization of Al–Si hypereutectic alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 419, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bian, X.; Qin, J.; Syliusarenko, S.L. The atomic–structure changes in Al–16 PCT Si alloy above the liquidus. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Lu, X.; Su, X. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–12.6Si Eutectic Alloy Modified with Al–5Ti Master Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Alloy No. | Modification Temperature/°C | Adding Amount of Al–3B/wt % |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 750 | 0 |
| 2 | 750 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 750 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 750 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 750 | 0.6 |
| 6 | 800 | 0 |
| 7 | 800 | 0.1 |
| 8 | 800 | 0.2 |
| 9 | 800 | 0.4 |
| 10 | 800 | 0.6 |
| 11 | 850 | 0 |
| 12 | 850 | 0.1 |
| 13 | 850 | 0.2 |
| 14 | 850 | 0.4 |
| 15 | 850 | 0.6 |
| Modification Temperature/°C | Added Amount of Al–3B (wt %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| 750 | 14.5 | 12.8 | 11.5 | 13.2 | 14.7 |
| 800 | 13.6 | 11.5 | 9.4 | 12.3 | 13.9 |
| 850 | 12.3 | 10.0 | 8.6 | 11.1 | 12.8 |
| Modification Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (SD) (N/mm2) | Elongation (SD) (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added Amount of Al–3B (wt %) | ||||||||||
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| 750 | 141 (±2.9) | 145 (±3.1) | 166 (±2.9) | 148 (±2.8) | 142 (±2.5) | 1.6 (±0.12) | 2.2 (±0.13) | 2.7 (±0.10) | 2.3 (±0.14) | 2.0 (±0.12) |
| 800 | 143 (±2.8) | 148 (±2.4) | 164 (±2.7) | 149 (±3.1) | 144 (±2.6) | 2.0 (±0.11) | 2.3 (±0.13) | 2.6 (±0.14) | 2.4 (±0.10) | 2.2 (±0.13) |
| 850 | 142 (±3.0) | 153 (±3.3) | 178 (±2.8) | 156 (±2.6) | 147 (±3.6) | 2.1 (±0.12) | 2.7 (±0.14) | 3.8 (±0.13) | 2.9 (±0.12) | 2.5 (±0.10) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, C.; Tu, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Modified with Al–3B. Materials 2018, 11, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030456
Gong C, Tu H, Wu C, Wang J, Su X. Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Modified with Al–3B. Materials. 2018; 11(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Chunjie, Hao Tu, Changjun Wu, Jianhua Wang, and Xuping Su. 2018. "Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Modified with Al–3B" Materials 11, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030456
APA StyleGong, C., Tu, H., Wu, C., Wang, J., & Su, X. (2018). Study on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hypereutectic Al–18Si Alloy Modified with Al–3B. Materials, 11(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11030456





