Application of PTFE/Al Reactive Materials for Double-Layered Liner Shaped Charge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of Penetration Behavior
3. Experiments of Penetration
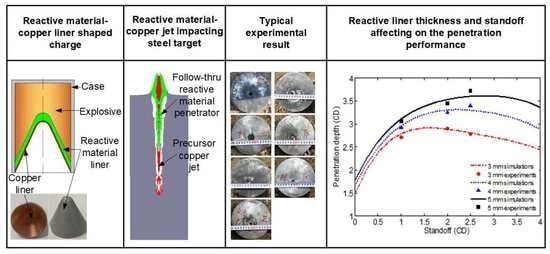
3.1. Reactive Material-Copper Liner Specimens
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Penetration Enhancement Mechanism
4.1. Numerical Method and Material Model
4.2. Jet Formation Characteristics of RM-CL Shaped Charge
4.3. Comparison of Simulated Results and Experimental Penetration Depth
4.4. Initiation Delay Time Effects on Penetration Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, R.J.; Mock, W.; Carney, J.R.; Holt, W.H.; Pangilinan, G.I.; Gamache, R.M.; Boteler, J.M.; Bohl, D.G.; Drotar, J.; Lawrence, G.W. Reactive materials studies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 845, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mock, W.; Drotar, J.T. Effect of aluminum particle size on the impact initiation of pressed PTFE/Al composite rods. AIP Conf. Proc. 2007, 955, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, C.L.; Wang, Z.C.; Niu, H.H. Experimental study on impact-induced reaction characteristics of PTFE/Ti composites enhanced by W particles. Materials 2017, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.H.; Yin, J.P.; Cui, Z.Q.; Liu, T.X. Numerical simulation of modified low-density jet penetrating shell charge. Int. J. Simul. Model 2015, 14, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Shi, A.S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, L.; He, Y.; Guan, Z.W. Thermochemical modeling of temperature controlled shock-induced chemical reactions in multifunctional energetic structural materials under shock compression. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Walley, S.M.; Hunt, R.J.A.; Proud, W.G.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Meyers, M.A. High-strain, high-strain-rate flow and failure in PTFE/Al/W granular composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 472, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.G. Energy Release Characteristics of Impact-Initiated Energetic Materials; Materials Research Society: Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.F.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Liu, Z.W.; Liu, W.M. Impact-induced initiation and energy release behavior of reactive materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 110, 074904. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, C.; Dong, Y.X.; Maimaitituersun, W.; Ren, Y.M.; Feng, S.S. Experimental study on impact-induced initiation thresholds of Polytetrafluoroethylene/Aluminum composite. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; He, Y.; He, Y. Investigation on impact initiation characteristics of fluoropolymer-matrix reactive materials. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Dong, Y.X.; Maimaitituersun, W. Microscale simulation on mechanical properties of Al/PTFE composite based on real microstructures. Materials 2016, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.X.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, X.B. Investigation on reaction energy, mechanical behavior and impact insensitivity of W-PTFE-Al composites with different W percentage. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, H.F. Experimental study on penetration behavior of reactive material projectile impacting aluminum plate. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 95, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.Y.; Yu, Q.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Lei, M.A.; Wang, H.F. Damage effects of double-spaced aluminum plates by reactive material projectile impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 104, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.X.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Lan, J.; Li, S.K.; He, C.; Xue, X.Y. Effects of multi-component co-addition on reaction characteristics and impact damage properties of reactive material. Mater. Des. 2018, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.W.; Wang, H.F.; Lei, M.A.; Yu, Q.B. Enhanced initiation behavior of reactive material projectiles impacting covered explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.F. Enhanced ignition behavior of reactive material projectiles impacting fuel-filled tank. Def. Technol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.F. Interval rupturing damage to multi-spaced aluminum plates impacted by reactive materials filled projectile. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 130, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, A.S.; Baker, E.L.; De Fisher, S.E.; Ng, K.W.; Pham, J. Bam bam: Large scale unitary demolition warheads. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Ballistics, Tarragona, Spain, 16–20 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolich, S. Reactive materials enhanced lethality EFP. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Armament Systems: Gun and Missile Systems Conference and Exhibition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 23–26 April 2007; National Defence Industrial Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, E.L.; Daniels, A.S.; Ng, K.W.; Martin, V.O.; Orosz, J.P. Barnie: A unitary demolition warhead. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Ballistics, Interlaken, Switzerland, 7–11 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Xiao, J.G.; Yu, Q.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Wang, H.F. Armor penetration aftereffect overpressure produced by reactive material liner shaped charge. Acta Armamentarii 2016, 37, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.G.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, F.Y.; Wang, H.F. Demolition mechanism and behavior of shaped charge with reactive liner. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2016, 41, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.G.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, Q.B.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.F. Penetration behavior of reactive liner shaped charge jet impacting steel plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 126, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.R.; Arulanandam, R.; Hille, S.M. Polymers as potential shaped charge liner materials. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Ballistics, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Yin, J.P.; Zhang, Z.M. Simulation study on expansive jet formation characteristics of polymer liner. Materials 2019, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.G.; Zhang, X.P.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, H.F. Enhanced damage effects of multi-layered concrete target produced by reactive materials liner. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2018, 43, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.G.; Zheng, Y.F.; Tang, L.; Yu, Q.B.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.F. Effect of wave shaper on reactive materials jet formation and its penetration performance. Defence Technol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.P.; Cornish, R. Formation model for shaped charge liners comprising multiple layers of different materials. In Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium on Ballistics, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–19 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, R.; Ng, W.; Weiman, K. Testing and analysis of multi of multi-liner EFP warheads. In Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Ballistics, Orlando, FL, USA, 23–27 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, B.; Wang, Z.J.; Dong, F.D. Numerical simulation of jet forming for nylon-copper composite charge liner. Acta Armamentarii 2014, 35, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Li, W.B. Numerical simulation on double-layered shaped charge liner penetration into semi-infinite target. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 32, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Voitenko, Y.I.; Goshovskii, S.V.; Drachuk, A.G.; Bugaets, V.P. Mechanical Effect of shaped charge with Porous Liners. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2013, 49, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftenberg, M.N.; Mock, W.; Kirby, G.C. Modeling the Impact Deformation of Rods of a Pressed PTFE/Al Composite Mixture. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Long, Y.; Ji, C.; Zhong, M.S.; Liu, Q. The influence of liner material on the dynamic response of the finite steel target subjected to high velocity impact by explosively formed projectile. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 109, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt, B. Explosive properties of the Mg-Al/PTFE composition. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2007, 15, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
















| No. | b1 (mm) | H (CD) | Pd (CD) | D0 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | |||||||
| Entrance | Exit | Entrance | Exit | Entrance | Exit | Entrance | ||||
| 1 | 3 | 1.0 | 2.71 | Φ25.7 | Φ10 | 7 × 9 | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 3 | 2.0 | 2.90 | 25 × 29 | Φ6.5 | 5 × 6.5 | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.78 | 24 × 31 | 6 × 7 | 5 × 6 | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | 4 | 1.0 | 2.92 | Φ26 | Φ12 | 9 × 11 | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | 4 | 2.0 | 3.24 | Φ25 | Φ6.5 | Φ6.5 | Φ6 | Φ6 | - | - |
| 6 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.40 | Φ25 | Φ8 | Φ5.5 | Φ6 | Φ6 | - | - |
| 7 | 5 | 1.0 | 3.06 | Φ27 | Φ7.5 | 12 × 13 | Φ12 | Φ14 | - | - |
| 8 | 5 | 2.0 | 3.44 | Φ26 | Φ6 | Φ6 | Φ6 | Φ9 | - | - |
| 9 | 5 | 2.5 | 3.72 | Φ26 | Φ6 | Φ6 | Φ5 | 7.5 × 8.6 | Φ6 | Φ7 |
| Part | Materials | EOS | Strength Model | Erosion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Air | Ideal Gas | None | None |
| Outer liner | Reactive materials | Shock | Johnson Cook | None |
| Inner liner | Copper | Shock | Johnson Cook | None |
| Explosive | 8701 | JWL | None | None |
| Case | #45 steel | Shock | Johnson Cook | None |
| Steel target | #45 steel | Shock | Johnson Cook | Geometric Strain 1.5 |
| Materials | ρ (kg/m3) | G (GPa) | A (MPa) | B (MPa) | n | C | m | Tm (K) | Troom (K) | Γ | c0 (m/s) | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactive liner | 2.27 | 0.67 | 8.04 | 250.6 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1 | 500 | 294 | 0.9 | 1450 | 2.2584 |
| Copper | 8.97 | 46.5 | 90 | 292 | 0.31 | 0.025 | 1.09 | 1356 | 293 | 2.02 | 3940 | 1.49 |
| #45 steel | 7.83 | 77 | 792 | 510 | 0.26 | 0.014 | 1.03 | 1793 | 300 | 2.17 | 4570 | 1.49 |
| Material | ρ (kg/m3) | D (km/s) | PCJ (GPa) | E (GPa) | A (GPa) | B (GPa) | R1 | R2 | ω | v0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explosive | 1.71 | 8.315 | 28.6 | 8.499 | 524.23 | 7.678 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 0.34 | 1.00 |
| Material | ρ (kg/m3) | γ | Cp (kJ/kg·K) | Cv (kJ/kg·K) | T (K) | E0 (kJ/kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | 1.225 | 1.4 | 1.005 | 0.718 | 288.2 | 2.068 × 105 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Geng, B.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Y. Application of PTFE/Al Reactive Materials for Double-Layered Liner Shaped Charge. Materials 2019, 12, 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172768
Wang H, Guo H, Geng B, Yu Q, Zheng Y. Application of PTFE/Al Reactive Materials for Double-Layered Liner Shaped Charge. Materials. 2019; 12(17):2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172768
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haifu, Huanguo Guo, Baoqun Geng, Qingbo Yu, and Yuanfeng Zheng. 2019. "Application of PTFE/Al Reactive Materials for Double-Layered Liner Shaped Charge" Materials 12, no. 17: 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172768
APA StyleWang, H., Guo, H., Geng, B., Yu, Q., & Zheng, Y. (2019). Application of PTFE/Al Reactive Materials for Double-Layered Liner Shaped Charge. Materials, 12(17), 2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172768