Study on Nonlinear Conductivity of CCTO/EPDM Rubber Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Performance Testing of Composites
3. Results
3.1. Microstructures Characterization
3.2. The Conductivity of Composites
3.2.1. The Characteristic of Conductivity (Γ)—Electric Field (E)
3.2.2. The Characteristic of Conductivity (γ)—Temperature (T)
3.3. The Dielectric Properties of Composites
3.4. The Breakdown of Composites
4. Simulation Results and Analysis of Electrical Field Distribution in DC Cable Termination
4.1. Distribution Characteristics of Steady Electrical Field in Cable Termination
4.2. Distribution Characteristics of Transient Electrical Field in Cable Termination
4.2.1. The Electric Field Distribution of Cable Termination during Polarity Reversal
4.2.2. The Electric Field Distribution of Cable Termination during Lightning Process
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CCTO particles are fabricated by the sol-gel method, and dispersed evenly in CCTO/EPDM composites. CCTO/EPDM composites have good nonlinear conductance characteristics. When the content of CCTO particles is low, the conductivity of CCTO/EDPM does not exhibit nonlinear characteristics; with the increase of the doping content, the conductivity of CCTO/EDPM shows a nonlinear increase with the increase of the electric field strength. Moreover, the Eth reduces and β increases with the increase of CCTO particle content.
- (2)
- The increase of CCTO particle content, leading to the free volume decreases; and due to the high dielectric constant of CCTO particles, leading to the dielectric constant of CCTO/EDPM composites increases with the increase of CCTO particles content.
- (3)
- The simulation results of steady and transient electric field distributions show that CCTO/EPDM composites exhibit ability to homogenize the electric field distribution.
- (4)
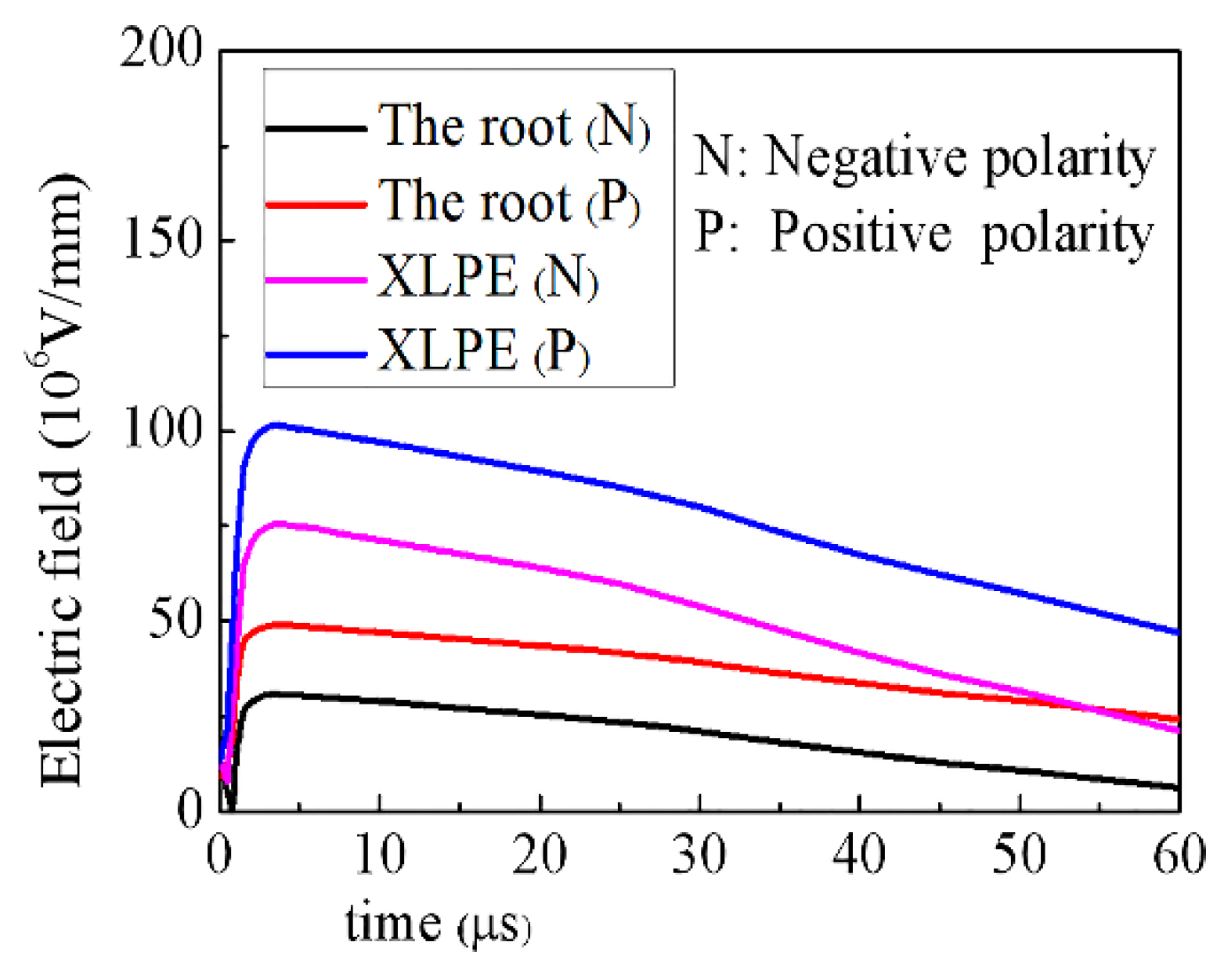
- In the lightning impulse process, the maximum electric field is concentrated on XLPE, and it does not change with the polarity of the lightning pulse process. The dielectric constant increase of reinforced insulation can significantly reduce the maximum electric field strength of the root.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Commission of the European Communities. Limiting Global Climate Change to 2 Degrees Celsius the Way ahead for 2020 and beyond; Communication from the Commission to the Council, the European Parliament, the Europe Economy and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; Commission of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, A.; Jeroense, M.; Sunnegårdh, P.; Saltzer, M.; Ghorbani, H.; Rapp, H. New developments within the area of extruded HVDC cables. In Proceedings of the11th IET International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission, Birmingham, UK, 10–12 February 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.prysmiangroup.com/en/corporate/media/news/Breakthrough-HVDC-cable-techology-for-power-transmission-grids/ (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Tang, G. The exploration of China advanced transmission technology innovation and the development of UHV technology. China Elect. Equip. Ind. 2015, 15, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liangzhong, Y.; Jing, W.; Zhibing, W.; Yan, L.; Zong-Xiang, L. Pattern analysis of future HVDC grid development. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 6007–6020. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, T.L.; Burford, R.P.; Fleming, R.J.; Barber, K.W. A general review of polymeric insulation for use in HVDC cables. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2003, 19, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yin, Y.; Lan, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, D. The influence of nano-filler concentration on space charge behavior in LDPE/Silica nanocompo-site. Proc. CSEE 2012, 32, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Zheng, Z.; Boggs, S. Engineering with nonlinear dielectrics. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2004, 20, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weida, D.; Steinmetz, T.; Clemens, M. Electro-quasistatic high voltage field simulations of large scale insulator structures including 2-D models for nonlinear field-grading material layers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Nelson, J.K.; Hillborg, H.; Zhao, S. Graphene oxide filled nanocomposite with novel electrical and dielectric properties. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3134–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, T.; Donzel, L.; Greuter, F. Nonlinear resistive electric field grading part 1: Theory and simulation. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2010, 26, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.P.; Varlow, B.R. Nonlinear dc and ac conductivity in electrically insulating composites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2003, 10, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virsberg, L.G.; Björklund, A. New type of turn insulation for medium-sized, high-voltage electrical machines. In Proceedings of the Electrical/Electronics Insulation Conference (EIC 13th), Chicago, IL, USA, 26–29 September 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, T.; Koyama, M.; Inoue, Y.; Tomimura, T.; Nakamura, S. Non-linear electrical property of composite materials with two kinds of filler. In Proceedings of the 20001 IEEE 7th International Conference on Solid Dielectrics, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 25–29 June 2001; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Auckland, D.W.; Rashid, A.; Tavernier, K. Stress relief by nonlinear fillers in insulating solids. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1994 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Arlington, TX, USA, 23–26 October 1994; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier, K.; Auckland, D.W.; Varlow, B.R. Improvement in the electrical performance of electrical insulation by nonlinear fillers. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Conference on Conduction and Breakdown in Solid Dielectrics, Vasteras, Sweden, 22–25 June 1998; pp. 533–538.
- Tavernier, K.; Varlow, B.R.; Auckland, D.W.; Ugur, M. Improvement in electrical insulators by nonlinear fillers. IEE Proc. Sci. Meas. Technol. 1999, 146, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onneby, C.; Martensson, E.; Gafvert, U.; Gustafsson, A.; Palmqvist, L. Electrical Properties of Field Grading Materials Influenced by the Silicon Carbide Grain Size. In Proceedings of the 20001 IEEE 7th International Conference on Solid Dielectrics (Cat. No.01CH37117), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 25–29 June 2001; pp. 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Donzel, L.; Christen, T.; Kessler, R.; Greuter, F.; Gramespacher, H. Silicone composites for HV applications based on microvaristors. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Solid Dielectrics, Toulouse, France, 5–9 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Subamanian, M.A.; Li, D.; Duan, N.; Reisner, B.A.; Sleight, A.W. High dielectric constant in ACu3Ti4O12 phases. J. Solid State Chem. 2000, 151, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Subramanian, M.A.; Rosenfeld, H.D.; Jones, C.Y.; Toby, B.H.; Sleight, A.W. Clues to the giant dielectric constant of CaCu3Ti4O12 in the defect structure of “SrCu3Ti4O12”. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5223–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Yin, Q.; Hu, W. Interface charge distribution between LDPE and carbon black filled EPDM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Dielectrics, Montpellier, France, 3–7 July 2016; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.X.; Li, J. Electrical and mechanical ageing behaviors of used heat-shrinkable insulation tubes. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.G.; Liu, H.Q.; Chi, M.H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Experimental study on influence of trap parameters on dielectric characteristics of nano-modified insulation pressboard. Materials 2017, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellon, J.; Nguyen, H.N.; Agnel, S.; Toureille, A.; Frechette, M.; Savoie, S.; Schmidt, L.E. Electrical properties analysis of micro and nano composite epoxy resin materials. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Mohammadzadeh, L.; Mehdipour, N. Anisotropic heat transport in nanoconfined polyamide-6,6 oligomers: Atomistic reverse nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, H.; Mohammadzadeh, L.; Mehdipour, N. Reverse nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation of thermal conductivity in nanoconfined polyamide-6,6. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 064703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Li, C.M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.L.; Han, B.Z. Doping effect of graphene nanoplatelets on electricalinsulation properties of polyethylene: From macroscopic to molecular scale. Materials 2016, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieda, M.; Mizutani, T.; Ikeda, S. Electrical Conduction and Chemical Structure of Insulating Polymers. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1986, 21, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.K.; Utracki, L.A.; Maccrone, R.K.; Reed, C.W. Role of the interface in determining the dielectric properties of nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of the IEEE Lasers and Electro-Optics Society, Boulder, CO, USA, 20–20 October 2004; pp. 314–317.
- Ye, X.; Han, B.; Huang, Q. Simulation of electrical field distribution of XLPE insulated HVDC cable. Electr. Mach. Control 2014, 18, 19–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, T. Behavior of Charge Carriers in Organic InsulatingMaterials. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Kansas City, MO, USA, 15–18 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, K.C. Dielectric Phenomena in Solids; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 460–462. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Z.H.; Guo, W.M.; Lu, X. Simulation of response characteristics of nonlinear insulating dielectrics in coaxial electrodes under the step voltage. High Voltage Eng. 2008, 34, 1363–1367. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Recommendations for Testing DC Extruded Cable Systems for Power Transmission at a Rated Voltage up to 500 kV. Available online: http://b1.cigre.org/Members-Area/WG-B1.32-Recommendations-for-testing-DC-extruded-cable-systems-for-power-transmission-at-a-rated-voltage-up-to-500-kV (accessed on 21 January 2018).














| Materials | Corporation |
|---|---|
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (≥ 99%) | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Cu(NO3)2·3H2O (≥ 99%) | |
| Ti(OC4H9)4 (≥ 99%) | |
| C3H8O2 (≥ 99%) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C. Study on Nonlinear Conductivity of CCTO/EPDM Rubber Composites. Materials 2018, 11, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091590
Li Z, Zhao H, Zhang C. Study on Nonlinear Conductivity of CCTO/EPDM Rubber Composites. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091590
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhongyuan, Hong Zhao, and Changhai Zhang. 2018. "Study on Nonlinear Conductivity of CCTO/EPDM Rubber Composites" Materials 11, no. 9: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091590
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhao, H., & Zhang, C. (2018). Study on Nonlinear Conductivity of CCTO/EPDM Rubber Composites. Materials, 11(9), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091590




