Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu Cast Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
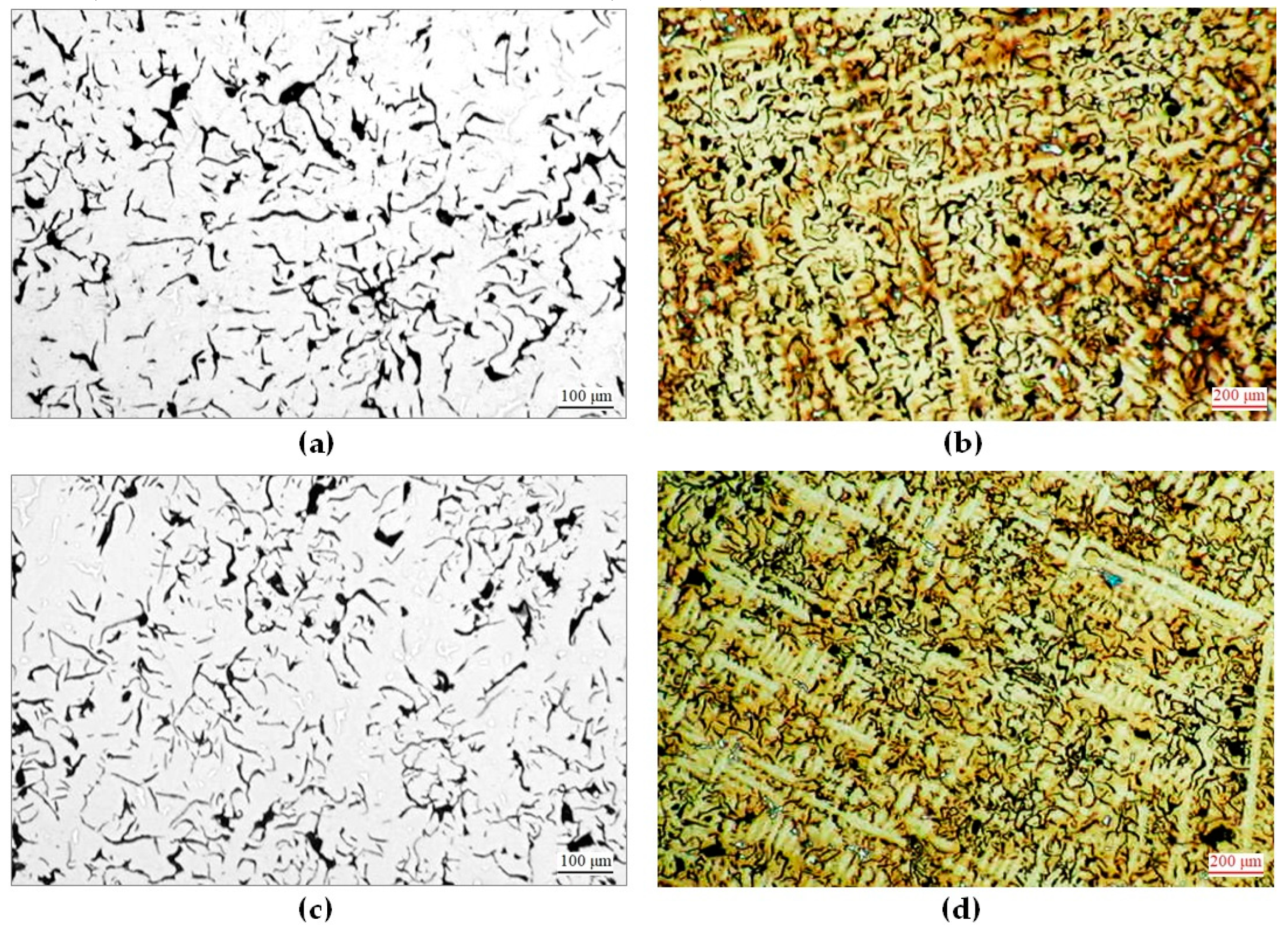
3.1. Microscopic Observations and Hardness Measurements of Raw Castings
3.2. Microscopic Observations and Hardness Measurements of Heat-Treated Castings
3.3. Abrasive-Wear Resistance Testing
3.4. Corrosion Resistance Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni-Resist/Austenitic Cast Iron (EN-GJLA/EN-GJSA). Available online: https://www.esterer-giesserei.de/fileadmin/user_files/pdf/Ni-Resist__GJSA_.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Janus, A. Forming of Castings Structure of Austenitic Cast Iron Ni–Mn–Cu; Editorial Office of Wroclaw University of Technology: Wroclaw, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Janus, A.; Granat, K. Abrasion Resistant Austenitic-Bainitic Cast Iron; Report of Institute of Machine Engineering and Automation of Wroclaw University of Technology; SPR 28; Institute of Machine Engineering and Automation of Wroclaw University of Technology: Wroclaw, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Effect of Chemical composition on structure and corrosion resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Effect of austenite transformation on abrasive wear and corrosion resistance of spheroidal Ni-Mn-Cu cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A.; Zaborski, S. Effect of heat-treatment parameters of cast iron GJS-X350NiMnCu7-3-2 on its structure and mechanical properties. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2017, 17, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Effect of heat treatment parameters on abrasive wear and corrosion resistance of austenitic nodular cast iron Ni–Mn–Cu. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Abrasive-wear resistance of austenitic cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2018, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A. Effect of nickel equivalent on structure and corrosion resistance of nodular cast iron Ni-Mn-Cu. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2015, 15, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Medyński, D.; Janus, A.; Chęcmanowski, J. Effect of annealing on nature of corrosion damages of medium-nickel austenitic cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2017, 17, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumienny, G. Carbidic bainitic and ausferritic ductile cast iron. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2013, 58, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-Kołodziejczyk, D.; Regulski, K.; Gumienny, G. Comparative analysis of the properties of the nodular cast iron with carbides and the austempered ductile iron with use of the machine learning and the support vector machine. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, M.; Liantao, L.; Zeng, D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of austempered ductile iron with different strength grades. Mater. Lett. 2014, 119, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahalla, N.; Hussein, O. Microstructure, mechanical properties, toughness, wear characteristics and fracture phenomena of austenitized and austempered low-alloyed ductile iron. Open Access Libr. J. 2015, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Panneerselvama, S.; Putatundaa, S.K.; Gundlachb, R.; Boileauc, J. Influence of intercritical austempering on the microstructure and mechanical properties of austempered ductile cast iron (ADI). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 694, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junjun, C.; Liqing, C. Microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of an alloyed ductile iron subjected to deep cryogenic and austempering treatments. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Konca, E.; Tur, K.; Koç, E. Effects of Alloying Elements (Mo, Ni and Cu) on the austemperability of GGG-60 ductile cast iron. Metals 2017, 7, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, G.; Wang, L.; He, B. Effects of austenitization temperature and compressive stress during bainitic transformation on the stability of retained austenite. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Bose, P.K.; Sutradhar, G. Mechanical and tribological characteristics of copper alloyed austempered gray cast iron (AGI). Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 3664–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.; Harris Samuel, D.G.; Dinakaran, D.; Premkumar, V.P.; Li, Z.; Seetharaman, S. Influence of austempering temperature on microstructure, mechanical and wear properties and energy consumption. Metals 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalava, K.; Soivio, K.; Laine, J.; Orkas, J. Elevated temperature thermal conductivities of some as-cast and austempered cast irons. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujara, J.; Kothari, K.; Gohil, A. An investigation of material removal rate and kerf on WEDM through grey relational analysis. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2018, 12, 3633–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, D.; He, K.; Ye, W.; Qu, S.; Shangguan, J. The role of bainite in wear and friction behavior of austempered ductile iron. Materials 2019, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duenas, J.R.; Hormaza, W.; Castro Güiza, G.M. Abrasion resistance and toughness of a ductile iron produced by two molding processes with a short austempering. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, A.A.; Amal, S.I.; Ghanem, W.A.; Hussein, W.A.; El-dabaa, N.K. The effect of austempering heat treatments on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of cast iron in 3.5% sodium chloride soliton. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 7, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrzucki, C. Cast Iron: Structure, Properties and Application; T 1/2; ZG STOP: Krakow, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bala, H. Corrosion of Materials—Theory and Practice; Editorial Office of Process Engineering, Materials and Applied Physics of Czestochowa University of Technology: Czestochowa, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz, T. Electrochemistry for Surface Engineering; Editorial Office of Koszalin University of Technology: Koszalin, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz, T.; Rokosz, K. Theoretical Basis and Practical Aspects of Corrosion; Editorial Office of Koszalin University of Technology: Koszalin, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rączka, J.S.; Tabor, A.; Kowalski, A. Resistance of austenitic-bainitic nodular cast iron to corrosive action of sulphuric, nitric and hydrochloric acids. Solidif. Met. Alloys 2000, 2, 527–535. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Hsun, H.; Ming-Li, C. Corrosion behavior of nickel alloyed and austempered ductile iron in 3.5% sodium chloride. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2945–2949. [Google Scholar]
- Chung-Kwei, L.; Cheng-Hsun, H.; Yin-Hwa, C.; Keng-Liang, O.; Sheng-Long, L. A study on the corrosion and erosion behavior of electroless nickel and TiAlN/ZrN duplex coatings on ductile iron. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Tian, Y. Effects of chloride ions on corrosion of ductile iron and carbon steel in soil environments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Alloy No. | Chemical Composition [wt %] | SC [ / ] | EquNi [wt %] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | Cu | Cr | Mo | Al | P | S | |||
| 1 | 3.5 | 1.9 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 1.9 | − | − | − | 0.19 | 0.01 | 1.02 | 16.3 |
| 2 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 0.4 | − | − | 0.19 | 0.01 | 1.03 | 16.1 |
| 3 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 4.4 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 0.7 | − | − | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 16.0 |
| 4 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 0.9 | − | 0.4 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 1.02 | 16.1 |
| 5 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 1.8 | − | 0.4 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 16.0 |
| 6 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 0.7 | 0.2 | − | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 16.2 |
| 7 | 3.6 | 1.9 | 4.3 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.2 | − | 0.16 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 16.1 |
| 8 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 4.2 | 3.3 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 16.0 |
| 9 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 16.0 |
| Alloy No. | EquNi [wt%] | Matrix | High-Carbon Phases %Fe3C – %Cgr* /type of Cgr/ | HBSAVR 2.5/187.5kG [/] (+/−2) | HV0.01NAVR of Austenite [/] (+/−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.3 | austenite | 0% Fe3C – 100%Cgr /IA4/ | 160 | 168 |
| 2 | 16.1 | austenite | 0% Fe3C – 100%Cgr /IE4/ | 170 | 182 |
| 3 | 16.0 | austenite | 0% Fe3C – 100%Cgr /IE4/ | 185 | 192 |
| 4 | 16.1 | austenite | 10% Fe3C – 90%Cgr /IE5/ | 280 | 204 |
| 5 | 16.0 | austenite | 95% Fe3C – 5%Cgr /IE6/ | 380 | 230 |
| 6 | 16.2 | austenite | 45% Fe3C – 55%Cgr /ID5/ | 205 | 195 |
| 7 | 16.1 | austenite | 50% Fe3C – 50%Cgr /ID5/ | 220 | 203 |
| 8 | 16.0 | austenite | 55% Fe3C – 45%Cgr /ID5/ | 210 | 214 |
| 9 | 16.0 | austenite | 60% Fe3C – 40%Cgr /ID4/ | 250 | 207 |
| Alloy No. | EquNi [wt %] | Matrix Components * A – Fem – P [%– % –%] | Form of Carbon in Eutectic Mixture ** | HBWAVR 2.5/187.5 [/] (+/−3) | Increase of HBW 2.5/187.5 [/] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16.3 | 50 – 50 – 0 | Cgr | 313 | 154 |
| 2 | 16.1 | 48 – 52 – 0 | Cgr | 347 | 178 |
| 3 | 16.0 | 47 – 53 – 0 | Cgr | 372 | 189 |
| 4 | 16.1 | 45 – 55 – 0 | Cgr + Fe3C | 411 | 129 |
| 5 | 16.0 | 45 – 25 – 30 | Cgr + Fe3C | 492 | 112 |
| 6 | 16.2 | 45 – 55 – 0 | Cgr + Fe3C | 362 | 157 |
| 7 | 16.1 | 40 – 60 – 0 | Cgr + Fe3C | 383 | 163 |
| 8 | 16.0 | 10 – 90 – 0 | Cgr + Fe3C | 441 | 230 |
| 9 | 16.0 | 15 – 85 – 0 | Cgr + Fe3C | 454 | 205 |
| Alloy No. | Increase of HBW 2.5/187.5 [/] | Wear Rate [mg/m∙104] | Decrease in Wear Rate Compared to Alloy No. 1 | Index of Surface Topography [μm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RpAVR (+/−0.02) | RvAVR (+/−0.02) | RzAVR (+/−0.02) | RaAVR (+/−0.02) | RqAVR (+/−0.02) | ||||
| 1 | 154 | 2.14 | − | 5.17 | 12.19 | 17.36 | 0.87 | 1.44 |
| 2 | 178 | 1.62 | −0.57 | 4.18 | 10.88 | 15.06 | 0.54 | 0.85 |
| 3 | 189 | 1.52 | −0.67 | 4.19 | 10.83 | 15.02 | 0.56 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 129 | 1.24 | −0.95 | 4.16 | 10.84 | 15.00 | 0.52 | 0.85 |
| 5 | 112 | 0.57 | −1.62 | 4.01 | 10.02 | 14.03 | 0.48 | 0.83 |
| 6 | 157 | 1.14 | −1.05 | 4.17 | 10.78 | 14.95 | 0.50 | 0.84 |
| 7 | 163 | 1.05 | −1.14 | 4.14 | 10.74 | 14.88 | 0.49 | 0.83 |
| 8 | 230 | 0.85 | −1.33 | 4.05 | 10.53 | 14.58 | 0.45 | 0.81 |
| 9 | 205 | 1.62 | −1.29 | 4.09 | 10.68 | 14.77 | 0.44 | 0.84 |
| Alloy No. | VP [mm/year] After Exposure for Specified Time (days) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 13 | 18 | 24 | ||
| 1 | as cast | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.39 |
| heat-treated | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.37 | |
| 2 | as cast | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.37 |
| heat-treated | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.38 | |
| 3 | as cast | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.35 |
| heat-treated | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.37 | |
| 4 | as cast | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.33 |
| heat-treated | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.34 | |
| 5 | as cast | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.30 |
| heat-treated | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.31 | |
| 6 | as cast | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.35 |
| heat-treated | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.36 | |
| 7 | as cast | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.33 |
| heat-treated | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.34 | |
| 8 | as cast | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.31 |
| heat-treated | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.31 | |
| 9 | as cast | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.30 |
| heat-treated | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.31 | |
| Alloy No. | E′ [mV] | EK-A [mV] | icorr [μA/cm2] | RP [kΩ·cm2] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 48 h | 30 min | 48 h | 30 min | 48 h | 30 min | 48 h | |
| 1 | −565 | −524 | −582 | −733 | 23.2 | 98.8 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| 2 | −569 | −535 | −643 | −739 | 20.1 | 92.3 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| 3 | −572 | −538 | −621 | −753 | 19.3 | 89.7 | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| 4 | −581 | −544 | −618 | −751 | 18.7 | 84.5 | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| 5 | −589 | −548 | −726 | −790 | 18.9 | 79.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| 6 | −568 | −533 | −635 | −758 | 19.8 | 94.0 | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| 7 | −572 | −539 | −669 | −773 | 19.8 | 88.5 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| 8 | −597 | −556 | −659 | −790 | 18.6 | 79.5 | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| 9 | −625 | −588 | −678 | −785 | 20.2 | 94.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| Alloy No. | EquNi [wt %] | Cr [wt %] | Mo [wt %] | Al [wt %] | Surface Topography Index [μm] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RpAVR (+/−0.03) | RvAVR (+/−0.03) | RzAVR (+/−0.03) | |||||
| 1 | 16.3 | − | − | − | 5.01 | 34.64 | 39.65 |
| 2 | 16.1 | 0.4 | − | − | 4.98 | 33.35 | 38.33 |
| 3 | 16.0 | 0.7 | − | − | 4.85 | 32.21 | 37.06 |
| 4 | 16.1 | 0.9 | − | 0.4 | 4.77 | 28.25 | 33.02 |
| 5 | 16.0 | 1.8 | − | 0.4 | 4.73 | 21.14 | 25.87 |
| 6 | 16.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 | − | 4.86 | 24.17 | 29.03 |
| 7 | 16.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 | − | 4.72 | 22.14 | 28.86 |
| 8 | 16.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 4.61 | 19.08 | 23.75 |
| 9 | 16.0 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 4.58 | 19.14 | 23.66 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medyński, D.; Samociuk, B.; Janus, A.; Chęcmanowski, J. Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu Cast Iron. Materials 2019, 12, 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213500
Medyński D, Samociuk B, Janus A, Chęcmanowski J. Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu Cast Iron. Materials. 2019; 12(21):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213500
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedyński, Daniel, Bartłomiej Samociuk, Andrzej Janus, and Jacek Chęcmanowski. 2019. "Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu Cast Iron" Materials 12, no. 21: 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213500
APA StyleMedyński, D., Samociuk, B., Janus, A., & Chęcmanowski, J. (2019). Effect of Cr, Mo and Al on Microstructure, Abrasive Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Ni-Mn-Cu Cast Iron. Materials, 12(21), 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213500





