Investigation of the Condition of the Gold Electrodes Surface in a Plasma Reactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- preparation of research material;
- (2)
- metallographic research of the electrode material in the scope of microstructure and geometry, construction and phase composition of the raids layers on their surface;
- (3)
- identification of interstitial phases in the raids layers using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy;
- (4)
- microanalysis of the chemical composition of the raids layers using the EDX (Energy Dispersive X-Ray) attachment in the scanning electron microscope.
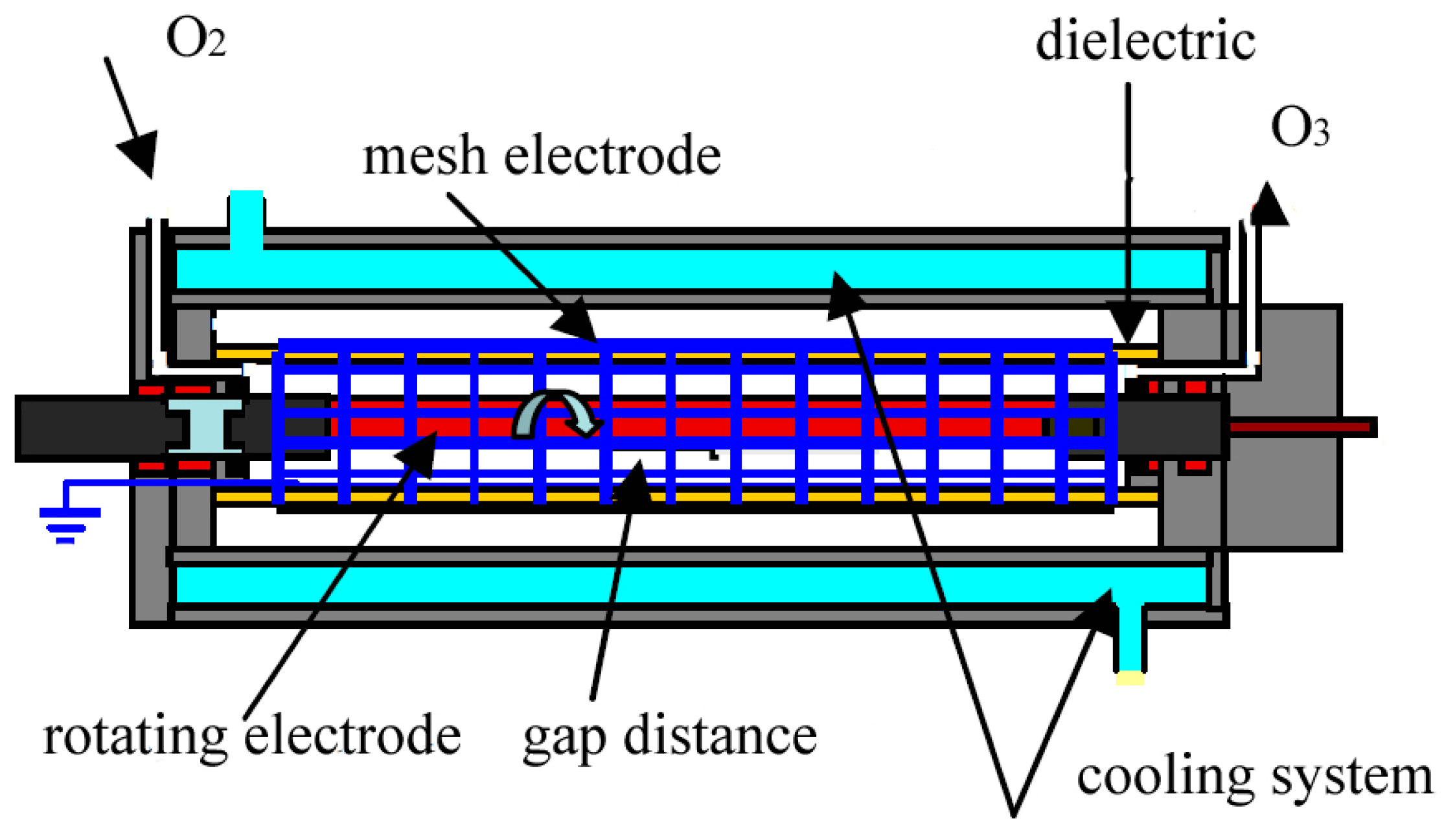
2. Materials and Methods
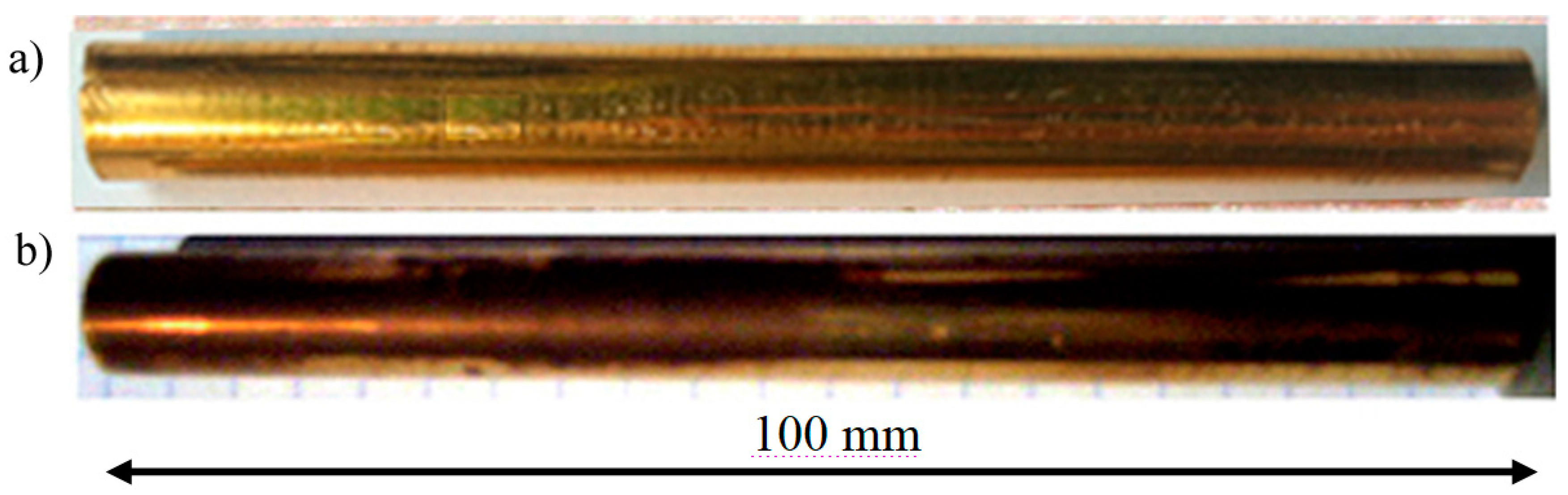
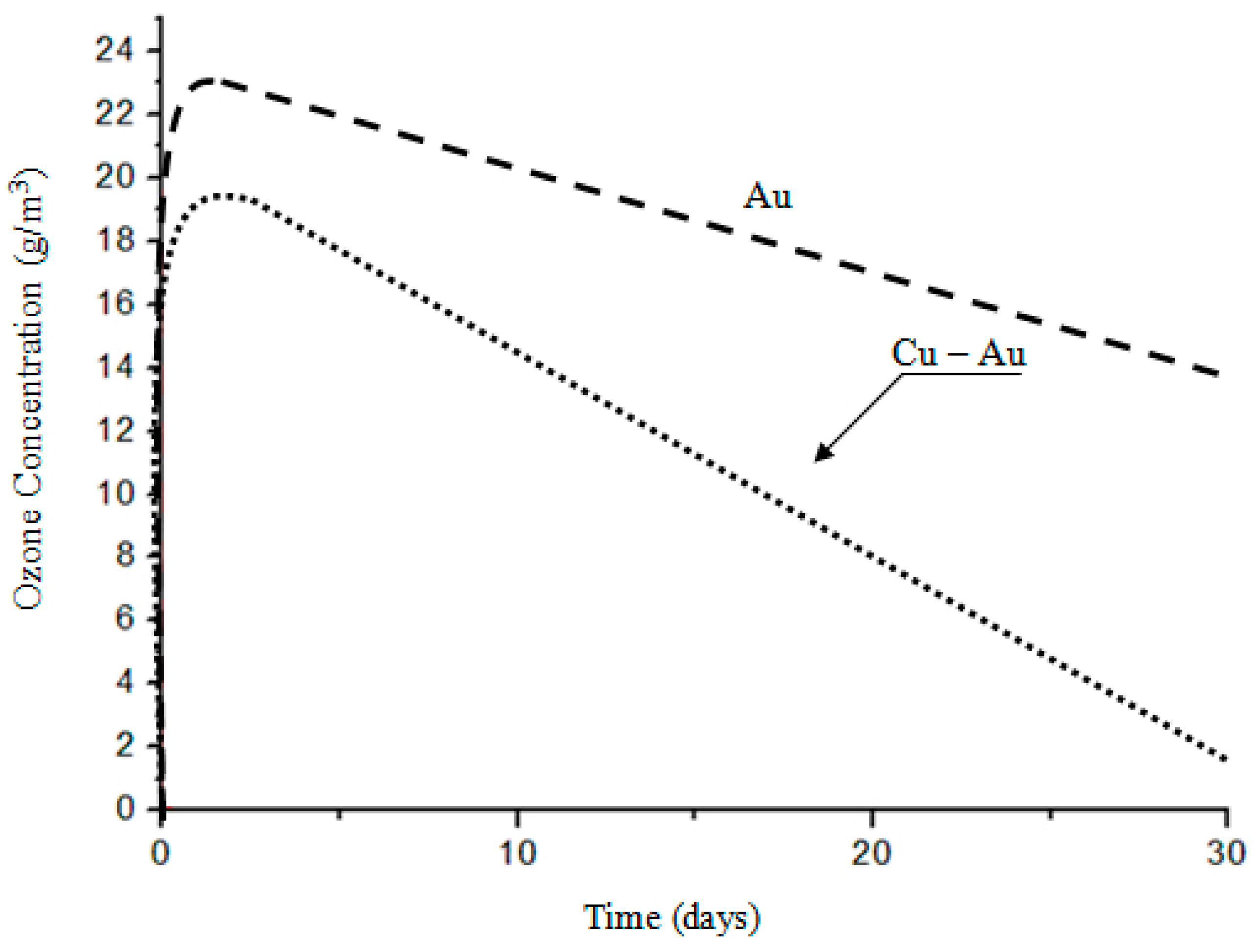
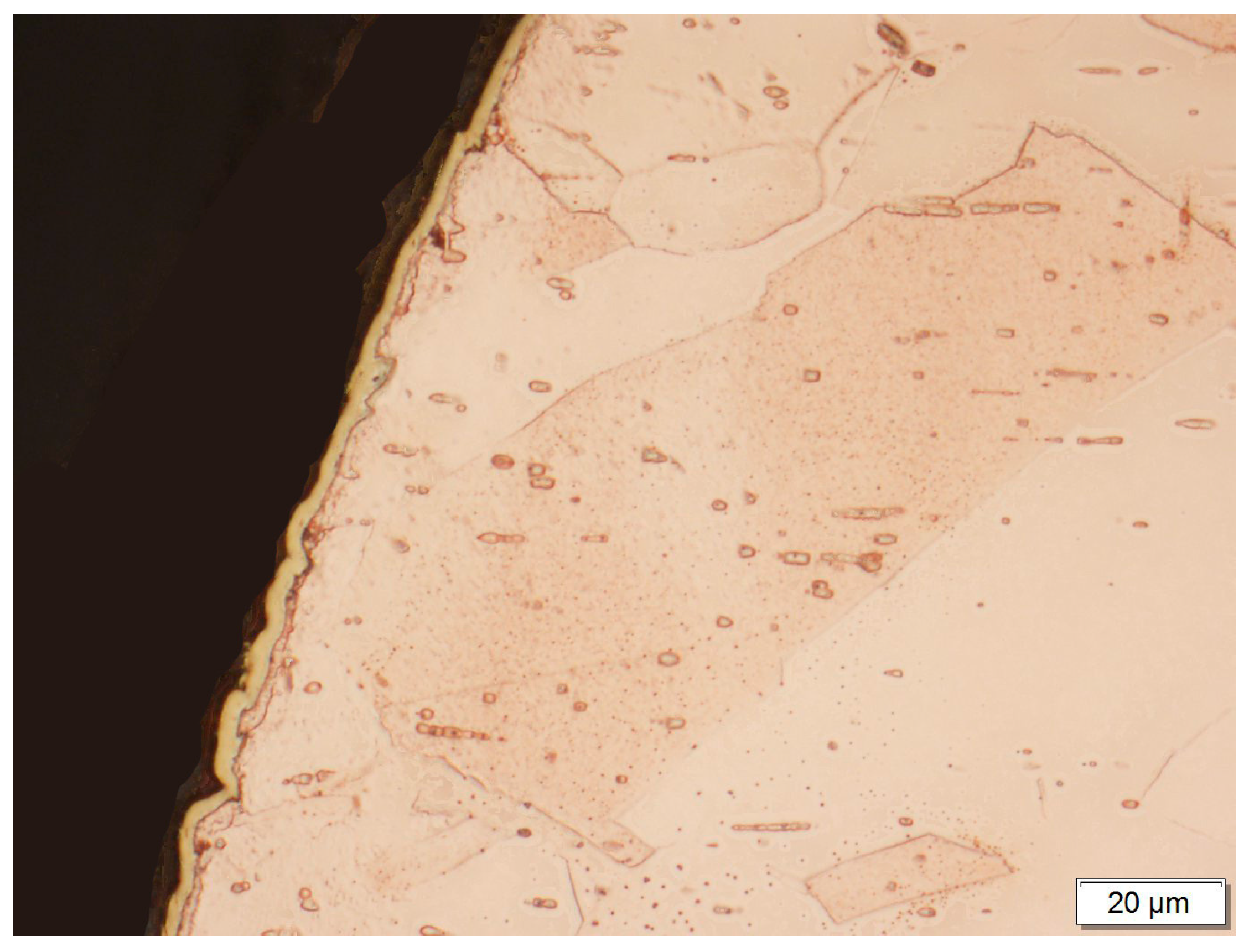
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhainaut, M.; Odicb, E.; Goldman, M.; Goldman, A.; Karimi, C. Dependence of the oxidation properties of a dielectric barrier discharge in air on the plasma and gas temperatures. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on High Pressure Low Temperature Plasma Chemistry, Tartu, Estonia, 21–25 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dimoff, K.; Antoine, P.; Vijh, A.K. Effects of enhanced heating by surface oxides on arc cathodes. IEE Proc. 1985, 132, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, S.; Gnapowski, E. Effects of Rotating Electrode during Plasma Generation; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, S.; Gnapowski, E.; Śniadkowski, M. Demand effect of nitrogen using reactor with a rotating type electrode. Ciência Técnica Vitivinícola J. 2015, 30, 36–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, S.; Gnapowski, E.; Śniadkowski, M.; Ciekanowski, Z. Using of pulsed plasma discharges and shock wave generator to identify the amber. Ciência Técnica Vitivinícola J. 2015, 30, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, S.; Yamabe, C.; Ihara, S. Ozone Generation Characteristics of Ozonizer with the Rotating Type Electrode. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2008, 128, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, S.; Yamabe, C.; Ihara, S.; Ozonek, J.; Lenik, K. Improving the Ozone Generation Using Ozonizer with the Rotating Type Electrode. Electr. Rev. 2009, 85, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Praca zbiorowa, Poradnik Galwanotechnika; WNT: Warszawa, Poland, 1985.
- Feynman, R.P. The Reason for Antiparticles Elementary Particles and the Laws of Physics; The 1986 Dirac Memorial Lectures; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Moylana, P.; Lombardib, J.; Moylanc, S. Einstein’s 1905 Paper on E=mc2. Am. J. Undergrad. Res. 2016, 13, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz, M. General Derivation of Mass-Energy Relation without Electrodynamics or Einstein’s Postulates. J. Mod. Phys. 2015, 6, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bahjat, R.; Muhyedeen, J. New Concept of Mass-Energy Equivalence. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 26, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bergsåker, H.; Ilyinsky, L.; Portnoff, G. Ion beam analysis of sputter-deposited gold films for quartz resonators. Surf. Interface Anal. 2000, 30, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, S.; Meunier, J.L. Theoretical prediction of non-thermionic arc cathode erosion rate including both vaporization and melting of the surface. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2000, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkson, B.J.; Steer, T.; Möbus, G.; Wagner, T. Subsurface nanoindentation deformation of Cu-Al multilayers mapped in 3D by focused ion beam microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 201, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.M.; Wells, R.K.; Badyal, J.P.S. Plasma Oxidation of Copper-Silver Alloy Surfaces. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 640–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, D.Y. Effects of dislocation on electron work function of metal surface. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2002, 18, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Su, Y.C. Review of surface tension data for metallic elements and alloys: Part 1—Pure metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 2006, 51, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitterauer, J.; Till, P. Computer simulation of the dynamics of plasma surface interactions in vacuum arc cathode spots. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1986, 15, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldera, F.A.; Mücklich, F. On the Erosion of Material Surfaces Caused by Electrical Plasma Discharging. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2005, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szente, R.N.; Drouet, M.G.; Munz, R.J. Current distribution of an electric arc at the surface of plasma torch electrodes. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.E.; Brandenburg, R.; Kozlov, K.V.; Sonnenfeld, A.; Michel, P.; Behnke, J.F. The barrier discharge. Basic properties and applications to surface treatment. Vacuum 2003, 71, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.F.; Hoflund, G.B. Surface Characterization Study of the Thermal Decomposition of Ag2O. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacki, Z. Biór Odczynników Metalograficznych; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, S.; Akiyama, H.; Hamid, S.; Hosseini, R.; Yamabe, C. Effect of Rotating Electrode. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Res. J. 2013, 7, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, S.; Lenik, K.; Akiyama, H. New possibility for the use of plasma discharges to identify amber and changes in amber structure. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2012, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabski, M.W. Istota Inżynierii Materiałowej; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej: Warszawa, Poland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, J.E.; Guerrero-Alvarez, J.L. Electro-Erosion of Metal Surfaces. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romankiewicz, F. Modyfikacja Miedzi i Jej Stopów; Wydawnictwo Komisja Nauki o Mate-riałach PAN: Zielona Góra, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Benilov, M.S.; Jacobsson, S.; Kaddani, A.; Zahrai, S. Vaporization of a solid surface in an ambient gas. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

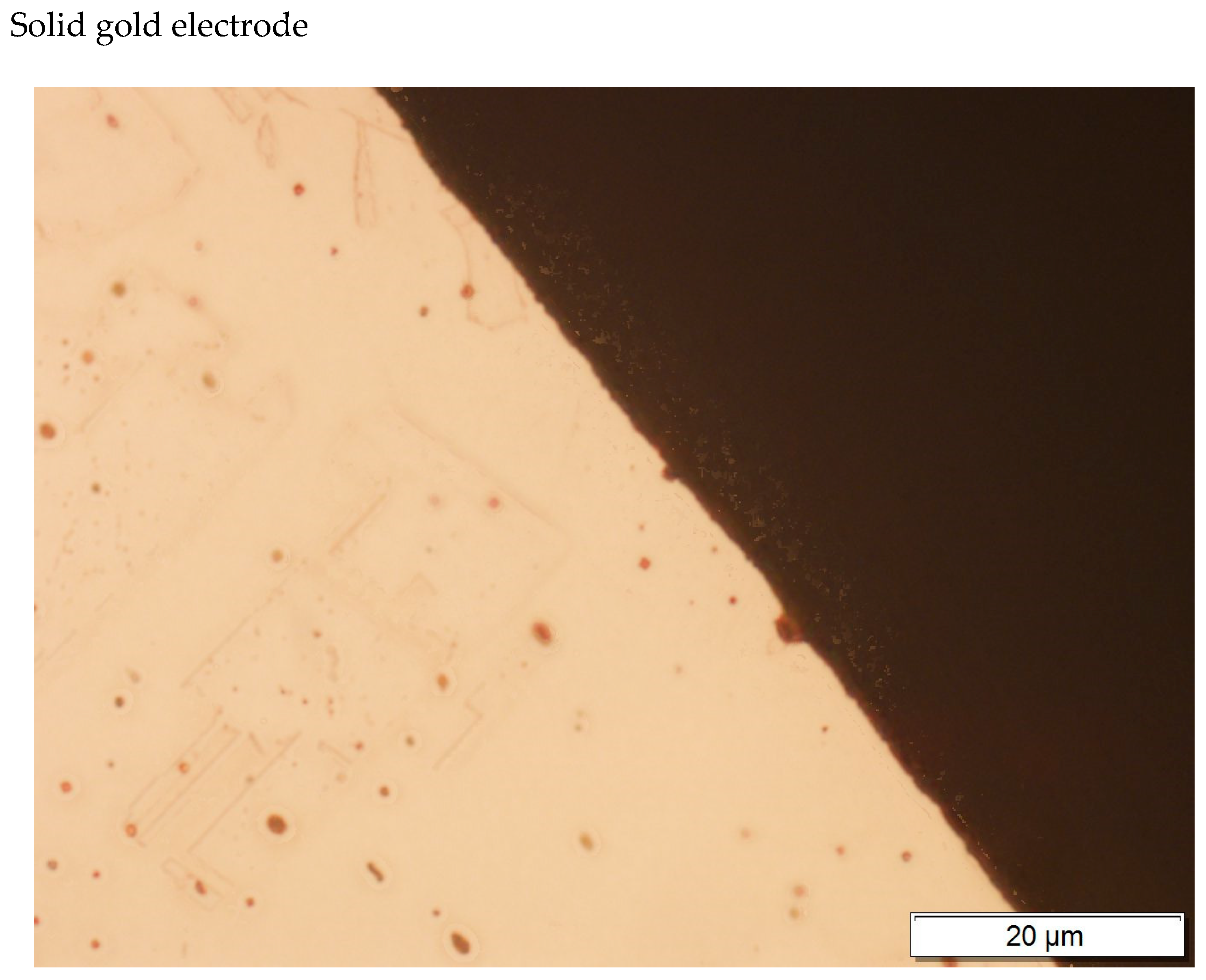

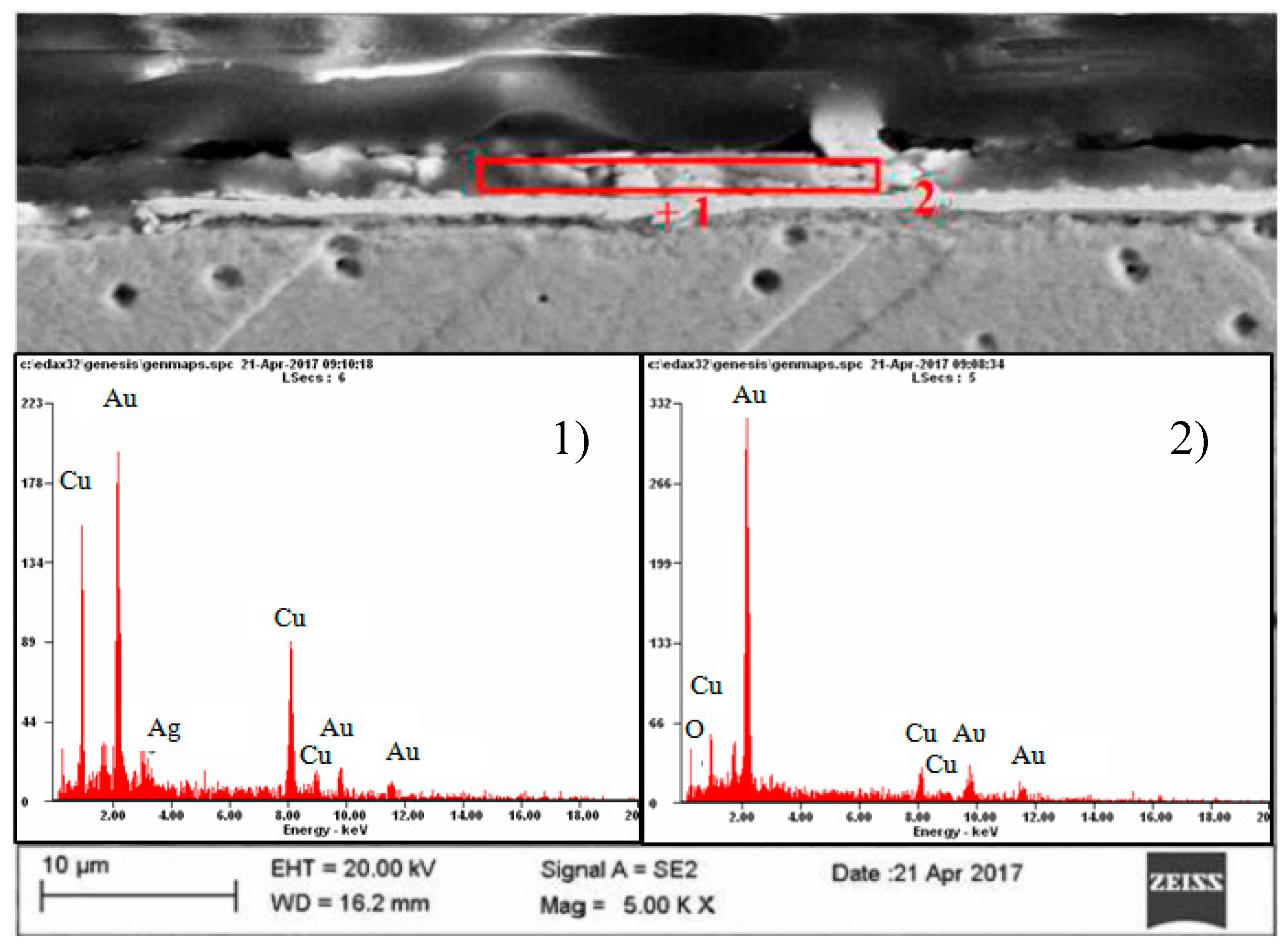

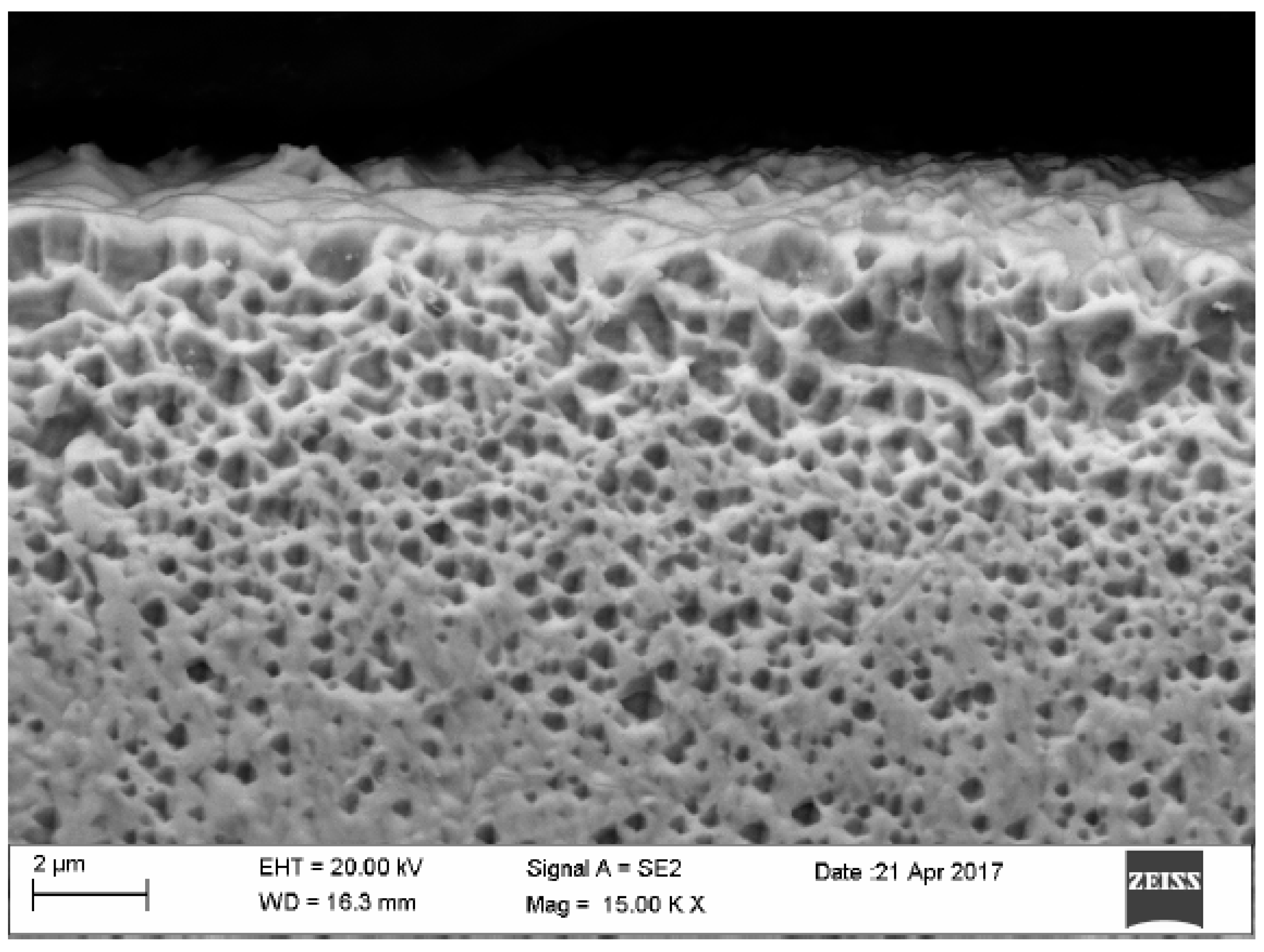
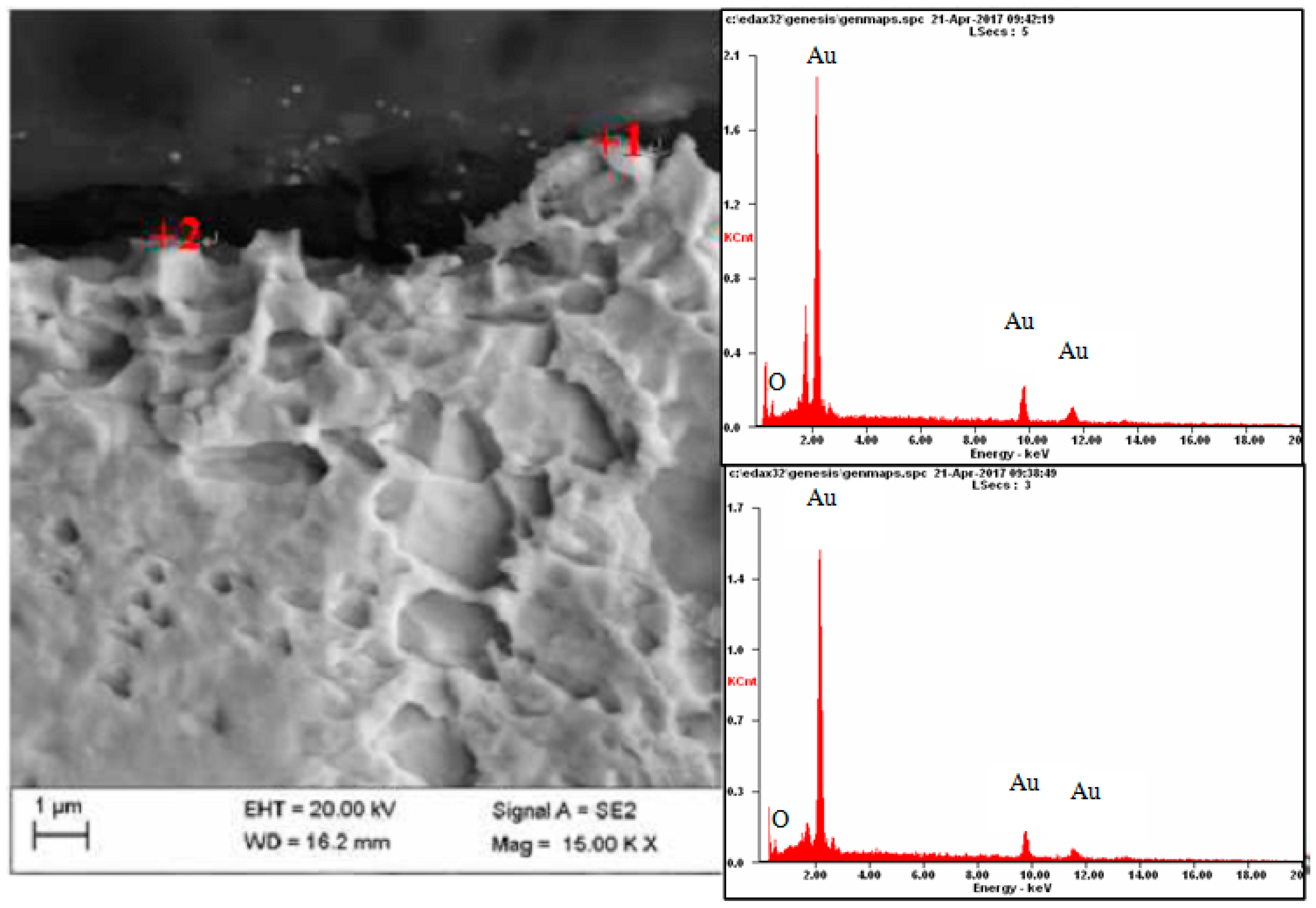
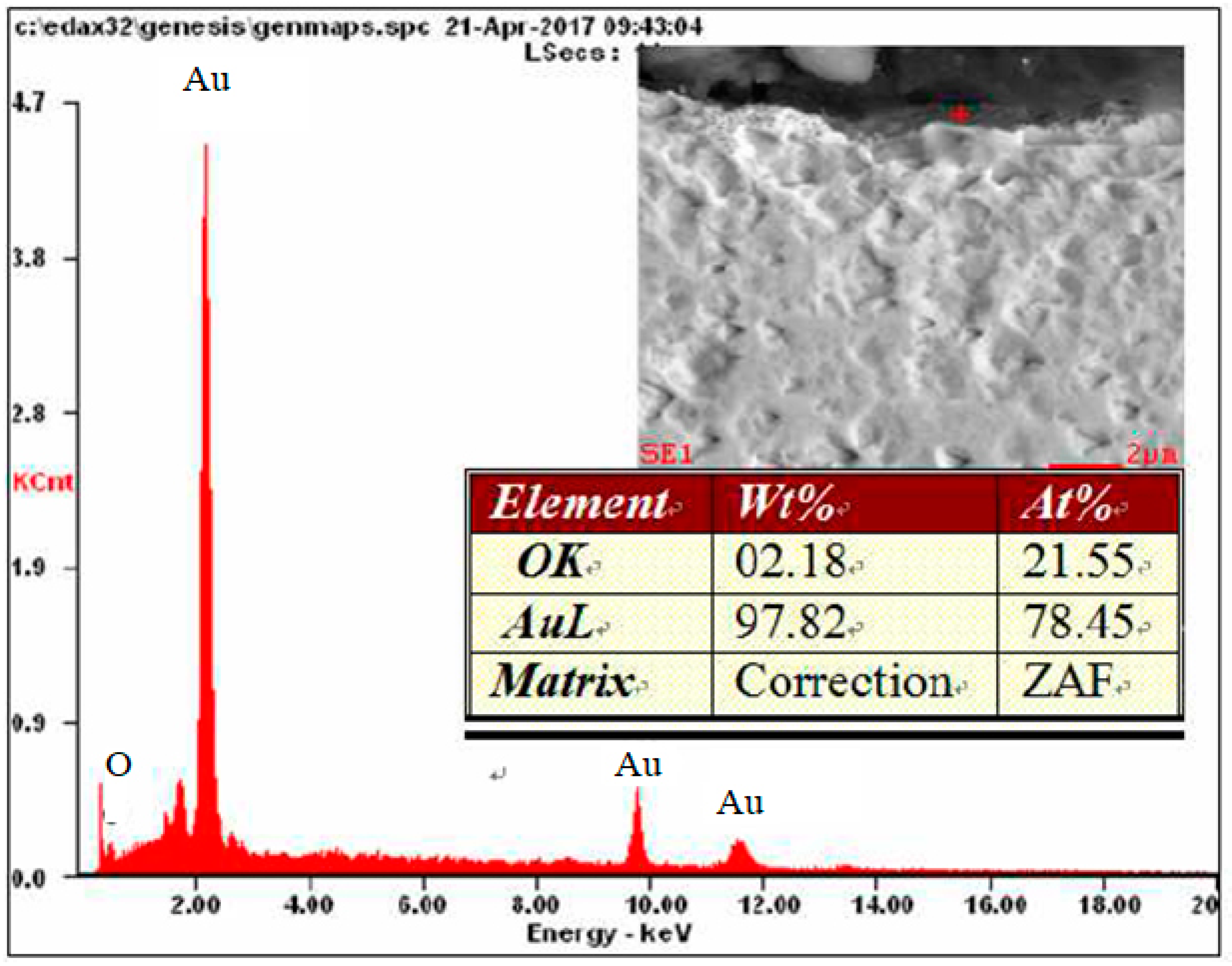

| Element | Place of Measurement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| % wag | % at | % wag | % at | |
| OK | 04.2 | 28.7 | --- | ---- |
| CuK | 14.9 | 25.9 | 38.1 | 63.3 |
| AuL | 80.9 | 45.4 | 54.2 | 29.0 |
| AgL | ---- | ----- | 07.7 | 07.5 |
| Element | Place of Measurement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| % wag | % at | % wag | % at | |
| OK | 05.1 | 40.0 | 02.3 | 22.4 |
| AuL | 94.9 | 60.0 | 97.7 | 77.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gnapowski, S.; Kalinowska-Ozgowicz, E.; Śniadkowski, M.; Pietraszek, A. Investigation of the Condition of the Gold Electrodes Surface in a Plasma Reactor. Materials 2019, 12, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132137
Gnapowski S, Kalinowska-Ozgowicz E, Śniadkowski M, Pietraszek A. Investigation of the Condition of the Gold Electrodes Surface in a Plasma Reactor. Materials. 2019; 12(13):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132137
Chicago/Turabian StyleGnapowski, Sebastian, Elżbieta Kalinowska-Ozgowicz, Mariusz Śniadkowski, and Aleksandra Pietraszek. 2019. "Investigation of the Condition of the Gold Electrodes Surface in a Plasma Reactor" Materials 12, no. 13: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132137
APA StyleGnapowski, S., Kalinowska-Ozgowicz, E., Śniadkowski, M., & Pietraszek, A. (2019). Investigation of the Condition of the Gold Electrodes Surface in a Plasma Reactor. Materials, 12(13), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132137





