Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti + N Ion Implanted Cronidur30 Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
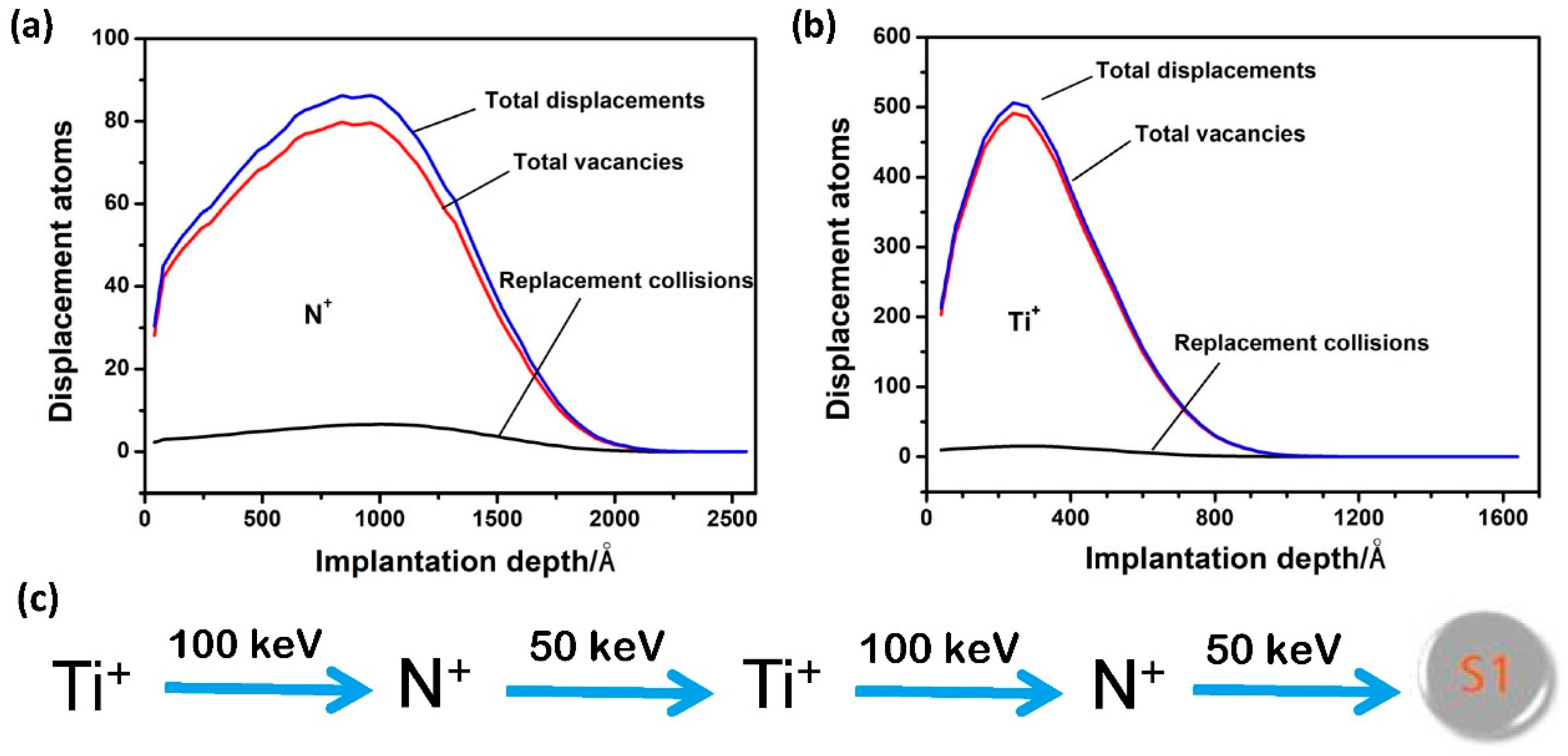
2.1. Ion Implantation and Characterization
2.2. Tribological Properties
3. Results
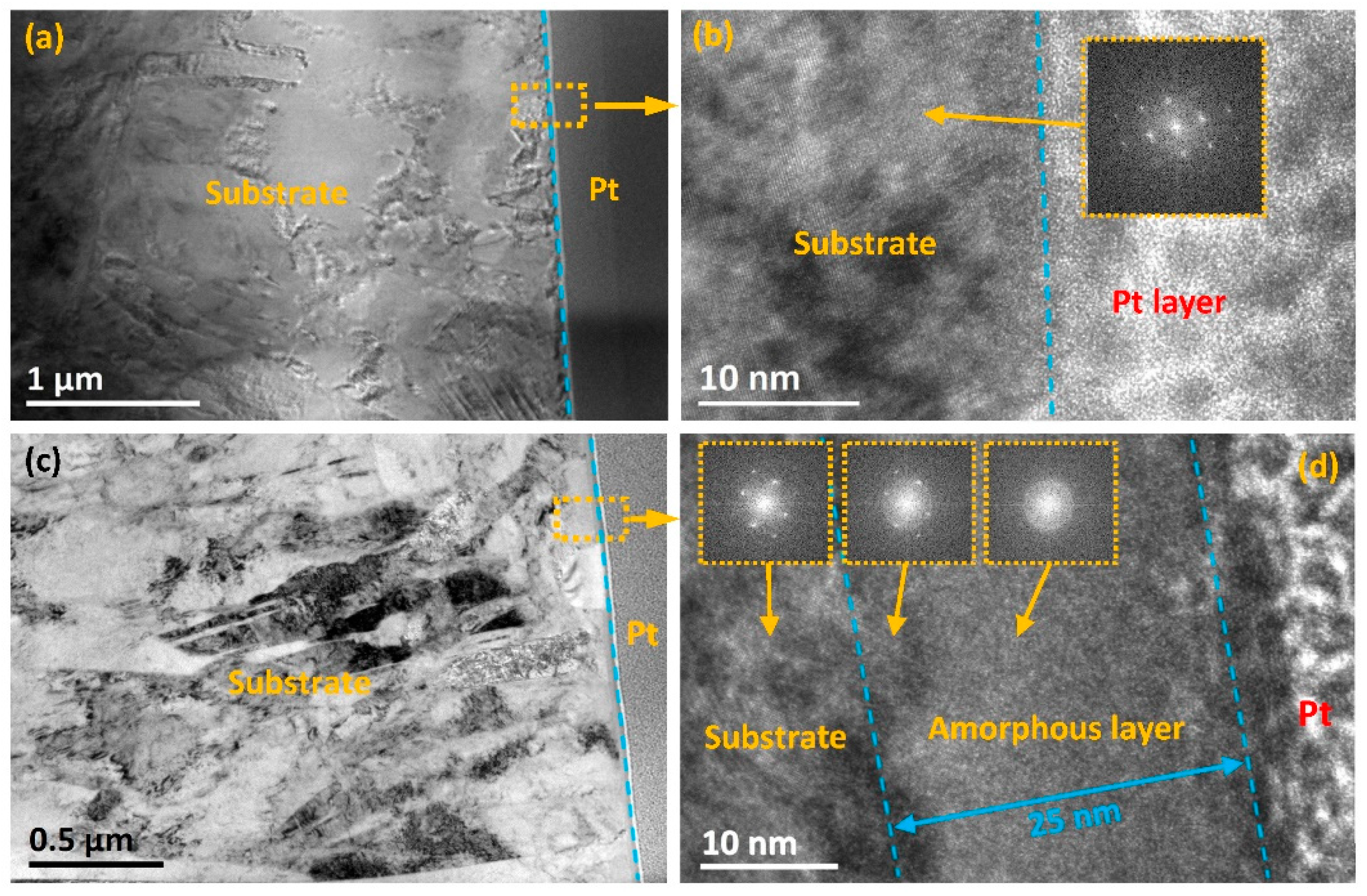
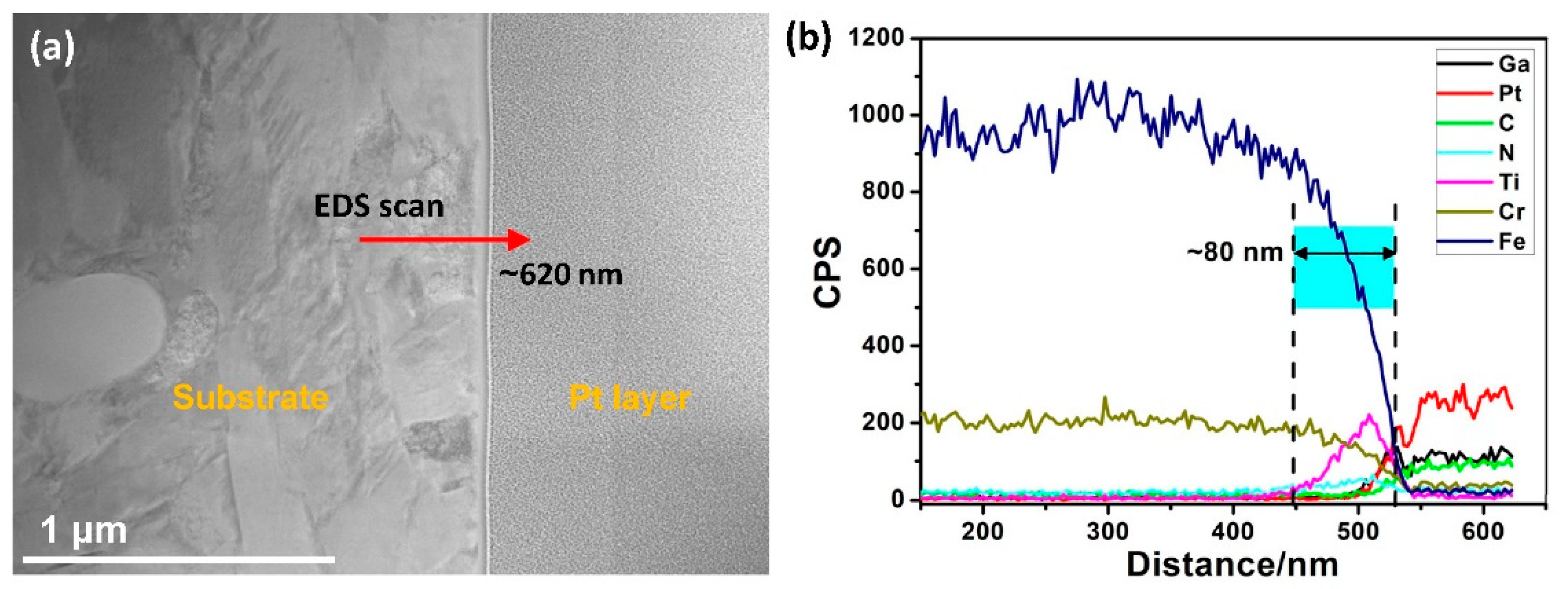
3.1. Surface Structure and Composition Evaluation
3.1.1. HRTEM Analysis
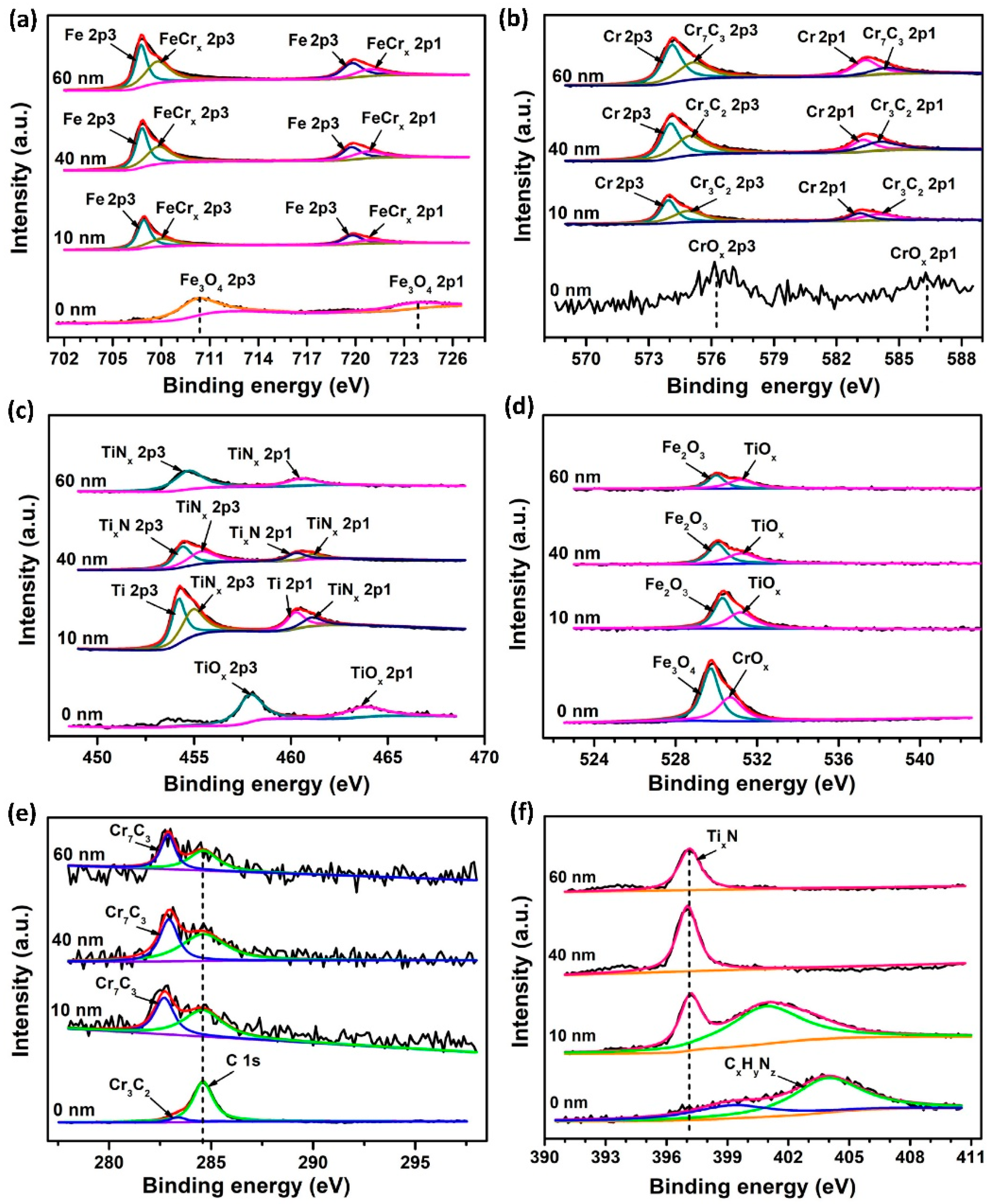
3.1.2. XPS Analysis
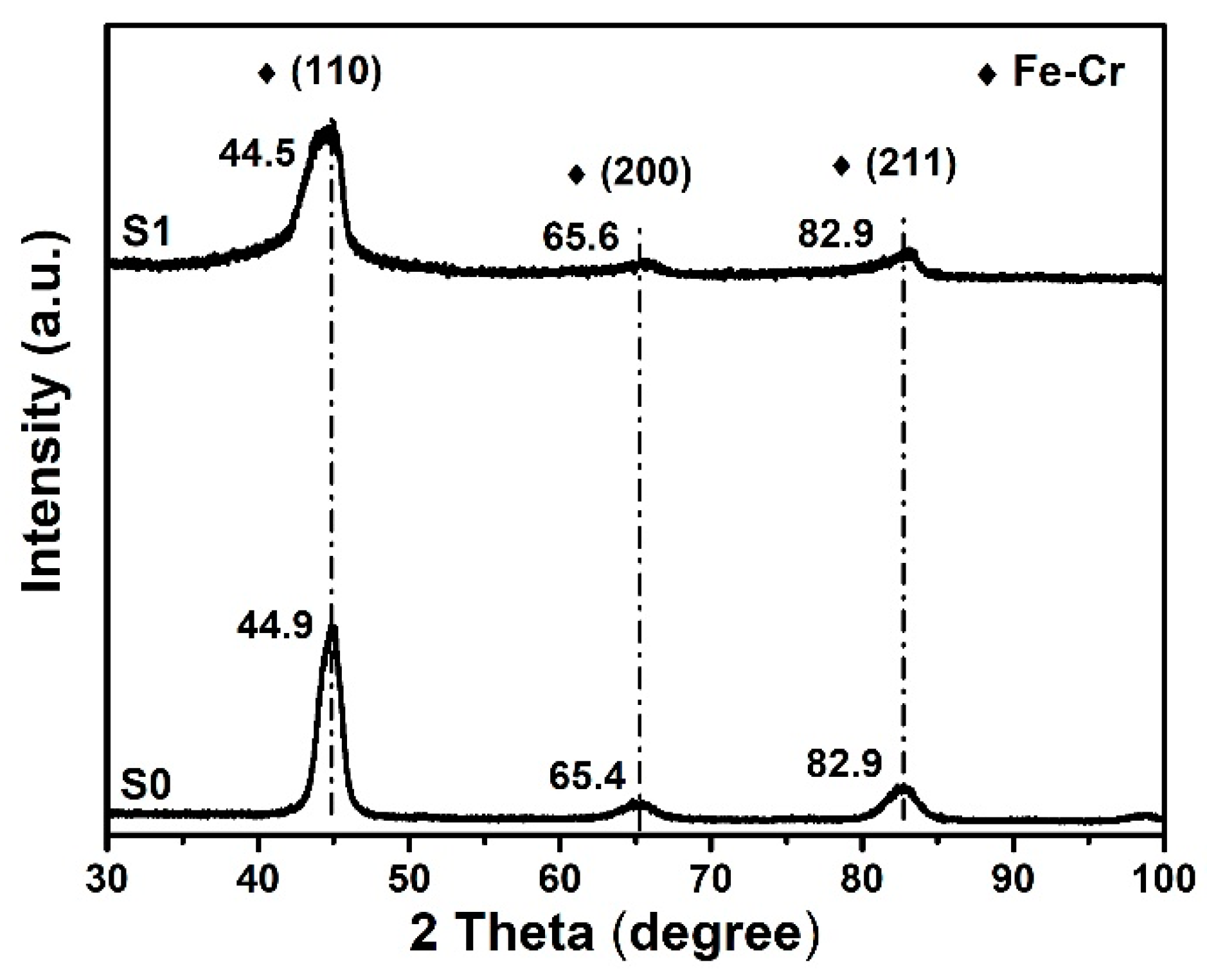
3.1.3. GIXRD Analysis
3.2. Mechanical Properties
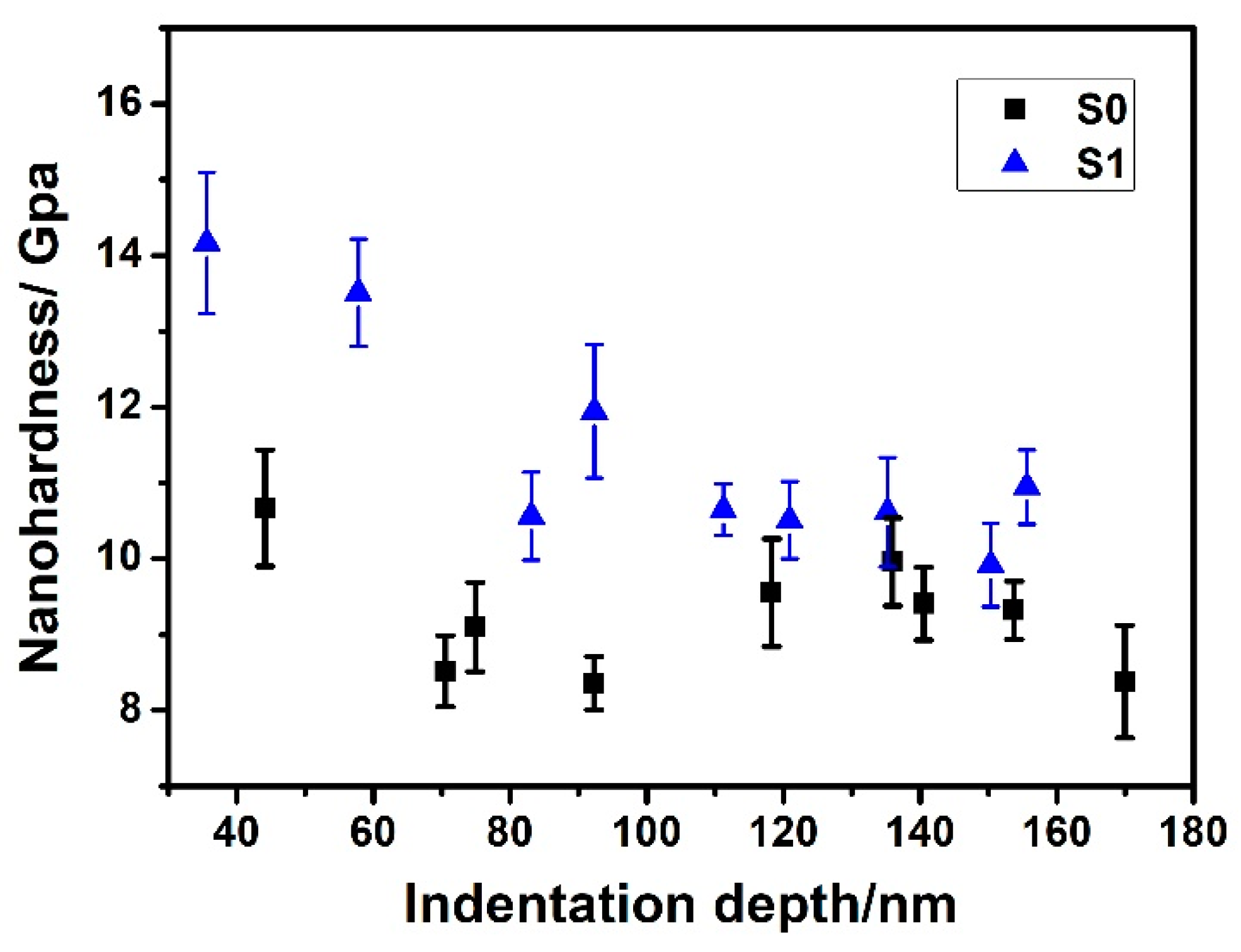
3.2.1. Nanohardness
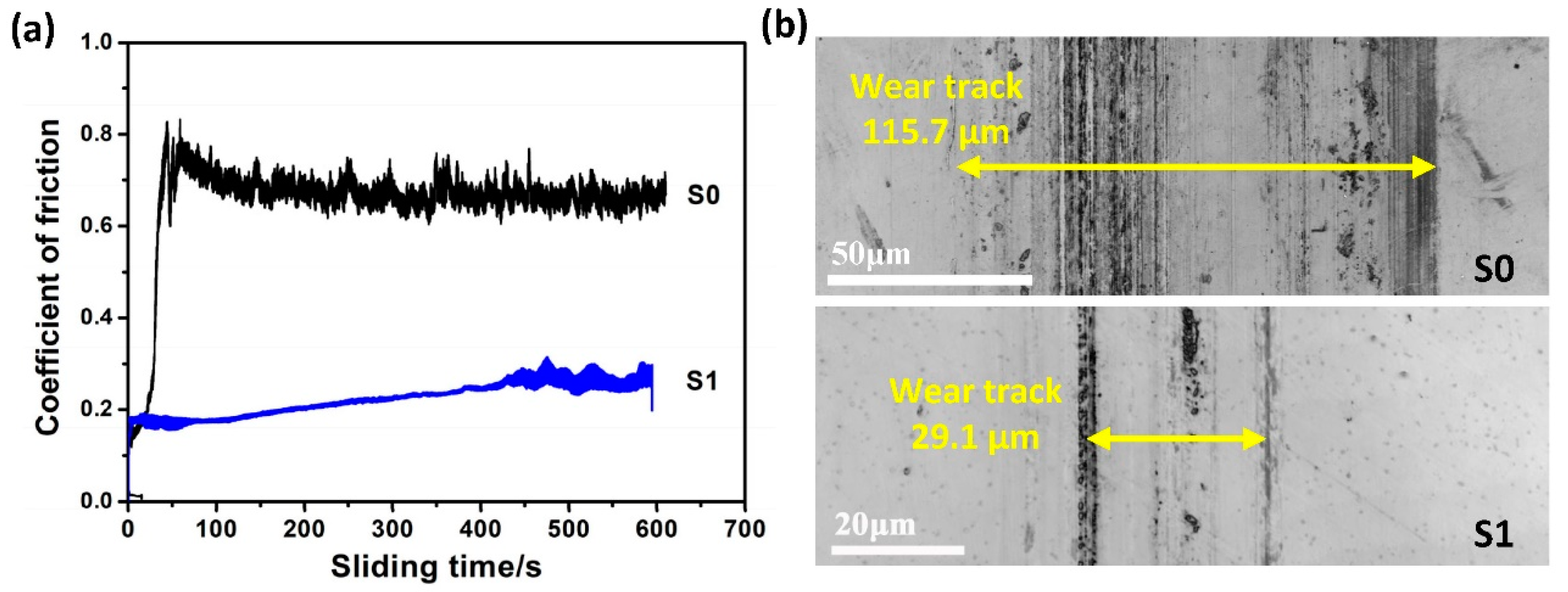
3.2.2. Tribological Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Implantation-Induced Structural Evolution
4.2. Characteristics of Ti + N Co-Implantation
4.3. Strengthening Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trojahn, W.; Streit, E.; Chin, H.A.; Ehlert, D. Progress in bearing performance of advanced nitrogen alloyed stainless steel, Cronidur 30. Materwiss. Werkst. 1999, 30, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucklenbroich, I.; Stein, G.; Chin, H.; Trojahn, W.; Streit, E. High Nitrogen Martensitic Steel for Critical Components in Aviation. Mater. Sci. Forum 1999, 318–320, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlak, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Werner, Z.; Konarski, P. Changes of tribological properties of Inconel 600 after ion implantation process. B Pol. Acad. Sci.-Tech. 2014, 62, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, P.F.; Carey, S. Bearing Steel Technologies: 9th Volume, Advances in Rolling Contact Fatigue Strength Testing and Related Substitute Technologies; Beswick, J., Ed.; ASTM Special Technical Publication: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 268–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.U.; Taylor, R. High Nitrogen Stainless Steel; DTIC Science & Technology: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mozdzen, G.; Scheerer, M.; Simon, Z.; Merstallinger, A.; Tesch, A. Behavior of Cronidur30 and 440C Steels under different SCC conditions. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Spacecraft Structures, Materials & Environmental Testing, Braunschweig, Germany, 1–4 April 2014; Volume 727. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Tribological behaviours of PVD TiN and TiCN coatings in artificial seawater. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 226, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, C.; Palombarini, G.; Poli, G.; Prandstraller, D. Sliding and abrasive wear behaviour of boride coatings. Wear 2004, 256, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, J.D.; Chandra, B.R.; Nath, A.K.; Manna, I. In situ dispersion of titanium boride on aluminium by laser composite surfacing for improved wear resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, K.C.; Nastasi, M. Ion Implantation, 4th ed.; KIRK-OTHMER Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Straede, C.A.; Mikkelsen, N.J. Implementation of ion implantation in European industry. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 84, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.J.; Treglio, J.R.; Schaffer, J.P.; Brunner, J.; Valvoda, V.; Rafaja, D. Non-destructive study of the ion-implantation-affected zone (the long-range effect) in titanium nitride. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1994, 66, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkeev, Y.P.; Kozlov, E.V. The long-range effect in ion implanted metallic materials: Dislocation structures, properties, stresses, mechanisms. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 158, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.A.; Budzynski, P.; Filiks, J.; Kobzev, A.P.; Sielanko, J. Improvement of wear and hardness of steel by nitrogen implantation. Vacuum 2004, 77, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervé, A. Improvement of tribological properties by ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1993, 60, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.R.; Wang, K.; Tie, J.; Tong, H.H.; Chen, Q.C.; Tang, D.L.; Fu, R.K.Y.; Chu, P.K. Modification of high-chromium cast iron alloy by N and Ti ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 196, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Bratushka, S.N.; Uglov, V.V.; Rusakov, V.S.; Beresnev, V.M.; Anischik, V.M.; Malikov, L.V.; Levintant, N.; Zukovski, P. Structures and properties of Ti alloys after double implantation. Vacuum 2009, 83, S240–S244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peruško, D.; Petrović, S.; Stojanović, M.; Mitrić, M.; Čizmović, M.; Panjan, M.; Milosavljević, M. Formation of intermetallics by ion implantation of multilatered Al/Ti nano-structures. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2012, 282, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabchikov, A.I.; Kashkarov, E.B.; Pushilina, N.S.; Syrtanov, M.S.; Shevelev, A.E.; Korneva, O.S.; Sutygina, A.N.; Lider, A.M. High-intensity low energy titanium ion implantation into zirconium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudjatmoko, L.S.R.M.; Wirjoadi, B.S. Effects of Nitrogen Ion Implantation on Hardness and Wear Resistance of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 18, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nikonenko, A.; Popova, N.; Nikonenko, E.; Kalashnikov, M.; Kurzina, I. Hardening by ion implantation of VT1-0 alloy having different grain size. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcak, P.; Drahokoupil, J.; Vertat, P.; Sepitka, J.; Duchon, J. Hardness response to the stability of a Ti(+N) solid solution in an annealed TiN/Ti(+N)/Ti mixture layer formed by nitrogen ion implantation into titanium. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 746, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Shao, T. Effects of single and dual-element ion implantation on tribomechanical properties of Cronidur30 bearing steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follstaedt, D.M.; Yost, F.G.; Pope, L.E.; Picraux, S.T.; Knapp, J.A. The amorphous phase and surface mechanical properties of 304 stainless steel implanted with Ti and C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1983, 43, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlak, M.; Piekoszewski, J.; Stanislawski, J.; Borkowska, K.; Sartowska, B.; Werner, Z.; Miskiewicz, M.; Jagielski, J.; Starosta, W. The effect of titanium ion implantation into carbon ceramic on its wettability by liquid copper. Vacuum 2007, 81, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Román, R.; Maffiotte, C.; González-Casablanca, J.; Perez, R.; Hole, D. A broad chemical and structural characterization of the damaged region of carbon implanted alumina. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2009, 267, 468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Knystautas, É.J.; Krishnadev, M. Enhanced microhardness of four modern steels following nitrogen ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 138, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Yao, M.; Gault, B.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D.; Hirata, A. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation. Nature 2017, 544, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulepov, M.A.; Akhmadeev, Y.K.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Kolubaeva, Y.A.; Krysina, O.V.; Kostyrya, I.D. Modification of surface layers of copper under the action of the volumetric discharge initiated by an avalanche electron beam in nitrogen and CO2 at atmospheric pressure. Russ. Phys. J. 2011, 53, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienes, G.J.; Vineyard, G.H. Radiation Effects in Solids; Interscience Publishers Ltd.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.; Wohlenberg, T.; Grant, W.A. Crystalline phase transitions produced by ion implantation. Phase Transit. 1979, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussin, S.; Margolese, D.I.; Tauber, R.N. Formation of amorphous layers by ion implantation. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynski, P. Long-range effect in nitrogen ion-implanted AISI 316L stainless steel. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2015, 342, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Biersack, J.P. The stopping and range of ions in matter. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picraux, S.T.; Pope, L.E. Tailored surface modification by ion implantation and laser treatment. Science 1984, 226, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Was, G.S.; Taller, S.; Jiao, Z.; Monterrosa, A.M.; Woodley, D.; Jennings, D.; Kubley, T.; Naab, F.; Toader, O.; Uberseder, E. Resolution of the carbon contamination problem in ion irradiation experiments. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2017, 412, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterrosa, A.M.; Woodley, D.; Jiao, Z.; Was, G.S. The influence of carbon on cavity evolution in ion-irradiated ferritic-martensitic steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 509, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigax, J.G.; Kim, H.; Aydogan, E.; Garner, F.A.; Maloy, S.; Shao, L. Beam-contamination-induced compositional alteration and its neutron-atypical consequences in ion simulation of neutron-induced void swelling. Mater. Res. Lett. 2017, 5, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Gigax, J.G.; Kim, H.; Garner, F.A.; Wang, J.; Toloczko, M.B. Carbon contamination, its consequences and its mitigation in ion-simulation of neutron-induced swelling of structural metals. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, Portland, OR, USA, 13–17 August 2017; Jackson, J., Paraventi, D., Wright, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. ISBN 978-3-319-67244-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Shao, T. Graded Microstructure and mechanical performance of Ti/N-implanted M50 steel with polyenergy. Materials 2017, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhong, N.; Rong, Y.H.; Hsu, T.Y.; Wang, L. Novel ultrahigh-strength nanolath martensitic steel by quenching-partitioning-tempering process. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.T.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C.Q.; Liu, Y.C. Nanometric-layered CrN/TiN thin films: Mechanical strength and thermal stability. Thin Solid Films 2003, 424, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Lousa, A.; Esteve, J. Evaluation of tribological and mechanical properties of CrC coatings deposited by R.F. magnetron sputtering. Dyna 2010, 77, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, J.; Rochotzki, R. Tribological behaviour and mechanical properties of physical-vapour-deposited hard coatings: TiNx, ZrNx, TiCx, TiCx/i-C. Thin Solid Films 1990, 192, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| at. % Depth/nm | C | N | O | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 51.55 | 1.48 | 37.40 | 4.16 | 5.41 |
| 10 | 4.27 | 1.46 | 5.68 | 15.68 | 72.90 |
| 40 | 4.01 | 2.73 | 5.53 | 15.75 | 71.98 |
| 60 | 3.29 | 1.99 | 4.85 | 15.96 | 73.91 |
| at.% Depth/nm | C | N | O | Ti | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 51.13 | 11.62 | 30.81 | 1.41 | 0.66 | 4.37 |
| 10 | 6.50 | 42.66 | 8.53 | 12.71 | 5.07 | 24.53 |
| 40 | 5.59 | 8.69 | 10.40 | 9.67 | 12.07 | 53.57 |
| 60 | 3.53 | 6.78 | 3.92 | 2.90 | 13.26 | 69.62 |
| Samples | Planes | 2 Theta/Degree | FWHM/Degree | D/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | (110) | 44.853 | 1.424 | 14.5 |
| S1 | (110) | 44.466 | 2.686 | 8.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, X. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti + N Ion Implanted Cronidur30 Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030427
Jin J, Wang W, Chen X. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti + N Ion Implanted Cronidur30 Steel. Materials. 2019; 12(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030427
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jie, Wei Wang, and Xinchun Chen. 2019. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti + N Ion Implanted Cronidur30 Steel" Materials 12, no. 3: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030427
APA StyleJin, J., Wang, W., & Chen, X. (2019). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti + N Ion Implanted Cronidur30 Steel. Materials, 12(3), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030427






