Highly Efficient Lithium Recovery from Pre-Synthesized Chlorine-Ion-Intercalated LiAl-Layered Double Hydroxides via a Mild Solution Chemistry Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
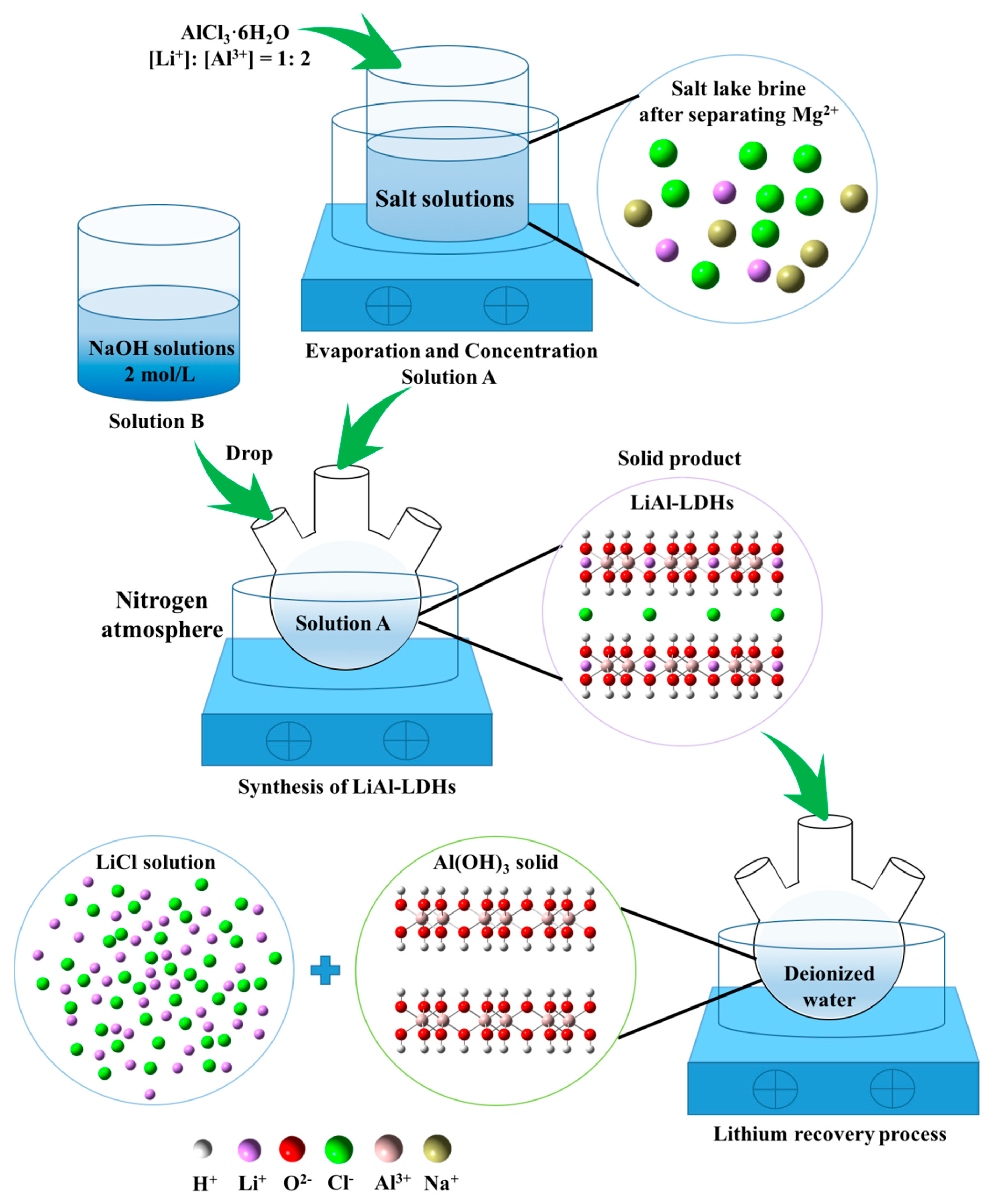
2.2. Synthesis
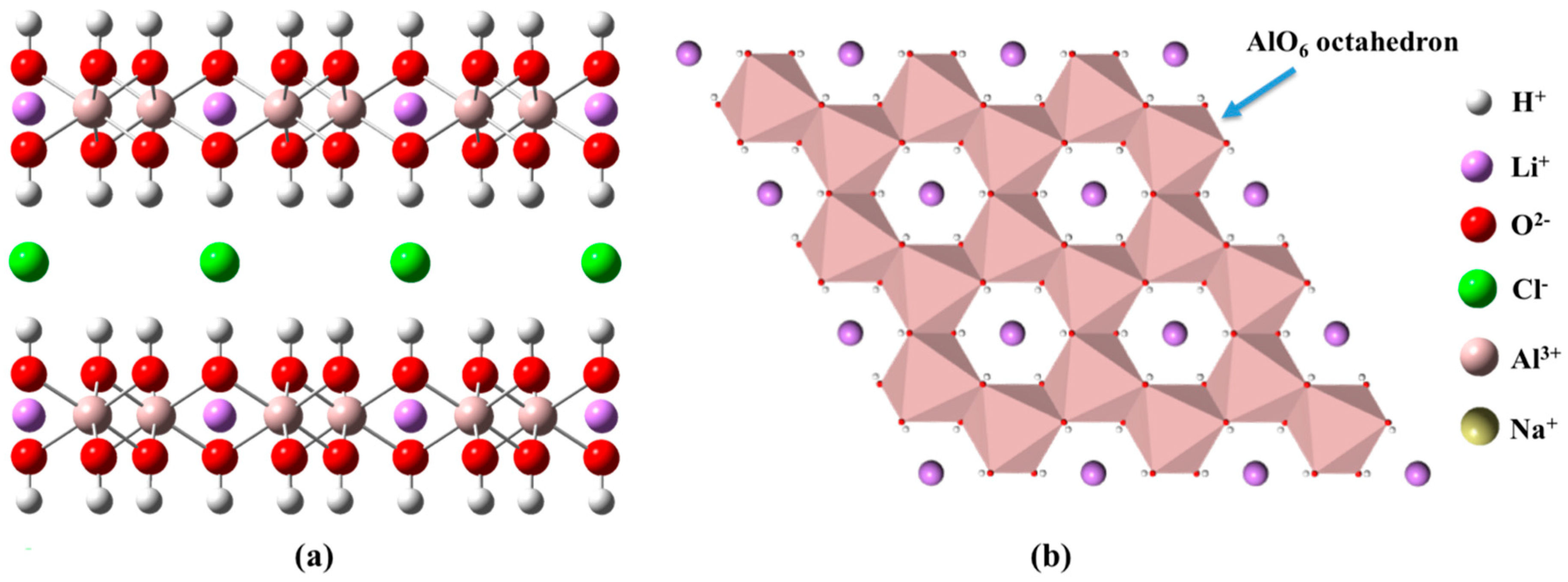
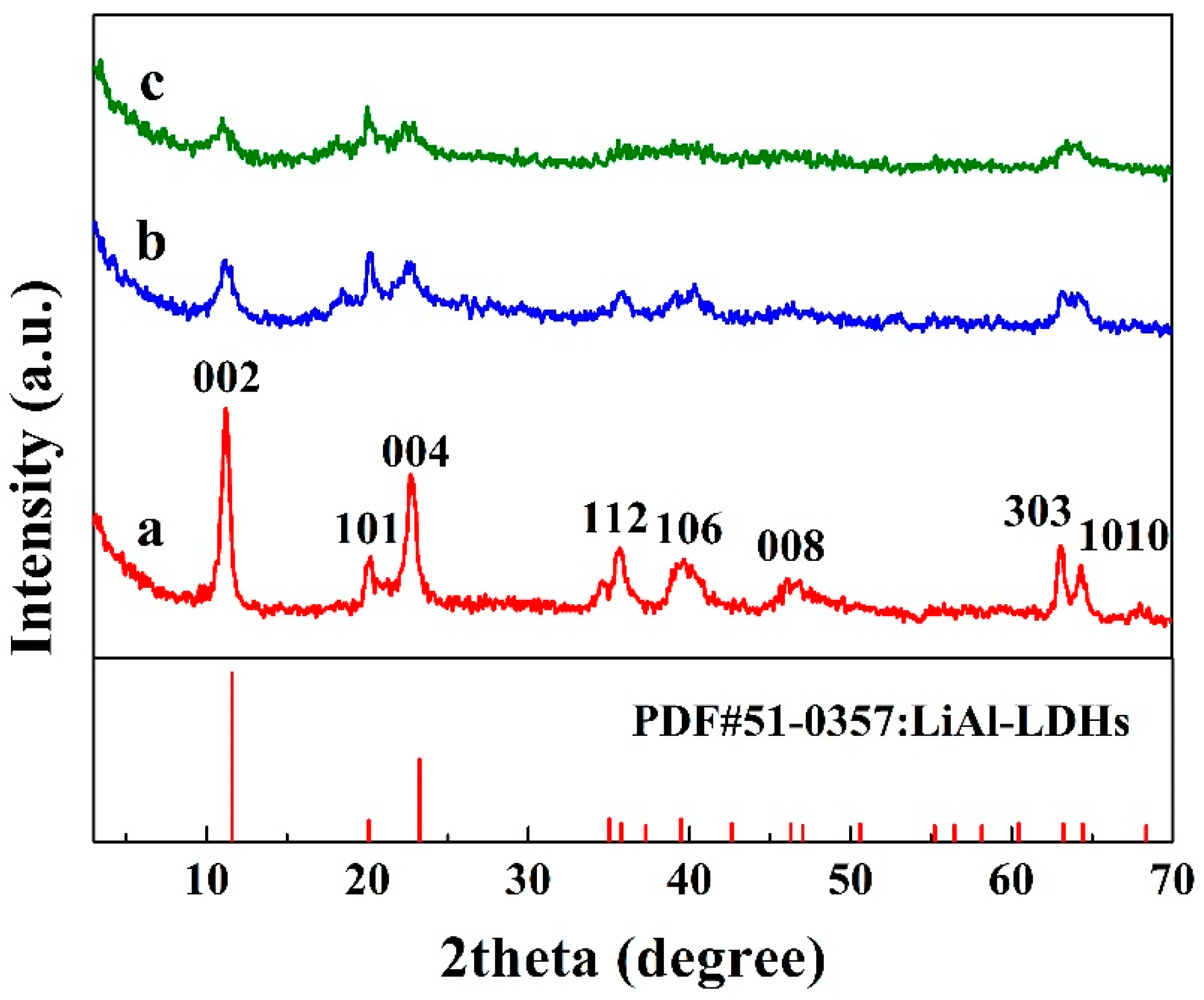
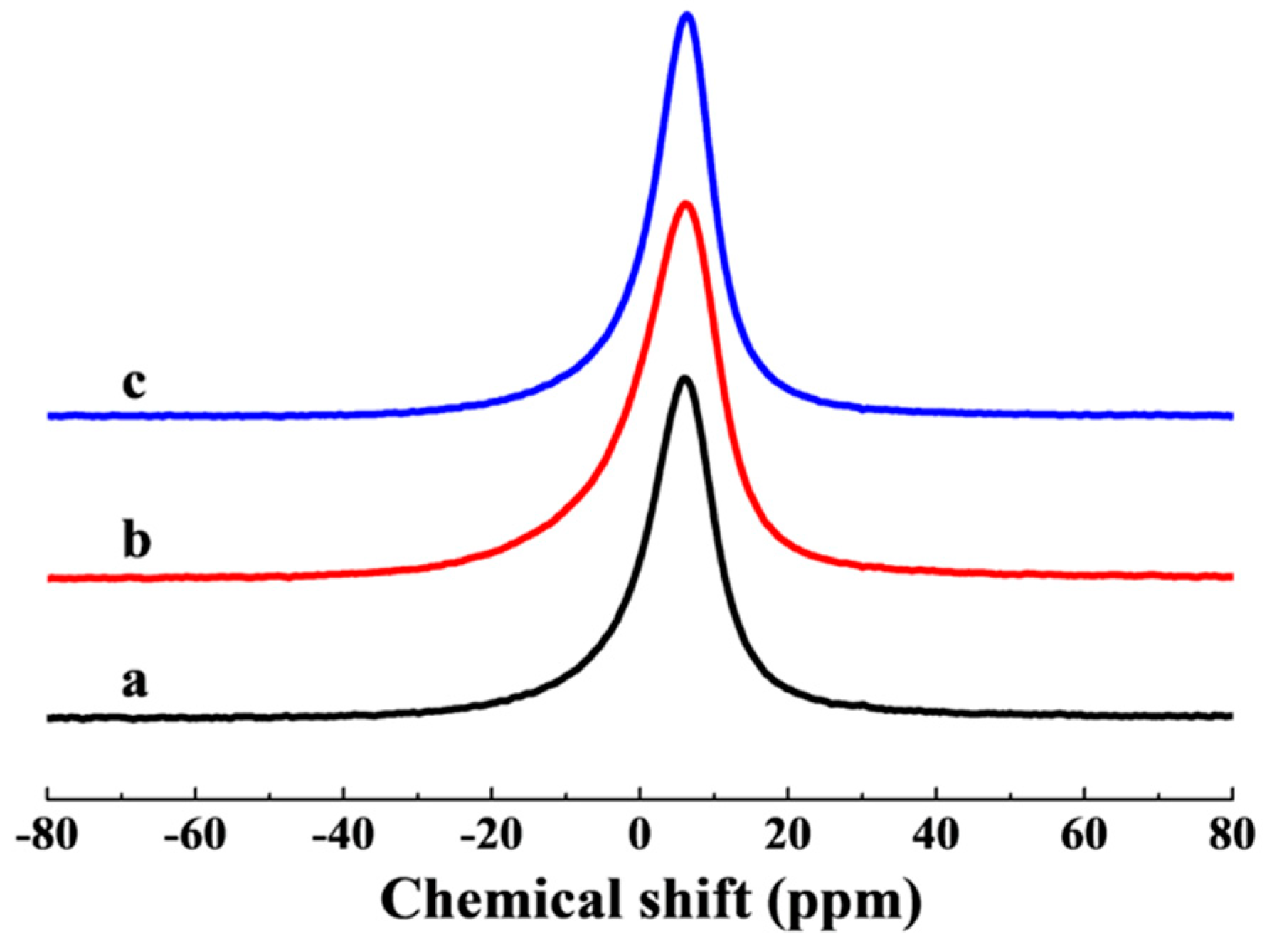
2.2.1. Crystallinity of LiAl-LDHs
2.2.2. Slurry Concentration of LiAl-LDHs-1
2.2.3. Lithium Recovery Temperature
2.2.4. Lithium Recovery Time
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
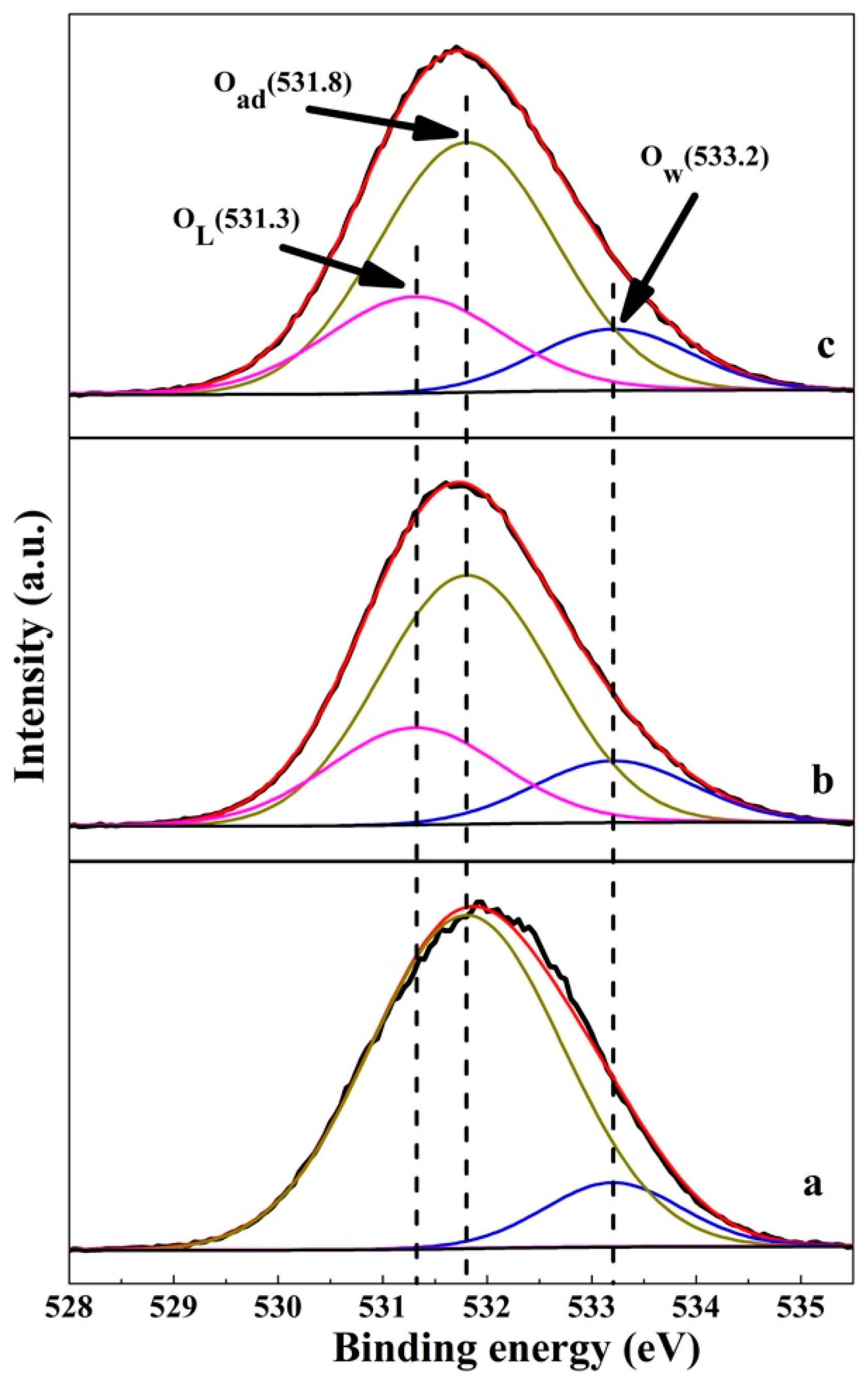
3.1. Crystallinity of LiAl-LDHs
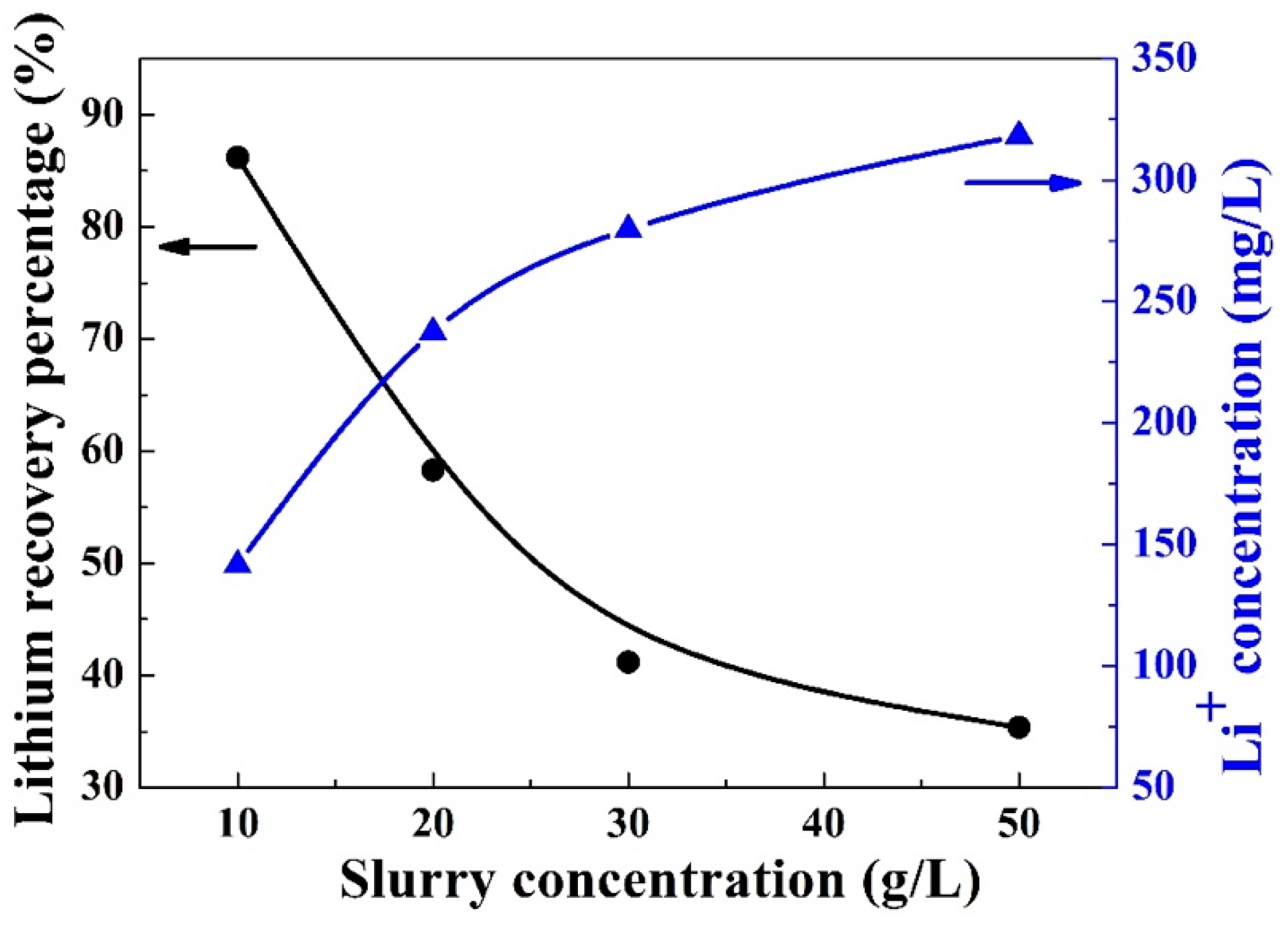
3.2. Slurry Concentration of LiAl-LDHs-1
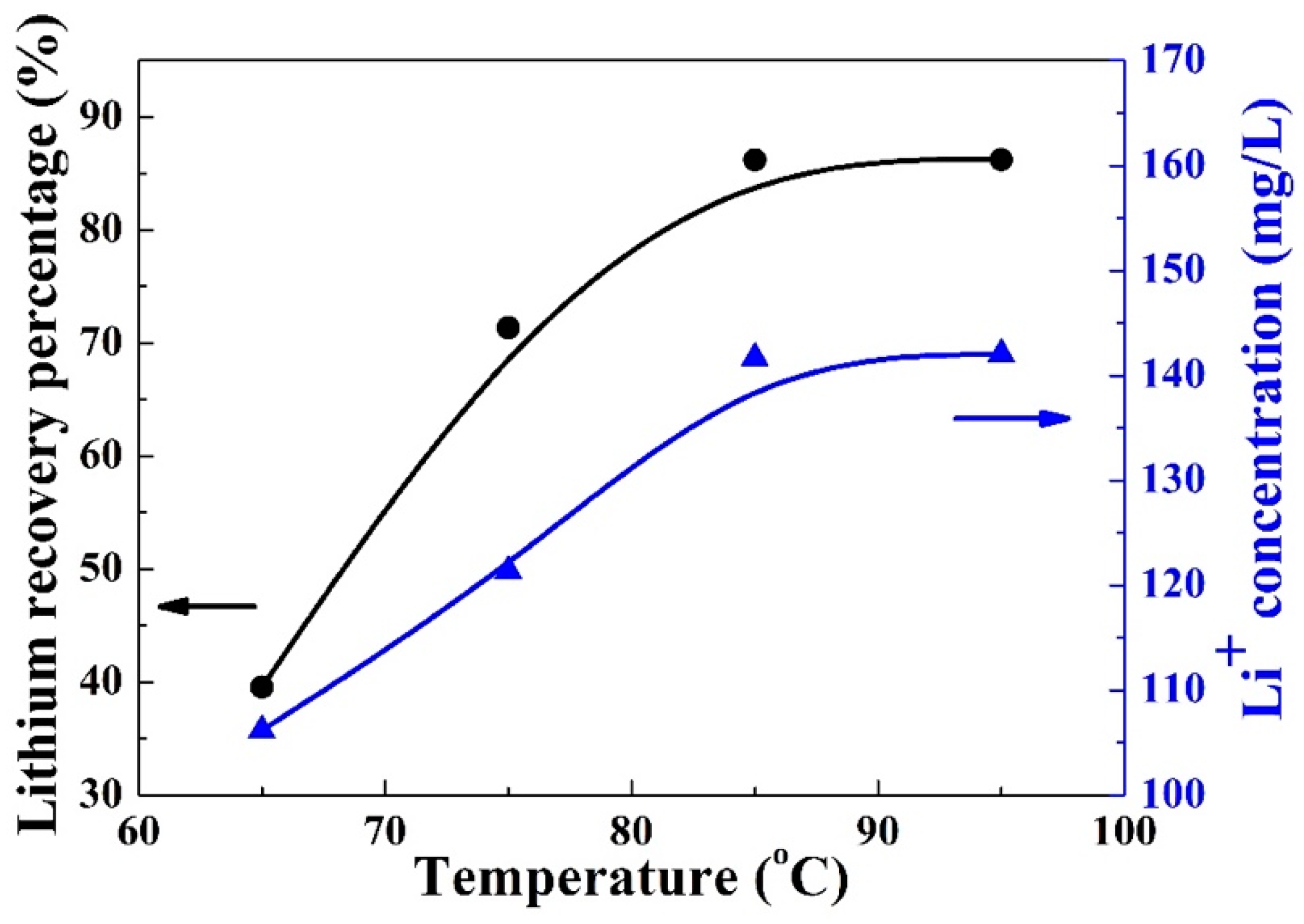
3.3. Lithium Recovery Temperature
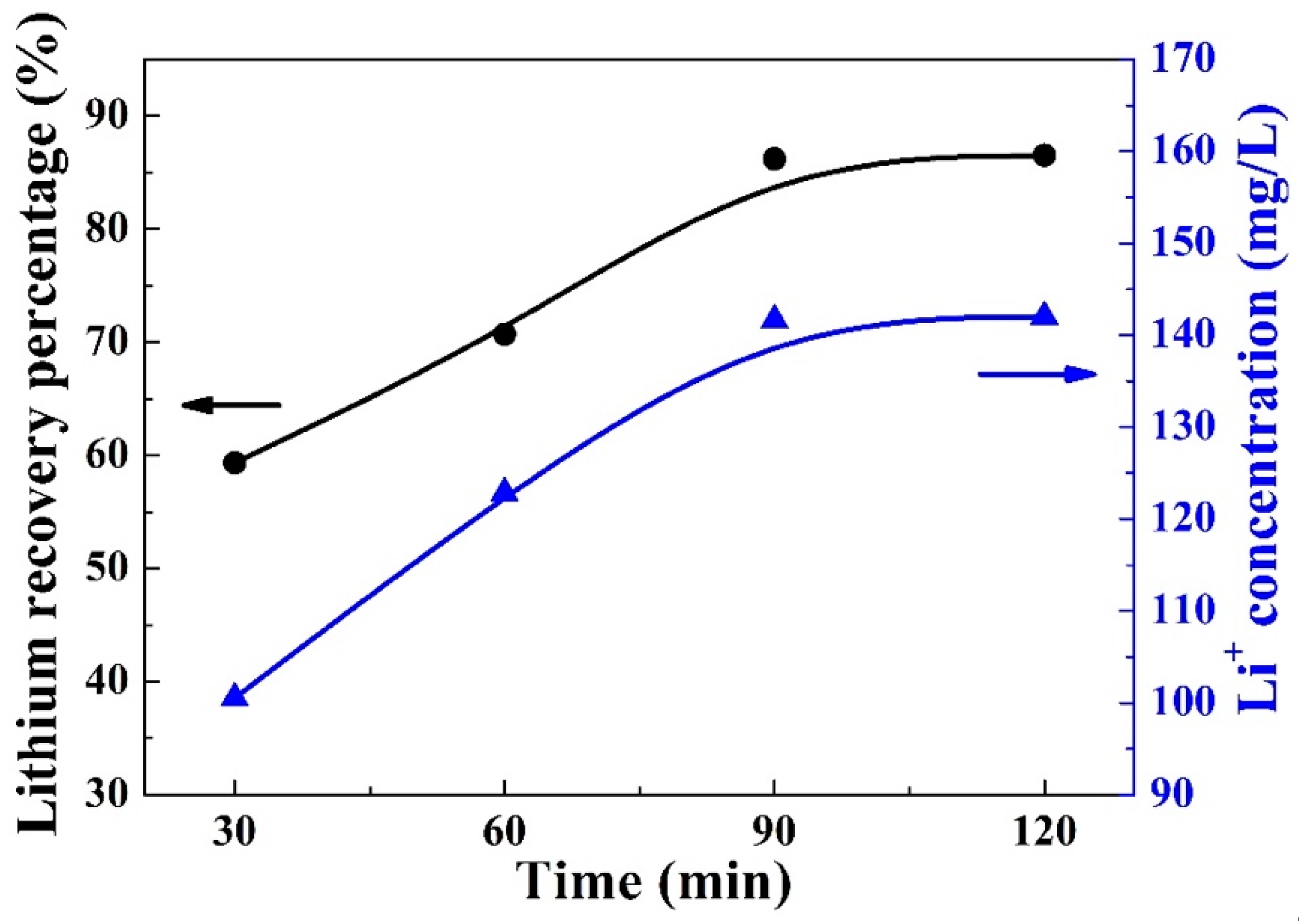
3.4. Lithium Recovery Time
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramakumar, S.; Deviannapoorani, C.; Dhivya, L.; Shankar, L.S.; Murugan, R. Lithium garnets: Synthesis, structure, Li+ conductivity, Li+ dynamics and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 325–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithium Outlook to 2028, 16th ed.; Roskill: Wimbledon, London, UK; Available online: https://roskill.com/market-report/lithium/ (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- BU-308: Availability of Lithium. Available online: https://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/availability_of_lithium (accessed on 2 May 2019).
- High Adoption of Electric Vehicles in China Attracts OEMs Looking to Expand Their Global Footprint. Available online: https://ww2.frost.com/news/high-adoption-of-electric-vehicles-in-china-attracts-oems-looking-to-expand-their-global-footprint/ (accessed on 14 May 2019).
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2019; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 98–99.
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Du, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. Recovery of both magnesium and lithium from high Mg/Li ratio brines using a novel process. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Gao, C.L.; Cheng, A.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, X.H. Geomorphic, hydroclimatic and hydrothermal controls on the formation of lithium brine deposits in the Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 50, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.F.; Nghiem, L.D.; Li, X.M.; He, T. Lithium extraction from chinese salt-lake brines: Opportunities, challenges, and future outlook. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S.; Yin, H.B.; Ji, Z.Y.; Deng, H.N. Effective recycling performance of Li+ extraction from spinel-type LiMn2O4 with persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9889–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Haldorai, Y.; Rengaraj, A.; Shin, J.; Hong, H.J.; Lee, G.W.; Han, Y.K.; Huh, Y.S.; Chung, K.S. Recovery of lithium ions from seawater using a continuous flow adsorption column packed with granulated chitosan-lithium manganese oxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7218–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Kurokawa, S.; Shiiba, H.; Wagata, H.; Yubuta, K.; Oishi, S.; Nishikiori, H.; Teshima, K. Exceptional flux growth and chemical transformation of metastable orthorhombic LiMnO2 cuboids into hierarchically-structured porous H1.6Mn1.6O4 rods as Li ion sieves. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6178–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Li, S.P.; Sun, S.Y.; Yin, X.S.; Yu, J.G. Lithium selective adsorption on low-dimensional titania nanoribbons. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.; Makita, Y.; Ooi, K.; Sonoda, A. Lithium recovery from salt lake brine by H2TiO3. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 8933–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Jing, Y.; Jia, Y. Solvent extraction of lithium ions by tri-n-butyl phosphate using a room temperature ionic liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liang, S.; Qin, W.; Fei, W. Extraction equilibria of lithium with tributyl phosphate, diisobutyl ketone, acetophenone, methyl isobutyl ketone, and 2-heptanone in kerosene and FeCl3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7912–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.Y.; Chen, Q.B.; Yuan, J.S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Feng, W.X. Preliminary study on recovering lithium from high Mg2+/Li+ ratio brines by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Feng, H.; Xu, T. Production of lithium hydroxide from lake brines through electro-electrodialysis with bipolar membranes (EEDBM). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6103–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Kang, J.Y.; Yan, N.; Suh, Y.W.; Jung, J.C. Simple preparation method for Mg-Al hydrotalcites as base catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 423, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conterosito, E.; Gianotti, V.; Palin, L.; Boccaleri, E.; Viterbo, D.; Milanesio, M. Facile preparation methods of hydrotalcite layered materials and their structural characterization by combined techniques. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 470, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Hu, S.F.; Wang, C.X.; Duan, H.H.; Xiang, X. Highly efficient separation of magnesium and lithium and high-valued utilization of magnesium from salt lake brine by a reaction-coupled separation technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6618–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, A.M.; Freij, A.J.; Parkinson, G.M. Synthesis and anion exchange chemistry of rhombohedral Li/Al layered double hydroxides. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Chen, T.Y.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M.; Chiang, P.N.; Lee, J.F. Mechanistic study of arsenate adsorption on lithium/aluminum layered double hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Lin, C.H.; Yan, Y.Y.; Wang, M.K. Synthesis of Li/Al LDH using aluminum and LiOH. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 72, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Hu, S.F.; Xiang, X. Highly efficient extraction of lithium from salt lake brine by LiAl-layered double hydroxides as lithium-ion-selective capturing material. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 34, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Lu, Y.L.; Wei, M.; Yang, L.; Li, C.J. Competitive intercalation of geometric isomers of hydroxybenzoic acid into [LiAl2(OH)6]Cl·yH2O layered double hydroxides. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 23, 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Besserguenev, A.V.; Fogg, A.M.F.; Price, S.J.; O’Hare, D. Synthesis and structure of the gibbsite intercalation compounds [LiAl2(OH)6]X·{X=Cl, Br, NO3} and [LiAl2(OH)6]Cl·H2O using synchrotron X-ray and neutron powder diffraction. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Gao, Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Mann, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L. Solvothermal synthesis of Li-Al layered double hydroxides and their electrochemical performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Iyi, N.; Sasaki, T. Factors affecting the crystal size of the MgAl-LDH (layered double hydroxide) prepared by using ammonia-releasing reagents. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 37, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, R.J. Spectroscopy Methods in Mineralogy and Geology; Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; Volume 18, pp. 341–403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, S.; Xue, B. A facile approach to superhydrophobic LiAl-layered double hydroxide film on Al-Li alloy substrate. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, A.; Mekhalif, Z.; Detriche, S.; Fonder, G.; Boumaza, A.; Djelloul, A. Calcination products of gibbsite studied by X-ray diffraction, XPS and solid-state NMR. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 215, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbrook, S.E.; Mcmanus, J.; Mackenzie, K.J.D.; Wimperis, S. Multiple-quantum and cross-polarized 27Al MAS NMR of mechanically treated mixtures of kaolinite and gibbsite. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 6408–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Duong, L.V.; Wood, B.J.; Frost, R.L. XPS study of the major minerals in bauxite: Gibbsite, bayerite and (pseudo-)boehmite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawrah, M.F.; El Defrawy, S.A.; Ali, O.A.M.; Sadek, H.E.H.; Ghanaym, E.E. Recycling of LCW produced form water plants for synthesizing of nano FeO(OH), Al(OH)3, and layered double hydroxide: Effect of heat-treatment. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9950–9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Y. Nanostructural characterization of Al(OH)3 formed during the hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 101, 4262–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Jadambaa, S.T.; Okada, K.; Mackenzie, K.J.D. Preparation of aluminosilicate precursor by mechanochemical method from gibbsite-fumed silica mixtures. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1998, 21, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.R.; Bastow, T.J.; Celotto, S.; Hill, A.J. Integrated study of the calcination cycle from gibbsite to corundum. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2877–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyalikh, A.; Zesewitz, K.; Scheler, U. Hydrogen bonds and local symmetry in the crystal structure of gibbsite. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mg2+ | Li+ | K+ | Na+ | B2O3 | Cl- | SO42- | CO32- | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (g/L) | 0.054 | 0.675 | 0.84 | 32.9 | 1.73 | 42.87 | 3.29 | 8.57 |
| LiAl-LDHs-1 | LiAl-LDHs-2 | LiAl-LDHs-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li (wt%) | 2.75 | 2.74 | 2.72 |
| Al (wt%) | 21.37 | 21.53 | 22.63 |
| Cl (wt%) | 14.05 | 14.02 | 13.89 |
| C (wt%) | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.47 |
| Li/Al molar ratio | 1:2.00 | 1:2.02 | 1:2.14 |
| Cl/C molar ratio | 9.91 | 9.89 | 9.80 |
| Li/Cl molar ratio | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Sample | Lithium Recovery Percentage (%) | Li+ Concentration in Filtrate (mg/L) | Al3+ Dissolution Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiAl-LDHs-1 | 86.2 | 141.6 | - |
| LiAl-LDHs-2 | 66.6 | 127.4 | - |
| LiAl-LDHs-3 | 56.2 | 107.4 | 0.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Yun, R.; Zang, Y.; Pu, M.; Xiang, X. Highly Efficient Lithium Recovery from Pre-Synthesized Chlorine-Ion-Intercalated LiAl-Layered Double Hydroxides via a Mild Solution Chemistry Process. Materials 2019, 12, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121968
Sun Y, Yun R, Zang Y, Pu M, Xiang X. Highly Efficient Lithium Recovery from Pre-Synthesized Chlorine-Ion-Intercalated LiAl-Layered Double Hydroxides via a Mild Solution Chemistry Process. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121968
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ying, Rongping Yun, Yufeng Zang, Min Pu, and Xu Xiang. 2019. "Highly Efficient Lithium Recovery from Pre-Synthesized Chlorine-Ion-Intercalated LiAl-Layered Double Hydroxides via a Mild Solution Chemistry Process" Materials 12, no. 12: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121968
APA StyleSun, Y., Yun, R., Zang, Y., Pu, M., & Xiang, X. (2019). Highly Efficient Lithium Recovery from Pre-Synthesized Chlorine-Ion-Intercalated LiAl-Layered Double Hydroxides via a Mild Solution Chemistry Process. Materials, 12(12), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121968







