Microstructure Evolution and Orientation Relationship of Reverted Austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
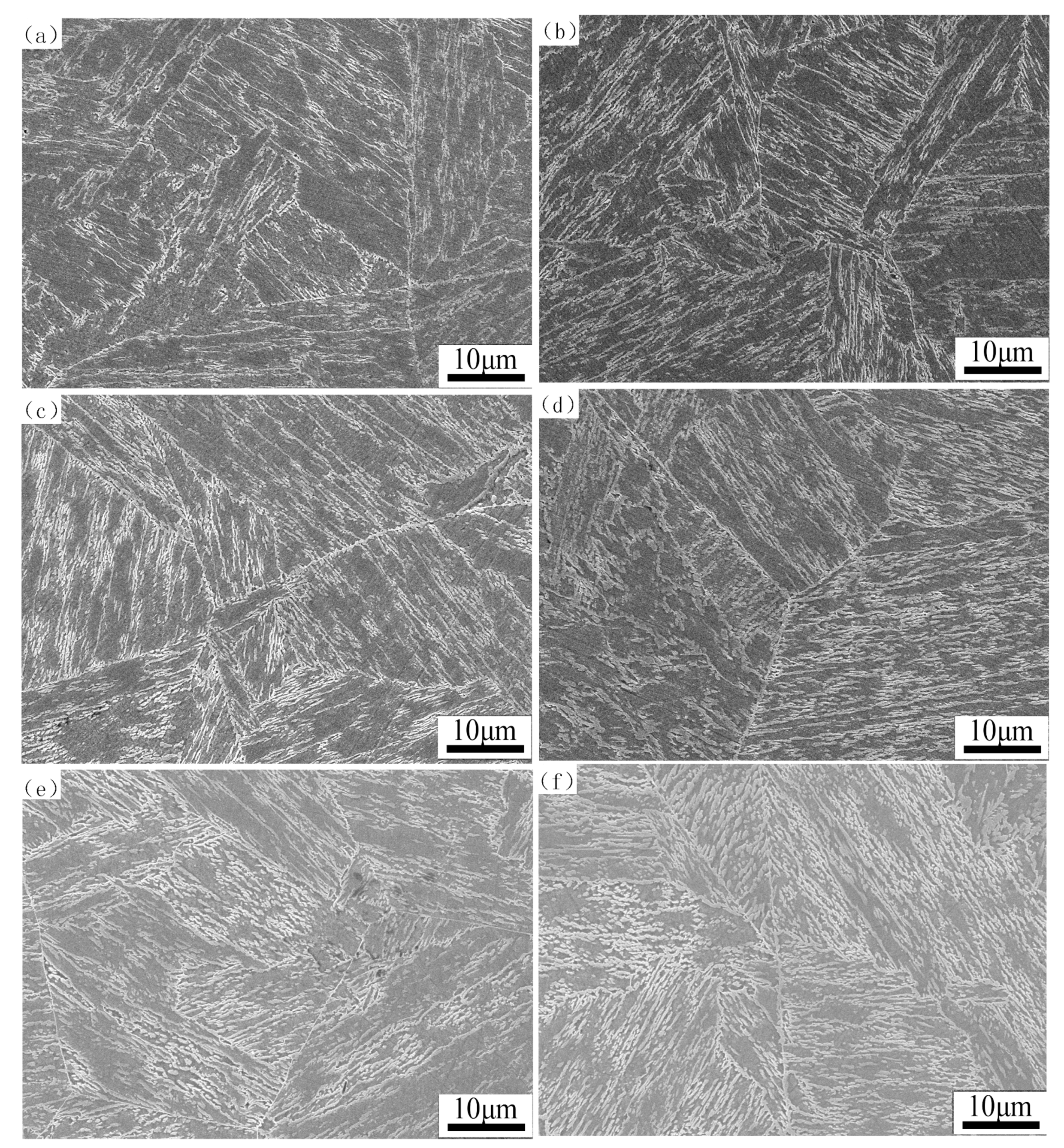
3.1. Microstructure Characterization of Reverted Austenite
3.2. The Effect of Reverted Autenite Contents on Mechanical Properties
3.3. The Misorientation Analysis of the Reverted Austenite
3.4. The mechanism of the Reverted Austenite
4. Conclusions
- The microstructure mainly consists of tempered martensite and reverted austenite in the supermartensitic stainless steel. The amount of reverted austenite at room temperature increases and the micro-hardness correspondingly decreases during tempering at 620 °C for 1 h to 32 h. The results suggest that the contents of reverted austenite have an effect on the mechanical properties;
- The reverted austenite nucleates uniformly and transforms at sub-block boundaries and prior grain austenite boundaries. As the tempering time increases, the low angle grain boundaries decrease and the dislocation density also exhibits a dramatic decline compared to the martensite matrix of tempering at 620 °C for 2 h to 32 h. The orientation relationship between reverted austenite and martensite is (111)γ//(011)α and [10]γ//[11]α, which meets the K–S relationship and the deviation angle is mainly concentrated at about 2 degrees;
- The transformation mechanism of martensite to reverted austenite is formed by a diffusional process. Considering the chemical composition of nickel contents, it is concluded that the reverted austenite is formed by nickel diffusion during the tempering process. It revealed that the growth kinetics of the reverted austenite are dominated by the diffusion of Ni contents and there is no shear of the martensite matrix in situ observation by HTLSCM.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zepon, G.; Nascimento, A.R.C.; Kasama, A.H.; Nogueira, R.P.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Design of wear resistant boron-modified supermartensitic stainless steel by spray forming process. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rovere, C.A.; Ribeiro, C.R.; Silva, R.; Baroni, L.F.S.; Alcântara, N.G.; Kuri, S.E. Microstructural and mechanical characterization of radial friction welded supermartensitic stainless steel joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 586, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, E.; Dhooge, A. Weldability Assessment of Thick Super-Martensitic 13Cr Stainless Steel Welds Made with Matching Consumables. Weld. World 2005, 49, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, J.M.; Rovere, C.A.D.; Kuri, S.E. Localized Corrosion Susceptibility of Supermartensitic Stainless Steel in Welded Joints. Corrosion 2008, 64, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, N.; May, J.E.; Mariano, N.A.; Nascente, P.A.P.; Kuri, S.E. Corrosion behavior of supermartensitic stainless steel in aerated and CO2-saturated synthetic seawater. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 428, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.H.; Shek, C.H.; Lai, J.K.L. Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 65, 39–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, A.; Yin, C.; Macdonald, D.D. Impact of Reversed Austenite on the Pitting Corrosion Behavior of Super 13Cr Martensitic Stainless Steel. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, T.J.; Chauveau, E.; Mantel, M.; Bouvier, N.; Koschel, D. Corrosion and metallurgical investigation of two supermartensitic stainless steels for oil and gas environments. Corros. Sci. 2014, 81, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, M.; Lovicu, G.; Valentini, R.; Dimatteo, A.; Ishak, R.; Migliaccio, U.; Montanari, R.; Pietrangeli, E. Microstructural Features Affecting Tempering Behavior of 16Cr–5Ni Supermartensitic Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Subramanian, S.V.; Liu, C. Studies on Nb Microalloying of 13Cr Super Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4475–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Su, J.; Zhao, K. Effect of Cu addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of 15% Cr super martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, W.; Zhao, C. Effect of 0.2 and 0.5% Ti on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 13Cr supermartensitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 4253–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.D.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Faria, G.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Oliveira, J.P.; Salvador, C.A.F.; Mei, P.R.; Babu, S.S.; Ramirez, A.J. Compositional analysis on the reverted austenite and tempered martensite in a Ti-stabilized supermartensitic stainless steel: Segregation, partitioning and carbide precipitation. Mater. Des. 2018, 140, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.A.D.; Bandeira, R.M.; Duarte, B.B.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G.; Jorge, A.M. Effect of phosphorus content on the mechanical, microstructure and corrosion properties of supermartensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 650, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.F.; Tavares, S.S.M.; Pardal, J.M.; Silva, M.R.; de Abreu, H.F.G. Influence of heat treatments on toughness and sensitization of a Ti–alloyed supermartensitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 7737–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Miyazaki, T. Effect of retained austenite on the microstructure and mechanical properties of martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, D.S.; Lee, Y.D.; Jun, J.H.; Choi, C.S. Amount of retained austenite at room temperature after reverse transformation of martensite to austenite in an Fe–13%Cr–7%Ni–3%Si martensitic stainless steel. Scripta Mater. 2001, 45, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, B.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Hassanli, A.M. Influence of Retained Austenite on the Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel Castings. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Rong, L.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Nagai, T. Reversed austenite in 0Cr13Ni4Mo martensitic stainless steels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 143, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojack, A.; Zhao, L.; Morris, P.F.; Sietsma, J. Austenite Formation from Martensite in a 13Cr6Ni2Mo Supermartensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, D.; Yong, Q.; Su, J.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, W. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Property of Cr13 Super Martensitic Stainless Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Shin, H.C.; Leem, D.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Jin, W.; Choi, C.S. Reverse transformation mechanism of martensite to austenite and amount of retained austenite after reverse transformation in Fe–3Si–13Cr–7Ni (wt-%) martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, J.D.; Faria, G.A.; Wu, L.; Oliveira, J.P.; Mei, P.R.; Ramirez, A.J. Austenite reversion kinetics and stability during tempering of a Ti-stabilized supermartensitic stainless steel: Correlative in situ synchrotron x-ray diffraction and dilatometry. Acta Mater. 2017, 138, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Su, J.; Zhao, K. Study on the crystallographic orientation relationship and formation mechanism of reversed austenite in economical Cr12 super martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2015, 109, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Su, J. Formation of Reversed Austenite in High Temperature Tempering Process and its Effect on Mechanical Properties of Cr15 Super Martensitic Stainless Steel Alloyed with Copper. Steel Res. Int. 2012, 84, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.; Matlock, D.K.; Cooman, B.C.D.; Schroth, J.G. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilmes, P.D.; Solari, M.; Llorente, C.L. Characteristics and effects of austenite resulting from tempering of 13Cr–NiMo martensitic steel weld metals. Mater. Charact. 2001, 46, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Yoo, D.K.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, J.H.; Sung, J.H.; Kang, C.Y. Formation of reversed austenite during tempering of 14Cr−7Ni−0.3Nb−0.7Mo−0.03C super martensitic stainless steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2004, 10, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojack, A.; Zhao, L.; Morris, P.F.; Sietsma, J. In-situ determination of austenite and martensite formation in 13Cr6Ni2Mo supermartensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2012, 71, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.C.; Liu, W.B.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.G. Reversed Austenite Growth Behavior of a 13%Cr–5%Ni Stainless Steel during Intercritical Annealing. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Z.G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.B. An in situ study on austenite memory and austenitic spontaneous recrystallization of a martensitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7204–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Terasaki, H.; Komizo, Y.I. In-situ observation of martensite transformation and retained austenite in supermartensitic stainless steel. Trans. JWRI 2010, 39, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Rong, L.; Li, Y. The influence of tempering temperature on the reversed austenite formation and tensile properties in Fe–13%Cr–4%Ni–Mo low carbon martensite stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4075–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojack, A.; Zhao, L.; Morris, P.F.; Sietsma, J. In Situ Thermo-magnetic Investigation of the Austenitic Phase During Tempering of a 13Cr6Ni2Mo Supermartensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5956–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Hui, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Weng, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled medium-Mn steel containing 3% aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsaz-Borujerdi, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Karam-Abian, M.; Ding, H.; Han, D.; Kheradmand, N. Room temperature mechanical properties and microstructure of a low alloyed TRIP-assisted steel subjected to one-step and two-step quenching and partitioning process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 725, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, Z.G.; Zhang, C. Effect of retained austenite on austenite memory of a 13% Cr–5% Ni martensitic steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, S654–S660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.S. Effect of tempering temperature on properties of 00Cr16Ni5Mo stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Chandan, A.K.; Kundu, S. Hot rolled and cold rolled medium manganese steel: Mechanical properties and microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 701, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicupira, F.L.; Sandim, M.J.R.; Sandim, H.R.Z.; Santos, D.B.; Renzetti, R.A. Quantification of retained austenite by X-ray diffraction and saturation magnetization in a supermartensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2016, 115, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Huang, X.; Furuhara, T.; Maki, T.; Hansen, N. The morphology and crystallography of lath martensite in alloy steels. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 5323–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S.; Hashizume, S. Variant Selection of Reversed Austenite in Lath Martensite. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grajcar, A.; Kwaśny, W.; Zalecki, W. Microstructure–property relationships in TRIP aided medium-C bainitic steel with lamellar retained austenite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Aindow, M.; Pond, R.C. Precipitate orientation relationships and interfacial structures in duplex stainless steel Zeron-100. Philos. Mag. 2003, 83, 1867–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Ni | Cr | Cu | Mo | V | Ti | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.011 | 0.001 | 5.8 | 12.5 | 0.085 | 2.05 | 0.054 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Li, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, S. Microstructure Evolution and Orientation Relationship of Reverted Austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process. Materials 2019, 12, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040589
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Yuan X, Li D, Yin Y, Li S. Microstructure Evolution and Orientation Relationship of Reverted Austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process. Materials. 2019; 12(4):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040589
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiwei, Chi Zhang, Xiaomin Yuan, Diankai Li, Yuande Yin, and Shengzhi Li. 2019. "Microstructure Evolution and Orientation Relationship of Reverted Austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process" Materials 12, no. 4: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040589
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, C., Yuan, X., Li, D., Yin, Y., & Li, S. (2019). Microstructure Evolution and Orientation Relationship of Reverted Austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process. Materials, 12(4), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040589




