Microstructural Evolution in High-Strain-Rate Deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Tests
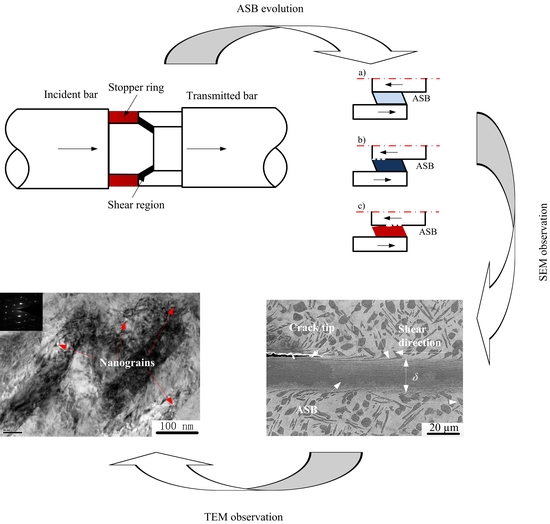
3.2. Microstructural Characterization
3.3. Estimation of ASB Width
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- The flow stress in the HS specimens of Ti-55511 alloy remains a constant of about 600 MPa, and is independent of punching depth.
- (b)
- The width of the shear band increases with the increase of punching depth and tends to saturate at 30 μm, and the estimation of the ASB width in HS specimens has been modified.
- (c)
- Thermal softening has a minor effect on the onset of ASB and DRX formation, and the nucleation mechanism for DRX is strain-induced boundary migration and subgrain rotation and coalescence.
- (d)
- For Ti-55511 alloy, the features of microstructural evolution in high-strain-rate loading situations are similar to those of adhesive fracture, and the concept of adhesive fracture is proposed as the dynamic failure mechanism for Ti-55511 alloy.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zener, C.; Hollomon, J. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel. J. Appl. Phys. 1944, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, B.; Bai, Y. Introduction to Adiabatic Shear Localization: Revised Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, R. An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 1996, 213, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtemam-Haghighi, S.; Prashanth, K.; Attar, H.; Chaubey, A.; Cao, G.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of mechanical and wear properties of Ti-xNb-7Fe alloys designed for biomedical applications. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okulov, I.; Volegov, A.; Attar, H.; Bönisch, M.; Ehtemam-Haghighi, S.; Calin, M.; Eckert, J. Composition optimization of low modulus and high-strength TiNb-based alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2017, 65, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.; Jackson, M. On mechanism of flow softening in Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.; Subhash, G.; Kad, B.; Prasad, L. Evolution of microstructure and shear-band formation on alpha-hcp titanium. Mech. Mater. 1994, 17, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Meyers, M.; Nesterenko, V. Self-organization of shear bands in titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 575–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittel, D.; Landau, P.; Venkert, A. Dynamic recrystallization as a potential cause for adiabatic shear failure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 165501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittel, D.; Wang, Z. Thermo-mechanical aspects of adiabatic shear failure of AM50 and Ti6Al4V alloys. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xue, Q.; Xu, Y.; Shen, L. Characteristics and microstructure in the evolution of shear localization in Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mech. Mater. 1994, 17, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, S. On evolution of thermo-plastic shear band. Acta Mech. Sin. 1986, 18, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, B.; Bai, Y. Width of adiabatic shear bands. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1985, 1, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, B.; Bai, Y. Width of adiabatic shear bands formed under combined stresses. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1989, 5, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meyers, M.; Nesterenko, V. Spontaneous and forced shear localization in high-strain-rate deformation of tantalum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 1999, 268, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Chen, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, W. Dynamic shear deformation and failure of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2017, 694, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Tian, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Effect of weld repair on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive manufactured Ti-55511 alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, X.; Tang, H.; Wang, H. Microstructural characterization of laser melting deposited Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe near β titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 572, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, M.; Zherebtsov, S.; Salishchev, G.; Semiatin, S. Influence of deformation on the Burgers orientation relationship between the α and β phases in Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 645, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shangguan, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, H. Fretting wear behavior of laser-nitrided Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy fabricated by laser melting deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 116, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Guo, H.; Ning, Y.; Peng, X.; Qin, C.; Shi, Z.; Nan, Y. Dynamic recrystallization behavior of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Ning, Y.; Liang, H.; Guo, H.; Yao, Z.; Fu, M.W. Work-hardening effect and strain-rate sensitivity behavior during hot deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 82, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Chen, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. High-strain-rate plastic deformation and fracture behaviour of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe titanium alloy at room temperature. Mech. Mater. 2018, 116, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, B.; Bai, Y. Adiabatic Shear Localization: Frontiers and Advances, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, U.; Meyers, M.; Vecchio, K.; Chokshi, A. Dynamic recrystallization in high-strain, high-strain-rate plastic deformation of copper. Acta Mater. 1994, 42, 3183–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.; Xu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Pérez-Prado, M.; McNelley, T. Microstructural evolution in adiabatic shear localization in stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1307–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.; Vecchio, K. Recrystallization kinetics within adiabatic shear bands. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, A. Adiabatic Shear Localization in a Near Beta Ti-5Al-5Mo-5 V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 639, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Chen, P. Dynamic Shear Deformation and Failure of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Cheng, C.; Ding, Y. Development of thermoplastic shear bands in simple shear. Res. Mech. 1987, 22, 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Possibility of Subgrain Rotation during Recrystallization. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 2958–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, B. The dependence of grain size on stress during dynamic recrystallisation. Acta Mater. 1991, 39, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Argon, A. Steady-state creep of single-phase crystalline matter at high temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 1976, 11, 1542–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Quinney, H. The latent energy remaining in a metal after cold working. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1934, 413, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clos, R.; Schreppel, U.; Veit, P. Temperature, microstructure and mechanical response during shear-band formation in different metallic materials. J. Phys. IV 2003, 110, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Al | Mo | V | Cr | Fe | C | N | H | O | Zr | Si | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.50 | 4.82 | 4.82 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.10 | balance |
| Pd/mm | v/ms−1 | tM/μm | tD/mm | γ | γloc | /s−1 | Tmax/K | δ/μm | δ/tM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 23.8 | 20.1 | 1.01 | 0.693 | 34.83 | 5.92 × 105 | 454 | 6.86 | 2.93 |
| 0.8 | 23.7 | 23.2 | 1.03 | 0.777 | 34.48 | 5.11 × 105 | 467 | 7.49 | 3.10 |
| 0.9 | 23.7 | 25.5 | 1.02 | 0.882 | 35.29 | 4.65 × 105 | 494 | 8.08 | 3.16 |
| 1 | 23.7 | 27.3 | 1.01 | 0.990 | 36.63 | 4.34 × 105 | 504 | 8.44 | 3.23 |
| 1.1 | 23.5 | 27.9 | 1.04 | 1.058 | 39.43 | 4.21 × 105 | 532 | 8.81 | 3.17 |
| Without stopper ring | 23.8 | 28.2 | 1.02 | 1.196 | 46.10 | 4.22 × 105 | 573 | 9.13 | 3.09 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, C.; Chen, P.; Sheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Microstructural Evolution in High-Strain-Rate Deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050839
Ran C, Chen P, Sheng Z, Li J, Zhang W. Microstructural Evolution in High-Strain-Rate Deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy. Materials. 2018; 11(5):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050839
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Chun, Pengwan Chen, Zemin Sheng, Jingbo Li, and Wangfeng Zhang. 2018. "Microstructural Evolution in High-Strain-Rate Deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy" Materials 11, no. 5: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050839
APA StyleRan, C., Chen, P., Sheng, Z., Li, J., & Zhang, W. (2018). Microstructural Evolution in High-Strain-Rate Deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe Alloy. Materials, 11(5), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050839