Rapid Ferric Transformation by Reductive Dissolution of Schwertmannite for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Schwertmannite
2.3. Catalytic Oxidation of RhB
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Computation Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Schwertmannite
3.2. Effect of HA on Degradation of RhB by PS on Schwertmannite
3.3. Release Files of Dissolved Iron from Schwertmannite
3.4. Effect of Fe(III) on the Degradation of RhB
3.5. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
3.6. Comparison of Heterogeneous Process and Homogeneous Process
3.7. Effect of pHpzc on the Heterogeneous Process
3.8. Activation Mechanism of PS on Schwertmannite in the Presence of HA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, M.C.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Murad, E. Iron oxide catalysts: Fenton and Fenton-like reactions a review. Clay Miner. 2012, 47, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E.; Ross, A.B. Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 1027–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (•OH/•O−) in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of organic contaminants in water with sulfate radicals generated by the conjunction of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Chu, W. Degradation of atrazine by cobalt-mediated activation of peroxymonosulfate: Different cobalt counteranions in homogenous process and cobalt oxide catalysts in photolytic heterogeneous process. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Fang, J.Y.; Chen, L.W. Influence of pH on the formation of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in the UV/Peroxymonosulfate system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Nagaoka, Y.; Murayama, M.; Kutsuna, S. Efficient decomposition of perfluorocarboxylic acids and alternative fluorochemical surfactants in hot water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7438–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Hayakawa, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Kutsuna, S.; Kiatagawa, H.; Arakawa, R. Efficient decomposition of environmentally persistent perfluorocarboxylic acids by use of persulfate as a photochemical oxidant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, T.K.; Chu, W.; Graham, N.J.D. The aqueous degradation of butylated hydroxyanisole by UV/S2O82−: Study of reaction mechanisms via dimerization and mineralization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Ai-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous-peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldemer, R.H.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L.; Nurmi, J.T. Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate: Kinetics and products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Huang, C.F.; Chen, Y.J. Potential for activated persulfate degradation of BTEX contamination. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4091–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.M.; Park, H.S.; Yoon, C. Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Guan, Y.; Xie, P.; Pan, C. Rapid acceleration of ferrous iron/peroxymonosulfate oxidation of organic pollutants by promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle with hydroxylamine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11685–11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Transition metal/UV-based advanced oxidation technologies for water decontamination. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 54, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, W. Degradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by a novel Electro-Fe(II)/Oxone process using iron sheet as the sacrificial anode. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3883–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.W.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J.Y.; Guan, Y.H.; Xie, P.C. Strong enhancement on Fenton oxidation by addition of hydroxylamine to accelerate the ferric and ferrous iron cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Effect of inorganic, synthetic and naturally occurring chelating agents on Fe(II) mediated advanced oxidation of chlorophenols. Water Res. 2009, 43, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Persulfate activation by subsurface minerals. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 115, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.; Huang, C.; Huang, Y.H. Heterogeneous and homogeneous catalytic oxidation by supported γ-FeOOH in a fluidized-bed reactor: Kinetic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, S.H.; Kwon, Y.J.; Kong, S.H. Effect of metal oxides on the reactivity of persulfate/Fe(II) in the remediation of diesel-contaminated soil and sand. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.M.; Jia, S.X. Han Schwertmannite as a new Fenton-like catalyst in the oxidation of phenol by H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Croue, J.P. Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: Efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.C.; Degraff, W.; Hankovszky, O.H.; Cecília, P.; Kálai, T.; Jeko, J.; Russo, A.; Mitchell, J.B.; Hideg, K. Studies of structure-activity relationship of nitroxide free radicals and their precursors as modifiers against oxidative damage. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigham, J.M.; Schwertmann, U.; Murad, E.; Carlson, L. A poorly crystallized oxyhydroxysulfate of iron formed by bacterial oxidation of Fe(II) in acid mine waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2743–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, J.M.; Schwertmann, U.; Traina, S.J.; Winland, R.L.; Wolf, M. Schwertmannite and the chemical modeling of iron in acid sulfate waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulat, F.A.; Chamorro, E.; Fuentealba, P.; Toro-Labbé, A. Condensation of frontier molecular orbital fukui functions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.E., Jr.; Smart, J.A.; Amis, E. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of iron(II) and total iron with 1,10-phenanthroline. Anal. Chem. 1955, 27, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.; Ruiz, P.; Aguillon, J.C.; Fehrmann, A. A new spectrophotometric method for the determination of ferrous iron in the presence of ferric iron. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1989, 44, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.; Bower, V. The ionization constant of hydroxylamine. J. Phys. Chem. 1961, 65, 1279–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.P.; Huang, Y.H. Comparison of catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and catalytic degradation of phenol by immobilized iron oxides. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 346, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.H.; Tu, Y.T.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, X.; Xiong, Y. Degradation of acid orange II at neutral pH using Fe2(MoO4)3 as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, J.; Casas, J.; Mohedano, A.; Gilarranz, M.; Rodriguez, J. Chemical pathway and kinetics of phenol oxidation by Fenton’s reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9295–9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; Miller, I.K. The chemistry of persulfate. I. The kinetics and mechanism of the decomposition of the persulfate ion in aqueous medium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 3055–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.; Masson, O. CCXIX.—The dynamics of the decomposition of persulphuric acid and its salts in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1910, 97, 2083–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bonino, F.; Damin, A.; Ricchiardi, G. Ti-peroxo species in the TS-1/H2O2/H2O system. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3573–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamello, E.; Calosso, L.; Fubini, B.; Geobaldo, F. Evidence of stable hydroxyl radicals and other oxygen radical species generated by interaction of hydrogen peroxide with magnesium oxide. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 5735–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Bokare, A.D.; Koo, M.S.; Choi, W. Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation of As(III) on nonferrous metal oxides in the presence of H2O2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3506–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lousada, C.M.; Johansson, A.J.; Brinck, T.; Jonsson, M. Mechanism of H2O2 decomposition on transition metal oxide surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9533–9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






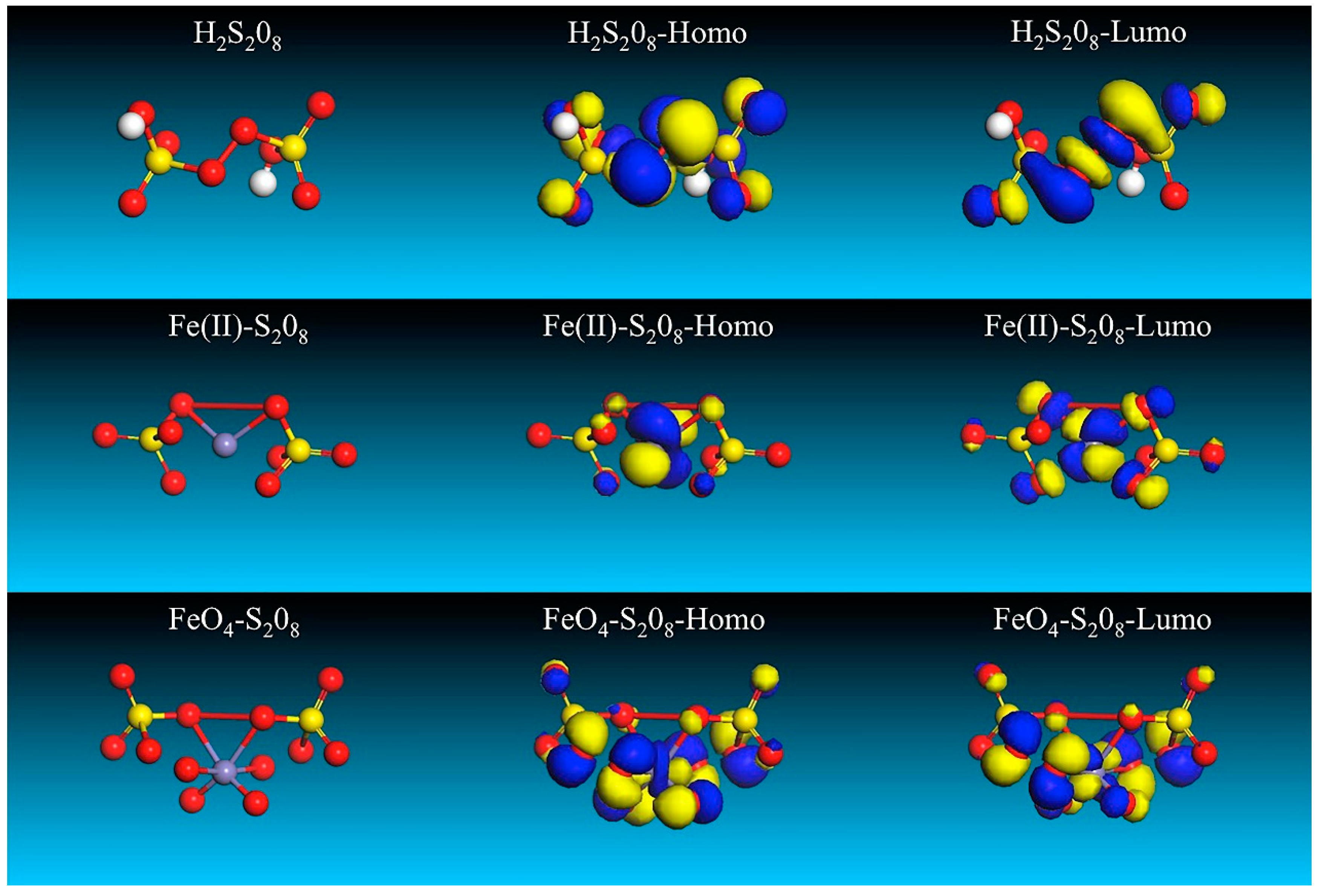



| Species | EHOMO/eV | ELUMO/eV | ΔE/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2S2O8 | −11.417 | −2.084 | 9.333 |
| Fe(II)-S2O8 | −11.745 | −2.543 | 9.202 |
| FeO4-S2O8 | −9.611 | −1.372 | 8.239 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, J.; Yu, B. Rapid Ferric Transformation by Reductive Dissolution of Schwertmannite for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. Materials 2018, 11, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071165
Ran J, Yu B. Rapid Ferric Transformation by Reductive Dissolution of Schwertmannite for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071165
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Jingyu, and Bo Yu. 2018. "Rapid Ferric Transformation by Reductive Dissolution of Schwertmannite for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B" Materials 11, no. 7: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071165
APA StyleRan, J., & Yu, B. (2018). Rapid Ferric Transformation by Reductive Dissolution of Schwertmannite for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. Materials, 11(7), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071165





