Experimental and Numerical Study of AISI 4130 Steel Surface Hardening by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
3. Numerical Model
4. Results and Discussion
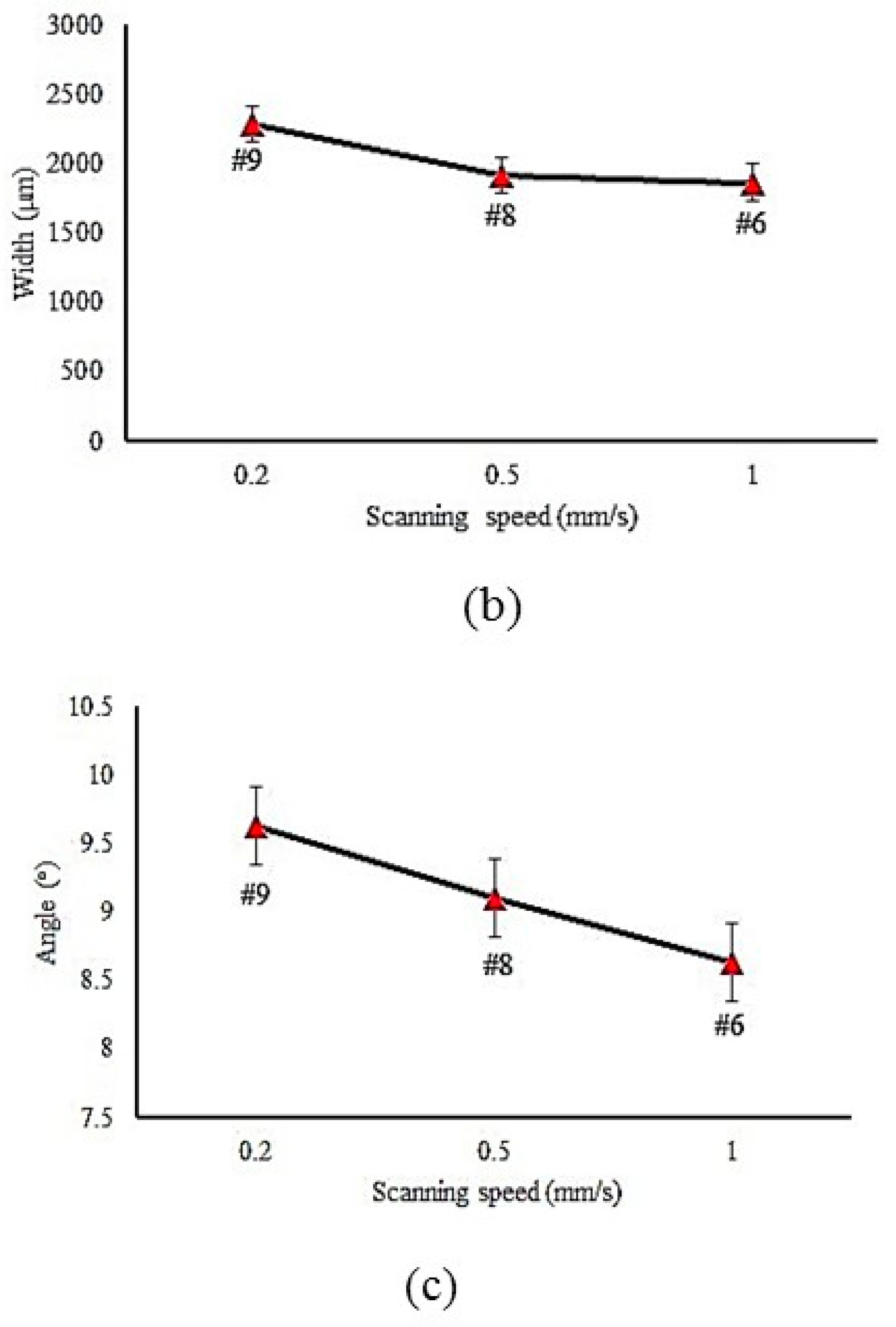
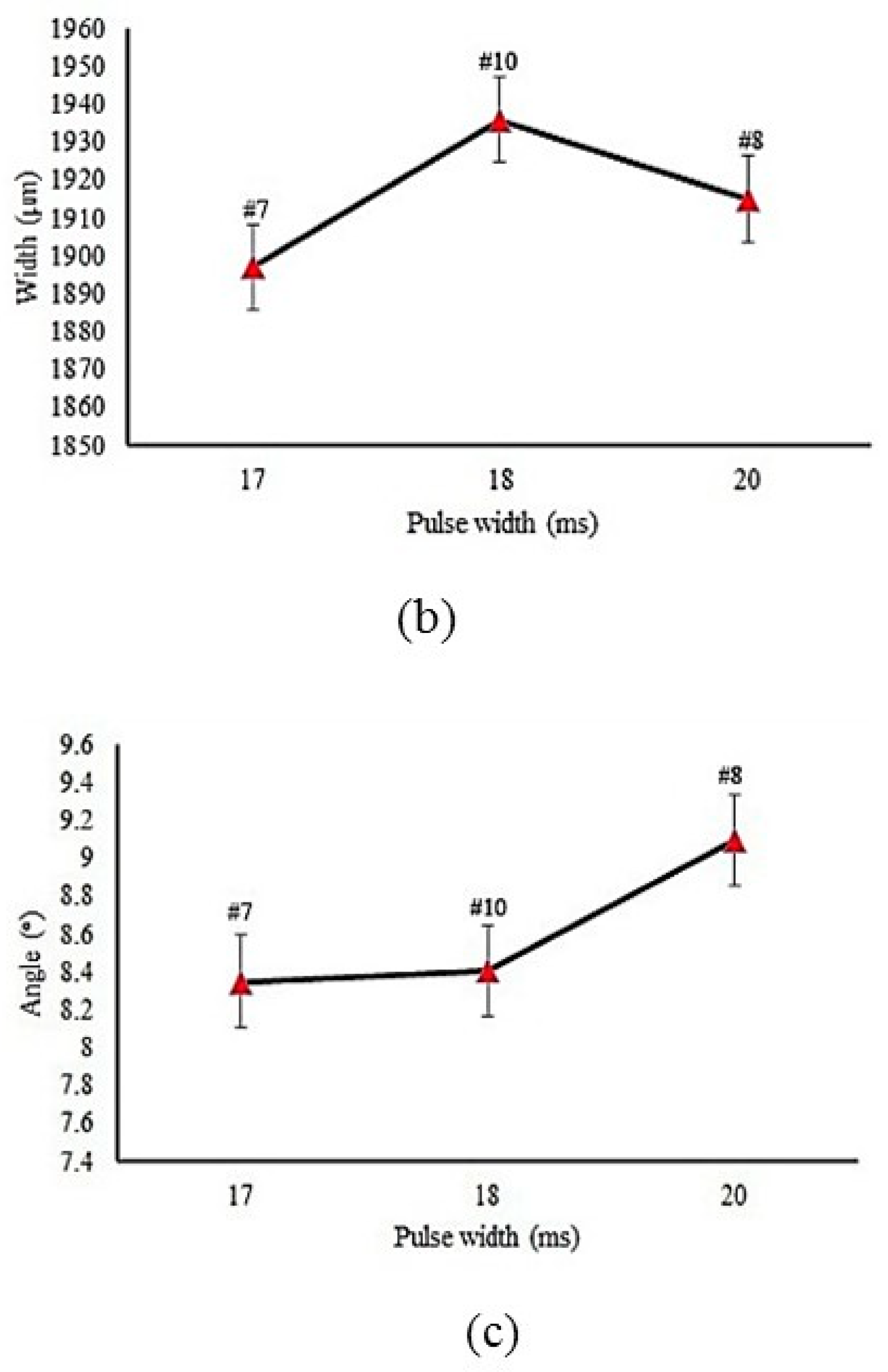
4.1. Hardened Case Geometry
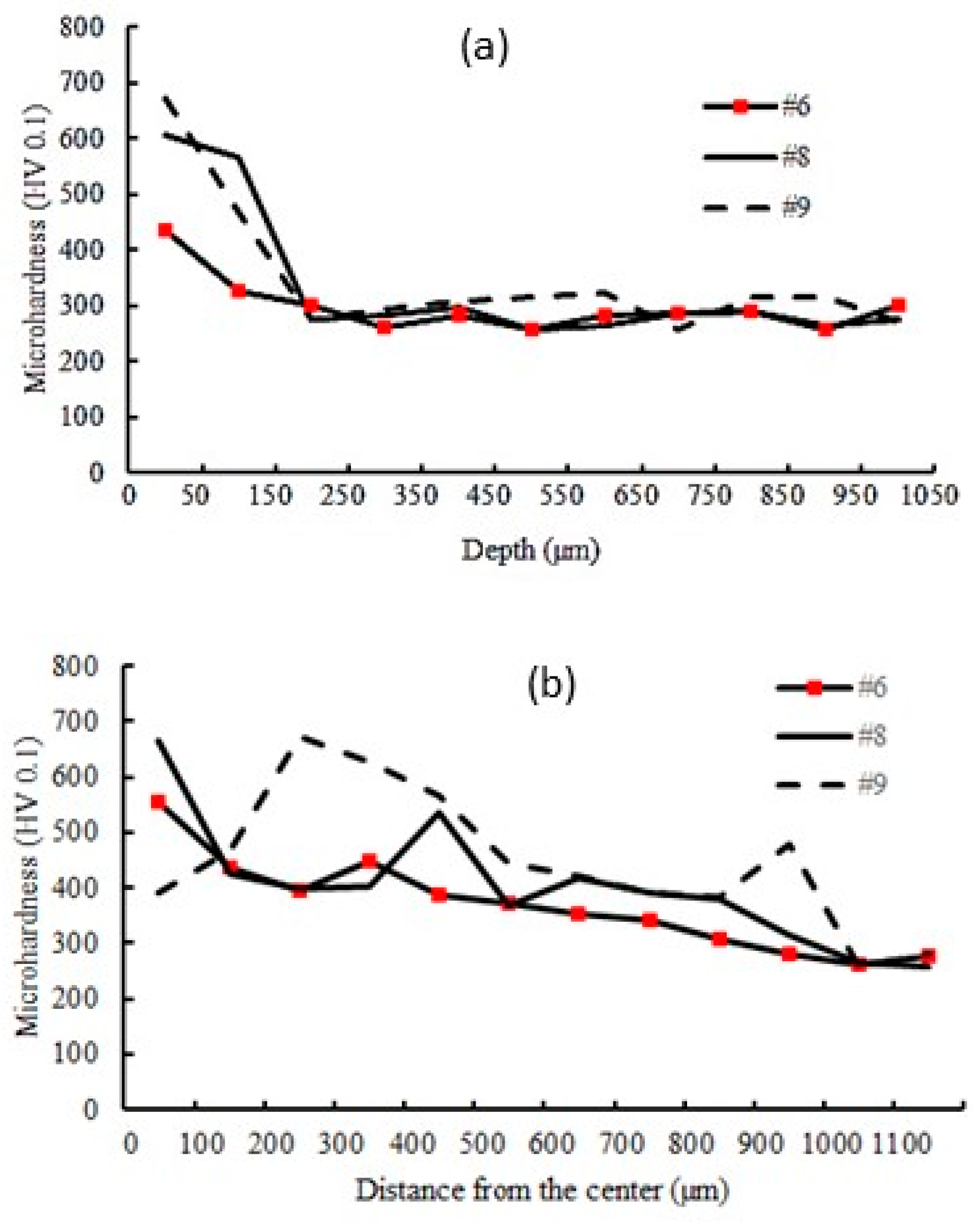
4.2. Micro-Hardness Distribution
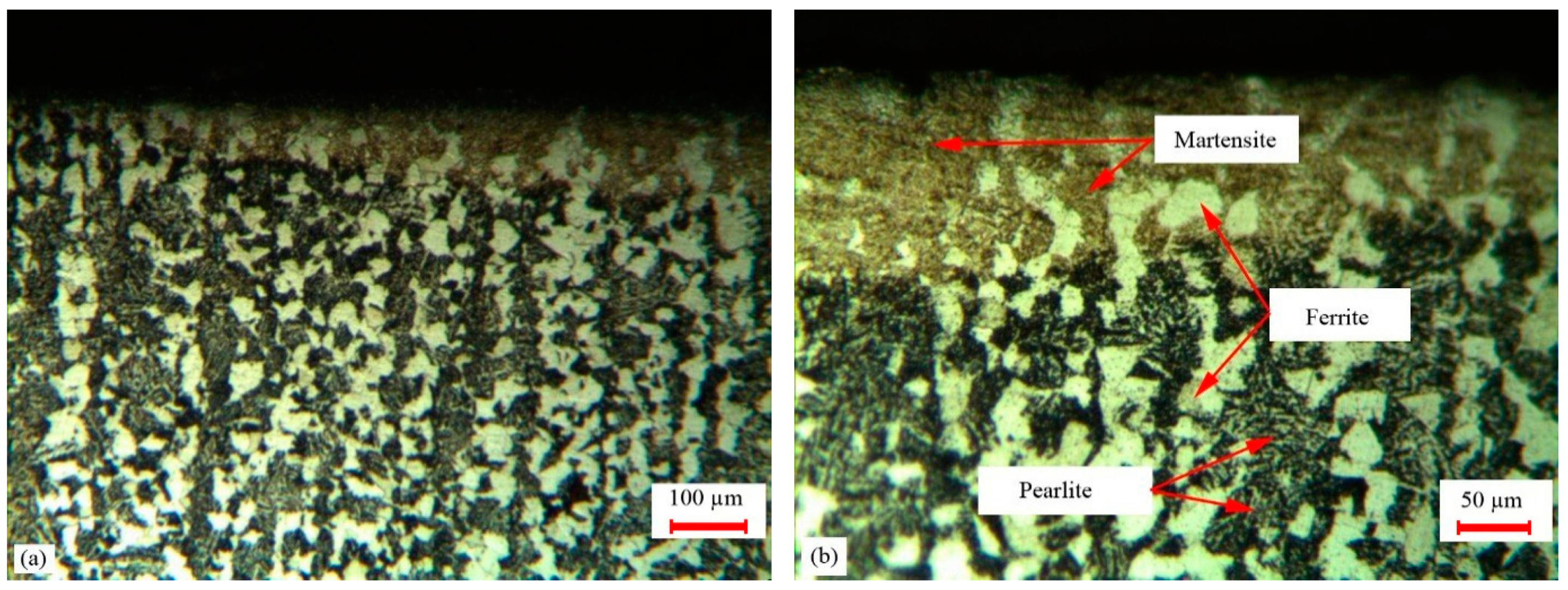
4.3. Microstructure Analysis
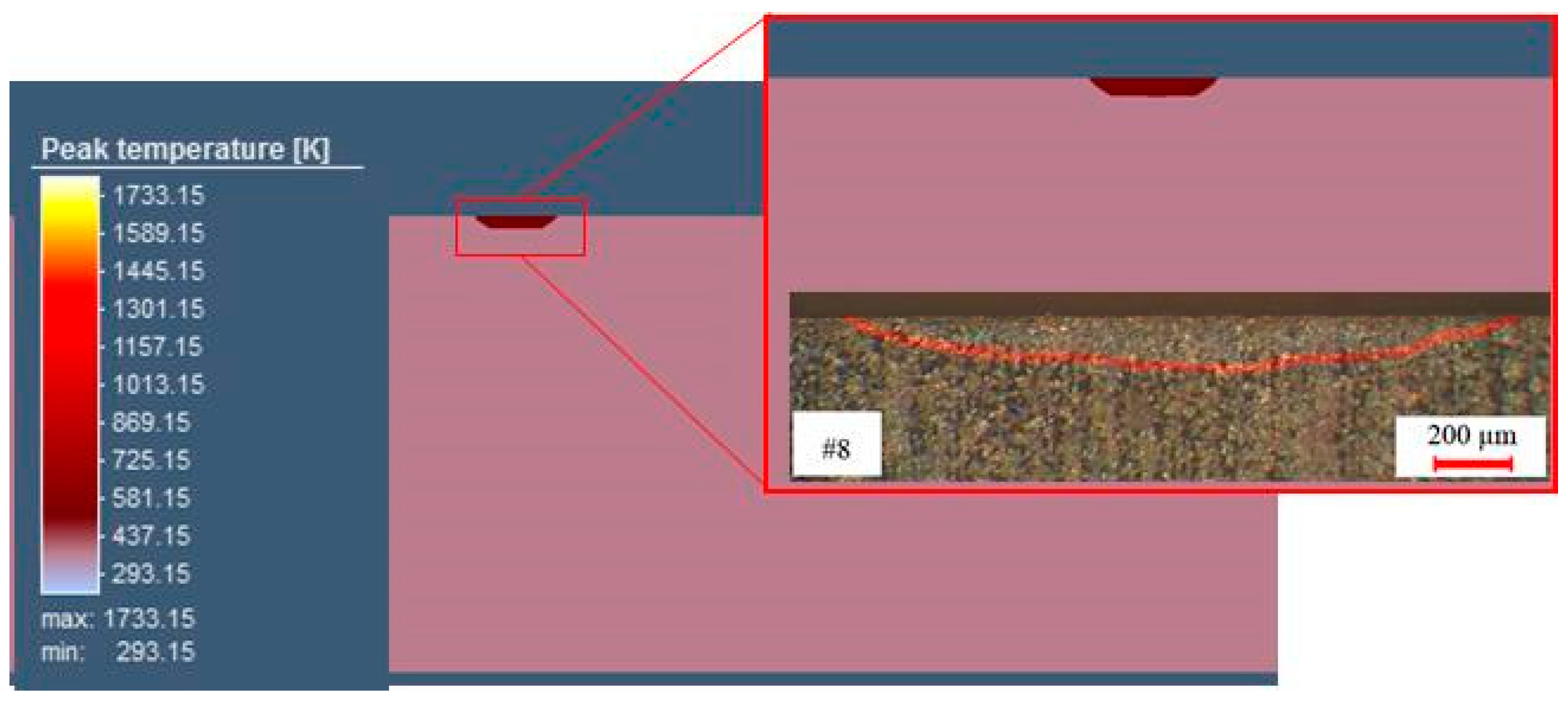
5. Calibration and Validation of the Numerical Model
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Pulse width has a significant effect on the pulsed laser surface hardening process. With increasing pulse width, the hardness value and hardened depth increase.
- (2)
- Decreasing LSS causes the hardness value to increase. There is a lower ferrite phase in the laser hardened layer.
- (3)
- By decreasing the focal plane position, laser energy density increases, which causes the hardness value to increase. The surface of samples #2, #3, and #4 were melted due to lower focal plane position distance, which led to higher energy concentration.
- (4)
- Sample #9 with the higher martensitic phase percentage had more hardness and higher MHD values. Additionally, in the laser hardened zone, some ferrite phase with some retained austenite was observed.
- (5)
- The maximum hardness value for the LH cases is 673 Vickers while this value for the furnace hardened cases is 572 Vickers, because there is a minor ferrite phase in LH cases compared to furnace hardened cases.
- (6)
- The results of the numerical model show that the heat source model can predict with accuracy the temperature profile and the size and the shape of the hardened region. The continuous cooling transformation (CCT) curve for AISI 4130 steel confirmed the validation of the numerical model at metallurgical transformation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moradi, M.; Ghoreishi, M.; Khorram, A. Process and Outcome Comparison Between Laser, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) and Laser-TIG Hybrid Welding. Laser Eng. 2018, 39, 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji, A.H.; Moradi, M.; Goodarzi, M.; Colucci, P.; Maletta, C. An investigation on capability of hybrid Nd:YAG laser-TIG welding technology for AA2198 Al-Li alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Golchin, E. Investigation on the Effects of Process Parameters on Laser Percussion Drilling Using Finite Element Methodology; Statistical Modelling and Optimization. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 14, 464–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.B.; Lee, H.K.; Park, H.C. Effect of grain size on the indentation hardness for polycrystalline materials by the modified strain gradient theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannatey, E.; Asibu, J. Principles of Laser Materials Processing; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, M.; Ghorbani, D.; Moghadam, M.K.; Kazazi, M.; Rouzbahani, F.; Karazi, S. Nd:YAG laser hardening of AISI 410 stainless steel: Microstructural evaluation, mechanical properties, and corrosion behavior. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 795, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.; Cheng, F.; Man, H. Laser transformation hardening of AISI 440C martensitic stainless steel for higher cavitation erosion resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 173, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, P.; Koshy, P.; Stenekes, J.; Elbestawi, M. High-power diode laser assisted hard turning of AISI D2 tool steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, B.; Torkamany, M.; Aghdam, A.S.R.; Sabbaghzade, J. Laser surface hardening of AISI 420 stainless steel treated by pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badkar, D.; Pandey, K.; Buvanashekaran, G. Effects of laser phase transformation hardening parameters on heat input and hardened-bead profile quality of unalloyed titanium. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Moghadam, M.K.; Kazazi, M. Improved laser surface hardening of AISI 4130 low alloy steel with electrophoretically deposited carbon coating. Opt. 2019, 178, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jin, Y.J.; Li, Z.G.; Qi, K. A comparative study of high-power diode laser and CO2 laser surface hardening of AISI 1045 steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinovic, M.; Mole, N.; Stok, B. A computer simulation study of the effects of temperature change rate on austenite kinetics in laser hardening. Surf Coat Technol. 2015, 273, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telasang, G.; Dutta Majumdar, J.; Padmanabham, G.; Manna, I. Wear and corrosion behavior of laser surface engineered AISI H13 hot working tool steel. Surf Coat Technol. 2015, 261, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien, A.; Szkodo, M. Surface treatment of C80U steel by long CO2 laser pulses. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2015, 217, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordovilla, F.; García-Beltrán, Á.; Sancho, P.; Domínguez, J.; De Lara, L.R.; Ocaña, J.L. Numerical/experimental analysis of the laser surface hardening with overlapped tracks to design the configuration of the process for Cr-Mo steels. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, S.; Barletta, M.; Afilal, A. High Power Diode Laser (HPDL) surface hardening of low carbon steel: Fatigue life improvement analysis. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, B.; Shariff, S.M.; Padmanabham, G.; Lenka, S.; Bhattacharya, B.; Kundu, S. Influence of laser surface hardened layer on mechanical properties of re-engineered low carbon steel sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 685, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, J.H.; Benyounis, K.Y.; Julifkar, H.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Material response with high power laser in surface treatment of ferrous alloys. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netprasert, O.; Tangwarodomnukun, V.; Dumkum, C. Surface Hardening of AISI 420 Stainless Steel by Using a Nanosecond Pulse Laser. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 911, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, O.; Yilmaz, S. Investigation of effect of various processing temperatures on abrasive wear behavior of high power diode laser treated R260 grade rail steels. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesyk, D.A.; Martínez, S.; Mordyuk, B.; Dzhemelinskyi, V.V.; Lamikiz, A.; Prokopenko, G.I.; Grinkevych, K.; Tkachenko, I.V. Laser-hardened and ultrasonically peened surface layers on tool steel AISI D2: Correlation of the bearing curves parameters, hardness and wear. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, N.; Brousseau, J. Case study of laser hardening process applied to 4340 steel cylindrical specimens using simulation and experimental validation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2018, 11, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Casalino, G.; Giorleo, L.; Capello, E. Post treatment laser irradiation for recovery of deformation induced by surface laser hardening. AIP Conference Proceedings 2019, 1181, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasiou, C.E.; Hongler, M.O.; Bellouard, Y. Unraveling Brittle-Fracture Statistics from Intermittent Patterns Formed During Femtosecond Laser Exposure. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, C.E.; Bellouard, Y. A Monolithic Micro-Tensile Tester for Investigating Silicon Dioxide Polymorph Micromechanics, Fabricated and Operated Using a Femtosecond Laser. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1365–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaee, I.; Khomami, M.N.; Attar, A.A. Corrosion of AISI 4130 steel alloy under hydrodynamic condition in ethylene Glycol+Water+NO2 L solution. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- John, W. Pridgeon, Metallography and Microstructures; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1992; pp. 803–805. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, H. Heat Treater’s Guide, Practices and Procedures for Nonferrous Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1996; pp. 96–97. [Google Scholar]
- Olabi, A.G.; Casalino, G. Mathematical Modeling of Weld Phenomena. Part 1: Finite-Element Modeling. Compr. Process. 2014, 6, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, D. Mathematical theory of heat distribution during welding and cutting. Welding J. 1941, 20, 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Pavelec, V.; Tanbakuchi, R.; Uyehara, O.A.; Myers, P.S. Experimental and computed temperature histories in gas tungsten arc welding of thin plates. Weld. J. Res. Suppl. 1969, 48, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Azizpour, M.; Ghoreishi, M.; Khorram, A. Numerical simulation of laser beam welding of Ti6Al4V sheet. J. Comput. Appl. Res. Mech. Eng. 2015, 4, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokhi, F.; Endelt, B.; Kristiansen, M. A numerical model for full and partial penetration hybrid laser welding of thick-section steels. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 111, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukkan, J.R.; Vasudevan, M.; Muthukumaran, S.; Kumar, R.R.; Chandrasekhar, N. Simulation of laser butt welding of AISI 316L stainless steel sheet using various heat sources and experimental validation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 219, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, E.D.; Yazdian, N.; Craft, B.; Smith, S.; Kovacevic, R. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of residual stress and welding distortion induced by laser-based welding processes of thin structural steel plates in butt joint configuration. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 104, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G.D.; Pandey, A.K. Pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam drilling: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 100, 183–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, F.; Heß, A.; Dausinger, F. Focusing of high power single mode laser beams. Int. Congr. Appl. Lasers-Electro-Opt. 2007, 2007, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Kuryntsev, S.; Gilmutdinov, A. Welding of stainless steel using defocused laser beam. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2015, 114, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowski, M. Influence of Parameters of Laser Beam Welding on Structure of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2019, 19, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abboud, J.; Fidel, A.; Benyounis, K.; Abboud, J. Surface nitriding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with a high power CO2 laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2008, 40, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, K. Investigating the multiple-pulse drilling on titanium alloy in picosecond laser. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 268, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkin, M.A.; Kiselev, A.S.; Slobodyan, M.S. Pulsed laser welding of Zr 1% Nb alloy. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 51, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Tsai, W.J.; Liu, S.H.; Horng, J.B. Picosecond laser pulse polishing of ASP23 steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Zheng, T.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. Superconducting properties and microstructures of CeO2 doped YBa2Cu3O7−δ films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1998–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, A.; Emamian, A.; Kowkabi, A.H. Effects of Fillerwire Composition along with Different Pre- and Post-Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of AISI 4130 Welded by the GTAW Process. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2010, 1, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

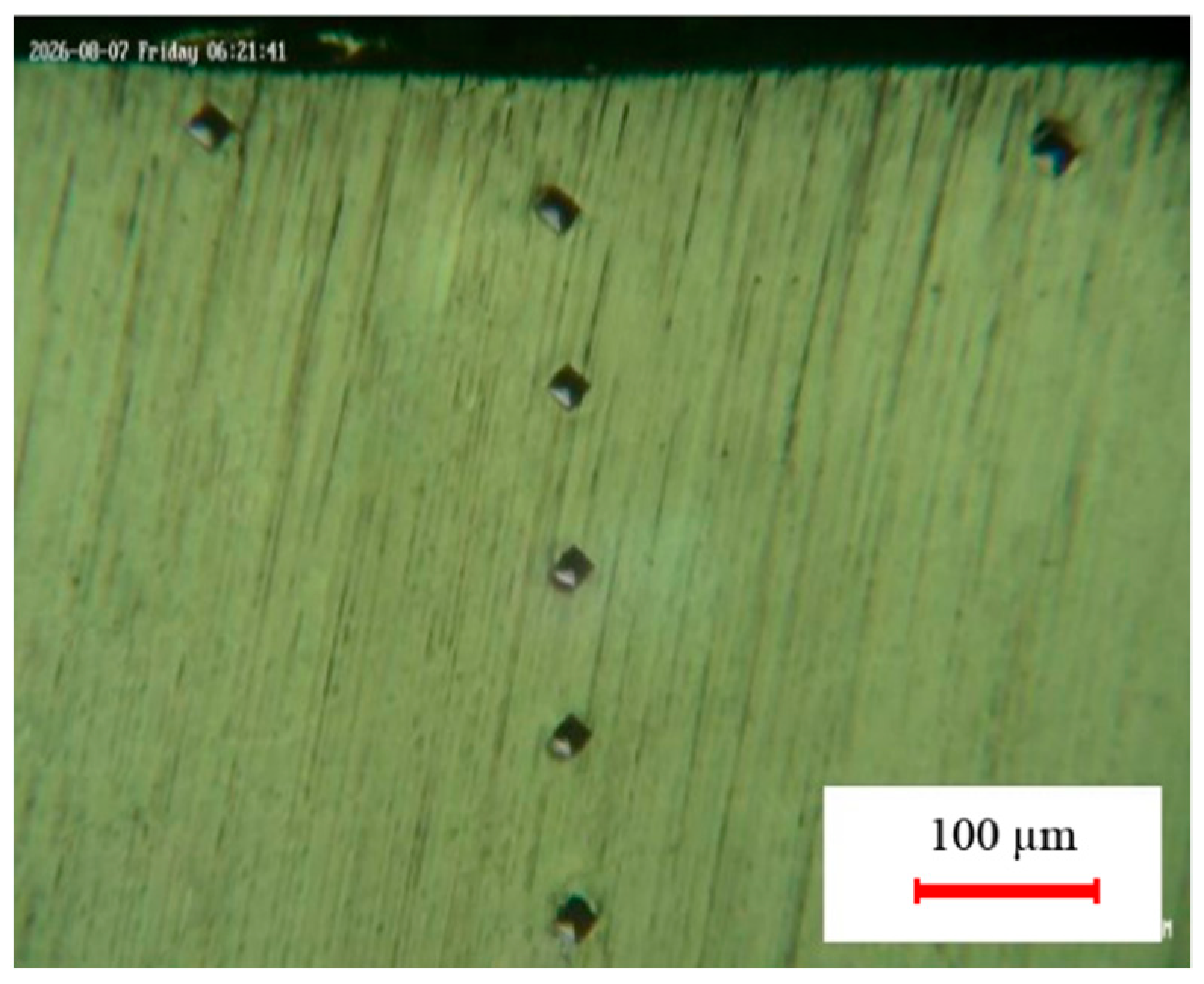

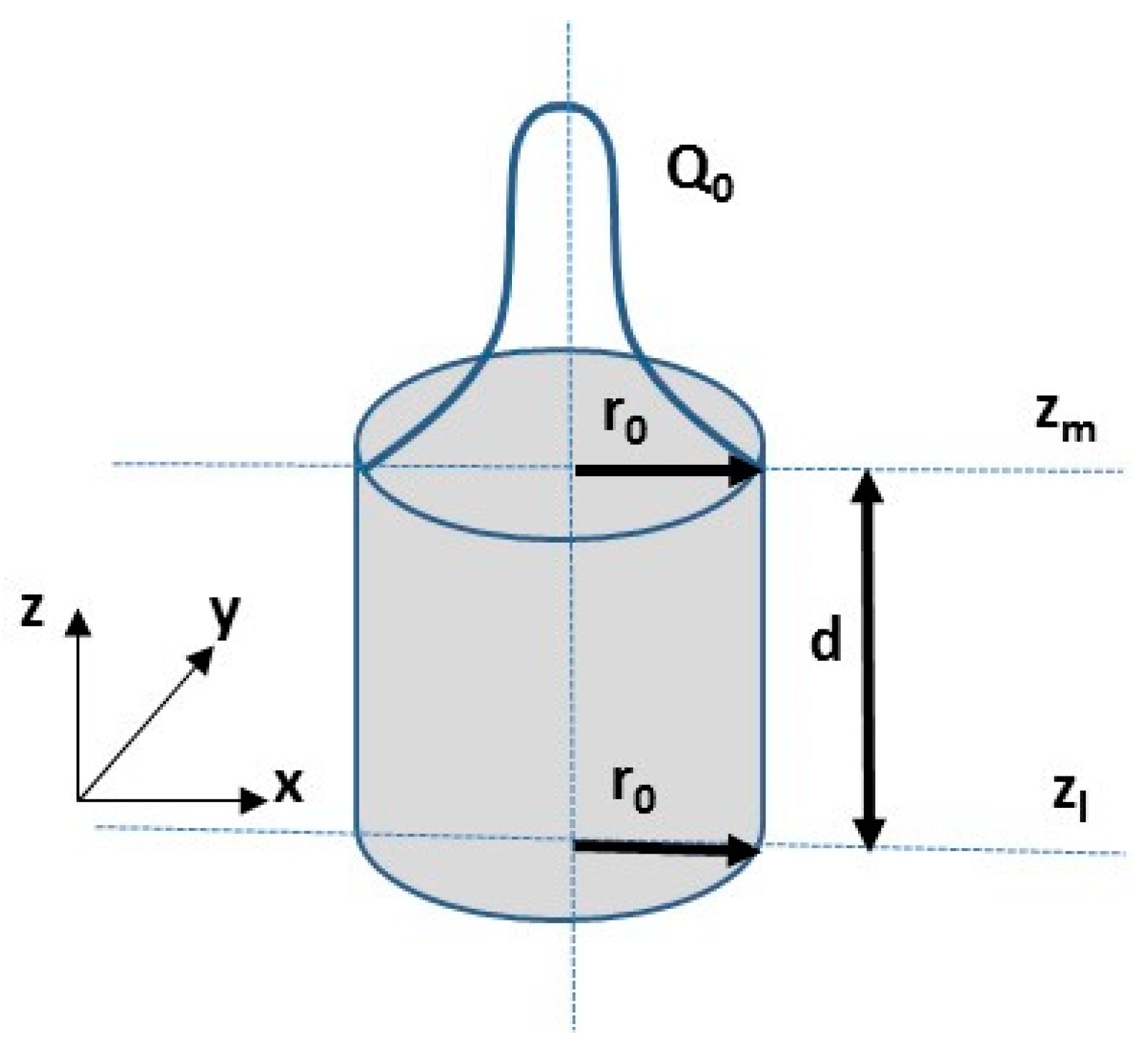

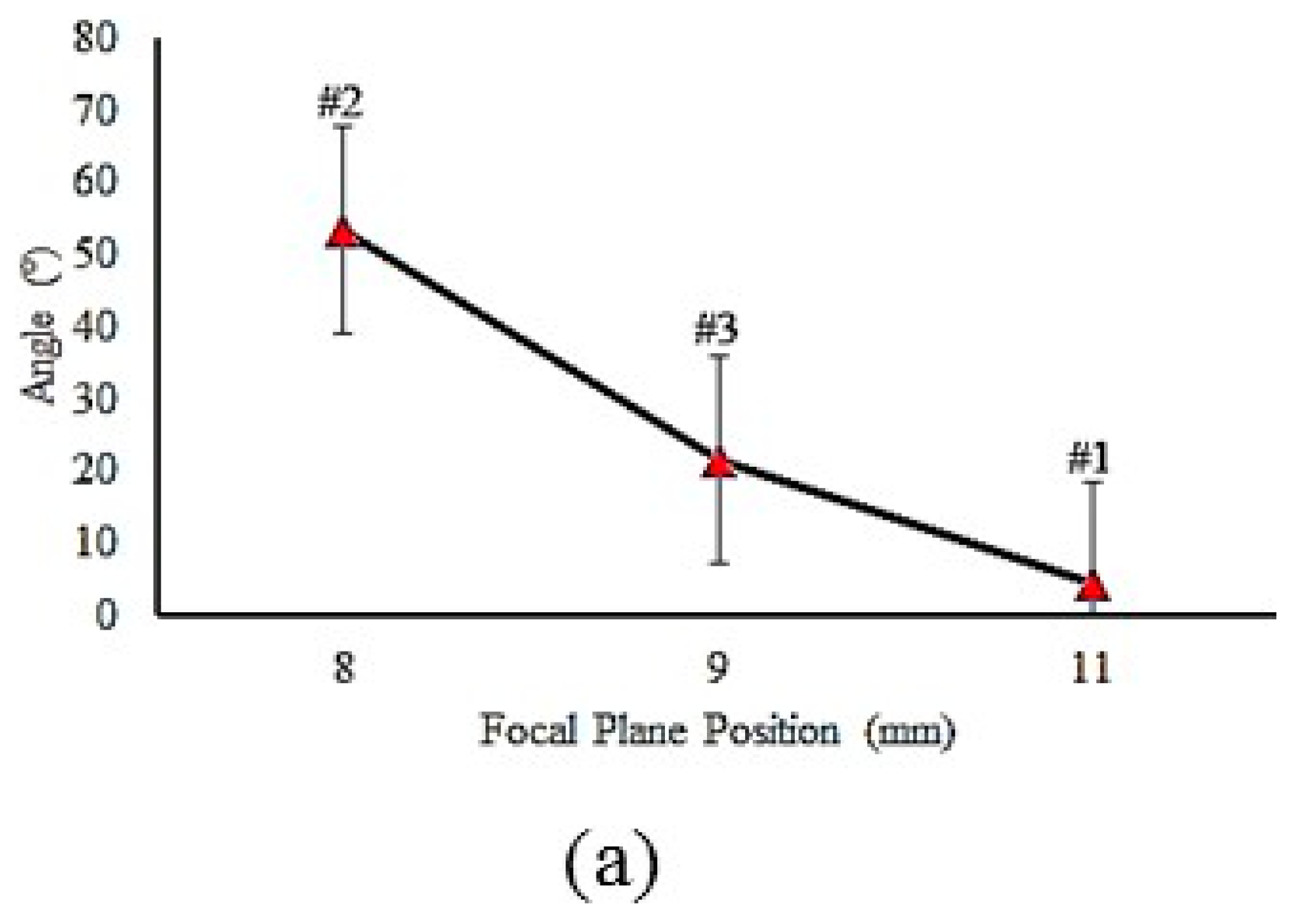
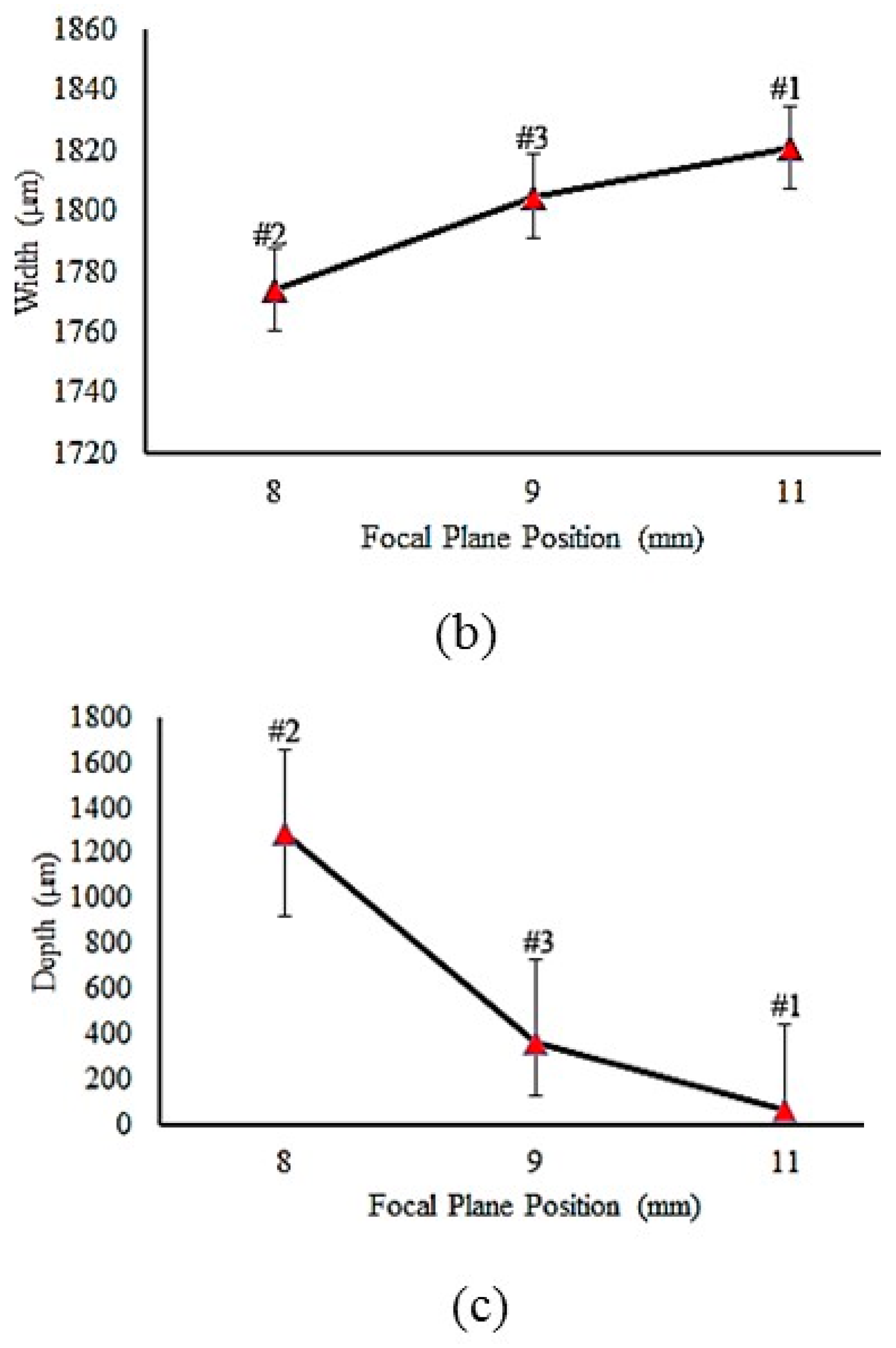




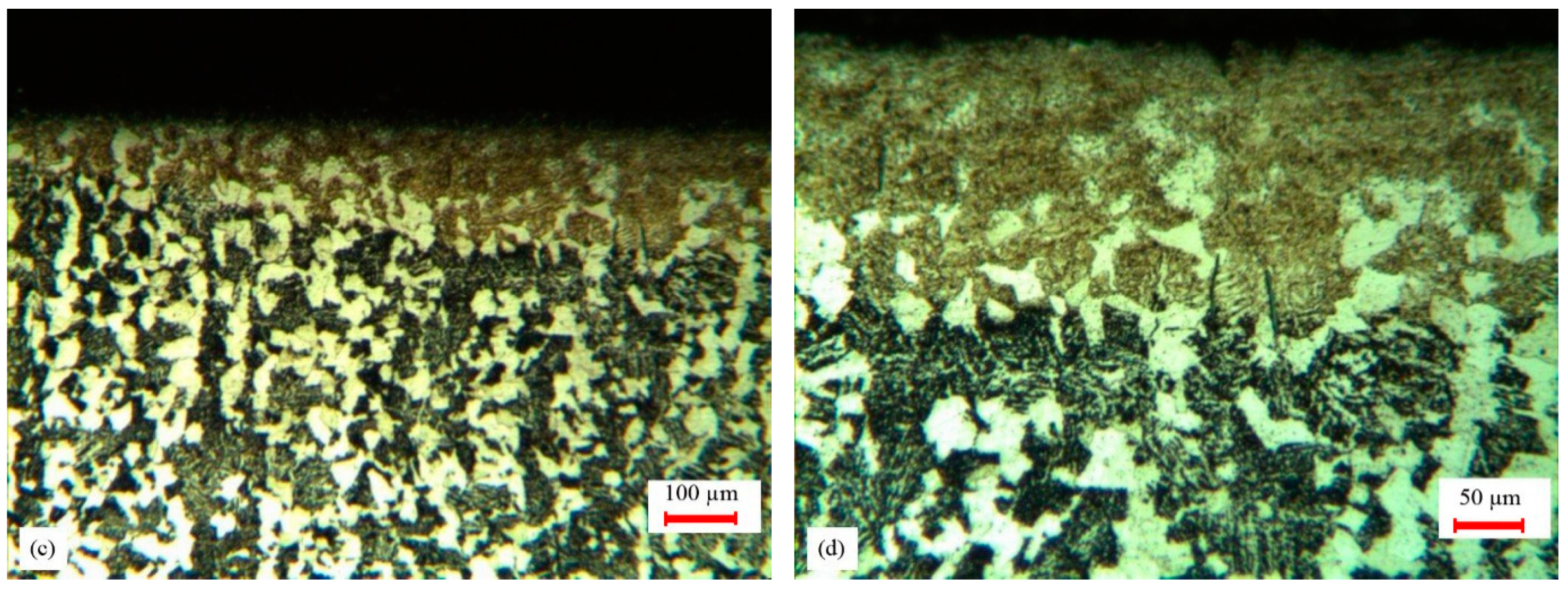
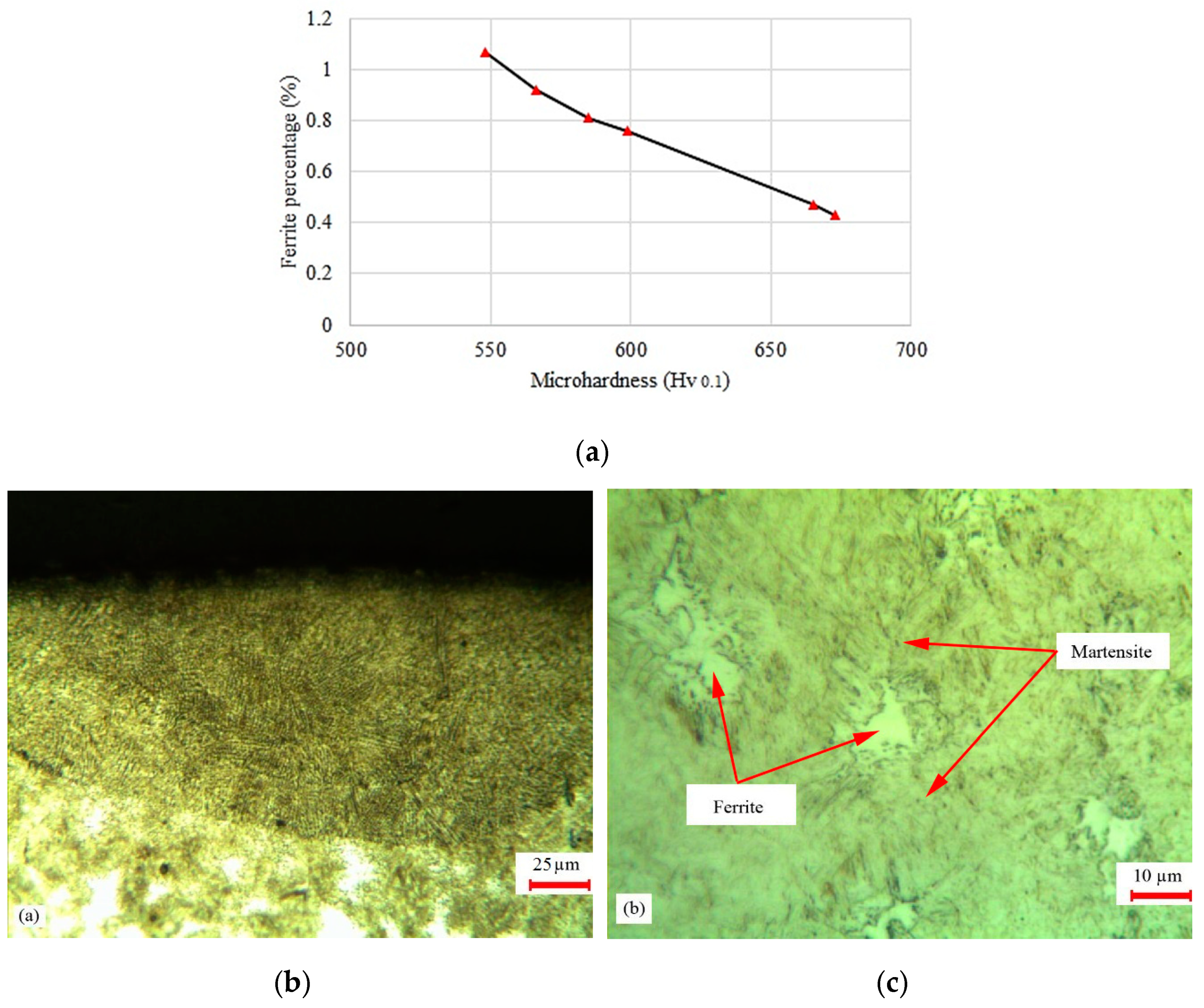

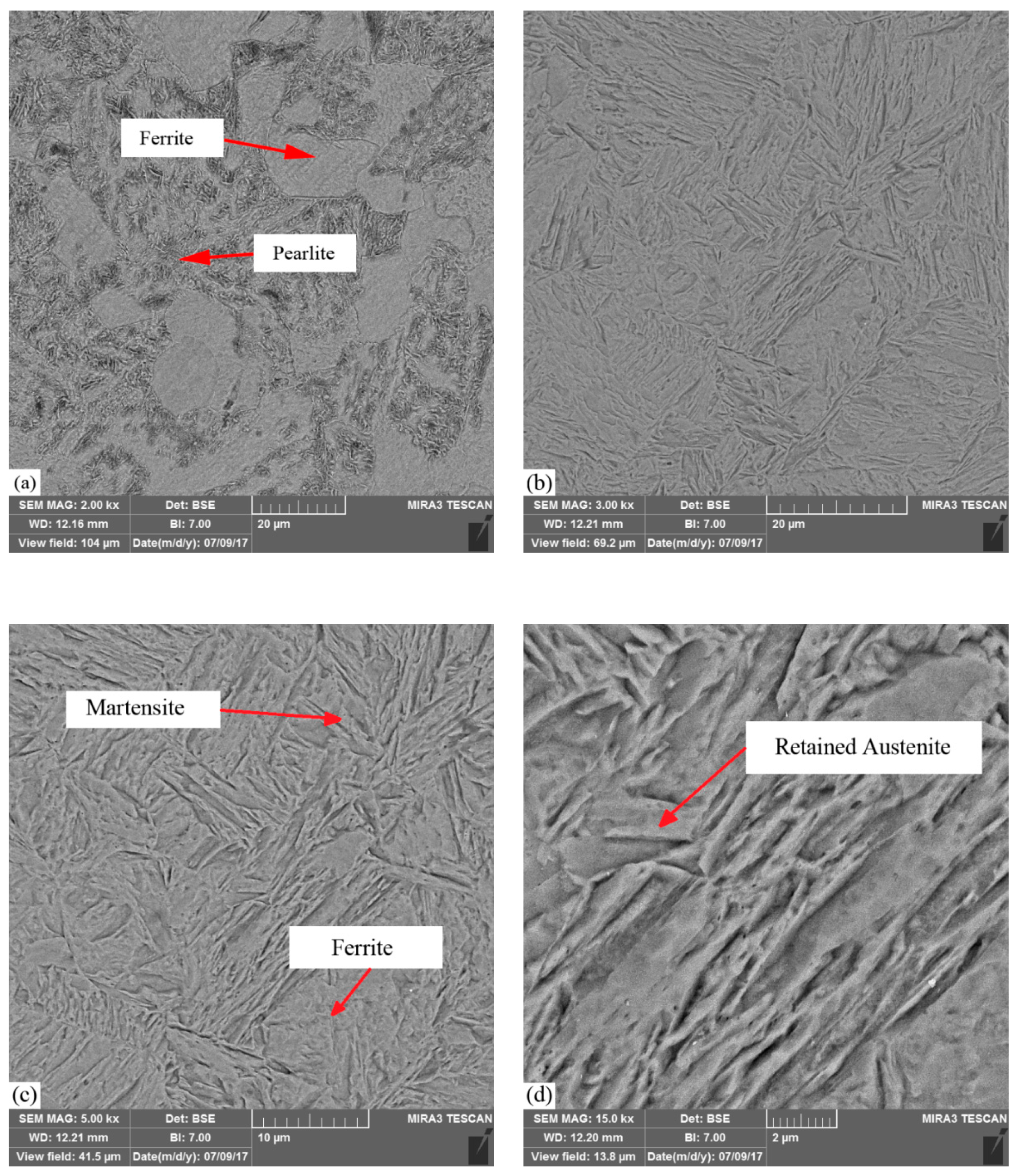

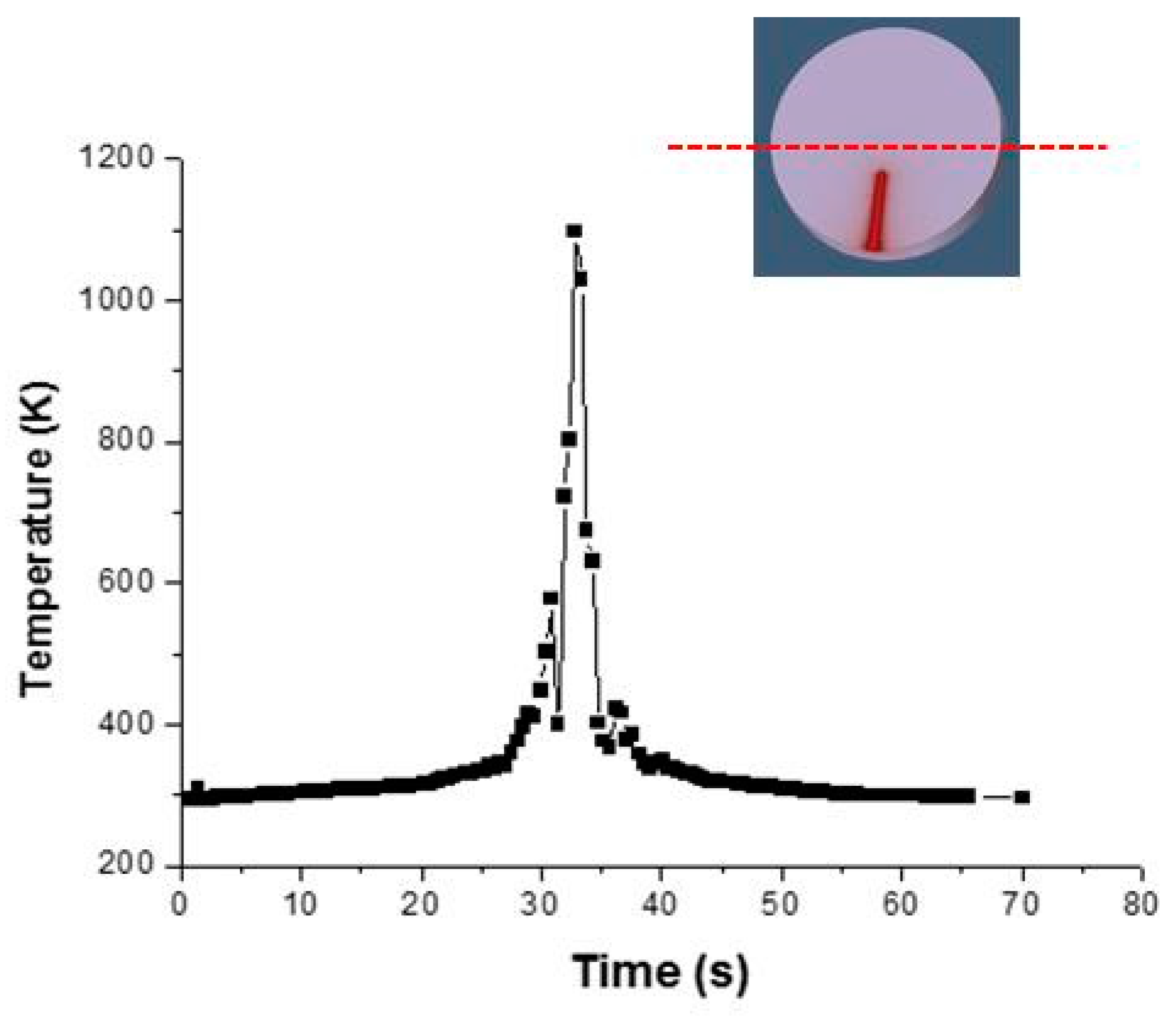
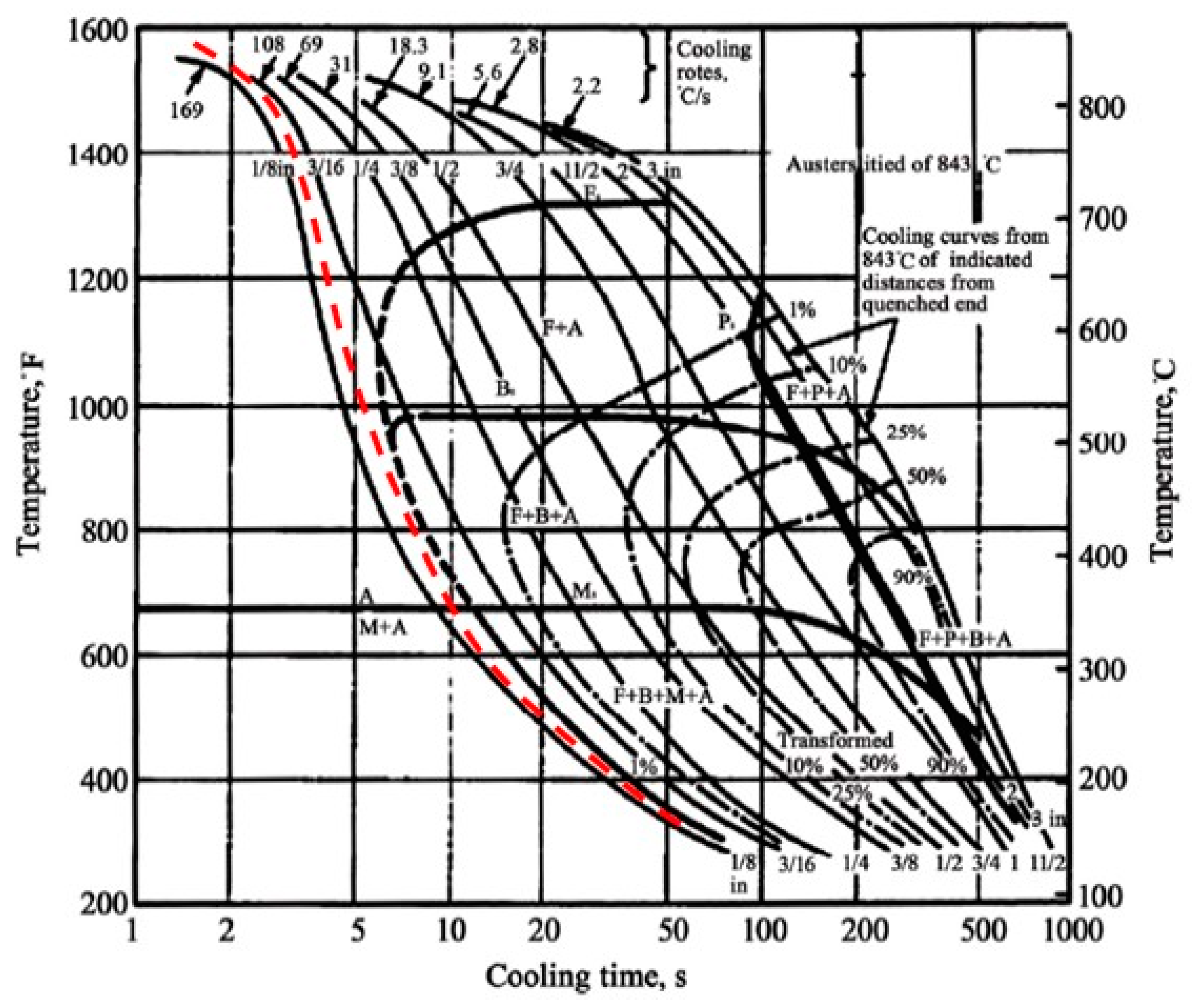
| Element Name | Cr | Fe | S | Al | Cu | Ni | Mn | V | S | C | Mo | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Percent | 0.03 | 0.024 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.012 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 1.01 | Balance |
| No. | Input Variables | Output Responses | Surface Melting | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focal Plane Position (mm) | Pulse Width (ms) | Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Depth of Hardness (µm) | Width of Hardness (µm) | Angle of Entry (°) | Maximum Hardness (hv) | Ferrite Percent (%) | MHD in Depth | MHD in Width | ||
| 1 | 11 | 15 | 130 | 1 | 71 | 1821 | 4.37 | 397 | 14.05 | 1592 | 21,474 | - |
| 2 | 8 | 15 | 130 | 1 | 1291 | 1774 | 53.3 | 698 | 0.25 | 19501 | 19,768 | yes |
| 3 | 9 | 15 | 130 | 1 | 360 | 1805 | 21.67 | 690 | 0.32 | 17,040 | 21,115 | yes |
| 4 | 9 | 17 | 135 | 1 | 271 | 1768 | 17.07 | 681 | 0.4 | 9242 | 7848 | yes |
| 5 | 11 | 17 | 135 | 1 | 100 | 1837 | 6.14 | 548 | 1.07 | 1932 | 22,042 | - |
| 6 | 11 | 20 | 155 | 1 | 141 | 1862 | 8.63 | 566 | 0.92 | 4730 | 26,435 | - |
| 7 | 11 | 17 | 135 | 0.5 | 143 | 1897 | 8.35 | 585 | 0.81 | 5520 | 34,454 | - |
| 8 | 11 | 20 | 155 | 0.5 | 157 | 1915 | 9.1 | 665 | 0.47 | 7300 | 37,136 | - |
| 9 | 11 | 20 | 155 | 0.2 | 193 | 2284 | 9.63 | 673 | 0.43 | 8563 | 43,202 | - |
| 10 | 11 | 18 | 140 | 0.5 | 146 | 1936 | 8.41 | 599 | 0.76 | 6430 | 39,079 | - |
| Property | AISI 4130 |
|---|---|
| Young modulus (GPa) | 190 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 7.85 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) | 42.7 |
| Liquidus temperature (K) | 1733 |
| Solidus temperature (K) | 1693 |
| Heat Treatment Cycle | Furnace Hardening Heat Treatment | LSTH |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling in oil | 572 Vickers | - |
| Cooling in water | 681 Vickers | - |
| Cooling in air | 421 Vickers | - |
| LSTH (#9 Table 2) | - | 673 Vickers |
| Sample #8 | Experimental Data (mm) | Numerical Data (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Width of hardness (mm) | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| Depth of hardness (mm) | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Meaning | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical heat source upper–lower radius (mm) | ro | 0.1 |
| Cylindrical heat source depth (m) | d | 0.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casalino, G.; Moradi, M.; Moghadam, M.K.; Khorram, A.; Perulli, P. Experimental and Numerical Study of AISI 4130 Steel Surface Hardening by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser. Materials 2019, 12, 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193136
Casalino G, Moradi M, Moghadam MK, Khorram A, Perulli P. Experimental and Numerical Study of AISI 4130 Steel Surface Hardening by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser. Materials. 2019; 12(19):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193136
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasalino, Giuseppe, Mahmoud Moradi, Mojtaba Karami Moghadam, Ali Khorram, and Patrizia Perulli. 2019. "Experimental and Numerical Study of AISI 4130 Steel Surface Hardening by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser" Materials 12, no. 19: 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193136
APA StyleCasalino, G., Moradi, M., Moghadam, M. K., Khorram, A., & Perulli, P. (2019). Experimental and Numerical Study of AISI 4130 Steel Surface Hardening by Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser. Materials, 12(19), 3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193136






