Substrate Temperature Dependent Microstructure and Electron-Induced Secondary Electron Emission Properties of Magnetron Sputter-Deposited Amorphous Carbon Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
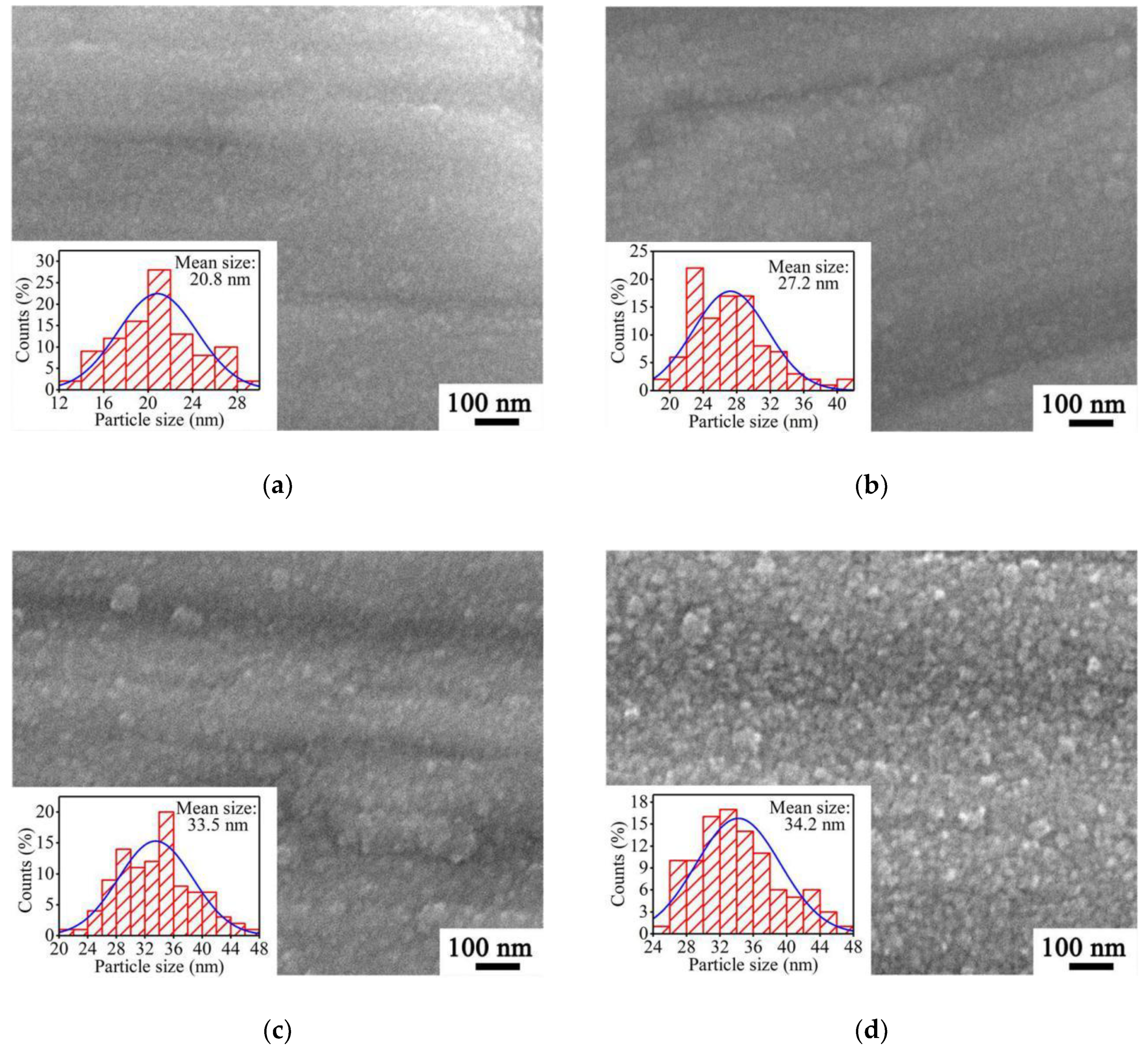
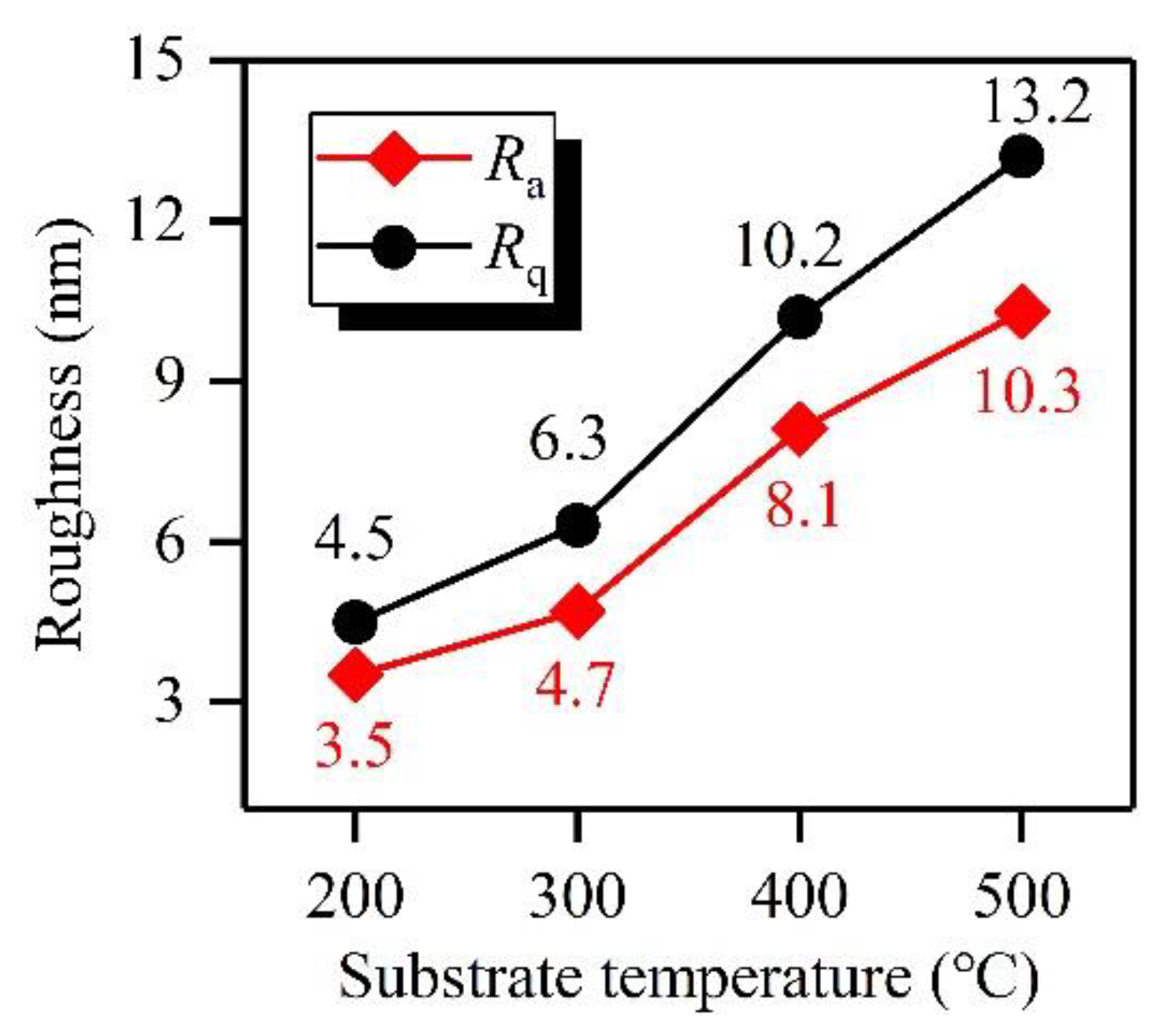
3.1. Surface Morphologies of a-C Films Prepared at Different Substrate Temperatures
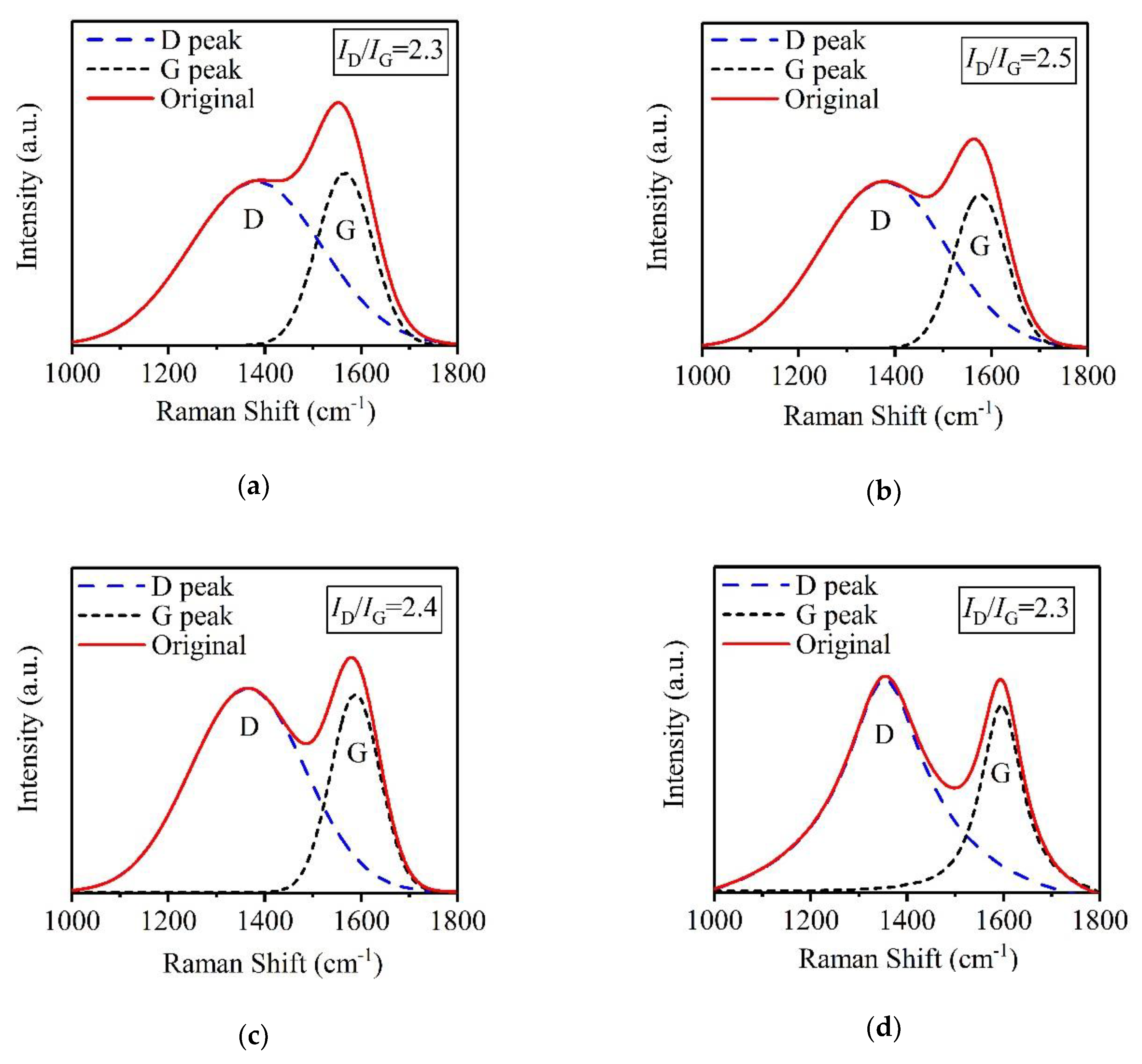
3.2. Microstructural Behaviors of a-C Films Prepared at Different Substrate Temperatures
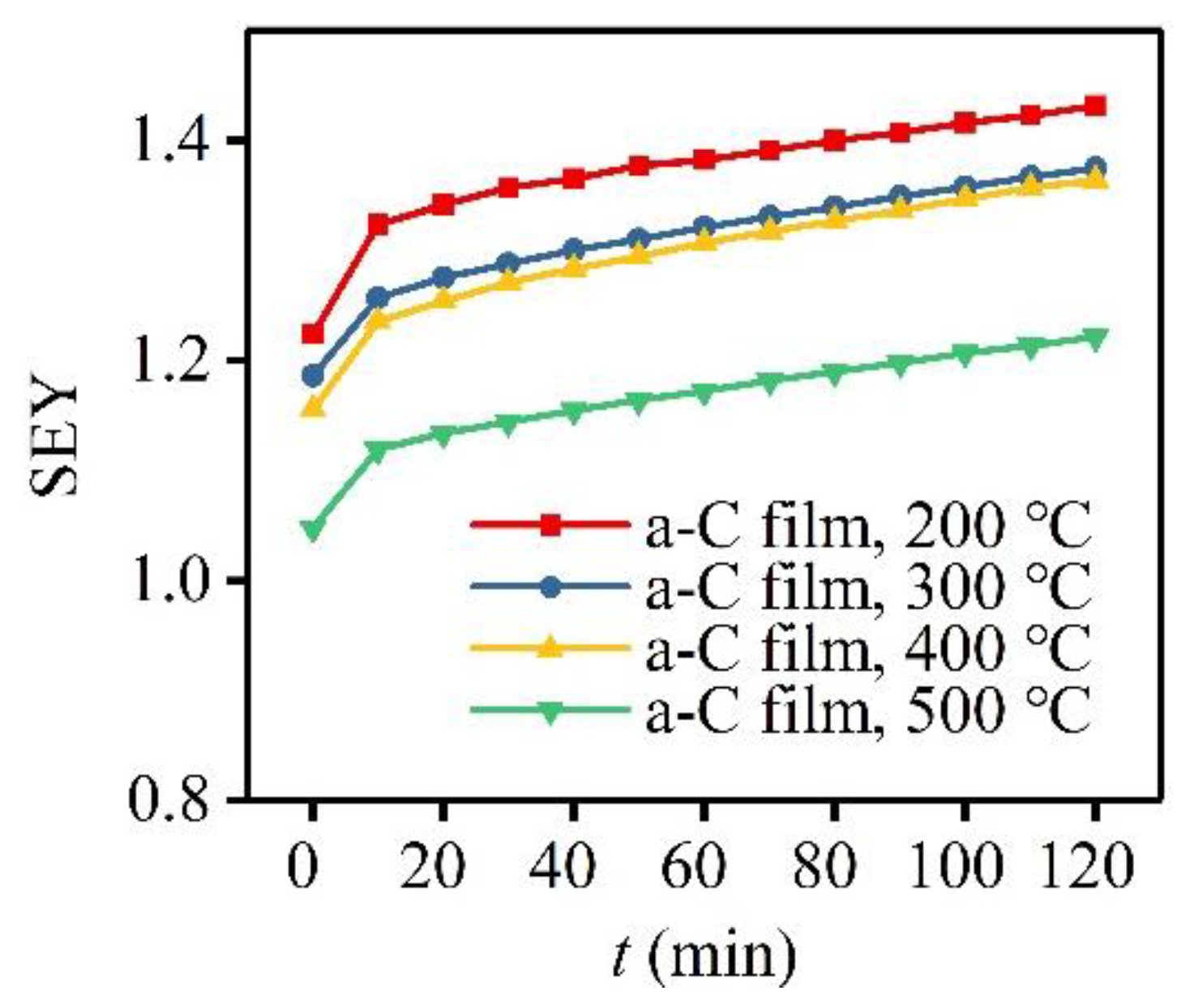
3.3. SEE Properties of a-C Films Prepared at Different Substrate Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, S.X.; Chan, H.W.; Graaf, H.V.D. Secondary electron emission materials for transmission dynodes in novel photomultipliers: A review. Mater. 2016, 9, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.B.; Deng, S.Q.; Yuan, W.J.; Yan, Y.J.; Li, J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhu, J. Disparity of secondary electron emission in ferroelectric domains of YMnO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 032901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, W.B.; Wang, K.; Gao, B.Y.; Li, Y.D.; Wu, S.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Fan, H.Q. Au doping effect on the secondary electron emission performance of MgO films. Mater. 2018, 11, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, I.A.; Vizgalov, I.V.; Kurnaev, V.A.; Brandt, C.; Kreter, A.; Linsmeier, C. In-situ mass-spectrometer of magnetized plasmas. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2017, 12, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Soffitta, P.; Bellazzini, R.; Brez, A.; Lumb, N.; Spandre, G. An efficient photoelectric X-ray polarimeter for the study of black holes and neutron stars. Nat. 2001, 411, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirby, R.E.; King, F.K. Secondary electron emission yields from PEP-II accelerator materials. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2001, 469, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, W.H.; Asner, D.M.; Conway, J.V.; Denett, C.A.; Greenwald, S.; Kim, J.S.; Li, Y.; Moore, T.P.; Omanovic, V.; Palmer, M.A.; et al. In-situ measurements of the secondary electron yield in an accelerator environment: Instrumentation and methods. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2015, 783, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumolo, G.; Arduini, G.; Métral, E.; Shaposhnikova, E.; Benedetto, E.; Calaga, R.; Papotti, G.; Salvant, B. Dependence of the electron-cloud instability on the beam energy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 144801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Liu, G.Z.; Tang, C.X.; Chen, C.H.; Shao, H.; Huang, W.H. Suppression of high-power microwave dielectric multipactor by resonant magnetic field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.P.; Shen, W.W.; Mu, H.B.; Deng, J.B.; Hao, X.W.; Zhang, G.J. Measurement of secondary electron emission from dielectric window materials. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2013, 41, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.X.; Liu, L. Effect of surface produced secondary electrons on the sheath structure induced by high-power microwave window breakdown. Phys. Plasma 2011, 18, 033507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, K.; Damamme, G.; Ahmed, A.S.; Moya, G.; Kallel, A. Dependence of secondary electron emission on surface charging in sapphire and polycrystalline alumina: Evaluation of the effective cross section for recombination and trapping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 297, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcon, N.; Payan, D.; Belhaj, M.; Tondu, T.; Inguimbert, V. Secondary electron emission on space materials: Evaluation of the total secondary electron yield from surface potential measurements. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2012, 40, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halekas, J.S.; Lin, R.P.; Mitchell, D.L. Large negative lunar surface potentials in sunlight and shadow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, I.; Aguilera, L.; Dávila, M.E.; Nistor, V.C.; González, L.A.; Galán, L.; Raboso, D.; Ferritto, R. Secondary electron emission under electron bombardment from graphene nanoplatelets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 291, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michizono, S.; Saito, Y.; Suharyanto; Yamano, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Secondary electron emission of sapphire and anti-multipactor coatings at high temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 235, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.Q.; Huang, M.G.; Feng, J.J.; Bai, G.D.; Yan, T.C. Ion surface modification for space TWT multistage depressed collectors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2196–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, J.M.; Coutu, R.A.; Lake, R.; Laurvick, T.; Back, T.; Fairchild, S. Modeling micro-porous surfaces for secondary electron emission control to suppress multipactor. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 055304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; He, Y.N.; Hu, S.G.; Wang, R.; Hu, T.C.; Yang, J.; Cui, W.Z. Suppression of secondary electron yield by micro-porous array structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 074904. [Google Scholar]
- Pivi, M.; King, F.K.; Kirby, R.E.; Raubenheimer, T.O.; Stupakov, G.; Pimpec, F.L. Sharp reduction of the secondary electron emission yield from grooved surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Zhang, N.; Hu, T.C.; Wang, F.; Cui, W.Z. Secondary electron emission from rough metal surfaces: A multi-generation model. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richterová, I.; Němeček, Z.; Beránek, M.; Šafránková, J.; Pavlů, J. Secondary emission from non-spherical dust grains with rough surfaces: Application to lunar dust. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, J.; Ohya, K.; Nishimura, K. Simulation of secondary electron emission from rough surfaces. J. Nucl. Mater. 1995, 220–222, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tian, P.; Pan, C.T.; Robertson, A.W.; Warner, J.H.W.; Hill, E.W.; Briggs, G.A.D. Ultralow secondary electron emission of graphene. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimpec, F.L.; Kirby, R.E.; King, F.K.; Pivi, M. The effect of gas ion bombardment on the secondary electron yield of TiN, TiCN and TiZrV coatings for suppressing collective electron effects in storage rings. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2006, 564, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, G.G.; Rodríguez, R.J.; García, M.; Galán, L.; Montero, I.; Segovia, J.L.D. Spectroscopic investigations of Cr, CrN and TiCr anti-multipactor coatings grown by cathodic-arc reactive evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7627–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewilogua, K.; Wagner, D. The effect of secondary electrons in the ion plating deposition of amorphous hydrogenated carbon (a-C: H) films. Vacuum 1991, 42, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Ayouchi, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.R.; Bundaleski, N.; Moutinho, A.; Teodoro, O.; Aguilera, L.; Taborelli, M.; Schwarz, R. Secondary electron emission yield (SEY) in amorphous and graphitic carbon films prepared by PLD. Phys. Status Solidi C 2012, 9, 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallgren, C.Y.; Ashraf, A.; Calatroni, S.; Chiggiato, P.; Pinto, P.C.; Marques, H.P.; Neupert, H.; Taborelli, M.; Vollenberg, W.; Wevers, I.; et al. Low secondary electron yield carbon coatings for electron cloud mitigation in modern particle accelerators. In Proceedings of the IPAC’10, Kyoto, Japan, 23–28 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Larciprete, R.; Grosso, D.R.; Trolio, A.D.; Cimino, R. ; Evolution of the secondary electron emission during the graphitization of thin C films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.F.; Fitton, B. Secondary-electron emission spectroscopy and the observation of high-energy excited states in graphite: Theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 1926–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mominuzzaman, S.M.; Krishna, K.M.; Soga, T.; Jimbo, T.; Umeno, M. Raman spectra of ion beam sputtered amorphous carbon thin films deposited from camphoric carbon. Carbon 2000, 38, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.G.; Lai, Q.B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.M. Quantitative measurements of sp3 content in DLC films with Raman spectroscopy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachfule, P.; Shinde, D.; Majumder, M.; Xu, Q. Fabrication of carbon nanorods and graphene nanoribbons from a metal-organic framework. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yi, X.; Hu, W.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J. Substrate Temperature Dependent Microstructure and Electron-Induced Secondary Electron Emission Properties of Magnetron Sputter-Deposited Amorphous Carbon Films. Materials 2019, 12, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162631
Li J, Yi X, Hu W, Gao B, Li Y, Wu S, Lin S, Zhang J. Substrate Temperature Dependent Microstructure and Electron-Induced Secondary Electron Emission Properties of Magnetron Sputter-Deposited Amorphous Carbon Films. Materials. 2019; 12(16):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162631
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Xingkang Yi, Wenbo Hu, Buyu Gao, Yongdong Li, Shengli Wu, Shu Lin, and Jintao Zhang. 2019. "Substrate Temperature Dependent Microstructure and Electron-Induced Secondary Electron Emission Properties of Magnetron Sputter-Deposited Amorphous Carbon Films" Materials 12, no. 16: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162631
APA StyleLi, J., Yi, X., Hu, W., Gao, B., Li, Y., Wu, S., Lin, S., & Zhang, J. (2019). Substrate Temperature Dependent Microstructure and Electron-Induced Secondary Electron Emission Properties of Magnetron Sputter-Deposited Amorphous Carbon Films. Materials, 12(16), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162631




