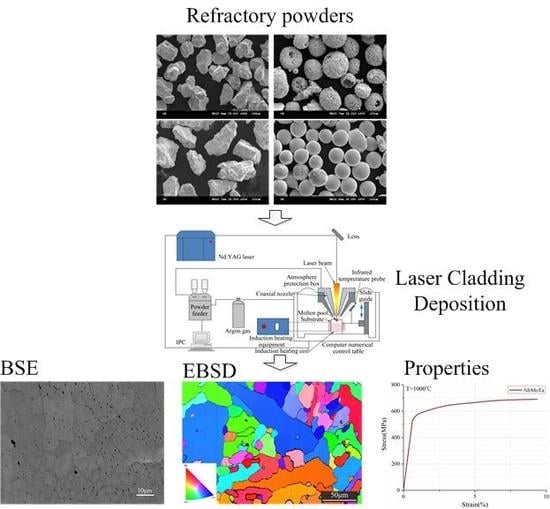
WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Chemical and Phase Composition
3.2. Density and Microstructure
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The crystal structures of each WxNbMoTa (x = 0, 0.16, 0.33, 0.53) alloys are all a single-phase solid solution of the BCC structure analyzed by XRD.
- (2)
- Due to the characteristic of rapid solidification, the size of the grains and dendrites on the microcosmic of WxNbMoTa refractory HEAs was 20 μm and 4 μm on average, smaller than that of the HEAs fabricated by VAM.
- (3)
- The increase of the tungsten concentration of WxNbMoTa led to four results of the Vickers microhardness, i.e., Hv = 459.2 ± 9.7, 476.0 ± 12.9, 485.3 ± 8.7, 497.6 ± 5.6, respectively.
- (4)
- The NbMoTa alloy has a compressive strain (εp) of 5.8% at room temperature and its yield strength (σb), compressive strength (σm) and compressive strain (εp) of 530 MPa, 684 Mpa and 8.5% respectively at 1000 °C. The effects show better performance than many traditional refractory metals such as T-111, Nb-1Zr, and C103, which are commonly used in aerospace.
- (5)
- The content of tungsten has no effect on the formation of a single-phase solid solution and the microstructure of the HEAs. In terms of mechanical behavior, the microhardness shows an increasing tendency with the increase of the content of tungsten. As a result, the yield strength and plasticity of the W-free alloy is improved compared with alloys containing tungsten at room temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Gouvea, L.; Hornik, V.; Kovacova, Z.; Kitzmantel, M.; Neubauer, E.; Dlouhy, I. Synergic strengthening by oxide and coherent precipitate dispersions in high-entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 157, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Huang, L.; He, W.; Liaw, P.K. Alloying and processing effects on the aqueous corrosion behavior of high-entropy alloys. Entropy 2014, 16, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. The effect of molybdenum on the corrosion behaviour of the high-entropy alloys Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mox in aqueous environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Maiti, S.; Steurer, W.; Spolenak, R. Size-dependent plasticity in an Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Ma, H.; Spolenak, R. Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juan, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Hsu, W.L.; Lin, C.M.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Simultaneously increasing the strength and ductility of a refractory high-entropy alloy via grain refining. Mater. Lett. 2016, 184, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Tian, F.; Wang, D. Thermodynamic properties of refractory high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 682, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körmann, F.; Sluiter, M.H.F. Interplay between lattice distortions, vibrations and phase stability in NbMoTaW high entropy alloys. Entropy 2016, 18, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Chen, N.; Zhao, S.F.; Fan, L.W.; Yang, G.N.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Effect of Ti additions on mechanical properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 84, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.C.; He, J.K.; Tian, X.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, A.F.; Lian, Q.; Jin, Z.M.; Lu, B.H. Additive manufacturing: integrated fabrication of macro/microstructures. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelstein, H.; Thiele, M.; Gurevich, E.L.; George, E.P.; Ostendorf, A. Direct metal deposition of refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaW. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, D. The thermal-mechanical behavior of WTaMoNb high-entropy alloy via selective laser melting (SLM): experiment and simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C.; Miracle, D.B. Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Irradiation Damage in Multicomponent Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.F.; Rajan, K. Statistically based assessment of formation enthalpy for intermetallic compounds. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 612, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liaw, P.K. Alloy design and properties optimization of high-entropy alloys. JOM 2012, 64, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Azer, M.; Ritter, A. Studies of standard heat treatment effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser net shape manufactured Inconel 718. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2009, 40, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, D.F.; Puskar, J.D.; Brooks, J.A.; Robino, C.V. Quantitative characterization of porosity in stainless steel LENS powders and deposits. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobryn, P.A.; Moore, E.H.; Semiatin, S.L. Effect of laser power and traverse speed on microstructure, porosity, and build height in laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.H.; Rosen, A.; Karch, J.; Gleiter, H. On the validity of the hall-petch relationship in nanocrystalline materials. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, M.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Microhardness measurements and the hall-petch relationship in an Al-Mg alloy with submicrometer grain size. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 4619–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N. Hall-petch relation and boundary strengthening. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Bai, Y.; Tsuji, N. Friction stress and Hall-Petch relationship in CoCrNi equi-atomic medium entropy alloy processed by severe plastic deformation and subsequent annealing. Scr. Mater. 2017, 134, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Soni, V.; Lee, M.; Mantri, S.A.; Ren, Y.; Banerjee, R. Optimizing the coupled effects of Hall-Petch and precipitation strengthening in a Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Tournier, J.M. A review of refractory metal alloys and mechanically alloyed-oxide dispersion strengthened steels for space nuclear power systems. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 340, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Metallic Element. | W | Nb | Mo | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Atomic Mass, u | 183.84 | 92.9 | 95.94 | 180.9 |
| r, Å | 1.37 | 1.43 | 1.36 | 1.43 |
| ρ, g/cm3 | 19.35 | 8.57 | 10.2 | 16.65 |
| Hv | 350 | 135 | 156 | 89 |
| Tm, K | 3695 | 2750 | 2896 | 3290 |
| Alloy ID/element | W | Nb | Mo | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NbMoTa | 0% | 31.26% | 32.90% | 35.84% |
| W0.16NbMoTa | 5.80% | 29.76% | 30.86% | 33.58% |
| W0.33NbMoTa | 12.42% | 27.40% | 30.01% | 30.17% |
| W0.53NbMoTa | 14.95% | 26.80% | 27.62% | 30.63% |
| Parameter/Alloy ID | NbMoTa | W0.16NbMoTa | W0.33NbMoTa | W0.53NbMoTa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ, % | 2.334 | 2.359 | 2.365 | 2.364 |
| ΔSmix, J·mol−1·K−1 | 9.14 | 10.33 | 10.93 | 11.28 |
| ΔHmix, J·mol−1 | −4.67 | −5.22 | −5.69 | −6.07 |
| Tm, K | 2979 | 3015 | 3050 | 3086 |
| Ω, | 5.83 | 5.96 | 5.86 | 5.74 |
| Alloy ID/Density | Theoretical Density; g/cm3 | Experimental Density; g/cm3 |
|---|---|---|
| NbMoTa | 11.913 | 10.486 |
| W0.16NbMoTa | 12.205 | 10.572 |
| W0.33NbMoTa | 12.595 | 10.634 |
| W0.53NbMoTa | 12.940 | 11.044 |
| Hv/Alloy ID | NbMoTa | W0.16NbMoTa | W0.33NbMoTa | W0.53NbMoTa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Hv | 459.2 ± 9.7 | 476.0 ± 12.9 | 485.3 ± 8.7 | 497.6 ± 5.6 |
| Alloy ID | Yield Strength at 1000 °C/MPa |
|---|---|
| Nb-1Zr | 113 |
| C103 | 144 |
| ODS-MA754 | 212 |
| Mo-14Re | 371 |
| T111 | 505 |
| NbMoTa | 530 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Yan, H. WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030533
Li Q, Zhang H, Li D, Chen Z, Huang S, Lu Z, Yan H. WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials. 2019; 12(3):533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030533
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingyu, Hang Zhang, Dichen Li, Zihao Chen, Sheng Huang, Zhongliang Lu, and Haoqi Yan. 2019. "WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition" Materials 12, no. 3: 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030533
APA StyleLi, Q., Zhang, H., Li, D., Chen, Z., Huang, S., Lu, Z., & Yan, H. (2019). WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials, 12(3), 533. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030533