Preparation of Magnetic g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Composite and Its Application in the Separation of Catechol from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Catechol Stock Solution
2.3. Preparations of g-C3N4, Fe3O4 and g-C3N4/Fe3O4
2.4. Characterizations of g-C3N4, Fe3O4 and g-C3N4/Fe3O4
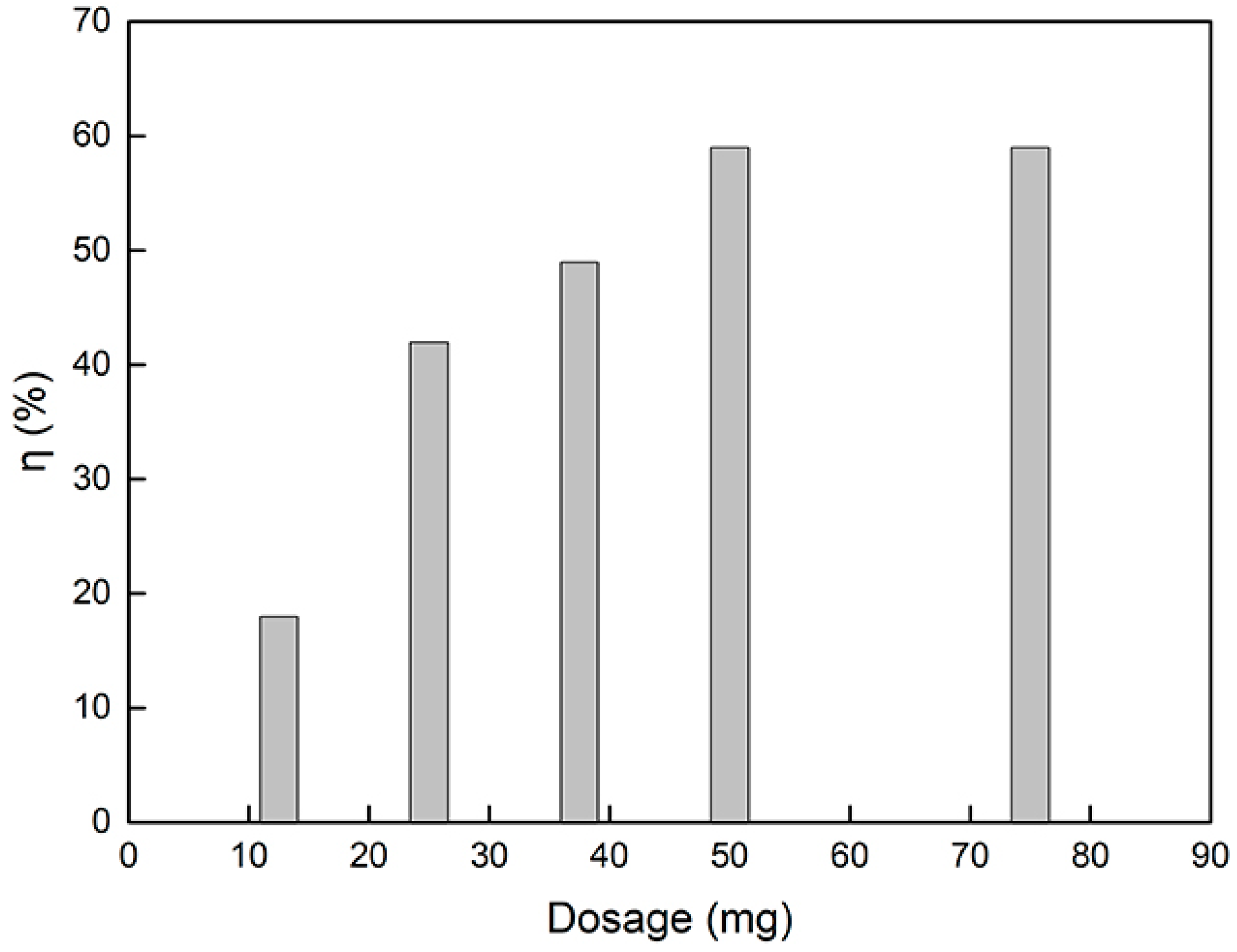
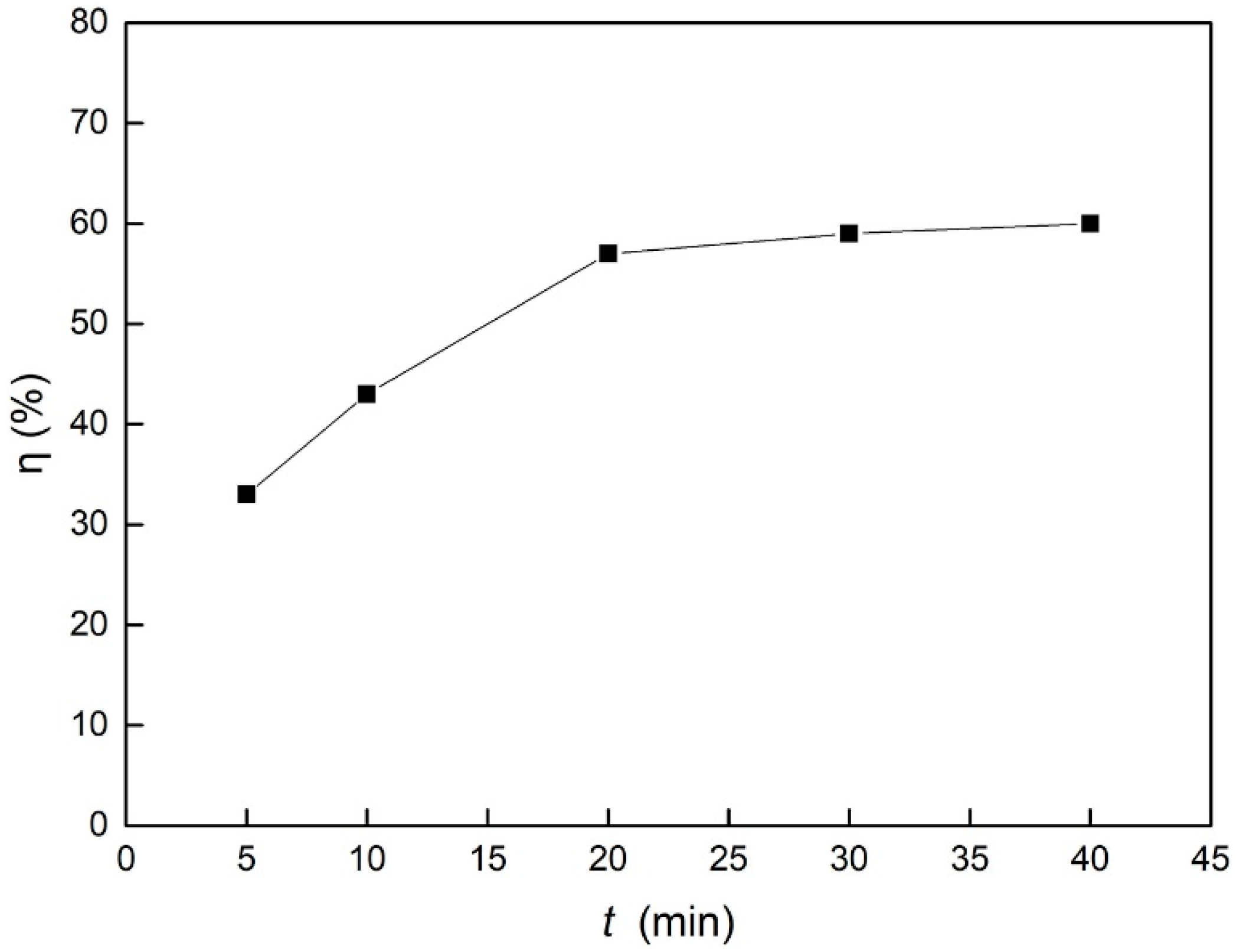
2.5. Adsorption Properties of g-C3N4/Fe3O4
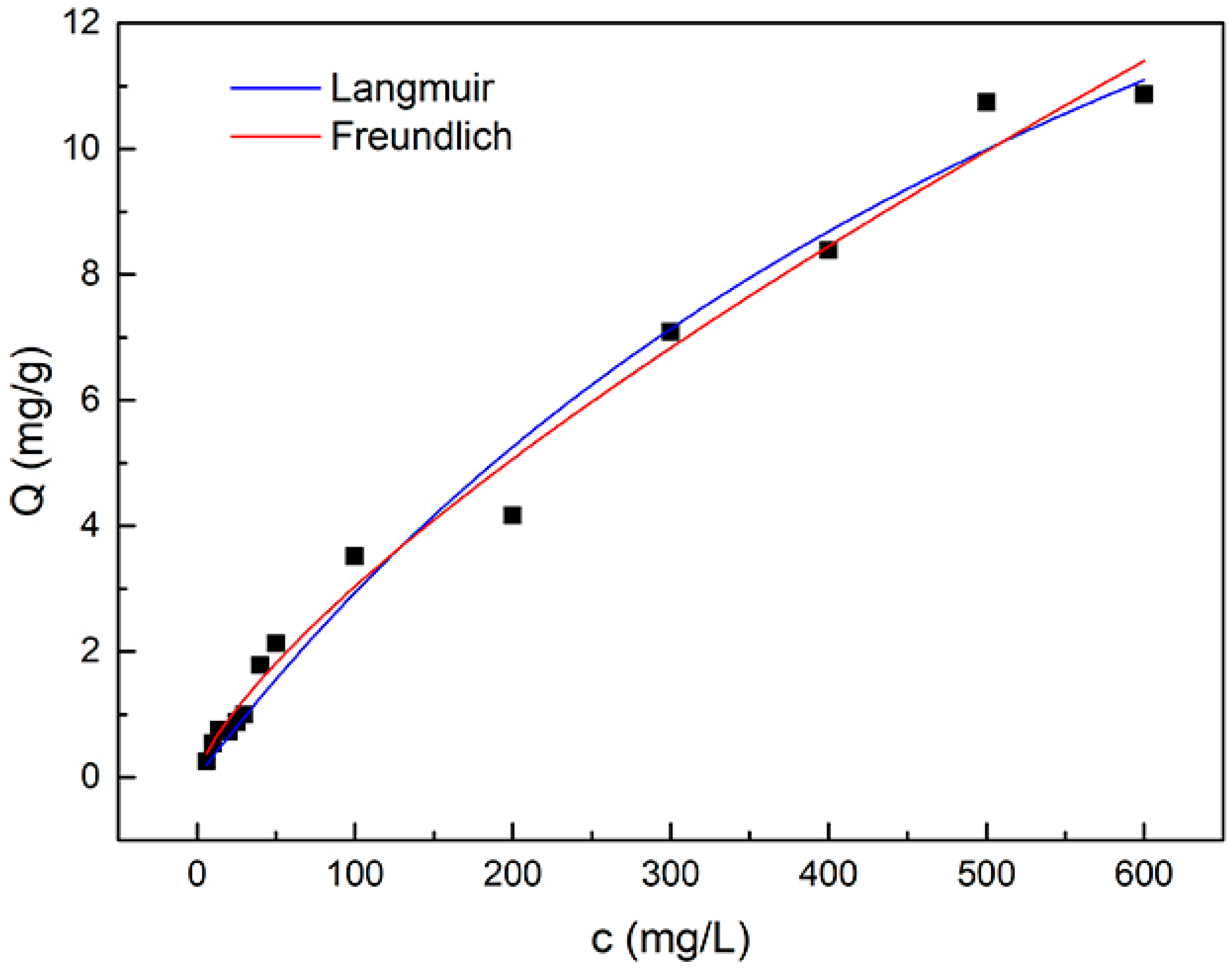
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
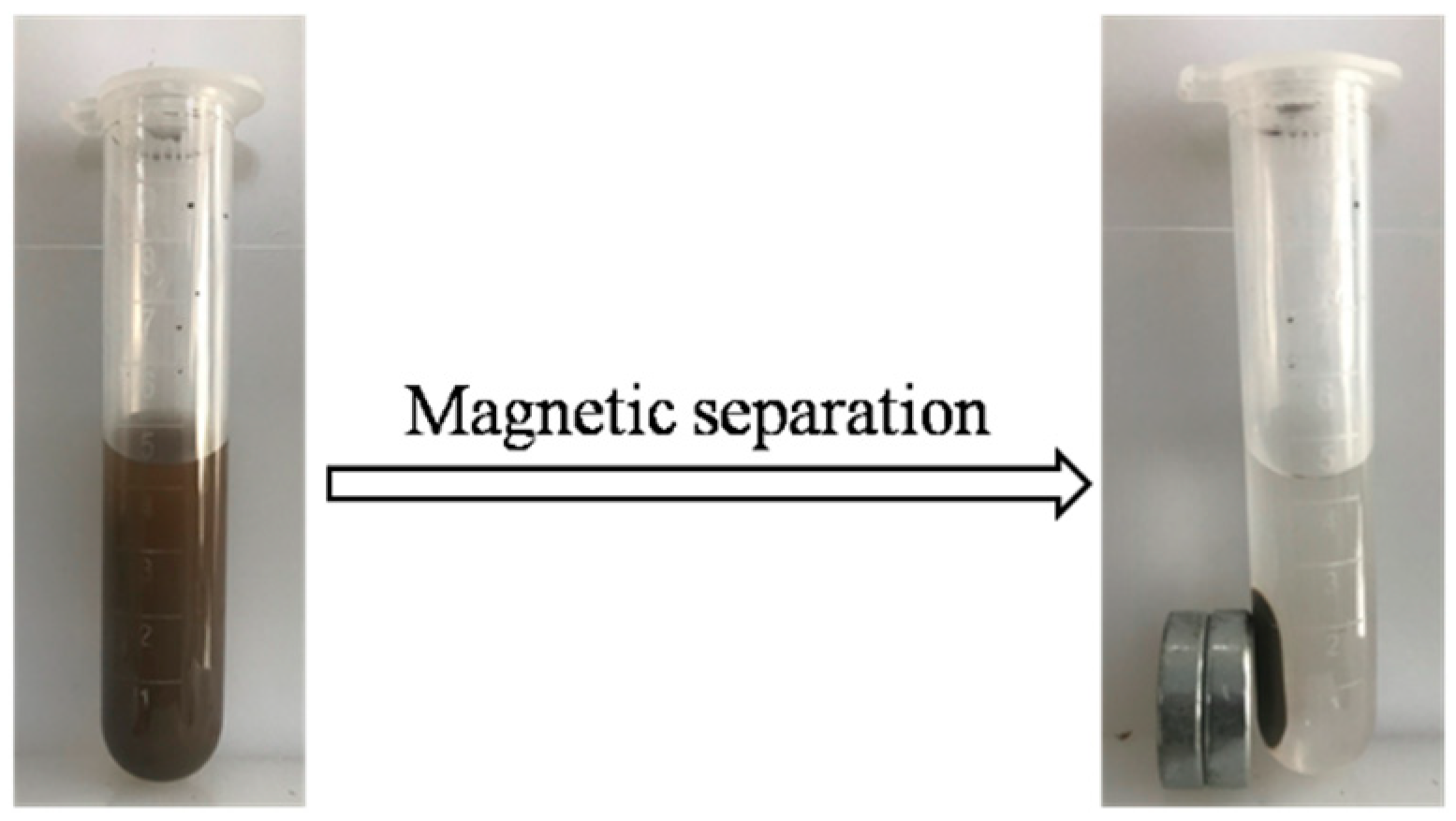
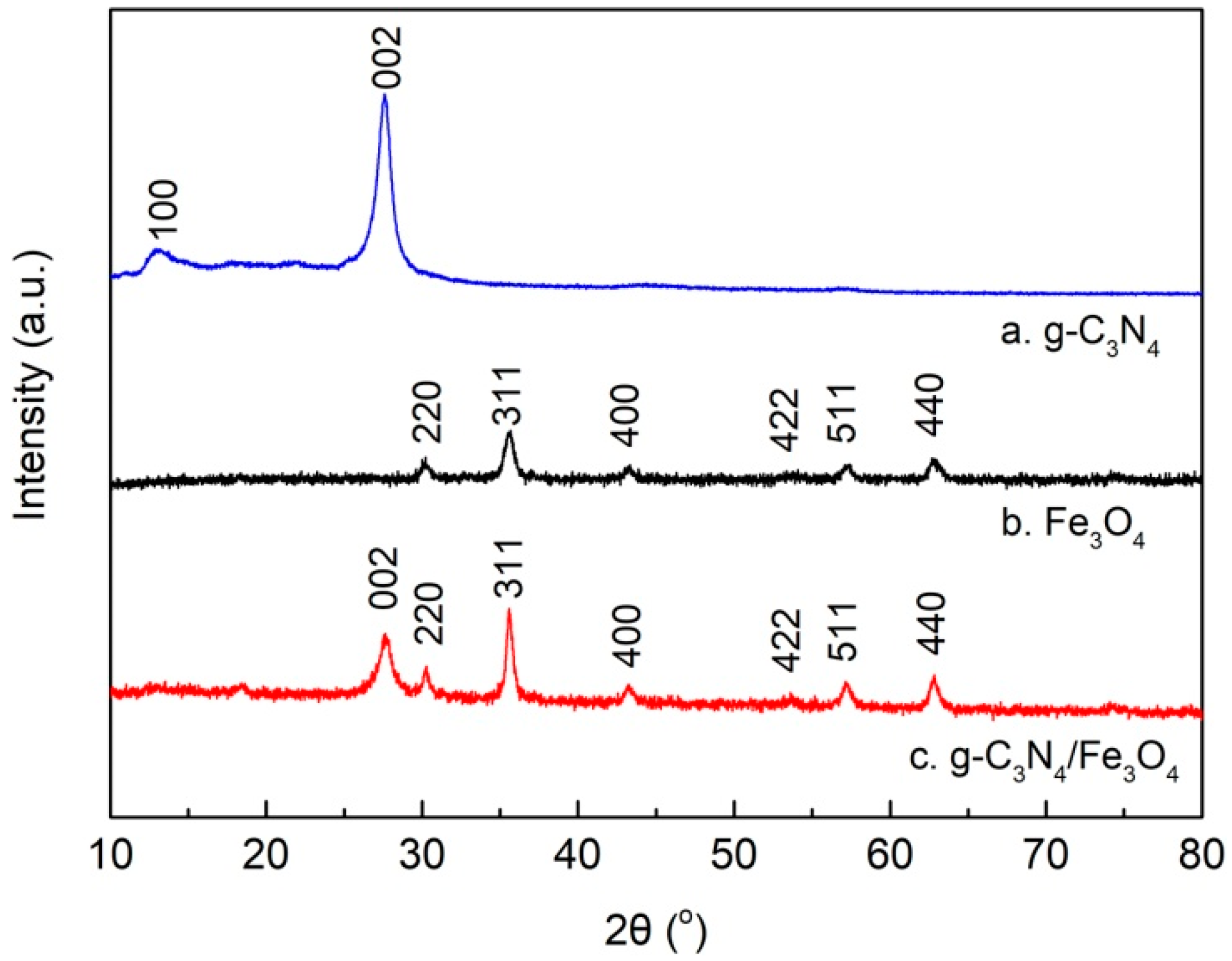
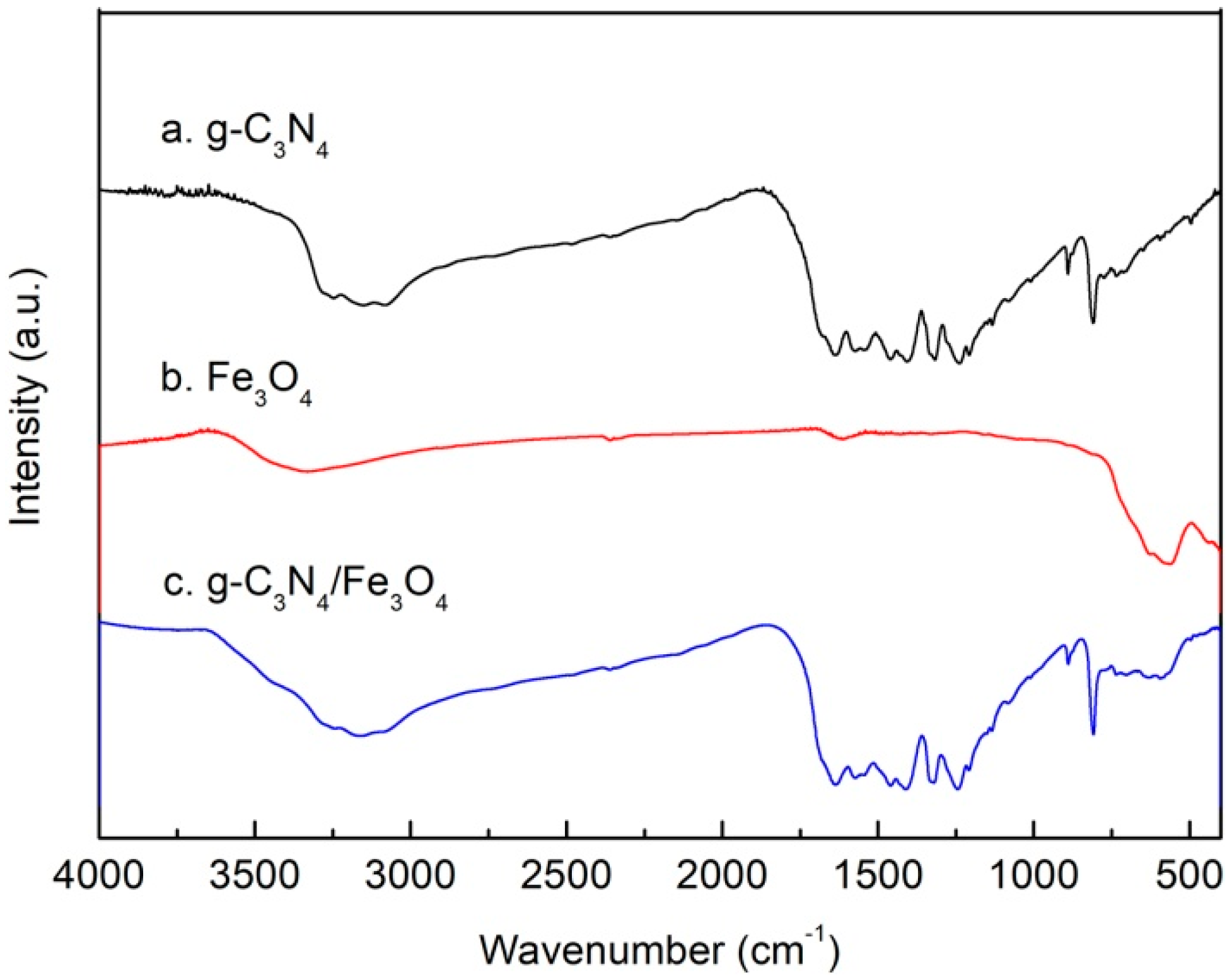
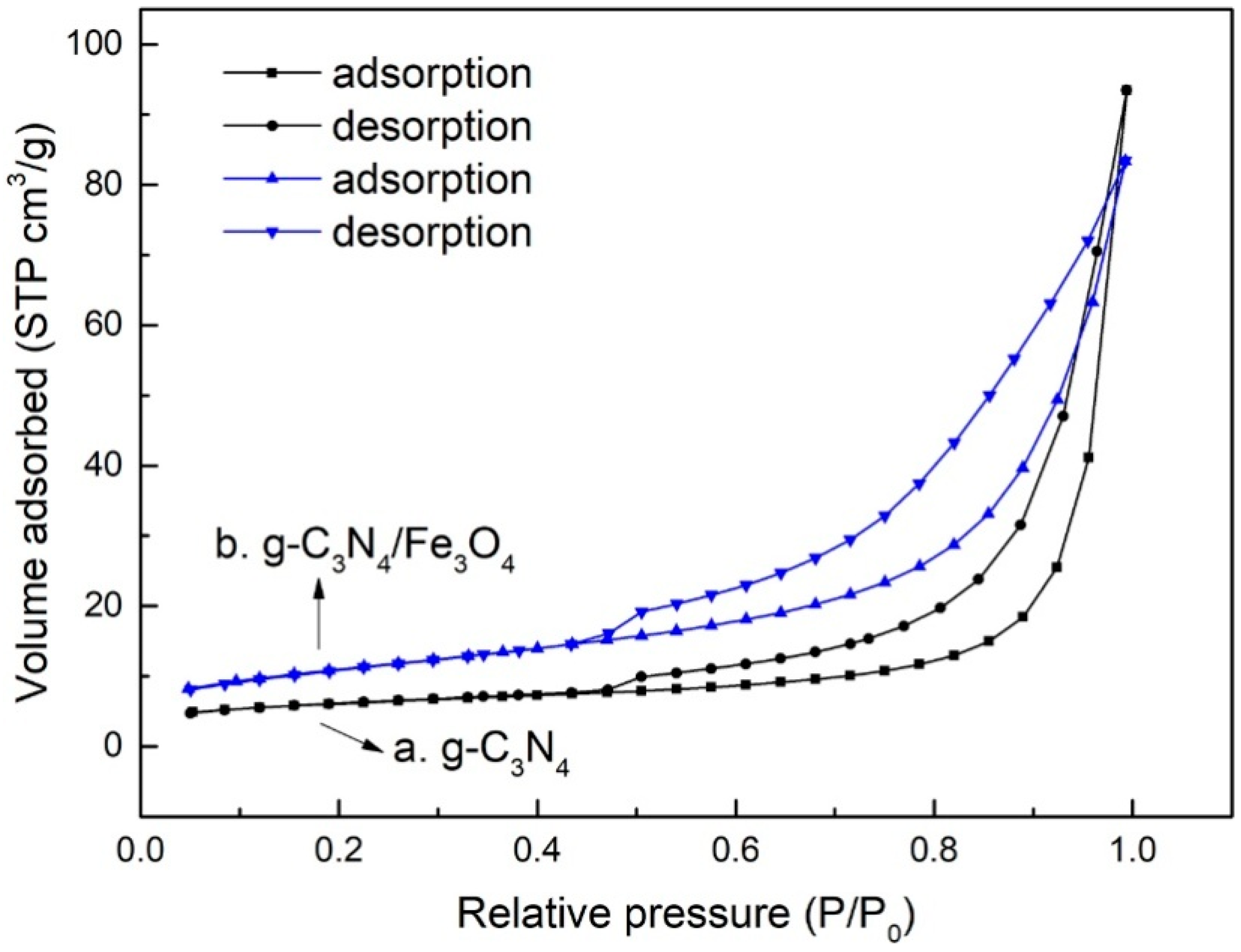
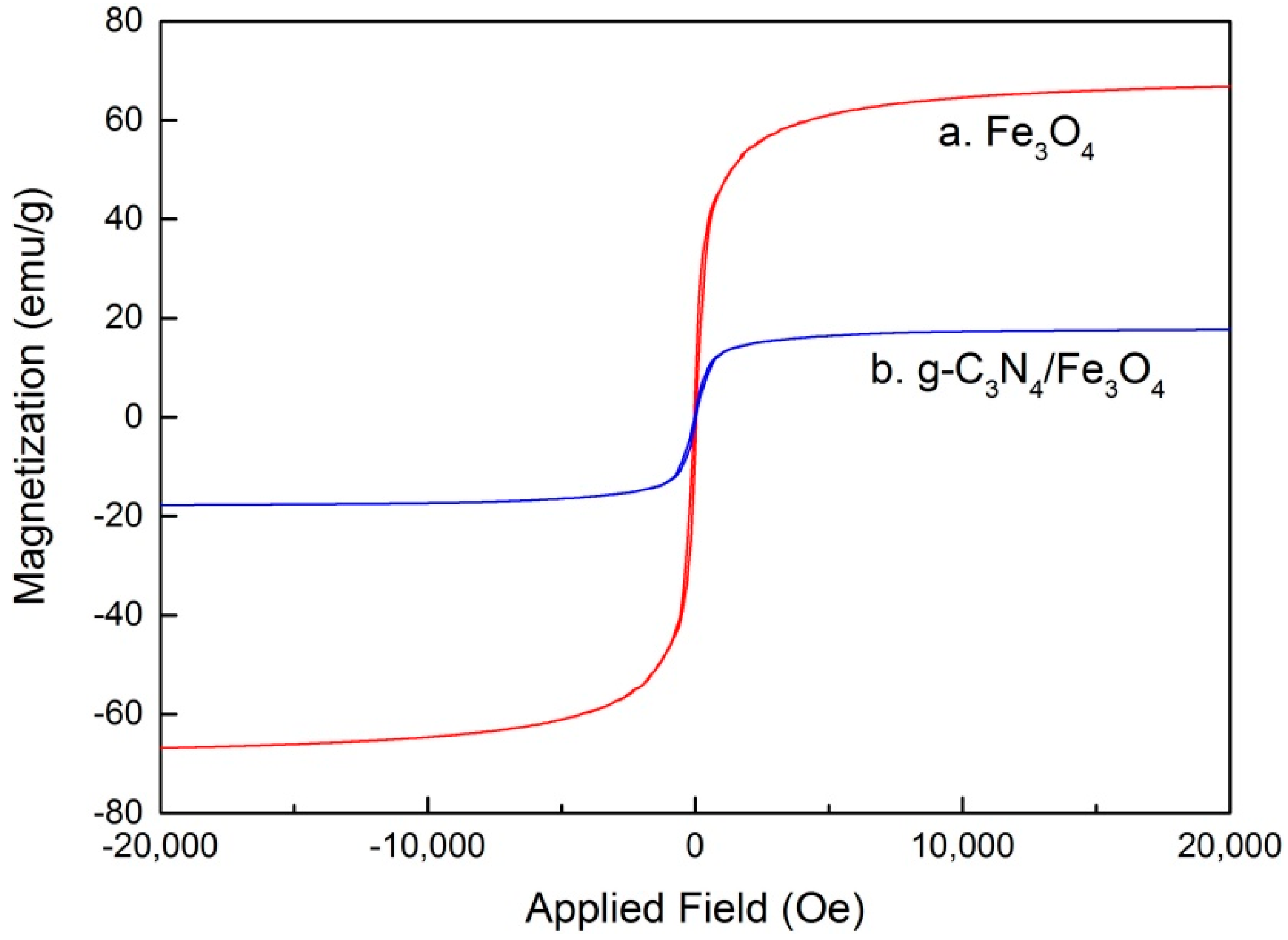
3.1. Characterizations
3.2. Adsorption of Catechol
3.3. Desorption of Catechol
3.4. Comparison with Other Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulley-Stahl, H.; Hogan, P.A.; Schmidt, W.L.; Wall, S.J.; Buhrlage, A.; Bullen, H.A. Surface Complexation of Catechol to MetalOxides: An ATR-FTIR, Adsorption, and Dissolution Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4116–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environment Canada and Health Canada. Priority Substances List Assessment Report: 1,2-Dihydroxybenzene; Canadian Environmental Protection Act: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1993.
- Moeder, M. Phenols Analysis in Environmental Samples. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gogate, P.R. Treatment of wastewater streams containing phenolic compounds using hybrid techniques based on cavitation: A review of the current status and the way forward. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.; Qu, J.Y. Research progress of methods for detecting catechol and hydroquinone in water. Chem. Res. 2015, 26, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Cui, J.; Li, G.H.; Zhang, J.N.; Li, D.W.; Huang, F.L.; Wei, Q.F. Laccase Immobilized on a PAN/Adsorbents Composite Nanofibrous Membrane for Catechol Treatment by a Biocatalysis/Adsorption Process. Molecules 2014, 19, 3376–3388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tušek, A.J.; Šalić, A.; Zelić, B. Catechol Removal from Aqueous Media Using Laccase Immobilized in Different Macro-and Microreactor Systems. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 182, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghapour, A.A.; Moussavi, G.; Yaghmaeian, K. Degradation and COD removal of catechol in wastewater using the catalytic ozonation process combined with the cyclic rotating-bed biological reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.Y.; Lu, Y.X.; Deng, Q.J.; Chen, S.L.; Pang, G.G.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, M.L.; Huang, Z. Performance of a novel ABR-bioelectricity-Fenton coupling reactor for treating traditional Chinese medicine wastewater containing catechol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 177, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; He, J.; Sun, Z.X.; Holmgren, A.; Wang, D.S. Effect of phosphate on heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of catechol by nano-Fe3O4: Inhibitor or stabilizer. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.G.; Wang, Y.; Irini, A. Effect of pH and H2O2 dosage on catechol oxidation in nano-Fe3O4 catalyzing UV-Fenton and identification of reactive oxygen species. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mishra, I.M. Study of Catechol and Resorcinol Adsorption Mechanism through Granular Activated Carbon Characterization, pH and Kinetic Study. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Blanco, D.; Giraldo, L. Relation Between the Adsorbed Quantity and the Immersion Enthalpy in Catechol Aqueous Solutions on Activated Carbons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfa, A.; Mellouk, S.; Khelifa, K.M.; Khelifa, A. Removal of catechol from water by modified dolomite: Performance, spectroscopy, and mechanism. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.N.; Gao, M.L.; Gu, Z.; Luo, Z.X.; Ye, Y.G.; Lu, L.F. Comparison between the removal of phenol and catechol by modified montmorillonite with two novel hydroxyl-containing Gemini surfactants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebei, H.; Minh, D.P.; Lyczko, N.; Sharrock, P.; Nzihou, A. Hydroxyapatite-based sorbents: Elaboration, characterization and application for the removal of catechol from the aqueous phase. Environ. Technol. 2016, 38, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shakir, K.; Ghoneimy, H.F.; Elkafrawy, A.F.; Beheir, S.G.; Refaat, M. Removal of catechol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto organophilic-bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 150, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, N.; Sarma, J.; Borah, J.M.; Mahiuddin, S. Adsorption of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid onto hematite surface in aqueous medium: Importance of position of phenolic-OH groups and understanding of the same using catechol as an auxiliary model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Yan, W.; Jing, C.Y. Dynamic Adsorption of Catechol at the Goethite/Aqueous Solution Interface: A Molecular-Scale Study. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14588–14597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersen, H.H.; Shea, J.E.; Metiu, H. Catechol and HCl Adsorption on TiO2(110) in Vacuum and at the Water-TiO2 Interface. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, J.M.; Sarma, J.; Mahiuddin, S. Adsorption comparison at the α-alumina/water interface: 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid vs. catechol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 387, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Li, Q.; Yan, J.J.; Zhu, Z.H.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, X.H. Research on the adsorption capability of CTMAB-magnetic vermiculite for catechol. Ind. Water Treat. 2019, 39, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.P.; Lin, L.Z.; Feng, Y.Z.; Zhao, M.M.; Li, X.T.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Xiao, Z.B. Enrichment of antioxidants from soy sauce using macroporous resin andidentification of 4-ethylguaiacol, catechol, daidzein, and 4-ethylphenol as key small molecule antioxidants in soy sauce. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sumithra, S. Adsorptive removal of catechol on waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide: Equilibrium and kinetics study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 7581–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Fischer, A.; Goettmann, F.; Antonietti, M.; Müller, J.O.; Schlögl, R.; Carlsson, J.M. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: Variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Ha, W.; Chen, J.; Qi, H.Y.; Shi, Y.P. Advances and applications of graphitic carbon nitride as sorbent in analytical chemistry for sample pretreatment: A review. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, Q.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Sun, B.; Wang, M.M. Determination of three hydroxyl polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urine using magnetic solid-phase extraction with magnetic carbon nitride composites coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 37, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cui, S.H.; Yang, X.D.; Bi, W.T. Synthesis of g-C3N4/Fe3O4 nanocomposites and application as a new sorbent for solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. Talanta 2015, 132, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Surendar, T.; Kumar, B.; Baruah, A.; Shanker, V. Synthesis of magnetically separable and recyclable g-C3N4−Fe3O4 hybrid nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 26135–26143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.Q.; Yu, L.H.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhong, S.T.; Jiang, W. One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst with synergistic catalytic performance under visible-light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2017, 335, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.S.; Jin, B.; Chen, R.Q.; Peng, F.; Fang, Y.P. Synthesis of porous Fe3O4/g-C3N4 nanospheres as highly efficient and recyclable photocatalysts. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.B.; Ding, J.; Zheng, S.J.; Zhu, G.T.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Facile synthesis of magnetic carbon nitride nanosheets and its application in magnetic solid phase extraction for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible oil samples. Talanta 2016, 148, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. Adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Gaydardzhiev, S.; Ay, P. Stabilization of aqueous silicon nitride suspen-sion with Dolapix A88. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xia, P.; Ho, W.; Yu, J. Isoelectric point and adsorption activity of porous g-C3N4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 344, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Conditions | Concentration of Catechol (mg/L) | g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Dosage (mg) | Adsorption Time (min) | pH Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of catechol (mg/L) | 6, 10, 14, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 | 50 | 30 | 6 |
| g-C3N4/Fe3O4 dosage (mg) | 10 | 12.5, 25, 37.5, 50, 75 | 30 | 7 |
| Adsorption time (min) | 10 | 50 | 5, 10, 20, 30, 40 | 7 |
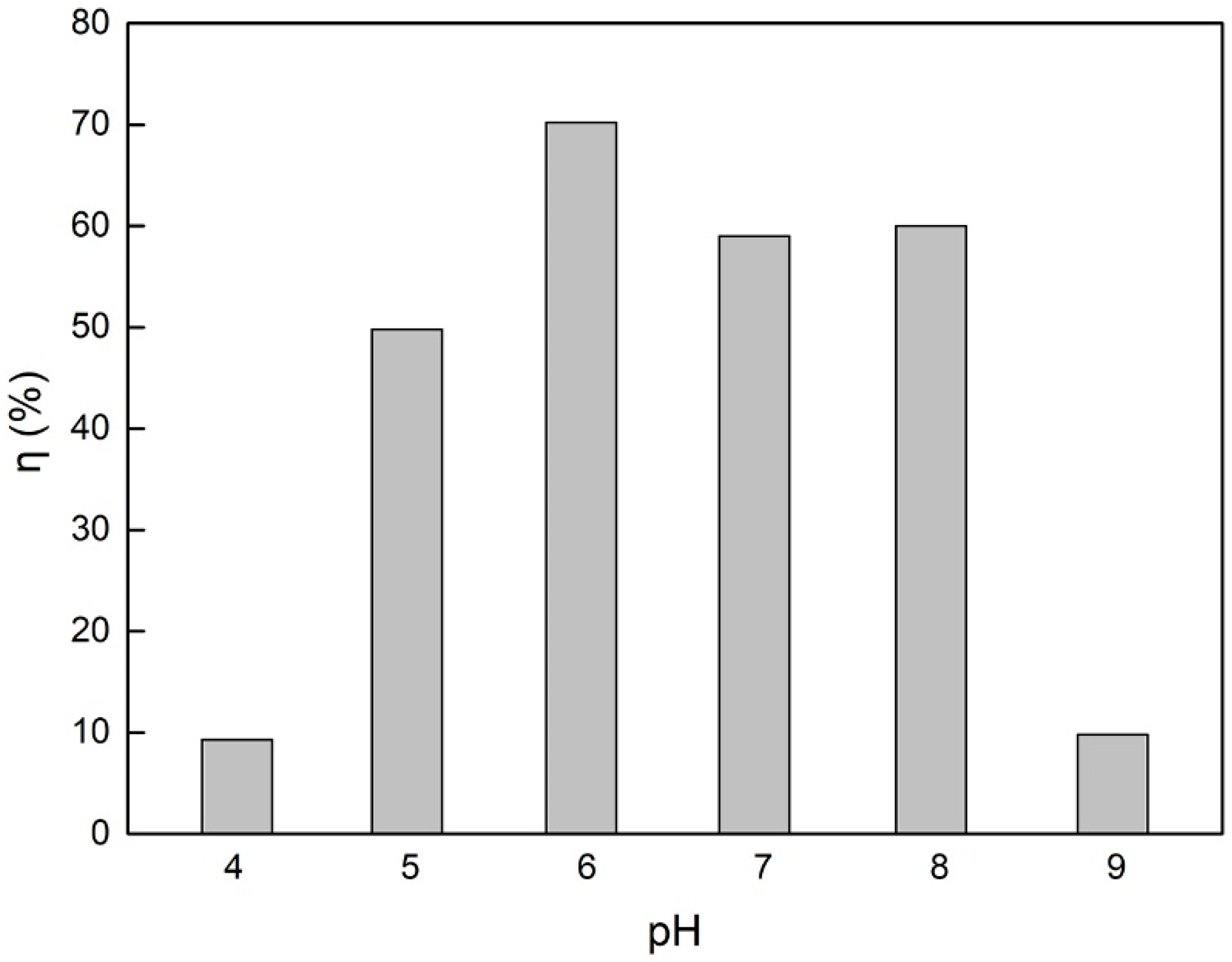
| pH value | 10 | 50 | 30 | 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
| Materials | SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 | 20.6 | 0.145 | 28.0 |
| g-C3N4/Fe3O4 | 38.8 | 0.129 | 13.3 |
| Langmuir Isotherm Parameters | Freundlich Isotherm Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | 24.9 | KF (L/mg) | 0.101 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.00134 | n | 1.354 |
| R2 | 0.9836 | R2 | 0.9872 |
| pH of Solutions | Possible Ionization Equations |
|---|---|
| Acid conditions | 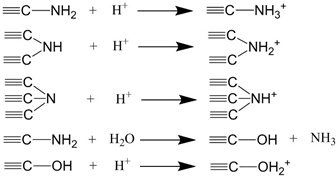 |
| Base conditions |  |
| Adsorbent | Qm (mg/g) | te | SBET (m2/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granular activated carbon | 977.6 | 12 h | 855 | [12] |
| Activated carbon | 238.10 | 48 h | 1140 | [13] |
| Modified dolomite | 74.1 | 120 min | 31.39 | [14] |
| Modified montmorillonite | 103.5796 | 30 min | - | [15] |
| Hydroxyapatite | 15 | 120 min | 145 | [16] |
| Organophilic-bentonite | 51.97 | 45 min | - | [17] |
| α-alumina | 2.4 | 60 min | - | [21] |
| Magnetic vermiculite | 75 | 240 min | 37.5 | [22] |
| Resin | 160.75 | 150 min | - | [23] |
| Waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide | 4.0 | 100 min | 156 | [24] |
| g-C3N4/Fe3O4 | 24.9 | 30 min | 38.8 | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Peng, Y. Preparation of Magnetic g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Composite and Its Application in the Separation of Catechol from Water. Materials 2019, 12, 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182844
Xu R, Peng Y. Preparation of Magnetic g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Composite and Its Application in the Separation of Catechol from Water. Materials. 2019; 12(18):2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182844
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ruilan, and Yong Peng. 2019. "Preparation of Magnetic g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Composite and Its Application in the Separation of Catechol from Water" Materials 12, no. 18: 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182844
APA StyleXu, R., & Peng, Y. (2019). Preparation of Magnetic g-C3N4/Fe3O4 Composite and Its Application in the Separation of Catechol from Water. Materials, 12(18), 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182844





