Excellent Tribological Properties of Lower Reduced Graphene Oxide Content Copper Composite by Using a One-Step Reduction Molecular-Level Mixing Process
Abstract
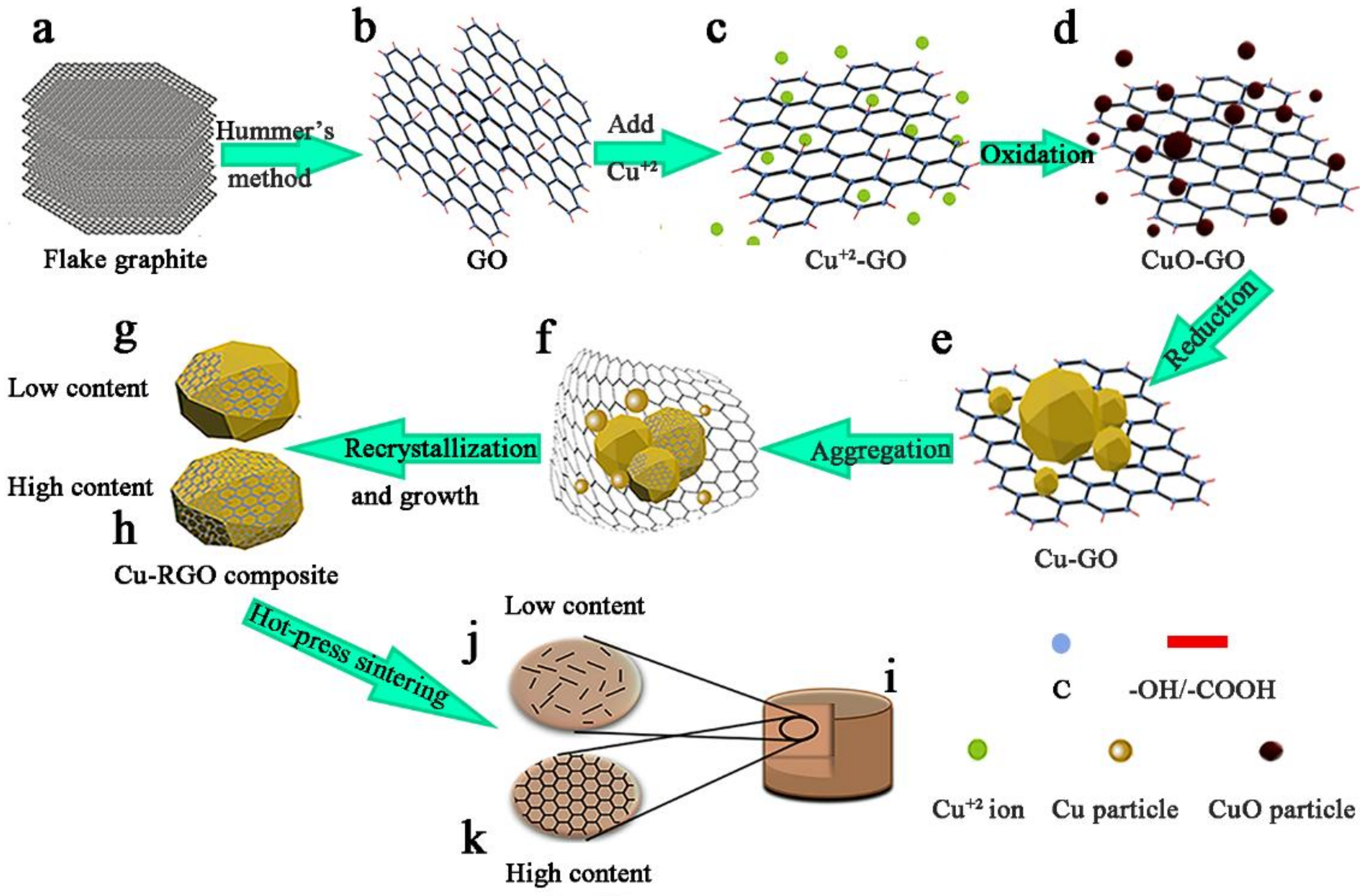
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Cu-RGO Composite Preparation
2.2. Material Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the Bulk Cu-RGO Composites
3.2. Tribological Properties of Cu/RGO Composites
3.3. Friction and Wear Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- Cu-RGO composites were successfully prepared by one-step reduction with a modified MLM method and hot-press sintering. For such composites, the RGO distribution in the Cu-RGO composites shifts from unordered to three-dimensional as the RGO increases to above 1.0 wt.%.
- There are benefits from this good, three-dimensional combination; the hardness of the composite with 2.0 wt.% RGO was without much deterioration, represented a 39% enhancement over pure Cu.
- Compared to the as-sintered pure Cu, the Cu composite with only 1.0 wt.% RGO presented a lower friction coefficient and wear rates. The RGO improves the tribological behavior of copper matrix composites by hindering deformation of the copper matrix and forming a continuous lubrication transfer layer on the worn surface.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, W. Investigation on wear and corrosion behavior of Cu–graphite composites prepared by electroforming. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futami, T.; Ohira, M.; Muto, H.; Sakai, M. Contact/scratch-induced surface deformation and damage of copper–graphite particulate composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, S.F.; El-Badry, S.A.; Sanad, A.M.; Kieback, B. Friction and wear of copper–graphite composites made with Cu-coated and uncoated graphite powders. Wear 2002, 253, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J.; Emmer, Š.; Bielek, J.; Keleši, L.U. Effect of composition on friction coefficient of Cu–graphite composites. Wear 2008, 265, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, I.W.; Tanenbaum, D.M.; van der Zande, A.M.; McEuen, P.L. Mechanical properties of suspended graphene sheets. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2007, 25, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, P.; Zhang, B.; Tang, S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W. Preparation and characterization of reduced graphene oxide/copper composites incorporated with nano-SiO2 particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 671, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, J.; Jia, X. Preparation and tribological properties of MoS2/graphene oxide composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Li, C. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/zinc sulfide hybrids for enhanced tribological properties of epoxy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 326, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Vajtai, R.; Fei, W. High apparent strengthening efficiency for reduced graphene oxide in copper matrix composites produced by molecule-lever mixing and high-shear mixing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51193–51200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Yao, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Guo, E.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Wang, B. Effect of ball-milling and graphene contents on the mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms of graphene nanosheets reinforced copper matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Yoon, T.; Jin, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.S.; Hong, S.H.; Jeon, S. Enhanced mechanical properties of graphene/copper nanocomposites using a molecular-level mixing process. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6724–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, H.; Gao, Z. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Graphene Composite Produced by High-Pressure Torsion. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.J.; Zhou, M.P.; Ling, H.J.; Chen, F.X.; Lian, W.Q.; Jie, X.H. Surfactant-free electrodeposition of reduced graphene oxide/copper composite coatings with enhanced wear resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Weng, L.; Zhu, H.; Fan, T.; Zhang, D. Simultaneously enhancing the strength, ductility and conductivity of copper matrix composites with graphene nanoribbons. Carbon 2017, 118, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Ni, J.; Li, H.; Shao, X. Synthesis, characterization and tribological properties of Cu/reduced graphene oxide composites. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Few layer graphene to reduce wear and friction on sliding steel surfaces. Carbon 2013, 54, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Shi, X.; Yao, J.; Ibrahim, A.M.M.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q. Investigation of mechanical and tribological behaviors of multilayer graphene reinforced Ni3Al matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-F.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.-K.; Zhou, K.-C. Sliding wear behavior of copper-based composites reinforced with graphene nanosheets and graphite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3354–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yue, H.; Guo, E.; Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, B.; Guan, E. Tribological properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with homogeneously dispersed graphene nanosheets. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Shi, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yao, J.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Grain refinement: A mechanism for graphene nanoplatelets to reduce friction and wear of Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composites. Wear 2014, 310, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhan, Z. Preparation of graphene nanoplatelets-copper composites by a modified semi-powder method and their mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yue, H.; Guo, E.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, B. Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of graphene reinforced copper matrix composites. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhan, Z. Strengthening effect of graphene derivatives in copper matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 654, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved Synthesis of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Velamakanni, A.; Bozoklu, G.; Park, S.; Stoller, M.; Piner, R.D.; Stankovich, S.; Jung, I.; Field, D.A.; Ventrice, C.A.; et al. Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and Micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2009, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Sheng, P.; Sun, F.; Xu, W.; Zhang, D. A new approach to reduced graphite oxide with tetrathiafulvalene in the presence of metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Cha, S.I.; Gemming, T.; Eckert, J.; Hong, S.H. The role of interfacial oxygen atoms in the enhanced mechanical properties of carbon-nanotube-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Small 2008, 4, 1936–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, R.; Cao, G.; Li, B.; Fei, W. Effect of H2 Reduction Temperature on the Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Copper Matrix Composites. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2014, 27, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzman, H.; Brener, R.; Haick, H.; Tannenbaum, R. Oxidation of Polycrystalline Copper Thin Films at Ambient Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ying, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Q. Effects of graphene content on the microstructure and properties of copper matrix composites. Carbon 2016, 96, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, P.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, K.; Chao, Y. Fabrication and tribological properties of copper matrix composite with short carbon fiber/reduced graphene oxide filler. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Eklund, P.; Xue, J.; Huang, F.; Du, S.; Huang, Q. Effect of carbide interlayers on the microstructure and properties of graphene-nanoplatelet-reinforced copper matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, H.; Hatipoglu, G.; Algul, H.; Tokur, M.; Kartal, M.; Uysal, M.; Cetinkaya, T. Co-deposition of Cu/WC/graphene hybrid nanocomposites produced by electrophoretic deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 284, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, P.; Muzyka, R.; Robak, Z.; Kaptacz, S. Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide–Copper Composites. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Geng, L.; Li, A.B.; Yang, F.Y.; Peng, H.X. In situ TiBw/Ti–6Al–4V composites with novel reinforcement architecture fabricated by reaction hot pressing. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, D.-L.; Jiang, D.-P.; Han, X.-L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, G.-H. Microstructural characteristics and evolution of Ti2AlN/TiAl composites with a network reinforcement architecture during reaction hot pressing process. Mater. Charact. 2013, 80, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Zone | C (wt.%) | O (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 2.01 | 0.03 | 97.96 |
| 2 | 0 | 1.55 | 0.20 | 98.26 |
| 3 | 0 | 4.43 | 0.66 | 94.92 |
| 4 | 0 | 3.62 | 0.33 | 96.05 |
| 5 | 4.68 | 0.70 | 0.24 | 94.39 |
| Zone | C (wt.%) | O (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.99 | 6.28 | 1.22 | 89.52 |
| 2 | 3.74 | 4.46 | 0.87 | 90.92 |
| 3 | 16.99 | 1.48 | 0.00 | 81.52 |
| 4 | 10.06 | 1.26 | 0.21 | 88.47 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, H.; Fu, L.; Zhu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, D.; Zhou, L. Excellent Tribological Properties of Lower Reduced Graphene Oxide Content Copper Composite by Using a One-Step Reduction Molecular-Level Mixing Process. Materials 2018, 11, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040600
Nie H, Fu L, Zhu J, Yang W, Li D, Zhou L. Excellent Tribological Properties of Lower Reduced Graphene Oxide Content Copper Composite by Using a One-Step Reduction Molecular-Level Mixing Process. Materials. 2018; 11(4):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040600
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Haibin, Licai Fu, Jiajun Zhu, Wulin Yang, Deyi Li, and Lingping Zhou. 2018. "Excellent Tribological Properties of Lower Reduced Graphene Oxide Content Copper Composite by Using a One-Step Reduction Molecular-Level Mixing Process" Materials 11, no. 4: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040600
APA StyleNie, H., Fu, L., Zhu, J., Yang, W., Li, D., & Zhou, L. (2018). Excellent Tribological Properties of Lower Reduced Graphene Oxide Content Copper Composite by Using a One-Step Reduction Molecular-Level Mixing Process. Materials, 11(4), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040600




