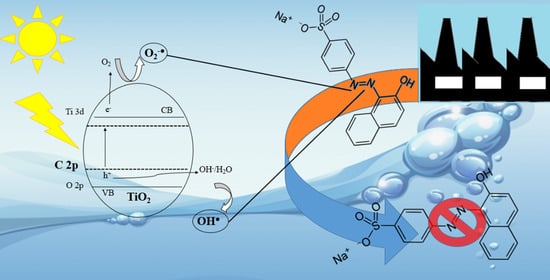
Novel Route to Obtain Carbon Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts for Environmental Remediation Processes under Visible Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Photocatalytic Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
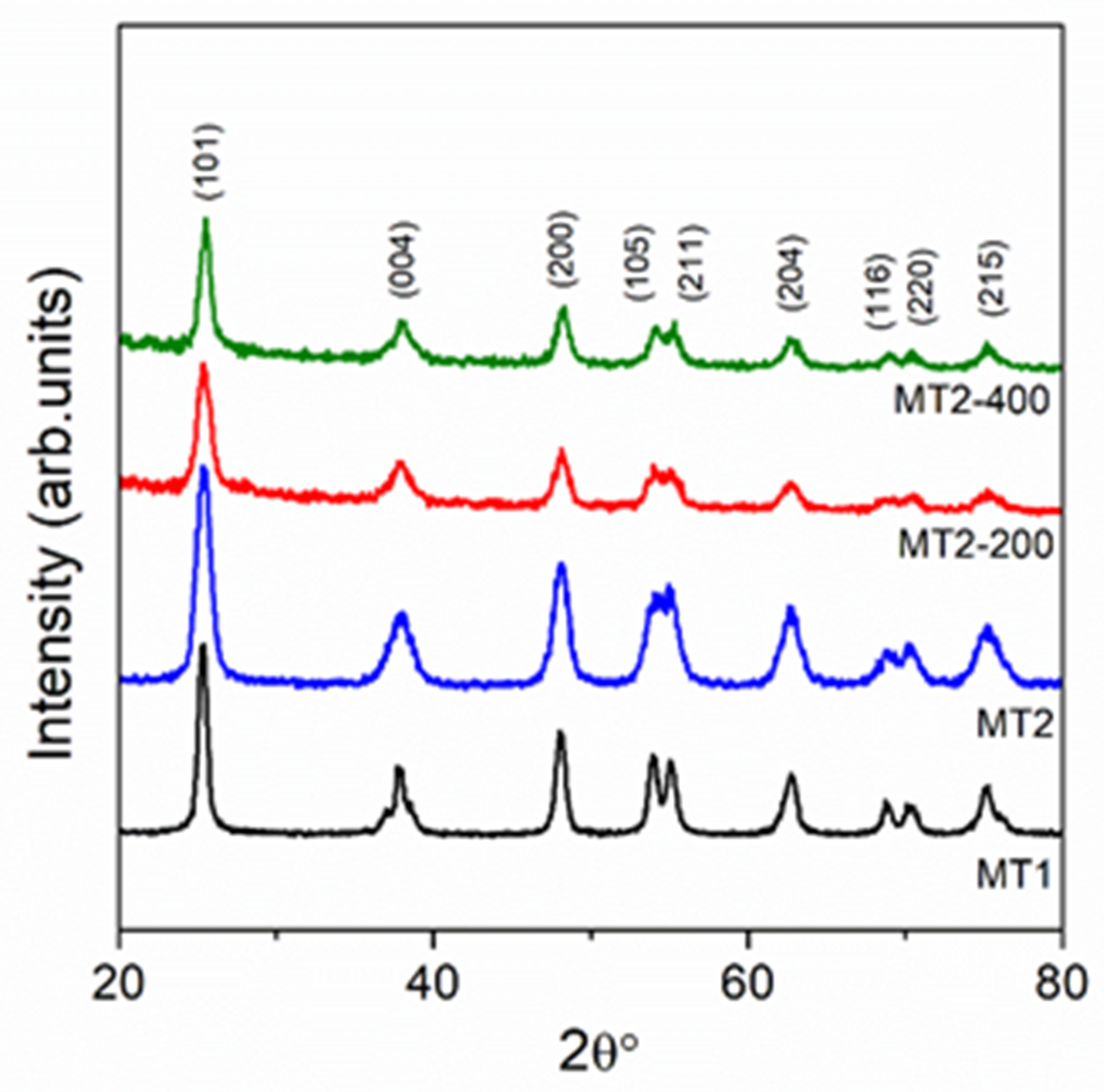
3.1. Characterization of Catalysts
3.2. Photocatalytic Degradation of Acid Orange 7
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bizani, E.; Fytianos, K.; Poulios, I.; Tsiridis, V. Photocatalytic decolorization and degradation of dye solutions and wastewaters in the presence of titanium dioxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anpo, M.; Kim, T.; Matsuoka, M. The design of Ti-, V-, Cr-oxide single-site catalysts within zeolite frameworks and their photocatalytic reactivity for the decomposition of undesirable molecules—The role of their excited states and reaction mechanisms. Catal. Today 2009, 142, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, I.; Albanis, T. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: Kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review. Appl. Catal. B 2004, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.G.; Faria, J.L. Photochemical and photocatalytic degradation of an azo dye in aqueous solution by UV irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 155, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; De Vito, S.C. Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 23, 249–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermenati, L.; Pichat, P.; Guillard, C.; Albini, A. Probing the TiO2 Photocatalytic Mechanisms in Water Purification by Use of Quinoline, Photo-Fenton Generated OH•Radicals and Superoxide Dismutase†. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryks, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, C1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.; Pillai, S.; Seery, M.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.; Dunlop, P.; Hamilton, J.; Byrne, J.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A Review on the Visible Light Active Titanium Dioxide Photocatalysts for Environmental Applications. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, H.; Dong, L.; Yin, Y. Nitrogen doped anatase TiO2 sheets with dominant {001} facets for enhancing visible-light photocatalytic activity. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 27, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Khan, M.M.; Ansari, M.O.; Cho, M.H. Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide (N-doped TiO2) for visible light photocatalysis. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Kisch, H. Daylight Photocatalysis by Carbon-Modified Titanium Dioxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4908–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Valentin, C.; Pacchioni, G.; Selloni, A. Theory of Carbon Doping of Titanium Dioxide. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6656–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Moon, J.H. Carbon-Deposited TiO2 3D Inverse Opal Photocatalysts: Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity and Enhanced Activity in a Viscous Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12526–12532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Que, W.; He, Y. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of sensitized mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles by carbon mesostructures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3332–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Carbon-doped anatase TiO2 powders as a visible-light sensitive photo-catalyst. Chem. Lett. 2003, 32, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.-C.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, S.; Sato, T.; Saito, F. Preparation of a visible sensitive carbon doped TiO2 photo-catalyst by grinding TiO2 with ethanol and heating treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 80, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, R.; Salonen, J.; Thiemann, S.; Song, Y.Y.; Kunze, J.; Lehto, V.P.; Schmuki, P.; Schmidt-Stein, F. Semimetallic TiO2 Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7236–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheikh, S.M.; Khedr, T.M.; Hakki, A.; Ismail, A.A.; Badawy, W.A.; Bahnemann, D.W. Visible light activated carbon and nitrogen co-doped mesoporous TiO2 as efficient photocatalyst for degradation of ibuprofen. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ho, W.; Lee, S.C.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Yu, J.C. Effect of Carbon Doping on the Mesoporous Structure of Nanocrystalline Titanium Dioxide and Its Solar-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of NOx. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3510–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Quan, L.; Jang, Y.H.; Stoerzinger, K.; May, K.J.; Jang, Y.J.; Kochuveedu, S.T.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Kim, D.H. Soft-template-carbonization route to highly textured mesoporous carbón—TiO2 inverse opals for efficient photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 9023–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. One-Step “Green” Synthetic Approach for Mesoporous C-Doped Titanium Dioxide with Efficient Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 16717–16723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, E.P.; Sun, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Transition Metal Modified TiO2-Loaded MCM-41 Catalysts for Visible- and UV-Light Driven Photodegradation of Aqueous Organic Pollutants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17198–17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, S.S.; Wu, G.; Chen, A. Synthesis of mesoporous nitrogen–tungsten co-doped TiO2 photocatalysts with high visible light activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liou, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Dong, C.; Chen, S.; Stucky, G. Mesoporous Fe-doped TiO2 sub-microspheres with en-hanced photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 127, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kwak, S.-Y. The hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 with high crystallinity, thermal stability, large surface area, and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 323, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Freyria, F.S.; Armandi, M.; Geobaldo, F.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. Fe-TiO2 and V- TiO2 mesoporous catalysts obtained by direct synthesis: Physico-chemical characterization and catalytic properties in the decomposition of azo-dyes. Catal. Today 2014, 227, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J.C. A sonochemical approach to hierarchical porous titania spheres with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2003, 16, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiden-Assmann, S.; Widoniak, J.; Maret, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Porous and Nonporous Monodisperse Colloidal TiO2Particles. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elías, V.; Vaschetto, E.; Sapag, K.; Oliva, M.; Casuscelli, S.; Eimer, G. MCM-41-based materials for the photo-catalytic degradation of Acid Orange 7. Catal. Today 2011, 172, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, V.; Jun, M.B.; Blackburn, A.; Herring, R.A. Significant improvement in visible light photocatalytic activity of Fe doped TiO2 using an acid treatment process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L.; Chang, J.; Sheng, W.; Hu, C.; Cao, S. C-doped hollow TiO2 spheres: In situ synthesis, controlled shell thickness, and superior visible-light photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkhade, S.K.; Gaikwad, G.; Zodape, S.P.; Pratap, U.; Maldhure, A.V.; Wankhade, A.V. Low temperature synthesis of pure anatase carbon doped titanium dioxide: An efficient visible light active photocatalyst. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 63, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20382–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etacheri, V.; Di Valentin, C.; Schneider, J.; Bahnemann, D.; Pillai, S.C. Visible-light activation of TiO2 photocatalysts: Advances in theory and experiments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2015, 25, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhesh, B. Drying Technology. In handbook of Industrial Drying, 4th ed.; Mujumdar, A.S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 33, pp. 128–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mistura, G.; Pozzato, A.; Grenci, G.; Bruschi, L.; Tormen, M. Continuous adsorption in highly ordered porousmatrices made by nanolithography. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Ai, Z.; Jia, F.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Zou, Z. Low temperature preparation and visible light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous carbon-doped crystalline TiO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 69, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, G.; Cheng, B.; Zhou, M. Effects of hydrothermal temperature and time on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of bimodal mesoporous TiO2 powders. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 69, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Z. Enhancement of the Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity of C-Doped TiO2 Nanomaterials Prepared by a Green Synthetic Approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13285–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Marien, C.B.; Marchal, C.; Koch, A.; Robert, D.; Drogui, P. Sol-gel synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles: Effect of Pluronic P123 on particle’s morphology and photocatalytic degradation of paraquat. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 12582–12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, E.M.; Mattle, M.J.; Loughrey, D.; Rajesh, B.; Rahman, M.; Don MacElroy, J.M.; Sullivan, J.A.; Thampi, K.R. Carbon-Doped TiO2 and Carbon, Tungsten-Codoped TiO2 through Sol–Gel Processes in the Presence of Melamine Borate: Reflections through Photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16511–16521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yin, S.; Dong, Q.; Guo, C.; Li, H.; Kimura, T.; Sato, T. Synthesis of high visible light active carbon doped TiO2 photocatalyst by a facile calcination assisted solvothermal method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, B.; Hunsicker, R.A.; Simmons, G.W.; Sudol, E.D.; Dimonie, V.L.; El-Aasser, M.S. XPS and FTIR Surface Characterization of TiO2Particles Used in Polymer Encapsulation. Langmuir 2001, 17, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Ho, W.; Yu, J.; Hark, S.K.; Iu, K. Effects of Trifluoroacetic Acid Modification on the Surface Microstructures and Photocatalytic Activity of Mesoporous TiO2Thin Films. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Avilés, A.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Bedia, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Belver, C. C-modified TiO2 using lignin as carbon precursor for the solar photocatalytic degradation of acetaminophen. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.E.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B.C.; Hu, Y.D. Facile preparation of micro-mesoporous carbon-doped TiO2 photocatalysts with anatase crystalline walls under template-free condition. Chem. Commun. 2008, 21, 2453–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K.; Kansal, S.K. Highly effective Fe-doped TiO₂ nanoparticles photocatalysts for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic compounds. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elías, V.; Sabre, E.; Sapag, K.; Casuscelli, S.; Eimer, G. Influence of the Cr loading in Cr/MCM-41 and TiO2/Cr/MCM-41 molecular sieves for the photodegradation of Acid Orange 7. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 413, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Weng, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Shiesh, C.-C.; Chen, F.-Y. Effect of C content and calcination temperature on the photocatalytic activity of C-doped TiO2 catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 116, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Bard, A.J. Novel Carbon-Doped TiO2Nanotube Arrays with High Aspect Ratios for Efficient Solar Water Splitting. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.F.; Xu, X.X.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Niu, M.C.; Gao, X.Y.; Yang, Y.T. Effect of calcination temperature on the structure and visible-light photocatalytic activities of (N, S and C) co-doped TiO2 nano-materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Burda, C. The Electronic Origin of the Visible-Light Absorption Properties of C-, N- and S-Doped TiO2Nanomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5018–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.H.; Jia, L.; Wu, X.L.; Lu, L.Q.; Xu, A.W. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped TiO2/C nanocomposites with high visible light photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Photocatalyst | SBET (m2 g−1)a | PD (nm)b | PV (cm3g−1)b | Band Gap (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT1 | 87 | 6.0 | 0.18 | 3.3 |
| MT2 | 150 | 6.2 | 0.25 | 3.1 |
| MT2-200 | 139 | 6.6 | 0.27 | 3.1 |
| MT2-400 | 93 | 7.9 | 0.22 | 3.2 |
| Sample | Ti–C | C–C | C–O | C–O–Ti | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE (eV) | % Area | BE (eV) | % Area | BE (eV) | % Area | BE (eV) | % Area | |
| MT2 | 281.6 | 2.1 | 284.5 | 73.5 | 285.8 | 12.0 | 288.5 | 12.4 |
| MT2–200 | 281.6 | 2.6 | 284.5 | 74.3 | 285.8 | 11.6 | 288.5 | 11.5 |
| MT2–400 | 281.0 | 0.9 | 284.7 | 71.2 | 285.6 | 16.8 | 288.6 | 11.1 |
| MT1 | 281.3 | 0.7 | 284.4 | 77.4 | 286.4 | 10.7 | 288.7 | 11.2 |
| Photocatalyst | % Degradation | % Mineralization |
|---|---|---|
| MT1 | 26 | 0 |
| MT2 | 84 | 27 |
| MT2–200 | 89 | 51 |
| MT2–400 | 14 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ochoa Rodríguez, P.A.; Benzaquén, T.B.; Pecchi, G.A.; Casuscelli, S.G.; Elías, V.R.; Eimer, G.A. Novel Route to Obtain Carbon Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts for Environmental Remediation Processes under Visible Light. Materials 2019, 12, 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203349
Ochoa Rodríguez PA, Benzaquén TB, Pecchi GA, Casuscelli SG, Elías VR, Eimer GA. Novel Route to Obtain Carbon Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts for Environmental Remediation Processes under Visible Light. Materials. 2019; 12(20):3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203349
Chicago/Turabian StyleOchoa Rodríguez, Pablo A., Tamara B. Benzaquén, Gina A. Pecchi, Sandra G. Casuscelli, Verónica R. Elías, and Griselda A. Eimer. 2019. "Novel Route to Obtain Carbon Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts for Environmental Remediation Processes under Visible Light" Materials 12, no. 20: 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203349
APA StyleOchoa Rodríguez, P. A., Benzaquén, T. B., Pecchi, G. A., Casuscelli, S. G., Elías, V. R., & Eimer, G. A. (2019). Novel Route to Obtain Carbon Self-Doped TiO2 Mesoporous Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalysts for Environmental Remediation Processes under Visible Light. Materials, 12(20), 3349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203349