Magnetic Field Patterning of Nickel Nanowire Film Realized by Printed Precursor Inks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ink Formulation
2.3. Aerosol Printing
2.4. Ink Characterization
2.5. Alignment Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
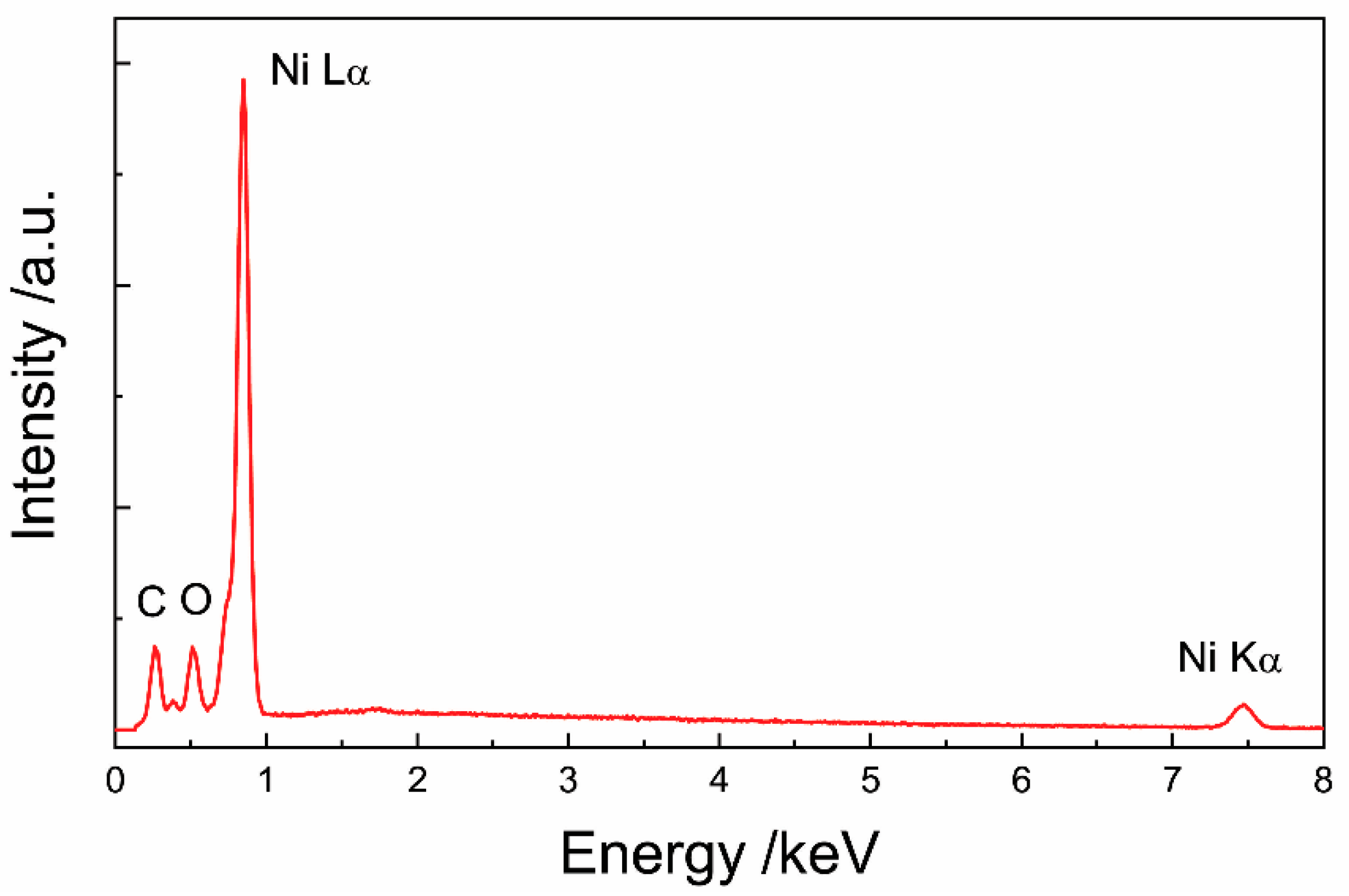
3.1. Ni Ink Characterization
3.2. Printing of Ni Ink
3.3. Reduction of Ni Ink
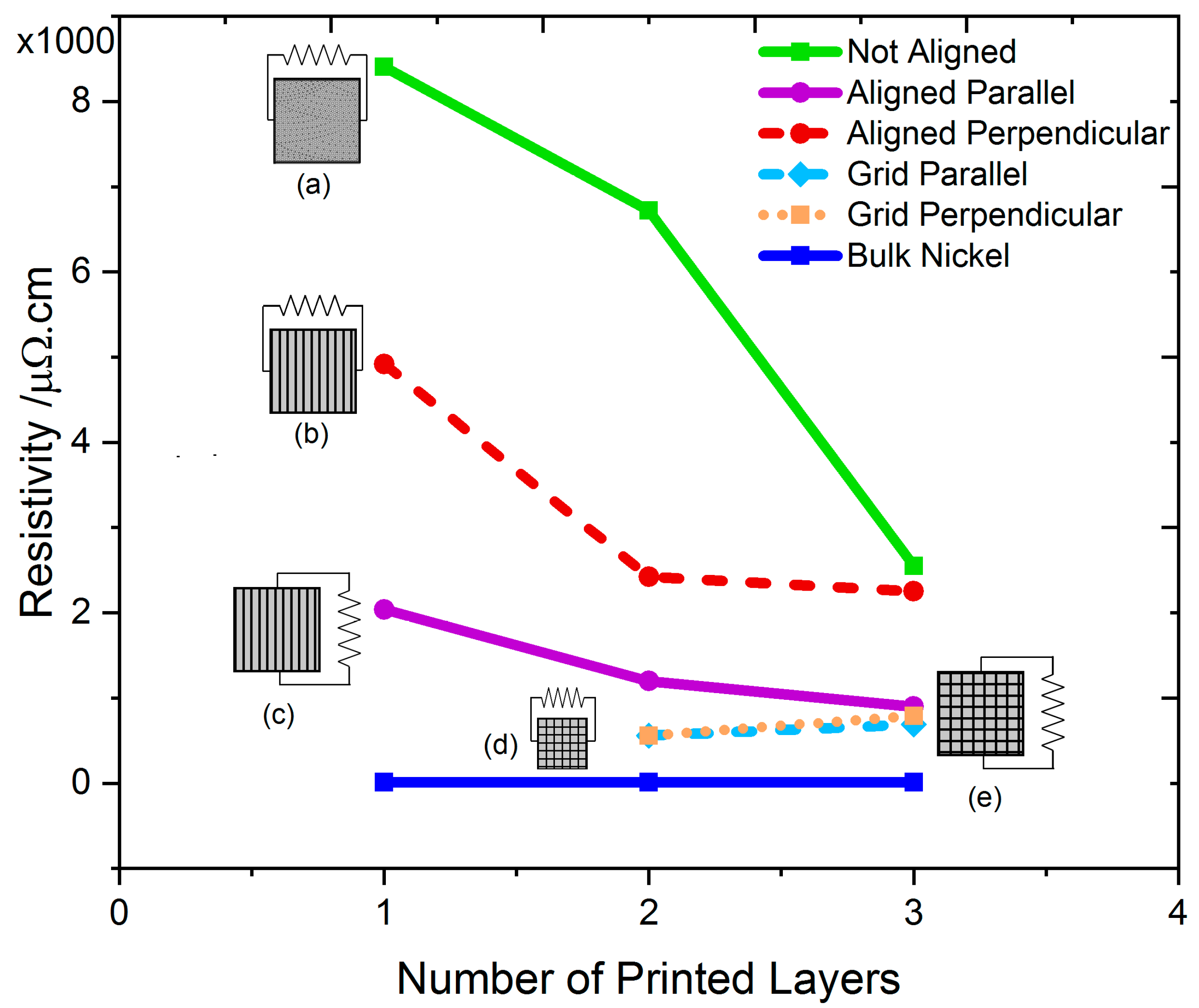
3.4. Electrical Characterization
3.5. Magnetic Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu-Khalaf, J.; Al-Ghussain, L.; Al-Halhouli, A.A. Fabrication of Stretchable Circuits on Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Pre-Stretched Substrates by Inkjet Printing Silver Nanoparticles. Materials 2018, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Al-Milaji, K.N.; Zhao, H. Inkjet printing of silver nanowires for stretchable heaters. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Rida, A.; Vyas, R.; Tentzeris, M.M. RFID tag and RF structures on a paper substrate using inkjet-printing technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2007, 55, 2894–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, T.P.; Kirshchenmann, K.J. Antennas with discrete resistive loading built by direct-write fabrication. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 9–15 June 2007; pp. 4080–4083. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.; Lim, N.; Lim, C.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Jung, K.; Leonard, A.D. All-printed and roll-to-roll-printable 13.56-MHz-operated 1-bit RF tag on plastic foils. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillancourt, J.; Zhang, H.; Vasinajindakaw, P.; Xia, H.; Lu, X.; Han, X.; Janzen, D.C.; Shih, W.-S.; Jones, C.S.; Stroder, M. All ink-jet-printed carbon nanotube thin-film transistor on a polyimide substrate with an ultrahigh operating frequency of over 5 GHz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 243301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.-J.; Oxley, C.H. Carbon based resistive strain gauge sensor fabricated on titanium using micro-dispensing direct write technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ding, H.; Lin, J.; Shen, F.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Fabrication of platinum-decorated single-walled carbon nanotube based hydrogen sensors by aerosol jet printing. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 505301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, M.; Marin, A.B. 3D Aerosol Jet® Printing-Adding Electronics Functionality to RP/RM. In Proceedings of the DDMC 2012 Conference, Berlin, Germany, 14–15 March 2012; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, H.; Chen, Q.; Ning, M.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X. Synthesis and one-dimensional self-assembly of acicular nickel nanocrystallites under magnetic fields. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3996–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J. Engineering Properties of Nickel and Nickel Alloys; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qi, T.; Xiao, F. Copper nanoparticles: Aqueous phase synthesis and conductive films fabrication at low sintering temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, T.; Schuppert, A.K.; Hummelgård, M.; BäckstrÖm, J.; Nilsson, H.-E.; Olin, H.K. Inkjet Fabrication of Copper Patterns for Flexible Electronics: Using Paper with Active Precoatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18273–18282. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.-T.; Chung, W.-H.; Jang, Y.-R.; Kim, H.-S. Intensive Plasmonic Flash Light Sintering of Copper Nanoinks Using a Band-Pass Light Filter for Highly Electrically Conductive Electrodes in Printed Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8591–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Flash light sintering of nickel nanoparticles for printed electronics. Thin Solid Films 2014, 550, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ong, B.S. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles useful for fabrication of high-conductivity elements for printed electronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3266–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Z.; Deng, M.; Wen, Y.; Song, Y. Synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for ink-jet printed flexible electronics. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 425601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Dong, T.-Y.; Chang, T.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, I. Using nanoparticles as direct-injection printing ink to fabricate conductive silver features on a transparent flexible PET substrate at room temperature. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 5914–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Cormier, D.; Williams, S. Improving run-time stability with aerosol jet printing using a solvent add-back bubbler. J. Print Media Technol. Res. 2016, 5, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, Y.; Grouchko, M.; Magdassi, S. Printing a Self-Reducing Copper Precursor on 2D and 3D Objects to Yield Copper Patterns with 50% Copper’s Bulk Conductivity. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1400448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Mo, L.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Ran, J.; Fu, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, L. Synthesis of nano-copper particles for conductive ink in gravure printing. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Suzhou, China, 7–10 April 2013; pp. 775–778. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.-H.; Woo, S.; Yem, H.; Cha, M.; Cho, S.; Kang, M.; Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.; Kang, K.; Piao, Y. A self-reducible and alcohol-soluble copper-based metal–organic decomposition ink for printed electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 6, 3312–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.-H.; Yeon, D.-H.; Byun, Y. Effect of copper concentration in printable copper inks on film fabrication. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 2731–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Hong, S.-H. Effect of the Amine Concentration on Phase Evolution and Densification in Printed Films Using Cu (II) Complex Ink. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8101–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-Y.; Yoo, T.-H.; Song, Y.-W.; Lim, D.-S.; Oh, Y.-J. Cu ion ink for a flexible substrate and highly conductive patterning by intensive pulsed light sintering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 5, 4113–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, R.D.; Belot, J.; Potash, R. Metal Alloys from Molecular Inks. U.S. Patent 9,920,212 B2, 20 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zope, K.R.; Cormier, D.; Williams, S. Reactive Silver Oxalate Ink Composition with Enhanced Curing Conditions for Flexible Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3830–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.B.; Lewis, J.A. Reactive silver inks for patterning high-conductivity features at mild temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Tai, Y. A facile approach to a silver conductive ink with high performance for macroelectronics. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.-G.; Sun, X. Facile synthesis of high silver content MOD ink by using silver oxalate precursor for inkjet printing applications. Thin Solid Films 2015, 589, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, D.; Zhang, M.; Wei, L. Shape-controlled synthesis of nickel wires using an external magnetic field. Chin. J. Catal. 2009, 30, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, Y. Magnetic properties of nickel film formed under magnetic fields. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 205011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Xie, K.; Liao, L. Preparation and thermal stability of nickel nanowires via self-assembly process under magnetic field. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, Y. Formation of one-dimensional nickel wires by chemical reduction of nickel ions under magnetic fields. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2844–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tian, J.; Zhao, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Formation of Ni chains induced by self-generated magnetic field. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, T.; Shaijumon, M.; Ci, L.; Ajayan, P.; Anantharaman, M. On the growth mechanism of nickel and cobalt nanowires and comparison of their magnetic properties. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sauer, G.; Brehm, G.; Schneider, S.; Graener, H.; Seifert, G.; Nielsch, K.; Choi, J.; Göring, P.; Gösele, U.; Miclea, P. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy employing monodisperse nickel nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 023106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnadas, K.; Sajanlal, P.; Pradeep, T. Pristine and hybrid nickel nanowires: Template-, magnetic field-, and surfactant-free wet chemical synthesis and Raman studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4483–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kuok, M.; Ng, S.; Lockwood, D.; Cottam, M.; Nielsch, K.; Wehrspohn, R.; Gösele, U. Spin-wave quantization in ferromagnetic nickel nanowires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 027201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, P. Thin film magnetic recording media. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1998, 31, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, M.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Makarov, D.; Karnaushenko, D.; Karnaushenko, D.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T.; Schmidt, O.G. Imperceptible magnetoelectronics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.f.; Mei, Y.; Kaltofen, R.; Mönch, J.I.; Schumann, J.; Freudenberger, J.; Klauß, H.J.; Schmidt, O.G. Towards Flexible Magnetoelectronics: Buffer-Enhanced and Mechanically Tunable GMR of Co/Cu Multilayers on Plastic Substrates. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3224–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MÖnch, I.; Makarov, D.; Koseva, R.; Baraban, L.; Karnaushenko, D.; Kaiser, C.; Arndt, K.-F.; Schmidt, O.G. Rolled-up magnetic sensor: Nanomembrane architecture for in-flow detection of magnetic objects. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7436–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Nagodawithana, K.; Searson, P.; Chien, C. Perpendicular giant magnetoresistance of multilayered Co/Cu nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Chu, J.; Zeng, X.; Fan, Y. Large-area flexible infrared nanowire grid polarizer fabricated using nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 5230–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Deng, X.; Deng, J.; Liu, F.; Sciortino, P.; Chen, L. High-performance nanowire-grid polarizers. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnaushenko, D.; Karnaushenko, D.D.; Makarov, D.; Baunack, S.; Schäfer, R.; Schmidt, O.G. Self-Assembled On-Chip-Integrated Giant Magneto-Impedance Sensorics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6582–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, F.; Jonsson, M.; Alm, K.; Kanje, M.J.E.c.r. Cell guidance by magnetic nanowires. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, B.E. Patterning processes for flexible electronics. Pro. IEEE 2015, 103, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essien, M. Apparatuses and Methods for Stable Aerosol Deposition Using an Aerodynamic Lens System. Google Patent US20160193627A1, 7 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ayres, C.E.; Jha, B.S.; Meredith, H.; Bowman, J.R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Henderson, S.C.; Simpson, D.G. Measuring fiber alignment in electrospun scaffolds: A user’s guide to the 2D fast Fourier transform approach. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farraj, Y.; Grouchko, M.; Magdassi, S. Self-reduction of a copper complex MOD ink for inkjet printing conductive patterns on plastics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.G.; Ehretsmann, J.; Brown, C.E. Development of internal structure during thermal decomposition: Nickel formate dihydrate. J. Catal. 1971, 20, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sutton, D.; Burgess, A.; Graham, D.; Calvert, P.D. Conductive copper and nickel lines via reactive inkjet printing. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, D.I.; Kirikova, M.N.; Bessonov, A.A.; Bailey, M.J. Nickel and copper conductive patterns fabricated by reactive inkjet printing combined with electroless plating. Mater. Lett. 2014, 132, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crangle, J.; Goodman, G. The magnetization of pure iron and nickel. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1971, 321, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Cho, S.; Shanker, R.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Um, D.-S.; Lee, Y.; Ko, H. Transparent and conductive nanomembranes with orthogonal silver nanowire arrays for skin-attachable loudspeakers and microphones. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahajan, C.G.; Alfadhel, A.; Irving, M.; Kahn, B.E.; Borkholder, D.A.; Williams, S.A.; Cormier, D. Magnetic Field Patterning of Nickel Nanowire Film Realized by Printed Precursor Inks. Materials 2019, 12, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060928
Mahajan CG, Alfadhel A, Irving M, Kahn BE, Borkholder DA, Williams SA, Cormier D. Magnetic Field Patterning of Nickel Nanowire Film Realized by Printed Precursor Inks. Materials. 2019; 12(6):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060928
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahajan, Chaitanya G., Ahmed Alfadhel, Mark Irving, Bruce E. Kahn, David A. Borkholder, Scott A. Williams, and Denis Cormier. 2019. "Magnetic Field Patterning of Nickel Nanowire Film Realized by Printed Precursor Inks" Materials 12, no. 6: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060928
APA StyleMahajan, C. G., Alfadhel, A., Irving, M., Kahn, B. E., Borkholder, D. A., Williams, S. A., & Cormier, D. (2019). Magnetic Field Patterning of Nickel Nanowire Film Realized by Printed Precursor Inks. Materials, 12(6), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12060928





