A Study of Laser Micromachining of PM Processed Ti Compact for Dental Implants Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Experimental Material
2.2. Experimental Methods
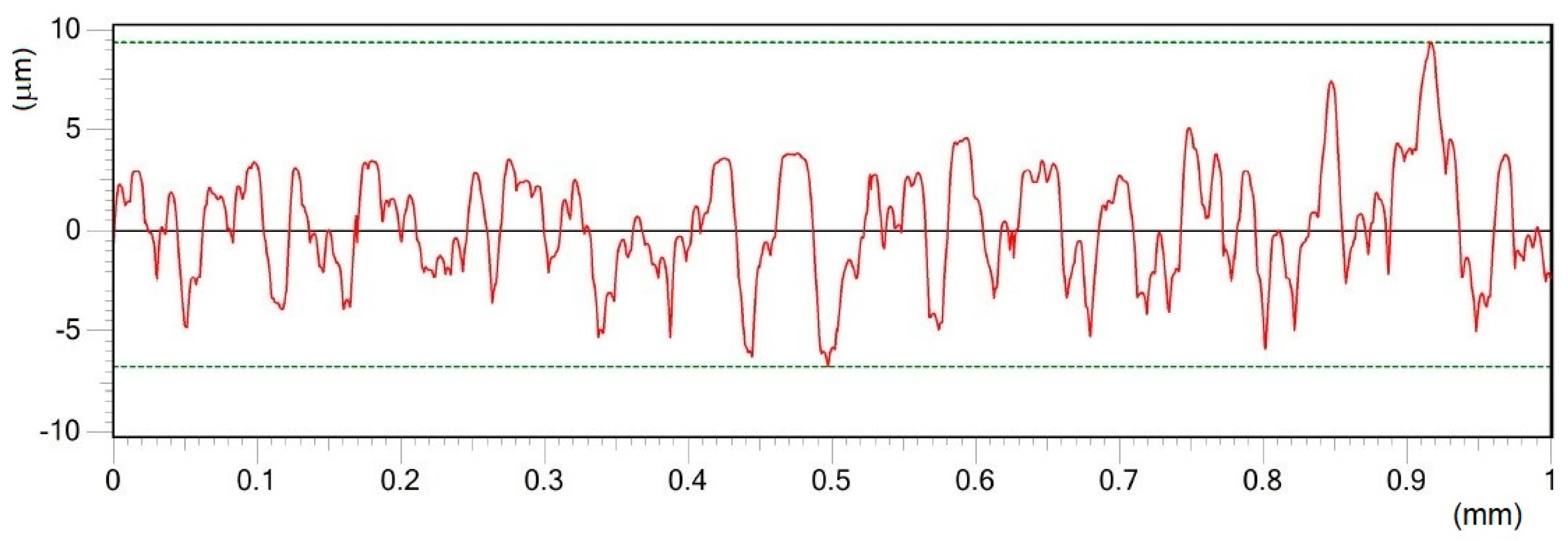
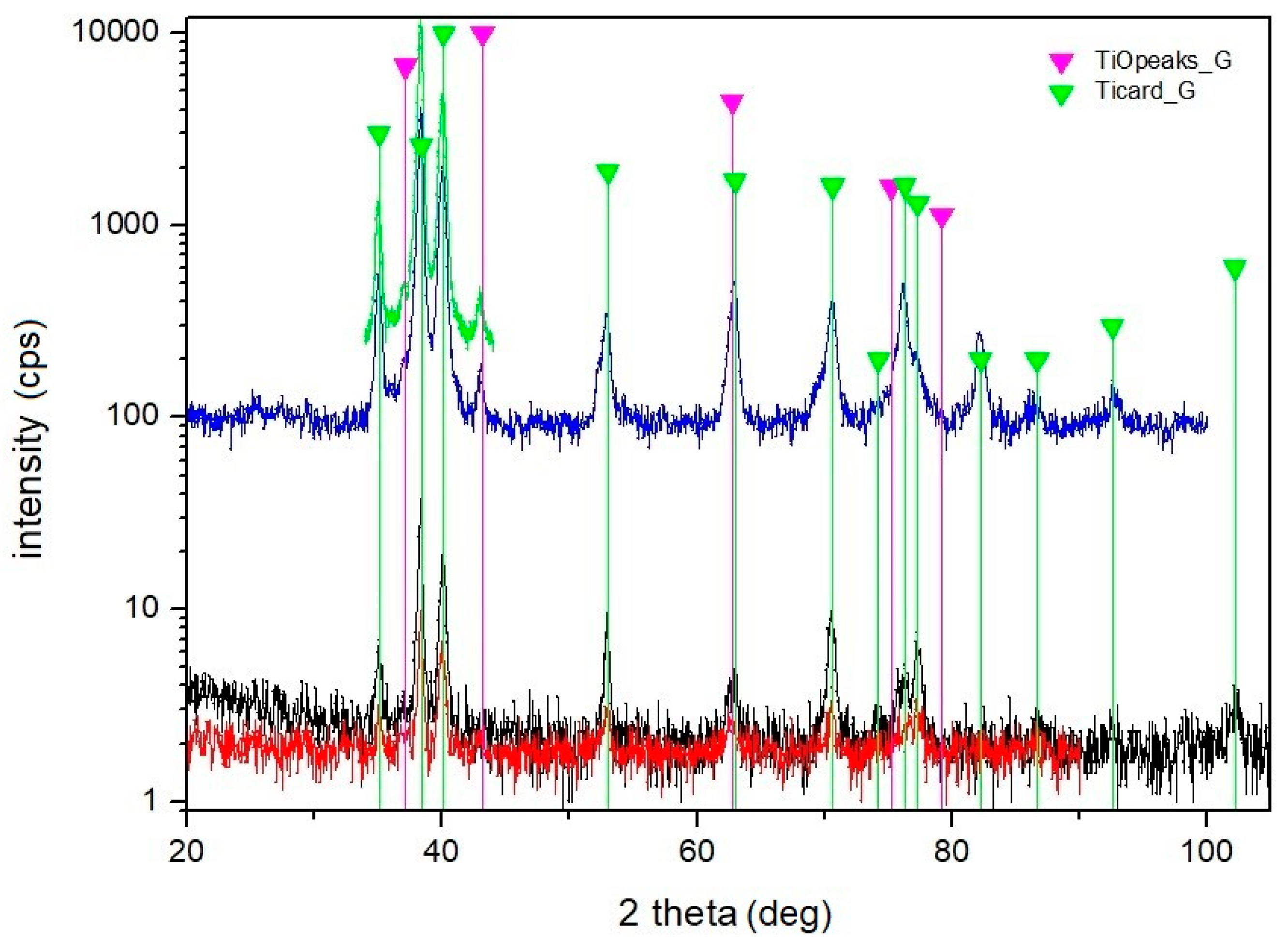
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
- (1)
- Different processing laser pulse energies were confirmed to have a great effect on the qualities of machined surfaces. It was observed that higher laser fluences lead to a rougher surface finish. The surfaces of porous-like appearances were revealed after laser treatment for every used pulse energy level.
- (2)
- The treated surface is formed of ridges of the molten and solidified titanium globules, craters and voids. It contains agglomerated particles with the irregular macro- and micro- pores of sizes of 10–25 μm and 1–3 μm, respectively.
- (3)
- The results of the one-way ANOVA analysis brought an overall statistically significant difference in the group means for all roughness evaluated parameters. The main differences between the surfaces A and E were confirmed by the Tukey post-hoc test.
- (4)
- Owing to the treatment in ambient air, the oxidation of titanium took place. With the increase of the laser beam pulse energy, the content of O increased significantly.
- (5)
- This study helps to identify the laser beam energy parameters for achieving a pre-defined surface geometry. The lower level of pulse energy is recommended for the optimal surface treatment of the studied PM titanium compact, when the large lateral pulse overlap is applied.
- (6)
- Recorded surface roughness parameters of laser treated Ti powder compact produced at low temperatures provide good conditions for applications in the field of dental surgery.
- (7)
- However, the contribution brings only partial insights into an otherwise wide problem, so for a wider application of the studied material, it is necessary to carry out a further series of experiments, especially focused on bio-testing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Najdahmadi, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Farghadani, F. Mechanical properties enhancement in Ti–29Nb–13Ta–4.6Zr alloy via heat treatment with no detrimental effect on its biocompatibility. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzejewska, Ž.A.; Hudák, R.; Sidun, J. Mechanical properties and microstructure of DMLS Ti6Al4V alloy dedicated to biomedical applications. Materials 2019, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, Y.; Yang, F.; Bolyoni, L. Mechanical properties and microstructure of Ti-Mn alloys produced via powder metallurgy for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 91, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Williams, J.C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 844–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuska, V.; Palan, J.; Kolaja, D.; Kulda, V.; Duchek, M.; Cerny, J.; Hrusak, D. Proliferation of Osteoblasts on Laser-Modified Nanostructured Titanium Surfaces. Materials 2018, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozcan, M.; Hammerle, C. Titanium as a reconstruction and implant material in dentistry: Advantages and. pitfalls. Materials 2012, 5, 1528–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, M.J.; Barão, R.A.V. Is there scientific evidence favoring the substitution of commercially pure titanium with titanium alloys for the manufacture of dental implants? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, F.; Liang, L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Scheideler, L.; Hüttig, F. Surface characteristics of dental implants: A review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurella, A.; Dahotre, N. Review paper: Surface Modification for Bioimplants: The Role of Laser Surface Engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2005, 20, 5–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, C.F.; Cheng, H.C.; Shen, Y.K. A modified surface on titanium alloy by micro-blasting process. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 797, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, D.V.; Zemtsova, E.G.; Solokhin, A.; Valiev, R.Z.; Smirnov, V.M. Modification of the surface topography and composition of ultrafine and coarse grained titanium by chemical etching. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappuis, V.; Buser, R.; Bragger, U.; Bornstein, M.M.; Salvi, G.E.; Buser, D. Long-term outcomes of dental implants with a titanium plasma-sprayed surface: A 20-year prospective case series study in partially edentulous patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.F.; Yang, T.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Peng, P.W. Nanoporous biocompatible layer on Ti–6Al–4V alloys enhanced osteoblast-like cell response. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2013, 5, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, D.M.; Dini, G.; Lanzetta, M.; Rossi, A. An experimental analysis of laser machining for dental implants. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.J.C.; Marques, R.F.; de A Filho, E.; Guastaldi, A.C. Surface modification of Ti dental implants by Nd: YVO4 laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 9203–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Krishna, V.B.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S. Processing and biocompatibility evaluation of laser processed porous titanium. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciganovic, J.; Stasic, J.; Gakovic, B.; Momcilovic, M.; Milovanovic, D.; Bokorov, M.; Trtica, M. Surface modification of the titanium implant using TEA CO2 laser pulses in controllable gas atmospheres—Comparative study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwahr, C.; Gunther, D.; Brinkmann, T.; Gulow, N.; Oswald, S.; Holthaus, M.G.; Lasagni, A.F. Laser surface pattering of titanium for improving the biological performance of dental implants. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1600858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtica, M.S.; Radak, B.B.; Gakovic, B.M.; Milovanovic, D.S.; Batani, D.; Desai, T. Surface modifications of Ti6A14V by a picosecond Nd: YAG laser. Laser Part. Beams 2009, 27, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bashir, S.; Akram, M.; Mahmood, K. Effect of dry and wet ambient environment on the pulsed laser ablation of titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, M.; Geethapriyan, T.; Senkathir, S.; Ashok, A.; Rajesh, A. Optimization of Machining Parameters on Laser Beam Machining of Titanium Alloy (Ti3Al-2.5V) Using Taguchi Method. In Advances in Manufacturing Processes; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Vijay Sekar, K., Gupta, M., Arockiarajan, A., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2019; pp. 481–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, A.; Bashir, S.; Rafique, M.S.; Akram, M.; Mahmood, K.; Iqbal, S.; Dawood, A. Spectroscopic and morphological study of laser ablated titanium. Opt. Spectrosc. 2016, 121, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionin, A.A.; Kudryashov, I.S.; Makarov, S.V.; Seleznev, L.V.; Sinitsyn, D.V.; Ligachev, A.E.; Golosov, E.V.; Kolobov, Y.R. Sub-100 nanometer transverse gratings written by femtosecond laser pulses on a titanium surface. Laser Phys. Lett. 2013, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochergin, S.A.; Morgunov, Y.A.; Saushkin, B.P. Surface manufacturing under pulse fiber laser. Procedia CIRP 2016, 42, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, O.; Shuja, Z.S.; Yilbas, S.B. Laser heating of titanium and steel: Phase change at the surface. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 54, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Son, B.I.; Choe, C.H. Formation of Surface Roughness on the Ti-35Nb-xZr Alloy Using Femtosecond Laser for Biocompatibility. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdogan, M.; Öktem, B.; Kalaycıoǧlu, H.; Yavaş, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K.; Eken, K.; Özgören, K.; Aykaç, Y.; Tazebay, U.H.; Ilday, F.Ö. Texturing of titanium (Ti6Al4V) medical implant surfaces with MHz-repetition-rate femtosecond and picosecond Yb-doped fiber lasers. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 10986–10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celen, S.; Özden, H. Laser-induced novel patterns: As smart strain actuators for new-age dental implant surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinonaga, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Tsukamoto, M.; Okada, A. Formation of periodic nanostructures with femtosecond laser for creation of new functional biomaterials. Procedia CIRP. 2016, 42, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, C.H.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.H. Bioactivities of a Ti surface ablated with a femtosecond laser through SBF. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Ausset, S.; Vilar, R. Surface micro/nanostructuring of titanium under stationary and non-stationary femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7556–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkov, A.A.; Barmina, V.E.; Shafeev, G.A.; Voronov, V.V. Laser ablation of titanium in liquid in external electric field. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 348, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfleging, W.; Kumari, R.; Besser, H.; Scharnweber, T.; Majumdar, J.D. Laser surface textured titaniu alloy (Ti6Al4V): Part 1–Surface characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 355, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, M.; Kiani, A. Effects of Laser Pulse Numbers on Surface Biocompatibility of Titanium for Implant Fabrication. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 6, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chikarakara, E.; Naher, S.; Brabayon, D. High speed laser surface modification of Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worts, N.; Jones, J.; Squier, J. Surface structure modification of additively manufactured titanium components via femtosecond laser micromachining. Opt. Commun. 2019, 430, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.T.; Chang, H.C.; Nanci, A.; Durand, R. Surface microtexturing of Ti6Al4V using an ultraviolet laser system. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.J.; Hong, S.J.; Lim, B.S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, T.I. Microgrooves on titanium surface affect peri-implant cell adhesion and soft tissue sealing; an in vitro and in vivo study. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2015, 45, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.; Francis, H.; Sam, F. Titanium Powder Metallurgy; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Balog, M.; Viskic, J.; Krížik, P.; Schauperl, Z.; Snajdar, M.; Stanec, Z.; Catic, A. CP TI fabricated by low temperature extrusion of HDH powder: Application in dentistry. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 704, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, J.; Emmer, Š.; Rodríguez, J.; Canadas, I. Sintering of HDH Ti powder in a solar furnace at Plataforma Solar de Almeria. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industrial Applications of Titanium and Zirconium; Kleefish, E.W. (Ed.) ASTM Internationa: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrukhov, O.; Huber, R.; Shi, B.; Berner, S.; Rausch-Fan, X.; Moritz, A.; Spencer, N.D.; Schedle, A. Proliferation, behavior, and differentiation of osteoblasts on surfaces of different microroughness. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwary, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of dental implant surface modification on osseointegration. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.A.; Johansson, M.L.; Omar, O.; Simonsson, H.; Palmquist, A.; Thomsen, P. Laser-Modified Surface Enhances Osseointegration and Biomechanical Anchorage of Commercially Pure Titanium Implants for Bone-Anchored Hearing Systems. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.F.; Liu, Q.; Brandt, M. Evaluation of fatigue crack propagation behaviour in Ti6Al4V manufactured by selective laser melting. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 104, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, P.K.; Ciuccio, R.; Neves, M.D.M. Development of Titanium Dental Implants Using Techniques of Powder Metallurgy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 775, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouziya, B.; Uthappa, M.A.; Amara, D. Surface modifications of titanium implants–The new, the old, and the never heard of options. J. Adv. Clin. Res. Insights 2016, 3, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Material | THD (%) | E (GPa) | Rp0.2 (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | At (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti compact | 99.13 | 94.5 | 541 | 686.7 | 4.08 |
| CP Ti Grade 1 | 100 | 105 | 170-310 | 240 | 24 |
| Surface | N | Ra (μm) | Rz (μm) | Rpk (μm) | Rvk (μm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| A | 25 | 2.18 | 0.20 | 14.80 | 1.15 | 2.97 | 0.37 | 1.78 | 0.35 |
| B | 25 | 4.38 | 0.38 | 30.48 | 1.51 | 5.19 | 0.58 | 5.31 | 1.45 |
| C | 25 | 6.16 | 0.50 | 38.39 | 0.97 | 8.80 | 2.06 | 6.62 | 1.36 |
| D | 25 | 11.31 | 0.86 | 59.35 | 1.73 | 11.73 | 0.34 | 8.92 | 1.35 |
| E | 25 | 11.70 | 0.18 | 70.16 | 5.61 | 10.05 | 4.92 | 15.68 | 3.21 |
| Roughness Parameter | DF1 | DF2 | F-value | p-value | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | 4 | 120 | 1865.18 | 0.000 * | 98.42 |
| Rz | 4 | 120 | 1582.94 | 0.000 * | 98.14 |
| Rpk | 4 | 120 | 55.5 | 0.000 * | 64.19 |
| Rvk | 4 | 120 | 206.65 | 0.000 * | 87.32 |
| Surface | N | Pulse Energy (mJ) | wt. % of Elements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | O | |||
| NI | 3 | – | 93.9 ± 1.1 | 5.5 ± 0.7 |
| A | 3 | 0.2 | 80.4 ± 0.9 | 21.5 ± 0.9 |
| B | 3 | 0.4 | 72.6 ± 1.1 | 28.5 ± 1.2 |
| C | 3 | 0.6 | 67.9 ± 0.6 | 31.7 ± 0.9 |
| D | 3 | 0.8 | 61.8 ± 1.3 | 34.6 ± 2.8 |
| E | 3 | 1 | 58.8 ± 1.6 | 37,9 ± 2.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šugár, P.; Kováčik, J.; Šugárová, J.; Ludrovcová, B. A Study of Laser Micromachining of PM Processed Ti Compact for Dental Implants Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142246
Šugár P, Kováčik J, Šugárová J, Ludrovcová B. A Study of Laser Micromachining of PM Processed Ti Compact for Dental Implants Applications. Materials. 2019; 12(14):2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142246
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠugár, Peter, Jaroslav Kováčik, Jana Šugárová, and Barbora Ludrovcová. 2019. "A Study of Laser Micromachining of PM Processed Ti Compact for Dental Implants Applications" Materials 12, no. 14: 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142246
APA StyleŠugár, P., Kováčik, J., Šugárová, J., & Ludrovcová, B. (2019). A Study of Laser Micromachining of PM Processed Ti Compact for Dental Implants Applications. Materials, 12(14), 2246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142246






