Microstructure Transformation on Pre-Quenched and Ultrafast-Tempered High-Strength Multiphase Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
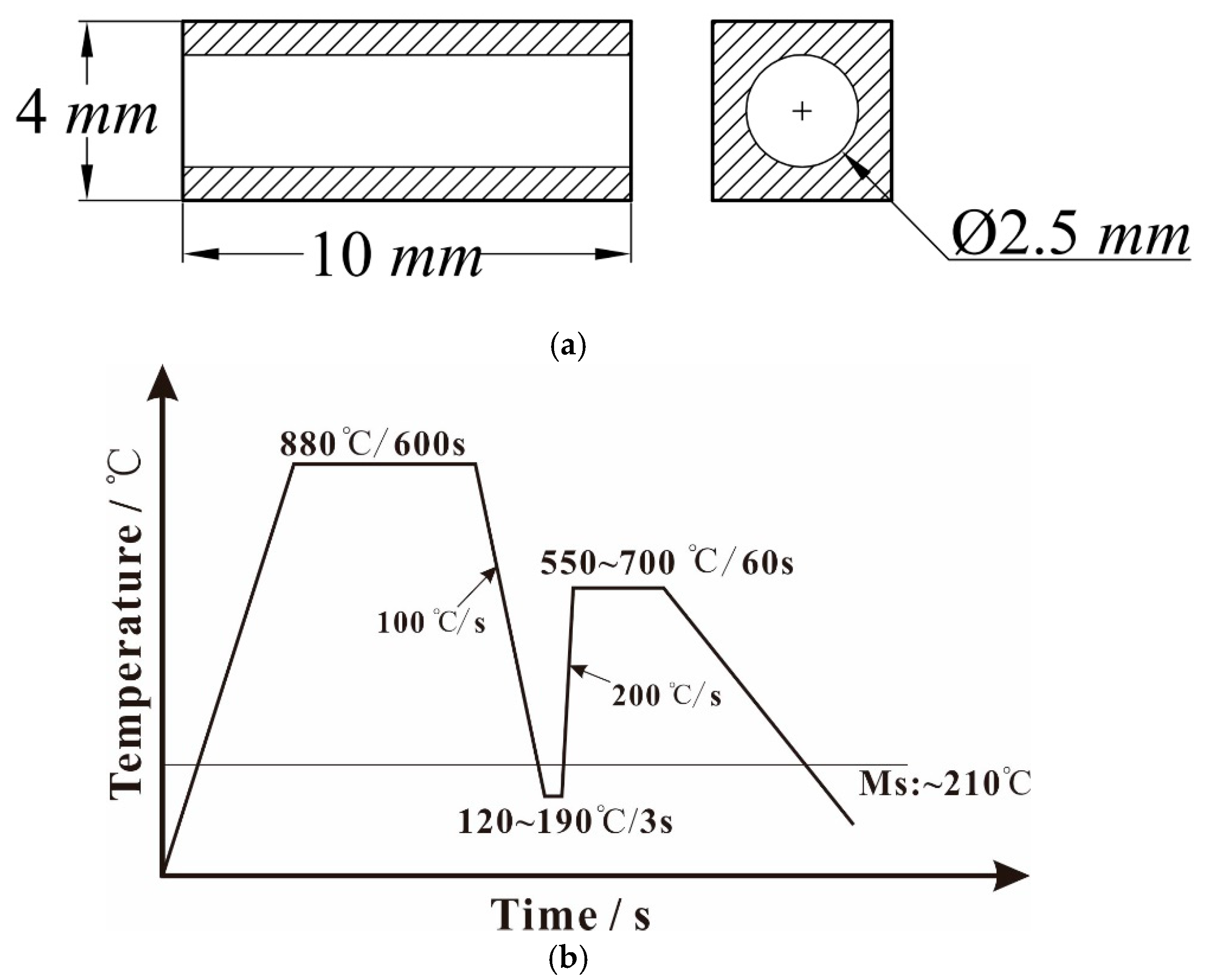
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
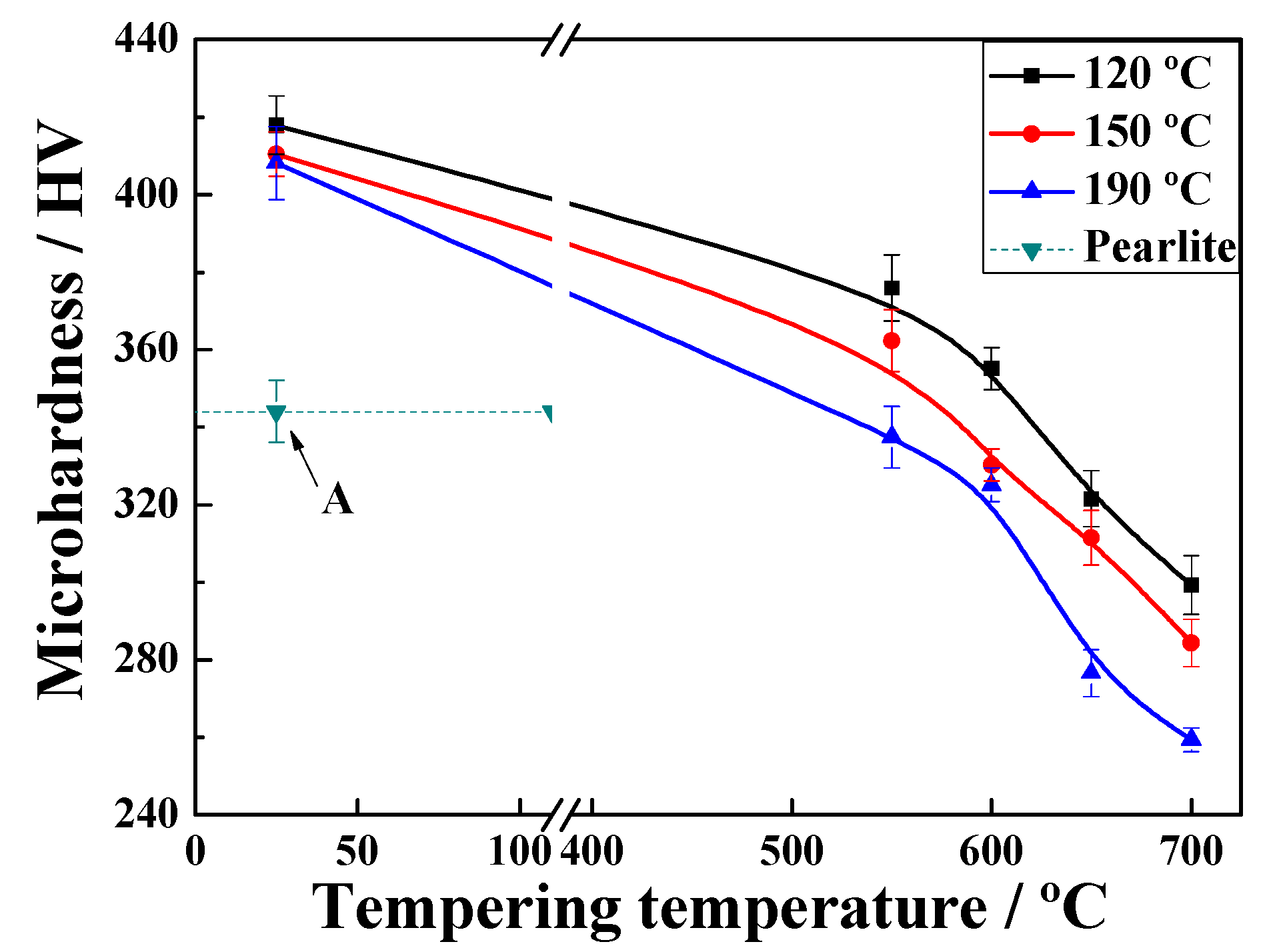
3.1. Microhardness Performance
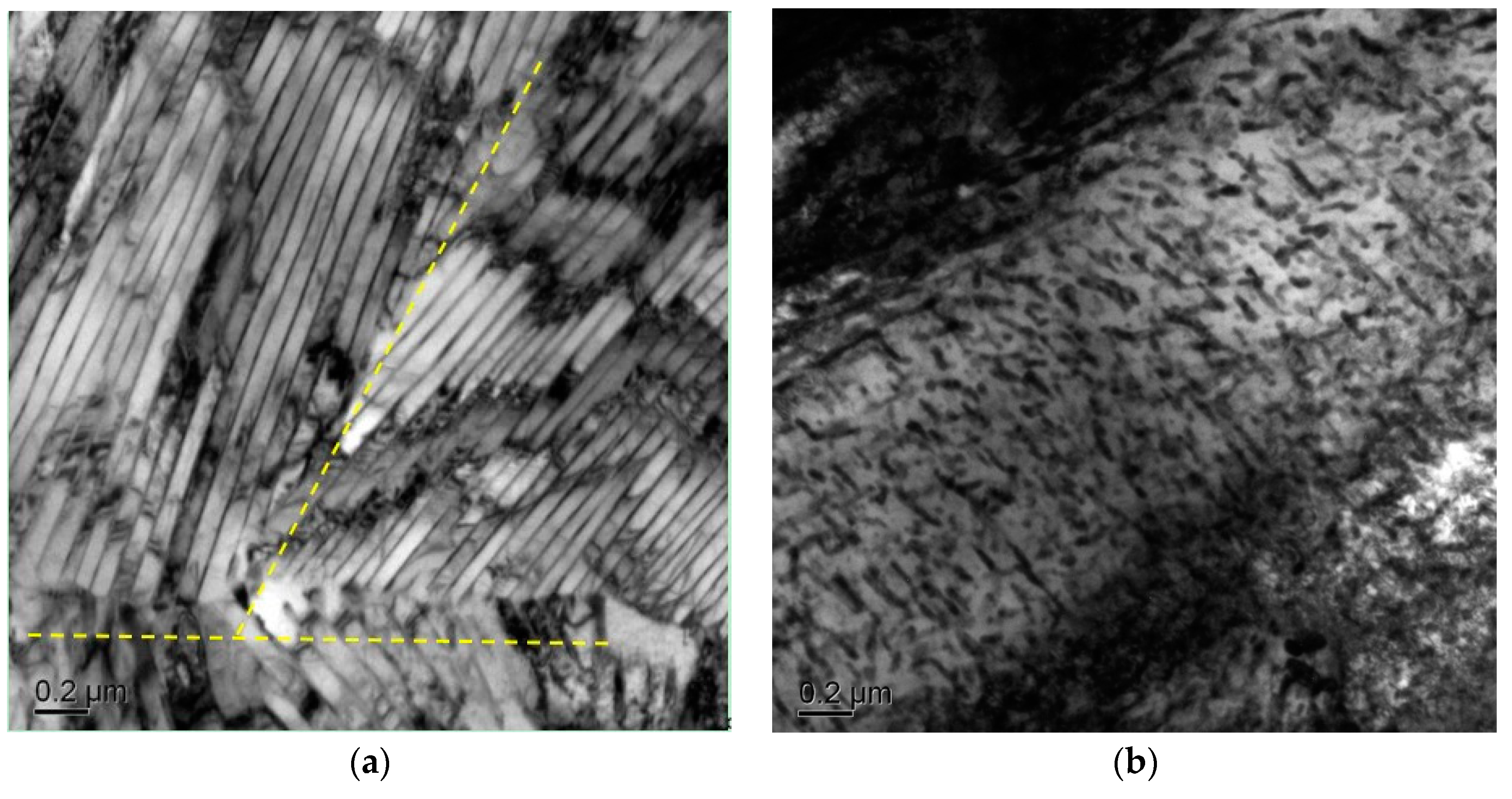
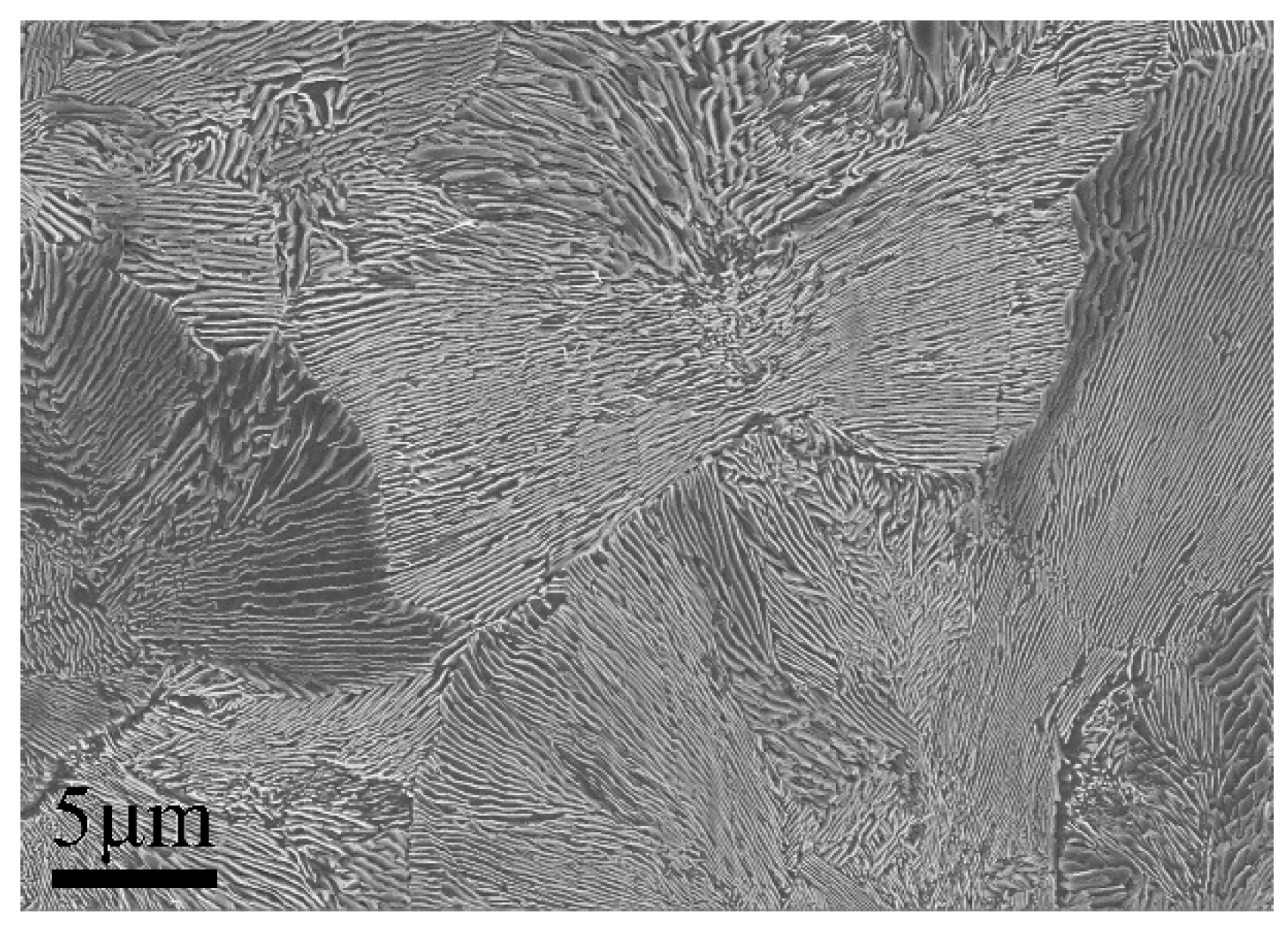
3.2. Microstructure Characterization
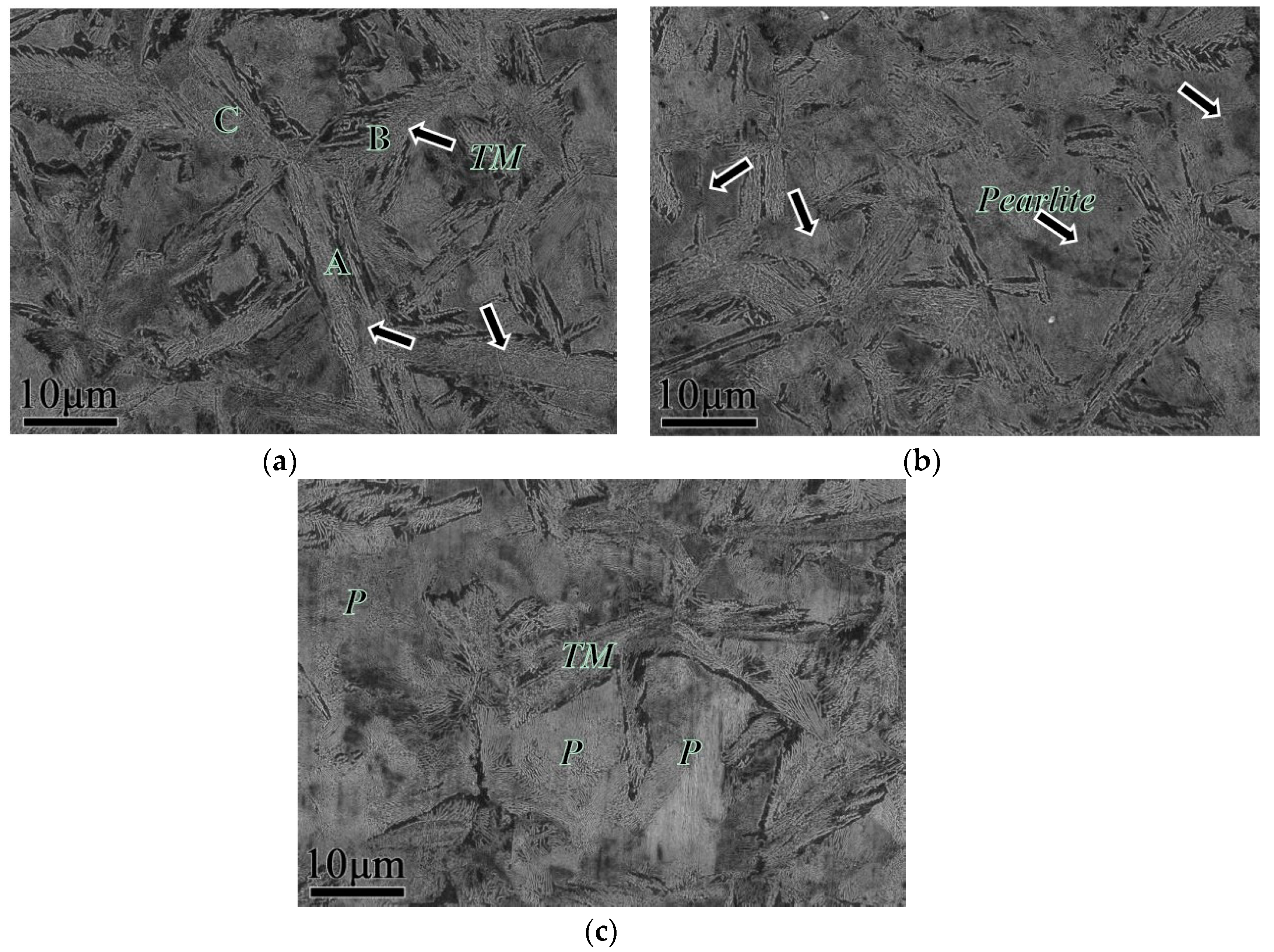
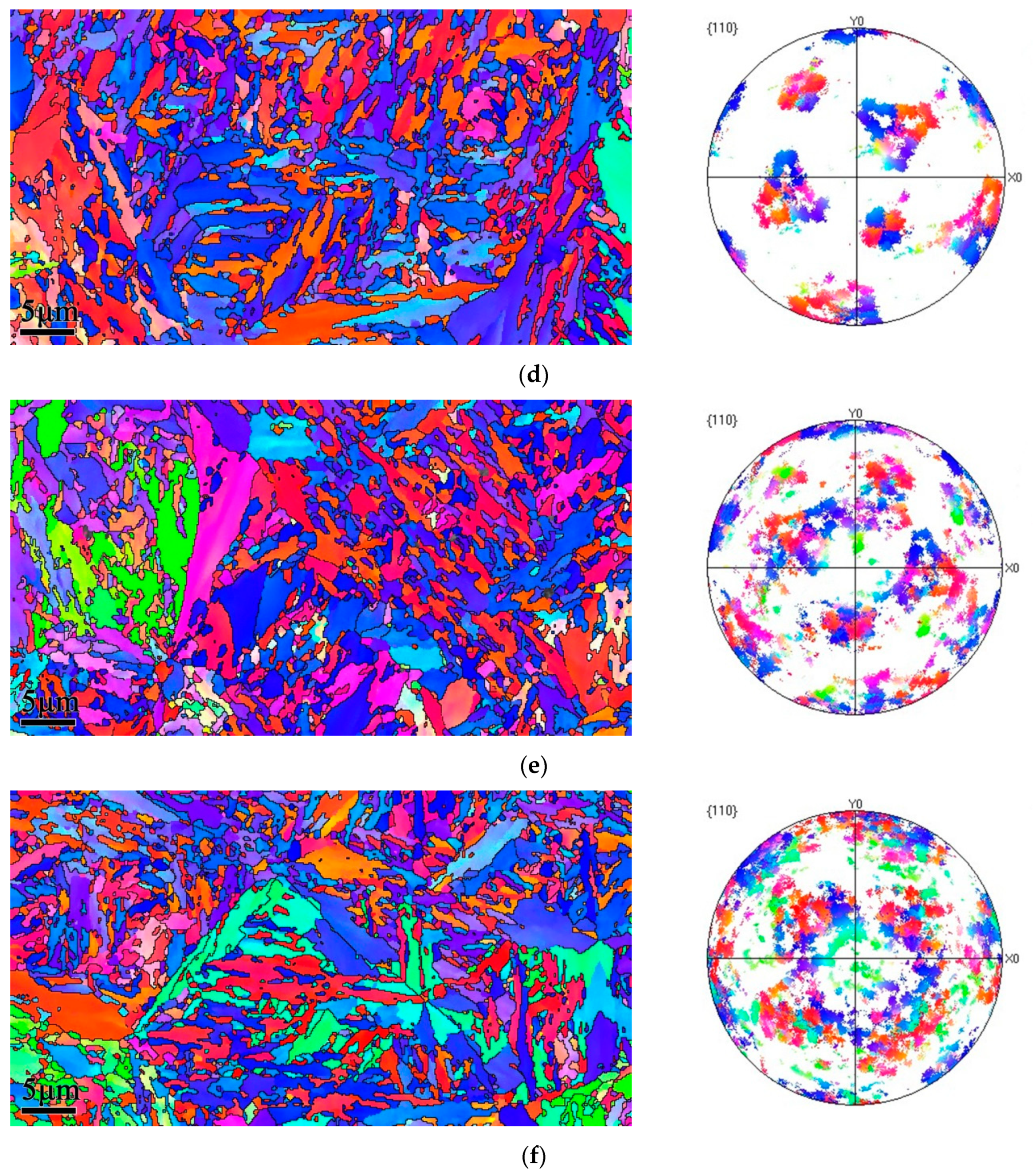
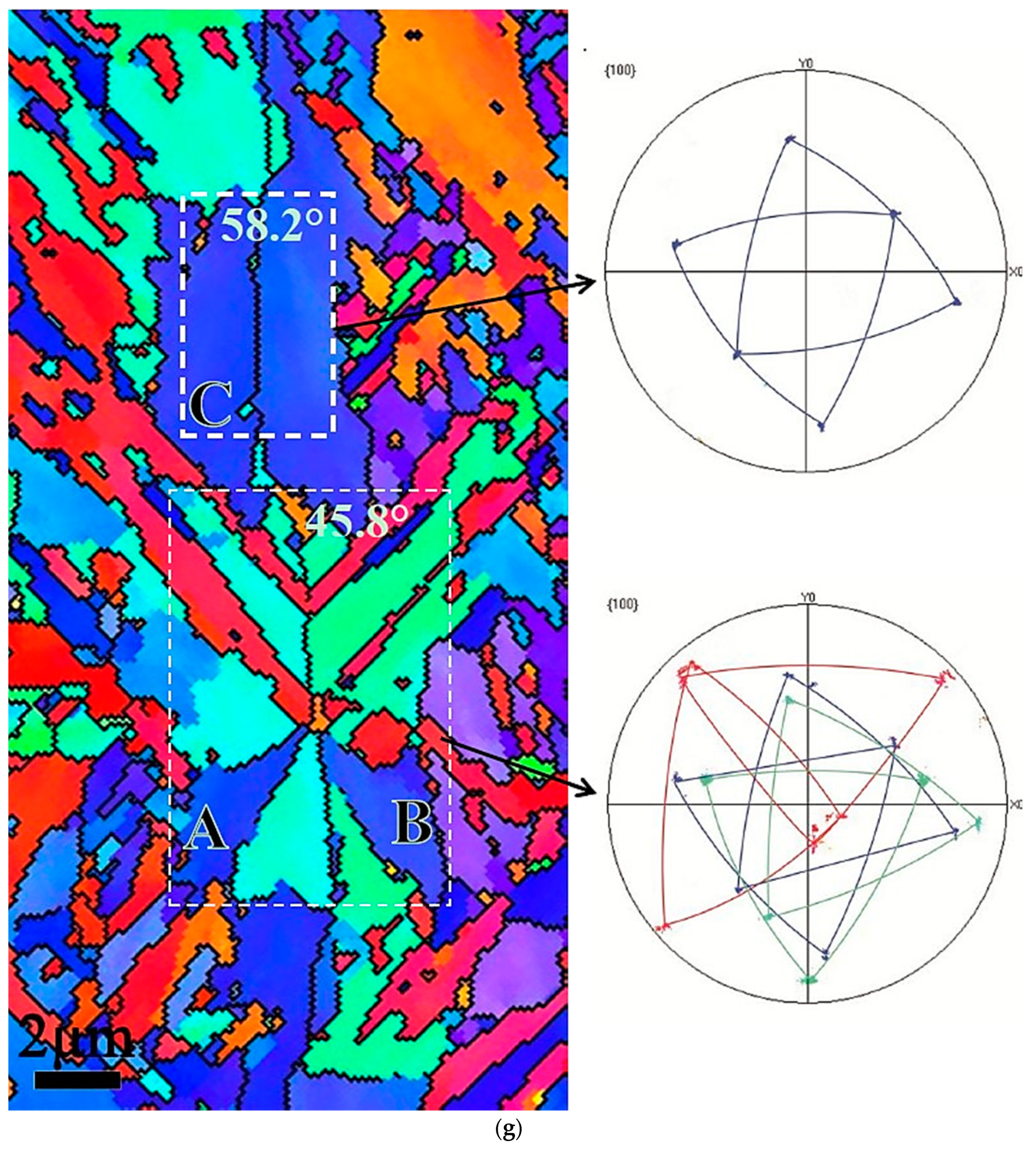
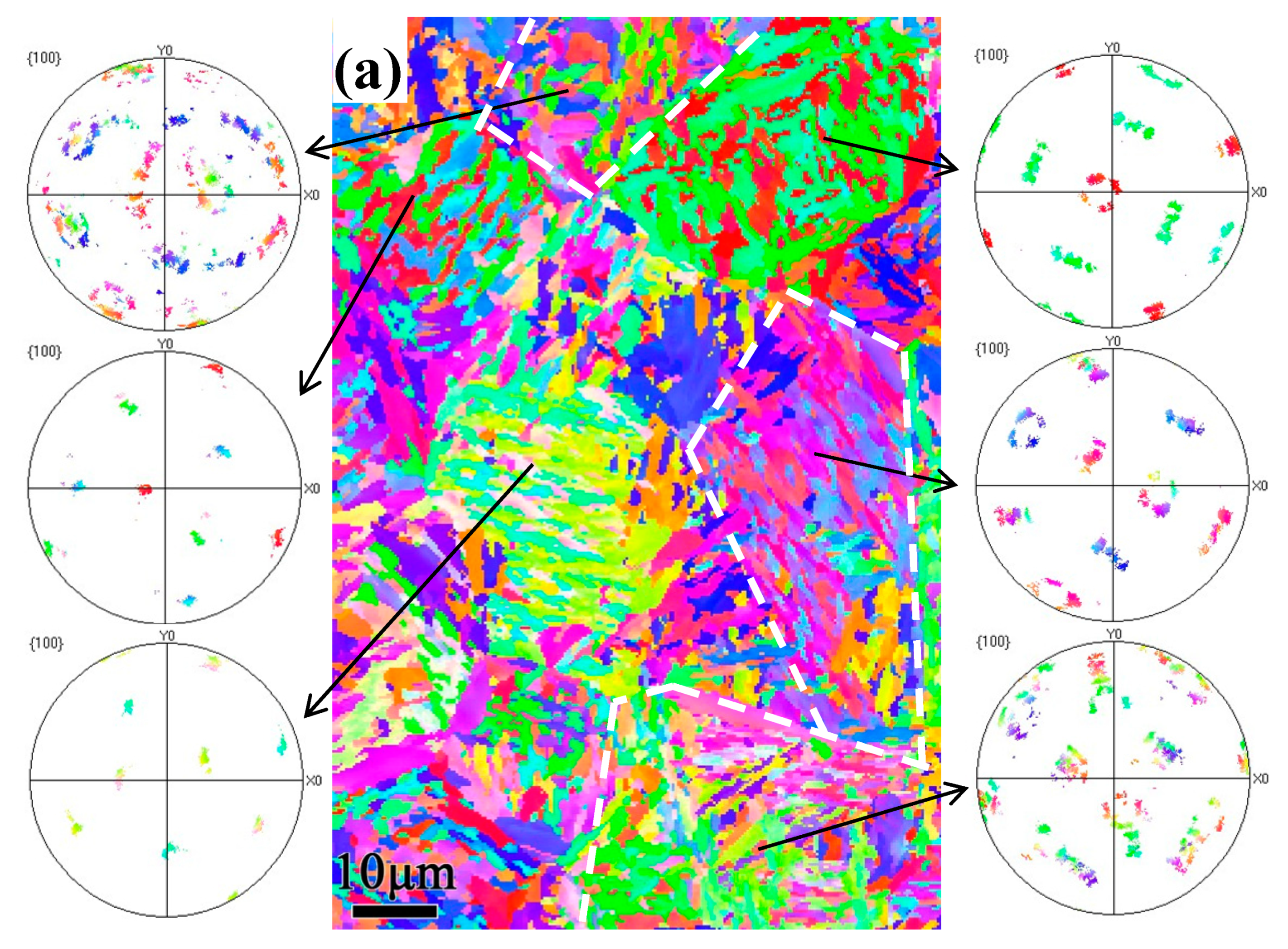
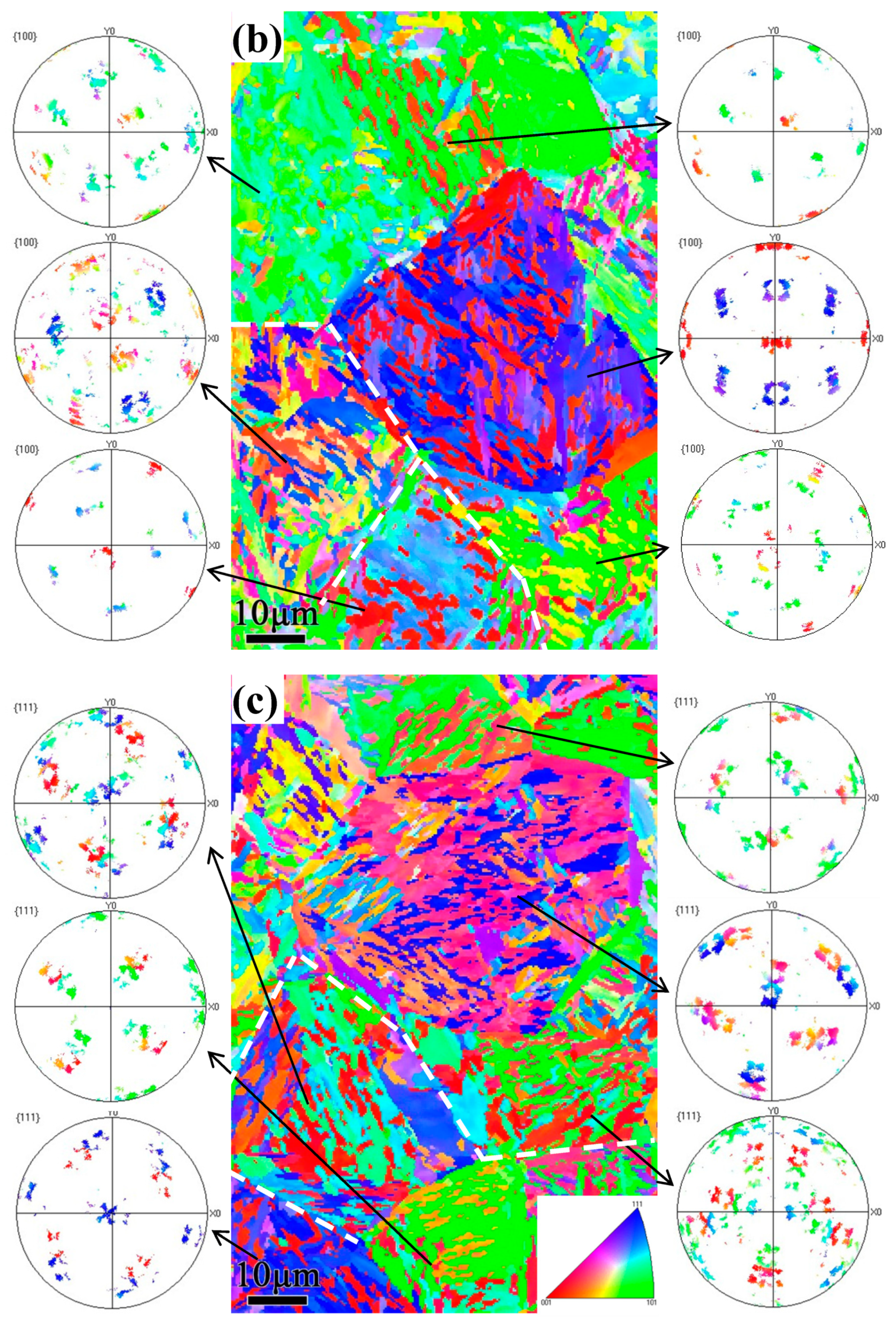
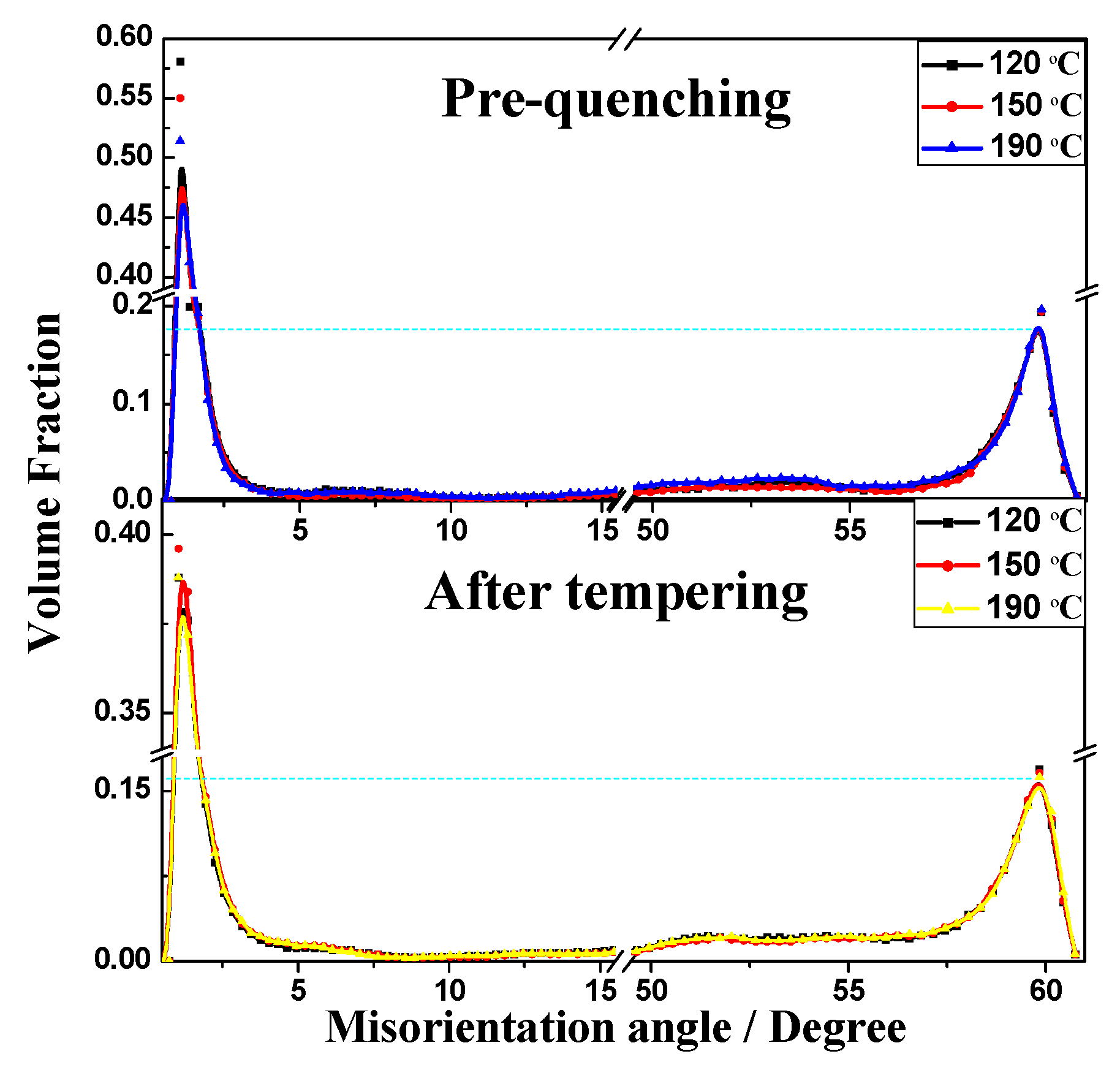
3.3. EBSD Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Crystallographic Relationship with the Tempering Multiphase Microstructure
4.2. Evolution Model of the Multiphase Microstructure
4.3. Softening Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The values at each quenching temperature clearly show a similar and decreasing tendency with increasing temperature. When the quenching temperature was set to 120 °C and isothermal treatment at 600 °C for 60 s, the multiphase structure showed highest strength, and the pearlite volume fraction after tempering was the lowest.
- (2)
- When the quenching temperature is higher, e.g., at 190 °C, the quenched martensite sheet nucleated via autocatalytic nucleation along the interface and showed an obvious symmetrical morphology.
- (3)
- After heat treatment process, the microstructure inside a nodule containing the pearlitic colonies and TM, the crystallographic orientation remains symmetric with increasing quenching temperature.
- (4)
- The microhardness of the tempered microstructure decreases with increasing quenching temperature and tempering temperature. In addition, the microhardness decreases according to a negative exponent for tempering time within 60 s.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sercombe, T.B. Sintering of Freeformed Maraging Steel with Boron Additions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 363, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, U.K.; Dey, G.K.; Asundi, M.K. Precipitation Hardening in 350 Grade Maraging Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1993, 24, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Van Der Zwaag, S. Stabilization Mechanisms of Retained Austenite in Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grässel, O.; Krüger, L.; Frommeyer, G.; Meyer, L.W. High Strength Fe–Mn–(Al, Si) Trip/Twip Steels Development—Properties—Application. Int. J. Plast. 2000, 16, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Han, Z.; Gui, X.; Luo, P.; Tan, Z.; Bai, B. Enhanced Ductility and Toughness in an Ultrahigh-Strength Mn–Si–Cr–C Steel: The Great Potential of Ultrafine Filmy Retained Austenite. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Chattopadhyay, P.P.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Manna, I. Microstructural Refinement of Bainite and Martensite for Enhanced Strength and Toughness in High-Carbon Low-Alloy Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, S.; Tian, Y.; Terada, D.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Influence of Tempering on Mechanical Properties of Ferrite and Martensite Dual Phase Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S667–S671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.C.; Sashank, S.; Nayak, E.B.; Gerlich, A.P.; Zhou, Y. Mechanism of Secondary Hardening in Rapid Tempering of Dual-Phase Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 6153–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speich, G.R.; Demarest, V.A.; Miller, R.L. Formation of Austenite During Intercritical Annealing of Dual-Phase Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1981, 12, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J. Theoretical Model for the Tensile Work Hardening Behaviour of Dual-Phase Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 147, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Yi, L.; Yun, J.; Yu, L.; Ming, Y.; Yan, L. Effect of Quenching Temperature on Martensite Multi-Level Microstructures and Properties of Strength and Toughness in 20crni2mo Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 676, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Ekrami, A. Effect of Martensite Volume Fraction on Work Hardening Behavior of Triple Phase (Tp) Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 528, 4422–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Tao, S.; Ji, X.; Yu, L. Substructure and Mechanical Properties of Pearlite Steel with Super-Cooling Technology. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 48, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, J.; Hui, W.; Dong, H. Effect of Microstructural Refinement on the Toughness of Low Carbon Martensitic Steel. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Subramanya Sarma, V.; Padmanabhan, K.A.; Jaeger, G.; Koethe, A. High Cycle Fatigue Behaviour of a Multiphase Microalloyed Medium Carbon Steel: A Comparison between Ferrite–Pearlite and Tempered Martensite Microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 362, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Lee, Y.B.; Nam, W.J. Ductility of Hypo-Eutectoid Steels with Ferrite-Pearlite Structures. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; He, T.; Guo, Z.; He, H.; Ren, F.; Volinsky, A.A. Mechanical Properties and Fracture Characteristics of High Carbon Steel after Equal Channel Angular Pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 563, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.L. Effect of Pre-Quenching on Martensite-Bainitic Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gcr15 Bearing Steel. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, B.; Mcdermid, J.R.; Vignier, S.; Zhou, N. Decoupling of the Softening Processes During Rapid Tempering of a Martensitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Varshney, A.; Verma, D.; Sangal, S.; Mondal, K. High Strength High Carbon Low Alloy Pearlite-Ferrite-Tempered Martensite Steels. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Godfrey, A.; Huang, X.; Hansen, N.; Liu, Q. Microstructure and Strengthening Mechanisms in Cold-Drawn Pearlitic Steel Wire. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3422–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ji, X.; Xiang, Z.; He, Y.; Song, X. In Situ Study of Cementite Deformation and Its Fracture Mechanism in Pearlitic Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; He, Y.; Shi, W.; Ji, X.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Ballinger, R.G. Chloride-Induced Corrosion Behavior of Cold-Drawn Pearlitic Steel Wires. Corros. Sci. 2018, 141, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, Y.; Ji, X.; Song, X. Microstructural Dependence of Anisotropic Fracture Mechanisms in Cold-Drawn Pearlitic Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinen, D.P.; Marburger, R.E. A General Equation Prescribing the Extent of the Austenite-Martensite Transformation in Pure Iron-Carbon Alloys and Plain Carbon Steels. Acta Metall. 1959, 7, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, S.; Hedstrom, P.; Borgenstam, A. A Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of Plate Martensite Formation in High-Carbon Low Alloy Steels. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, G.K.; Smallman, R.E. III. Dislocation Densities in Some Annealed and Cold-Worked Metals from Measurements on the X-Ray Debye-Scherrer Spectrum. Philo. Mag. 1956, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashchenko, M.P.; Konovalov, S.V.; Yablonskaya, T.N. Dislocation Centers in A-Martensite Formation and Dual Couplings of Thinly-Laminated Martensite Crystals. Russ. Phys. J. 1994, 37, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Khazaei, B.; Mollaahmadi, A. Rapid Tempering of Martensitic Stainless Steel Aisi420: Microstructure, Mechanical and Corrosion Properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massardier, V.; Goune, M.; Fabregue, D.; Selouane, A.; Douillard, T.; Bouaziz, O. Evolution of Microstructure and Strength During the Ultra-Fast Tempering of Fe–Mn–C Martensitic Steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 7782–7796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Phase Transformation During Intercritical Tempering with High Heating Rate in a Fe-13%Cr-4%Ni-Mo Stainless Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2013, 26, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xing, S. The Experimental Study on the Microstructure of Ss400 Steel with Traveling Magnetic Induced Rapid Tempering Process. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 189, 2818–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| C | Si | Mn | P | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.810 | 0.180 | 0.840 | 0.014 | 0.272 | Bal. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Xiang, S. Microstructure Transformation on Pre-Quenched and Ultrafast-Tempered High-Strength Multiphase Steels. Materials 2019, 12, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030396
Zhao Y, Xiang Z, Tan Y, Ji X, Zhang L, Zhang F, Xiang S. Microstructure Transformation on Pre-Quenched and Ultrafast-Tempered High-Strength Multiphase Steels. Materials. 2019; 12(3):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030396
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yonggang, Zijie Xiang, Yuanbiao Tan, Xuanming Ji, Ling Zhang, Fei Zhang, and Song Xiang. 2019. "Microstructure Transformation on Pre-Quenched and Ultrafast-Tempered High-Strength Multiphase Steels" Materials 12, no. 3: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030396
APA StyleZhao, Y., Xiang, Z., Tan, Y., Ji, X., Zhang, L., Zhang, F., & Xiang, S. (2019). Microstructure Transformation on Pre-Quenched and Ultrafast-Tempered High-Strength Multiphase Steels. Materials, 12(3), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030396






