Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Workpiece Materials and Cutting Tools
2.2. Machining Conditions
2.3. Hole Quality and Tool Wear Evaluation
- Diameter: The measurements were done with the digital bore gauge XT3 from Bowers (Bradford, England). Calibrated setting rings were used to check the repeatability and accuracy of the measurements and variations of ±2 µm were observed. To define each diameter, three measurements were done at the entrance and exit of each layer. The average value was taken.
- Hole surface quality: This was measured with a contact profilometer MARWIN XCR20 from Mahr (Esslingen, Germany), using a 5 µm styli, with a measurement speed of 0.5 mm/s. The roughness parameter used in this case was the average roughness parameter (Ra). Three consecutives measurements of the inner surface of the hole were done, taking the highest value obtained as the result was based on Standard DIN 4774, to ensure the fulfillment of the dimensional tolerance required in all cases. Additionally, the skewness parameter (Rsk) was also calculated. Figure 2 shows the contact profilometer equipment used to analyze the hole surface quality.
- Machining induced damage on the composite layer: Holes were visually inspected to look for damage in the form of delamination and scratching produced by metallic chips, fuzzing, or thermal degradation. No damages were observed in any of the holes analyzed in this study.
- Burr: This phenomenon is characteristic of the metallic layers and it is produced at the entrance and exit of the hole. A Mitotuyo 2046S dial gauge (Kawasaki, Japan) was used. Several measurements were done on the same hole, to determine the maximum value. Differences in the values obtained for each hole were in the order of 0.05 mm.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tool Wear Characterization
3.2. Hole Quality Analysis
3.2.1. Diameter Analysis
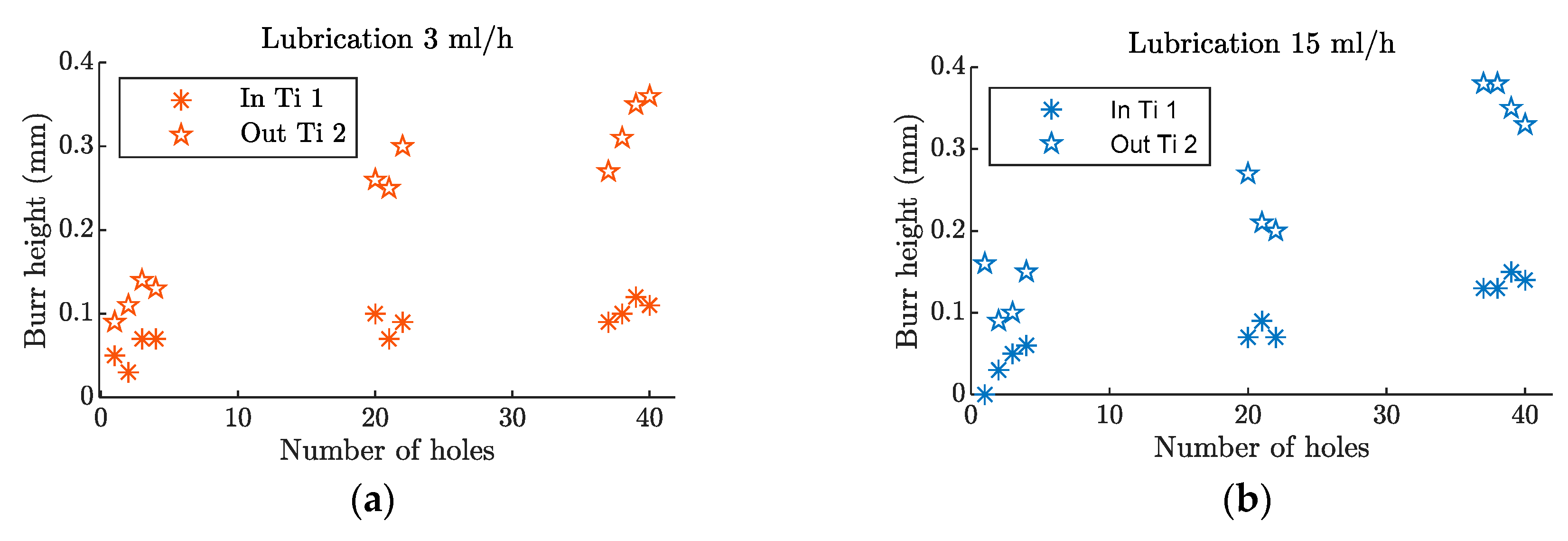
3.2.2. Burr Height Analysis
3.2.3. Hole Surface Quality Analysis
3.3. Power Consumption Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zweben, C. Advanced composites for aerospace applications: A review of current status and future prospects. Composites 1981, 12, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Ding, W.; Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, F.; Tao, J. Galvanic corrosion protection and durability of polyaniline-reinforced epoxy adhesive for bond-riveted joints in AA5083/Cf/Epoxy laminates. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Soo, S.L.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Carr, C.; Bradley, S.; M’Saoubi, R.; Leahy, W. Development of single step drilling technology for multilayer metallic-composite stacks using uncoated and PVD coated carbide tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Pinillos, U.; Girot-Mata, F.A.; Polvorosa-Teijeiro, R.; López-De-Lacalle-Marcaide, L.N. Taladrado de materiales compuestos: Problemas, prácticas recomendadas y técnicas avanzadas. DYNA 2017, 92, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, J.L.; Tardío, M.M.; Canteli, J.A.; Marcos, M.; Miguélez, M.H. Dry drilling of alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kwon, P.Y.; Sturtevant, C.; Kim, D.; Lantrip, J. Comparative tool wear study based on drilling experiments on CFRp/Ti stack and its individual layers. Wear 2014, 317, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramulu, M.; Branson, T.; Kim, D. A study on the drilling of composite and titanium stacks. Compos. Struct. 2001, 54, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Beal, A.; Kim, D.; Kwon, P.; Lantrip, J. Tool wear in drilling of composite/titanium stacks using carbide and polycrystalline diamond tools. Wear 2011, 271, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Vidal, S.R.; Fernandez-Vidal, S.; Batista, M.; Salguero, J. Tool wear mechanism in cutting of stack CFRP/UNS A97075. Materials 2018, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, B.A.; Silveira, M.L.; Vieira, L.M.G.; Abrão, A.M.; de Faria, P.E.; Rubio, J.C.C. Investigation on the effect of drill geometry and pilot holes on thrust force and burr height when drilling an aluminium/PE sandwich material. Materials 2016, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, J.; Cantero, J.L.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Miguélez, M.H. Influence of cutting parameters on tool wear and hole quality in composite aerospace components drilling. Compos. Struct. 2017, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantis, K.; Stavropoulos, P.; Chryssolouris, G. Fracture mechanics based assessment of manufacturing defects laying at the edge of CFRP-metal bondlines. Prod. Eng. 2018, 12, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Orazio, A.; El Mehtedi, M.; Forcellese, A.; Nardinocchi, A.; Simoncini, M. Tool wear and hole quality in drilling of CFRP/AA7075 stacks with DLC and nanocomposite TiAlN coated tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Beal, A.; Kang, K.; Kim, S.-Y. Hole Quality Assessment of Drilled CFRP and CFRP-TI Stacks Holes Using Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) Tools. Carbon Lett. 2017, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shyha, I.S.; Soo, S.L.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Bradley, S.; Perry, R.; Harden, P.; Dawson, S. Hole quality assessment following drilling of metallic-composite stacks. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2011, 51, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Rodríguez, A.; Calleja, A.; Fernández-Valdivielso, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Sustainability analysis of lubricant oils for minimum quantity lubrication based on their tribo-rheological performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, K.; Inasaki, I.; Sutherland, J.W.; Wakabayashi, T. Dry Machining and Minimum Quantity Lubrication. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 53, 511–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R. Effects of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) in machining processes using conventional and nanofluid based cutting fluids: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, N.A.C.; Samion, S.; Ghaderian, J.; Yazid, M.N.A.W.M. Recent progress on the application of nanofluids in minimum quantity lubrication machining: A review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasin, K.; Ayvar-Soberanis, S.; Hodzic, A. The effects of minimum quantity lubrication and cryogenic liquid nitrogen cooling on drilled hole quality in GLARE fibre metal laminates. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Lukitsch, M.J.; Alpas, A.T. Dry and minimum quantity lubrication drilling of cast magnesium alloy (AM60). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Papacharalampopoulos, A.; Vasiliadis, E.; Chryssolouris, G. Tool wear predictability estimation in milling based on multi-sensorial data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Wang, C.; Ko, S. Wear behaviour of CVD diamond-coated tools in the drilling of woven CFRP composites. Wear 2018, 398–399, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, D.; Gehin, D.; Gutierrez, M.E.; Girot, F. Modeling and tool wear in drilling of CFRP. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasin, K.; Ayvar-Soberanis, S.; Hodzic, A. Evaluation of cryogenic cooling and minimum quantity lubrication effects on machining GLARE laminates using design of experiments. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; An, Q.L.; Cai, X.J.; Ming, W.W.; Chen, M. Drilling temperature and hole quality in drilling of CFRP/aluminum stacks using diamond coated drill. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafeez, A.M.; Soo, S.L.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Dowson, A.; Arnold, D. Burr formation and hole quality when drilling titanium and aluminium alloys. Procedia CIRP 2015, 37, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, T.P.; Park, H.Y.; Ko, S.L. Experimental analysis of deburring process on inclined exit surface by new deburring tool. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, W.; Wulf, C.; Graß, P.; Willerscheid, H. Machining of Fibre Reinforced Plastics. CIRP Ann. 1985, 34, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; El Mansori, M. Experimental study on drilling mechanisms and strategies of hybrid CFRP/Ti stacks. Compos. Struct. 2016, 157, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPaolo, G.; Kapoor, S.G.; DeVor, R.E. An Experimental Investigation of the Crack Growth Phenomenon for Drilling of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Materials. J. Eng. Ind. 1996, 118, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S. Lubrication Effect of Liquid Nitrogen in Cryogenic Machining Friction on the Tool-chip Interface. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, A.K. Simulation and experimental investigation of drilling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2018, 1, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Material | Thickness (mm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Feed (mm/rev) | Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) Lubrication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | 9.3 | 15 | 0.05 | Yes |
| CFRP | 8.4 | 70 | 0.05 | No |
| Ti | 9.3 | 15 | 0.05 | Yes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Pérez, J.; Cantero, J.L.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Miguélez, M.H. Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels. Materials 2019, 12, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030448
Fernández-Pérez J, Cantero JL, Díaz-Álvarez J, Miguélez MH. Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels. Materials. 2019; 12(3):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030448
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Pérez, J., J. L. Cantero, J. Díaz-Álvarez, and M. H. Miguélez. 2019. "Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels" Materials 12, no. 3: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030448
APA StyleFernández-Pérez, J., Cantero, J. L., Díaz-Álvarez, J., & Miguélez, M. H. (2019). Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels. Materials, 12(3), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030448







