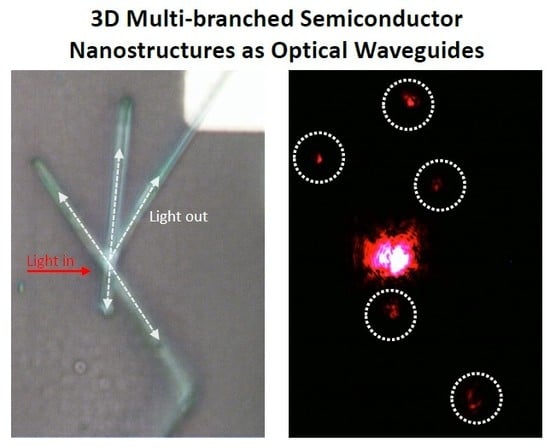
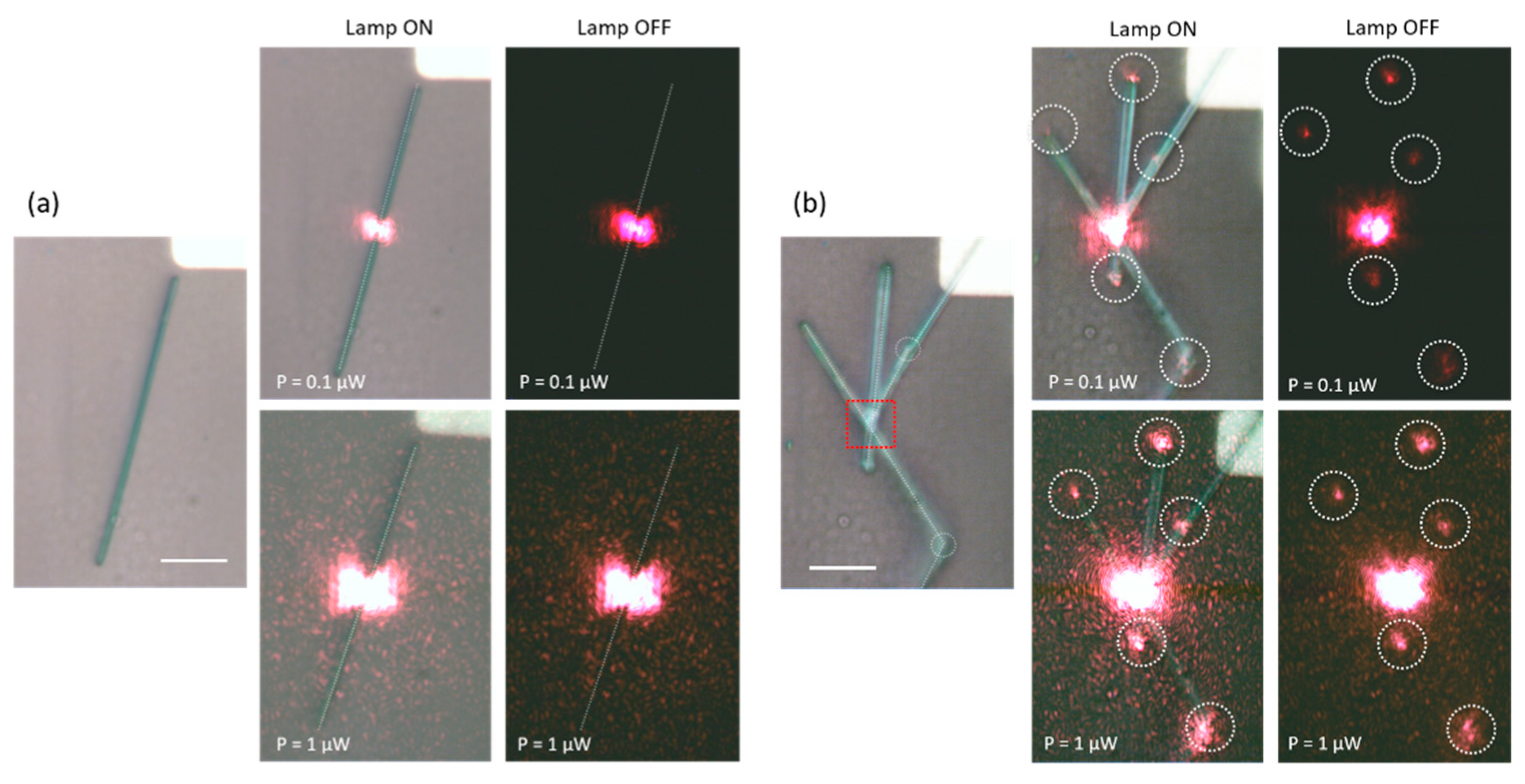
3D Multi-Branched SnO2 Semiconductor Nanostructures as Optical Waveguides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandaru, P.R.; Daraio, C.; Jin, S.; Rao, A.M. Novel electrical switching behaviour and logic in carbon nanotube Y-junctions. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, H.-F.; Guo, Y. Pure spin current in a three-terminal spin device in the presence of Rashba spin-orbit interaction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 092128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Xie, Y.E.; Sun, L.Z.; Zhong, J. Asymmetric transport in asymmetric T-shaped graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 092104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Wijeratne, S.; Zhang, Y.; Coskun, U.C.; Bao, W.; Lau, C.N. Phase-Coherent Transport in Graphene Quantum. Billiards Science 2007, 317, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, S.; Lorke, A.; Kotthaus, J.P.; Wegscheider, W.; Bichler, M. Rectification in Mesoscopic Systems with Broken Symmetry: Quasiclassical Ballistic Versus Classical Transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 056806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.W.; Lee, S.M.; Kang, N.J.; Cheon, J. Controlled synthesis of multi-armed CdS nanorod architectures using monosurfactant system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5150–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, L.; Scher, E.C.; Alivisatos, A.P. Synthesis of soluble and processable rod-, arrow-, teardrop- and tetrapod-shaped CdSe nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 12700–12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; He, R.; Johnson, J.; Law, M.; Saykally, R.J.; Yang, P. Dendritic nanowire ultraviolet laser array. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4728–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, L. Self-forming nanoscale devices. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomiero, A.; Concina, I.; Comini, E.; Soldano, C.; Ferroni, M.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. One-dimensional nanostructured oxides for thermoelectric applications and excitonic solar cells. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldano, C.; Comini, E.; Baratto, C.; Ferroni, M.; Faglia, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Metal Oxides Mono-Dimensional Nanostructures for Gas Sensing and Light Emission. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 831–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyatin, D.B.; Sun, J.; Fuhrer, A.; Wallin, D.; Fröberg, L.E.; Karlsson, L.S.; Maximov, I.; Wallenberg, L.R.; Samuelson, L.; Xu, H.Q. Electrical Properties of Self-Assembled Branched In As Nanowire Junctions. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Lu, Q.; Xie, S.; Zhao, D. A simple route for the synthesis of multi-armed CdS nanorod-based materials. Adv. Mat. 2002, 14, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plissard, S.R.; van Weperen, I.; Car, D.; Verheijen, M.A.; Immink, G.W.G.; Kammhuber, J.; Cornelissen, L.J.; Szombati, D.B.; Geresdi, A.; Frolov, S.M.; et al. Formation and electronic properties of InSb nanocrosses. Nat. Nanotech. 2013, 8, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.C.; Kesapragada, S.V.; Gall, D. Growth of Y-shaped nanorods through physical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 2008, 5, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z. Multi-branched Cu2O nanowires for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Mat. Res. Exp. 2018, 5, 035046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Guo, X.; Bi, Q.; Sajjad, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Cu2O Nanoparticles and Multi-Branded Nanowires as Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nano 2018, 13, 1850103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pu, M.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. Directional Coupling and Spin Routing in Catenary-Shaped SOI Waveguide. IEEE Phot. Tech. Lett. 2019, 31, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pu, M.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Luo, X. Ultra-broadband spin-controlled directional router based on single optical catenary integrated on silicon waveguide. Appl. Phys. Exp. 2018, 11, 092202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pu, M.; Li, X.; Song, S.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, X. Chip-integrated Geometric Metasurfacc As a Novel Platform for Directional Coupling and Polarization Sorting by Spin-Orbit Interaction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 4700107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoev, V.V.; Goschnick, J.; Schneider, T.; Strelcov, E.; Kolmakov, A. A gradient microarray electronic nose based on percolating SnO2 nanowire sensing elements. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, G.; Bae, M.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, S.K.; Yoon, C.H.; Zi, G.; Rogers, J.A.; Ha, J.S. SnO2 Nanowire Logic Devices on Deformable Nonplanar Substrates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 10009–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.M.; Sullivan, J.P.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.Q.; Mao, S.X.; Hudak, N.S.; Liu, X.H.; Subramanian, A.; et al. In Situ Observation of the Electrochemical Lithiation of a Single SnO2 Nanowire Electrode. Science 2010, 330, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Q.; Changshi, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, L. High-sensitivity humidity sensor based on a single SnO2 nanowire. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6070–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comini, E.; Bianchi, S.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Vomiero, A.; Sberveglieri, G. Functional nanowires of tin oxide. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 89, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaciulis, S.; Pandolfi, L.; Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Sberveglieri, G.; Kandasamy, S.; Shafiei, M.; Wlodarski, M. Nanowires ofmetal oxides for gas sensing applications. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orobtchouk, R. On Chip Optical Waveguide Interconnect: The Problem of the In/Out Coupling. In Optical Interconnects; Springer Series in Optical Sciences 119; Pavesi, L., Guillot, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Su, Y.; Pan, J.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Su, Y.; Pan, J.; Luo, S.; et al. A large misalignment tolerance multi-branch waveguide for high efficiency. Opt. Commun. 2019, 437, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittl, Z. The Principle of Reversibility and Thin Film Optics. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1962, 9, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peercy, P.S.; Morosin, B. Pressure and Temperature Dependences of the Raman-Active Phonons in SnO2. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardy, A.; Hung, W.-Z.; Tsai, D.-S.; Chou, C.-C.; Huang, Y.S. Structural Features of SnO2 Nanowires and Raman Spectroscopy Analysis. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Zhang, M.S.; Hong, J.M.; Yin, Z. Raman spectroscopic and photoluminescence study of single-crystalline SnO2 nanowires. Sol. State Commun. 2006, 138, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, R.S.; Dawson, P.; Hargreave, M.M.; Wilkinson, G.R. Dynamics of the rutile structure. III. Lattice dynamics, infrared and Raman spectra of SnO2. J. Phys. C 1971, 4, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, F.J.; Hyun, J.K.; Givan, U.; Kim, I.S.; Holsteen, A.L.; Lauhon, L.J. Diameter and Polarization-Dependent Raman Scattering Intensities of Semiconductor Nanowires. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2266–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsokkou, D.; Onoufriou, A.; Zervos, M. Carrier dynamics and conductivity of SnO2 nanowires investigated by time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tian, B.; Xiang, J.; Qian, F.; Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Mai, L.; Lieber, C.M. Rational growth of branched nanowire heterostructures with synthetically encoded properties and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12212–12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Hu, D.; Meng, D.; Jia, S. Nanoscale p–n junctions based on p-type ZnSe nanowires and their optoelectronic applications. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Branch (B) | Node (N) | Ratio (N/B) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raman | Eg (476 cm−1) | 833 | 1396 | 1.67 |
| A1g (633 cm−1) | 1378 | 4342 | 3.15 | |
| B2g (774 cm−1) | 611 | 1017 | 1.67 | |
| Rayleigh | 0.1 μW | 384 | 520 | 1.35 |
| 1 μW | 3181 | 6836 | 2.15 | |
| 10 μW | 37,819 | 59,448 | 1.57 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossella, F.; Bellani, V.; Tommasini, M.; Gianazza, U.; Comini, E.; Soldano, C. 3D Multi-Branched SnO2 Semiconductor Nanostructures as Optical Waveguides. Materials 2019, 12, 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193148
Rossella F, Bellani V, Tommasini M, Gianazza U, Comini E, Soldano C. 3D Multi-Branched SnO2 Semiconductor Nanostructures as Optical Waveguides. Materials. 2019; 12(19):3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193148
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossella, Francesco, Vittorio Bellani, Matteo Tommasini, Ugo Gianazza, Elisabetta Comini, and Caterina Soldano. 2019. "3D Multi-Branched SnO2 Semiconductor Nanostructures as Optical Waveguides" Materials 12, no. 19: 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193148
APA StyleRossella, F., Bellani, V., Tommasini, M., Gianazza, U., Comini, E., & Soldano, C. (2019). 3D Multi-Branched SnO2 Semiconductor Nanostructures as Optical Waveguides. Materials, 12(19), 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193148