Corrosion Behavior of SMA490BW Steel and Welded Joints for High-Speed Trains in Atmospheric Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
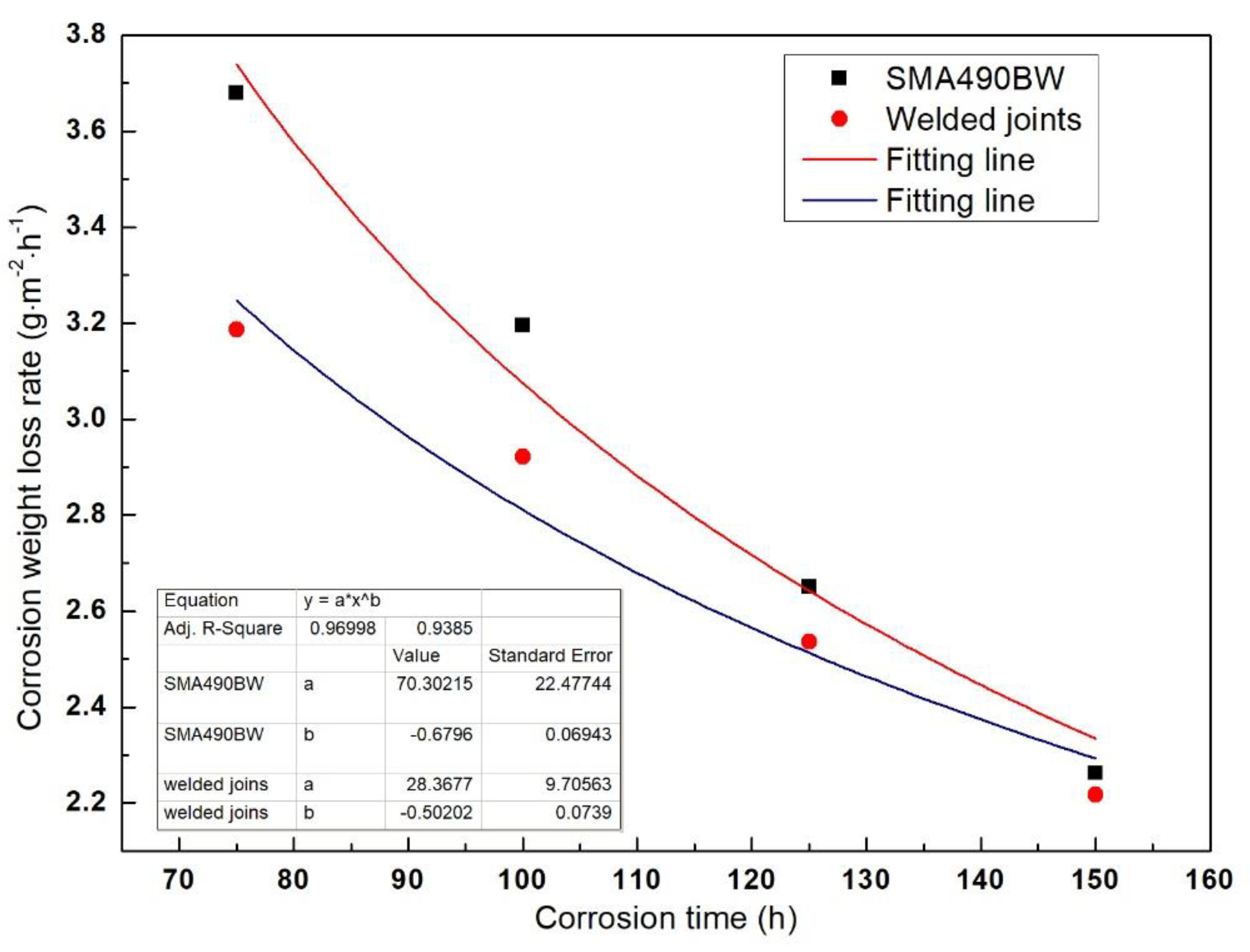
3.1. Corrosion Kinetics
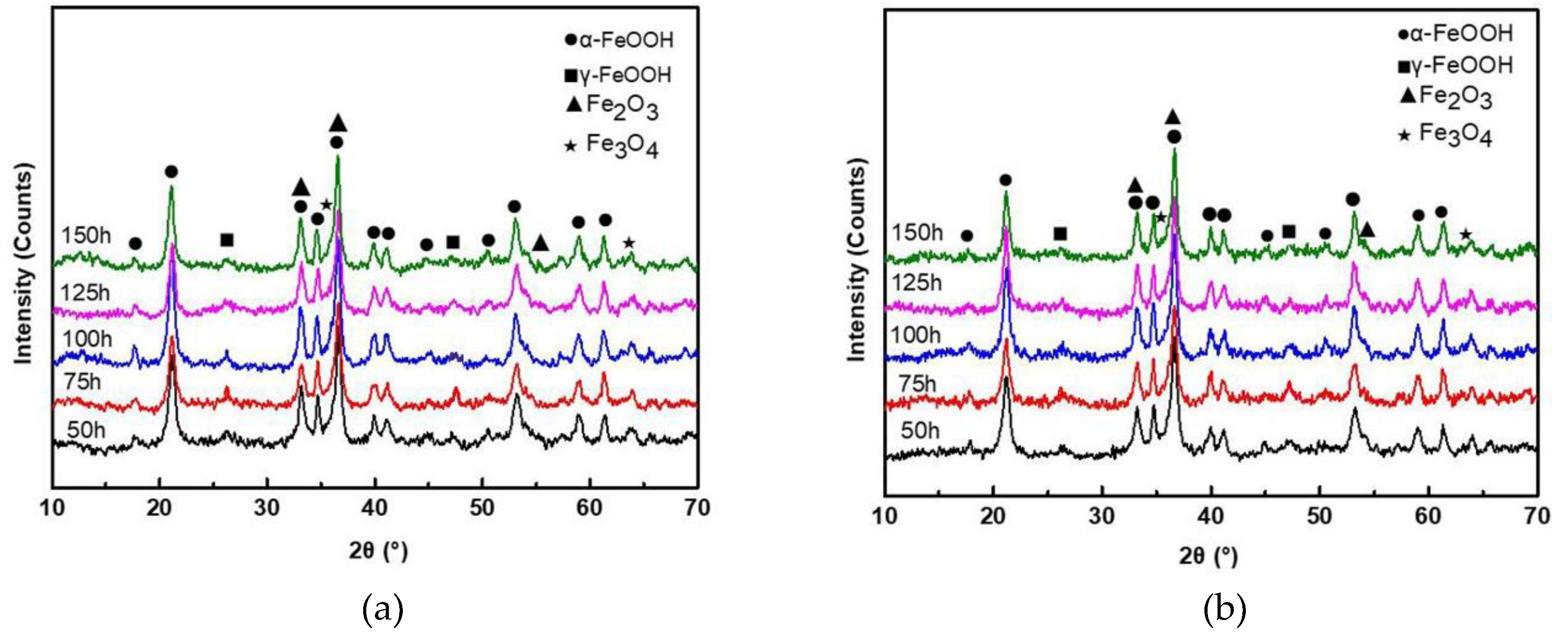
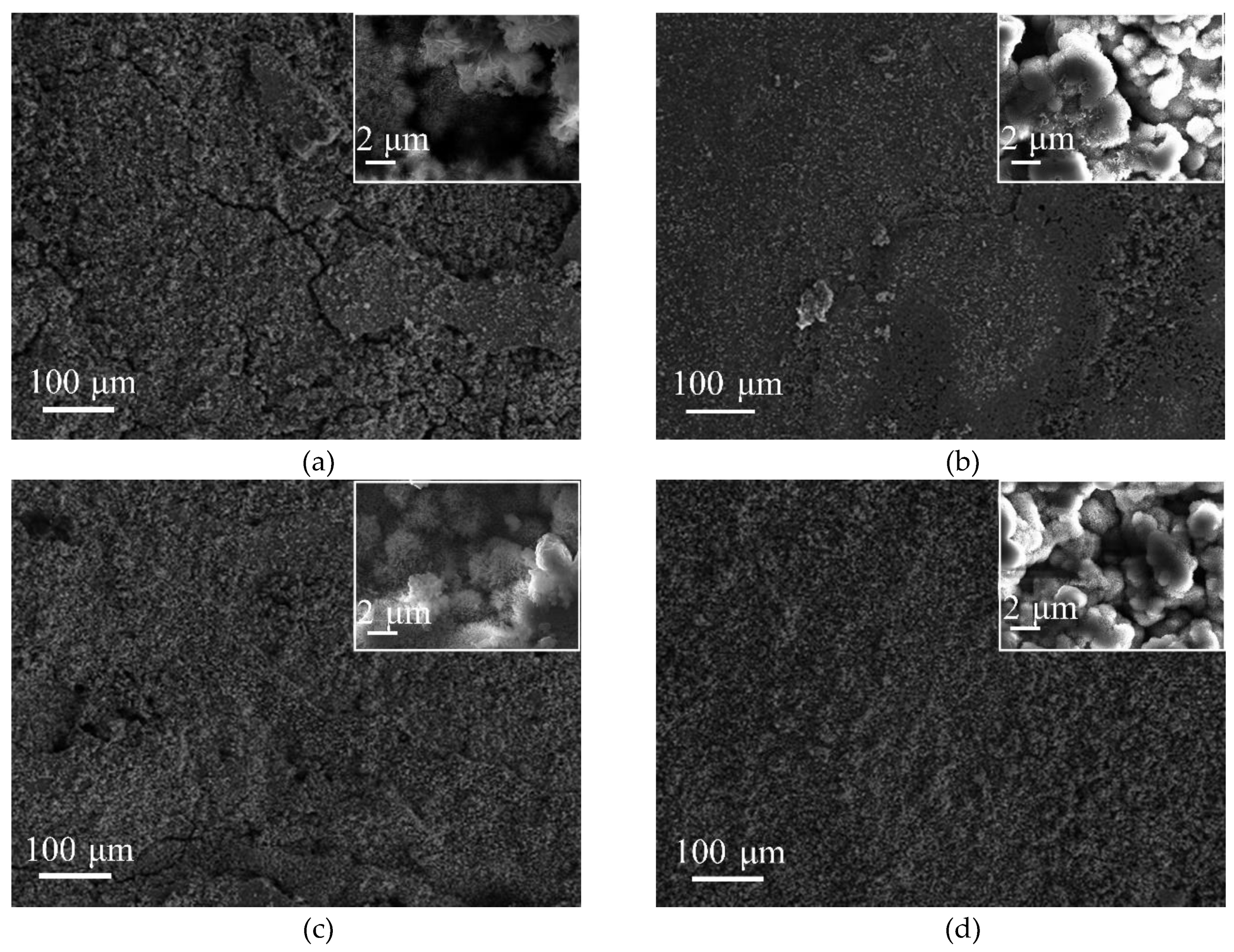
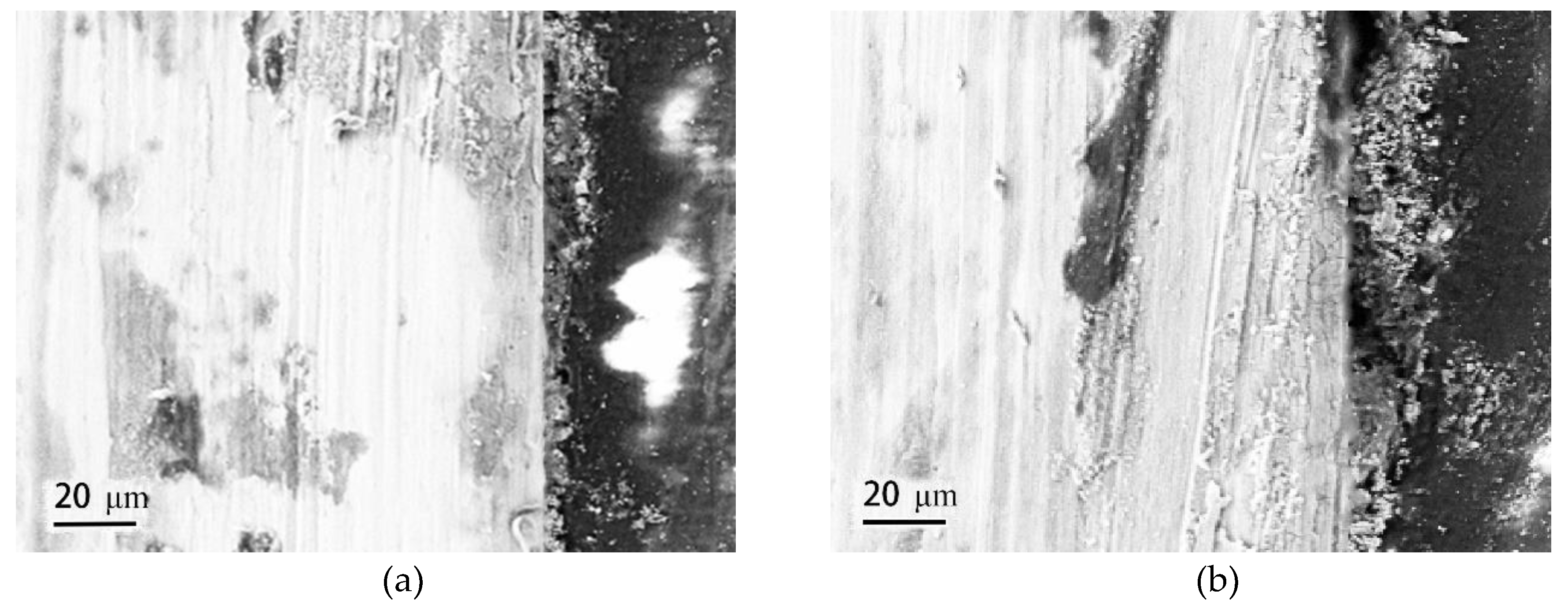
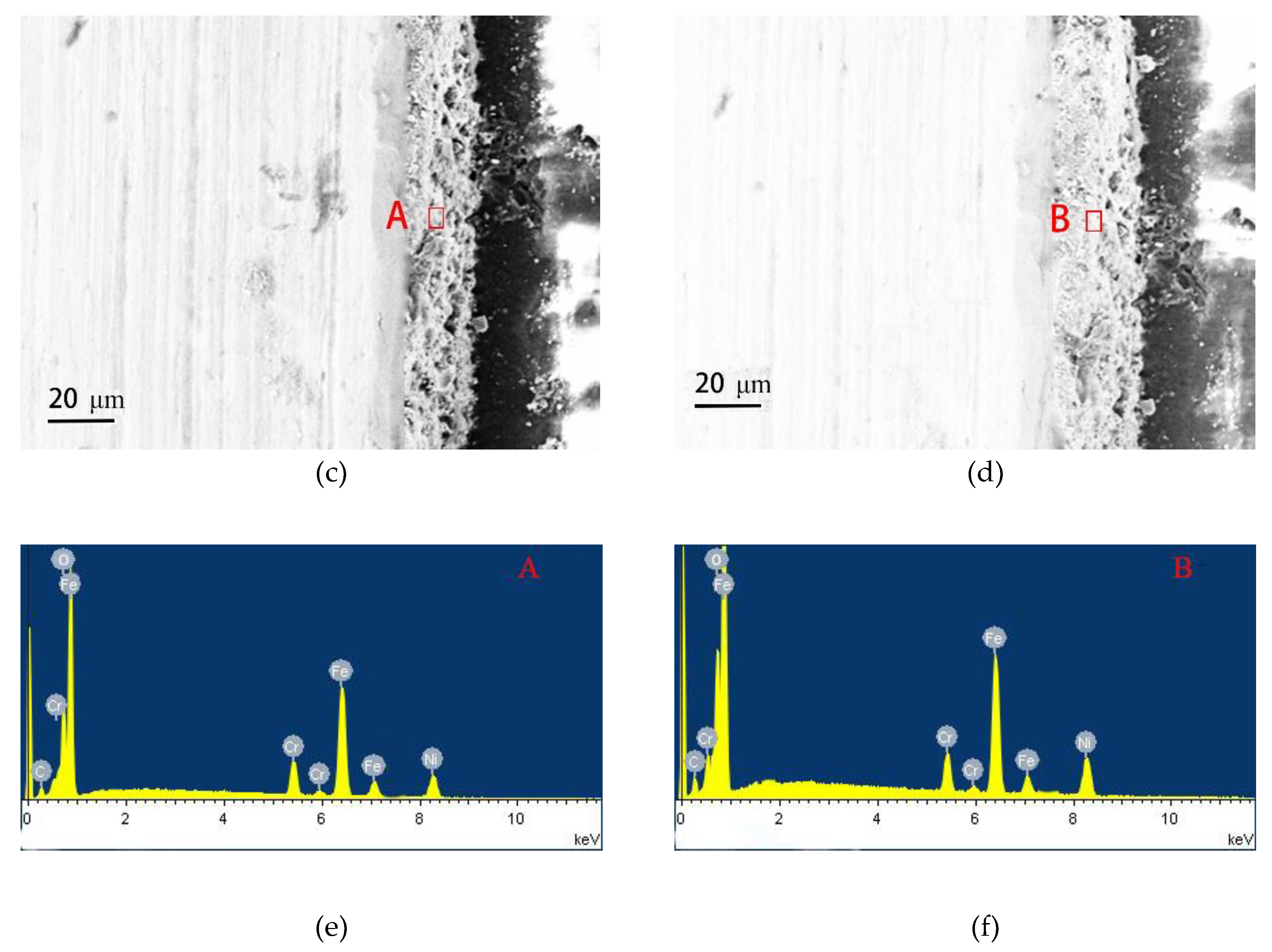
3.2. Surface Morphology and Phase Analysis of Rust Layers
3.3. Electrochemical Test
3.4. Corrosion Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Xiang, P.; Dong, P.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, J. Analysis of the effects of vibration modes on fatigue damage in high-speed train bogie frames. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 89, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chou, K. Effects of cerium on resistance to pitting corrosion of spring steel used in fasteners of high-speed railway. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Su, C. Corrosion inhibition of high speed steel by biopolymer HPMC derivatives. Materials 2016, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Chen, H.; Che, X.; Xu, L. Corrosion-fatigue crack propagation of aluminum alloys for high-speed trains. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 1744009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, J.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Effect of Ni on the ion-selectivity of rust layer on low alloy steel. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4050–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C. Corrosion behavior of nickel-containing weathering steel in simulated marine atmospheric environment. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Ke, W. Atmospheric corrosion resistance of MnCuP weathering steel in simulated environments. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 4187–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, W. Effects of inclusion on corrosion resistance of weathering steel in simulated industrial atmosphere. Anti. Corros. Method. Mater. 2016, 63, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, M.; Li, L. Surface grain refinement mechanism of SMA490BW steel cross joints by ultrasonic impact treatment. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2017, 4, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Corrosion of low carbon steel in atmospheric environments of different chloride content. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Han, R.; Sun, Y. Study of the corrosion behavior of weathering steels in atmospheric environments. Corros. Sci. 2013, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, I.; Kita, K. Evaluation of applicability for Ni-advanced weathering steels and bridge high-performance steels to railway steel bridges. Quart. Rep. Railw. Tech. Res. Inst. Jpn. 2010, 51, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tzeng, H.; Wei, L.; Wang, L.; Oung, J.; Shih, H. Corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of low-alloy steels under atmospheric conditions. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 1001–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente, D.; Díaz, I.; Simancas, J.; Chico, B.; Morcillo, M. Long-term atmospheric corrosion of mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 23, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, I.; Cano, H.; Fuente, D.; Chico, B.; Vega, J.; Morcillo, M. Atmospheric corrosion of Ni-advanced weathering steels in marine atmospheres of moderate salinity. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.; Han, W. A study on the initial corrosion behavior of carbon steel exposed to a simulated coastal-industrial atmosphere. Acta Metall. Sin. 2018, 54, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Guan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Pu, S. The corrosion resistance of ultralow carbon bainitic steel. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, S.; Shang, C.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Influence of carbon content and microstructure on corrosion behavior of low alloy steels in a Cl- containing environment. Corros. Sci. 2008, 51, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Mishima, R.; Hatanaka, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakayama, T. Formation of magnetite rust particles by reacting iron powder with artificial α-, β- and γ-FeOOH in aqueous media. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y.; Tao, D. Industrial atmospheric corrosion resistance of P-RE weathering steel. J. Iron. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Han, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, G. Evolution of initial atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel in an industrial atmosphere. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 5382–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, H.; Perrin, S.; Dillmann, P.; Legrand, L.; Chausse, A. Electrochemical study of indoor atmospheric corrosion layers formed on ancient iron artefacts. Electr. Acta 2007, 52, 7754–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, T.; Hara, S.; Miyuki, H.; Yamashita, M.; Uchida, H. Composition and protective ability of rust layer formed on weathering steel exposed to various environments. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. The atmospheric corrosion kinetics of low carbon steel in a tropical marine environment. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1796–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Effect of surface finishing on early-stage corrosion of a carbon steel studied by electrochemical and atomic force microscope characterizations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ma, C.; Niu, D.; Xu, J.; Li, M. Influence of alloyed chromium on the atmospheric corrosion resistance of weathering steels. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H. The role of rusts in corrosion and corrosion protection of iron and steel. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, C.; Briones, F.; Villarroel, M.; Vera, R. Effect of Atmospheric Corrosion on the Mechanical Properties of SAE 1020 Structural Steel. Materials 2018, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Suzuki, T.; Shigesato, G.; Kihira, H.; Tanabe, K. Fe(O,OH)6 network structure of rust formed on weathering steel surfaces and its relationship with corrosion resistance. Nippon. Steel Tech. Rep. 2003, 87, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, T.; Katayama, H.; Noda, K.; Kodama, T. Effect of Co and Ni on the corrosion behavior of low alloy steels in wet/dry environments. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Miyuki, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Magano, H.; Misawa, T. The long term growth of the protective rust layer formed on weathering steel by atmospheric corrosion during a quarter of a century. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Peng, Y.; Ma, C.; Tian, Z. Effects of alloy element and microstructure on corrosion resistant property of deposited metals of weathering steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2016, 23, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, H. Effects of alloying elements on the corrosion of steel in industrial atmospheres. Corrosion 2001, 57, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, X. New insight into high frequency impacting and rolling of 2A12 aluminum welded joint involving nanocrystallization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
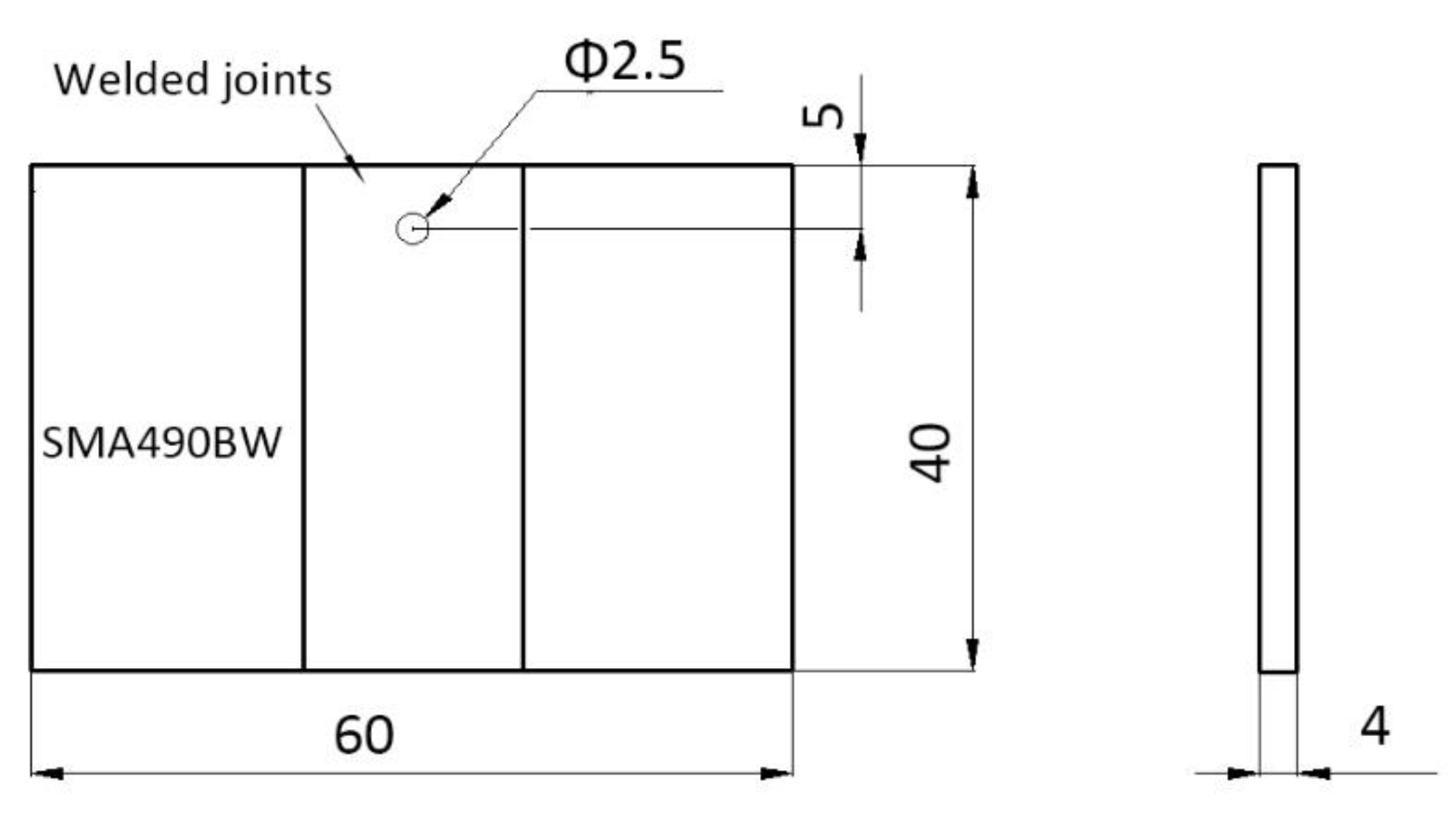


| Materials | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cu | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA490BW | ≤0.18 | 0.15–0.65 | ≤1.40 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.035 | 0.30–0.50 | 0.45–0.75 | 0.08–0.25 | Bal. |
| CHW-55CNH | ≤0.10 | 0.35–0.65 | 1.20–1.60 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | 0.20–0.50 | 0.30–0.90 | 0.20–0.60 | Bal. |
| Number of Weld Passes | Welding Current (I)/A | Arc Voltage (U)/V | Welding Speed (v)/(mm·s−1) | Welding Heat Input (E)/(kJ·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 240 | 25 | 8.3 | 4.3 |
| 2–4 | 245–250 | 27 | 5.0–8.3 | 6.4 |
| Material | Corrosion Rate of Weight Loss (W)/(g·m−2·h−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 h | 75 h | 100 h | 125 h | 150 h | |
| SMA490BW | 3.3212 | 3.6792 | 3.1943 | 2.6497 | 2.2619 |
| Welded joint | 3.0149 | 3.1862 | 2.9217 | 2.5361 | 2.2175 |
| Corrosion Time | SMA490BW | Welded Joints | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr(V/SCE) | icorr(×10−5A/cm2) | Ecorr(V/SCE) | icorr(×10−5A/cm2) | |
| 75 h | −0.553 | 1.749 | −0.489 | 1.654 |
| 100 h | −0.644 | 1.411 | −0.635 | 1.393 |
| 125 h | −0.716 | 1.187 | −0.698 | 1.135 |
| 150 h | −0.806 | 1.063 | −0.782 | 0.962 |
| Materials | Fe | O | Ni | Cu | Cr | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA490BW (before) | 92.9 | - | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.54 | - |
| SMA490BW (after) | 58.51 | 34.95 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 1.26 | 1.39 |
| Welded joints (before) | 89.94 | - | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.75 | - |
| Welded joints (after) | 56.21 | 36.21 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 1.81 | 1.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, W.; Tian, R.; Huang, S.; Shi, C. Corrosion Behavior of SMA490BW Steel and Welded Joints for High-Speed Trains in Atmospheric Environments. Materials 2019, 12, 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12183043
Wu X, Zhang Z, Qi W, Tian R, Huang S, Shi C. Corrosion Behavior of SMA490BW Steel and Welded Joints for High-Speed Trains in Atmospheric Environments. Materials. 2019; 12(18):3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12183043
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiangyang, Zhiyi Zhang, Weichuang Qi, Renyong Tian, Shiming Huang, and Chunyuan Shi. 2019. "Corrosion Behavior of SMA490BW Steel and Welded Joints for High-Speed Trains in Atmospheric Environments" Materials 12, no. 18: 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12183043
APA StyleWu, X., Zhang, Z., Qi, W., Tian, R., Huang, S., & Shi, C. (2019). Corrosion Behavior of SMA490BW Steel and Welded Joints for High-Speed Trains in Atmospheric Environments. Materials, 12(18), 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12183043




