Preparation and Investigation of Intelligent Polymeric Nanocapsule for Enhanced Oil Recovery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
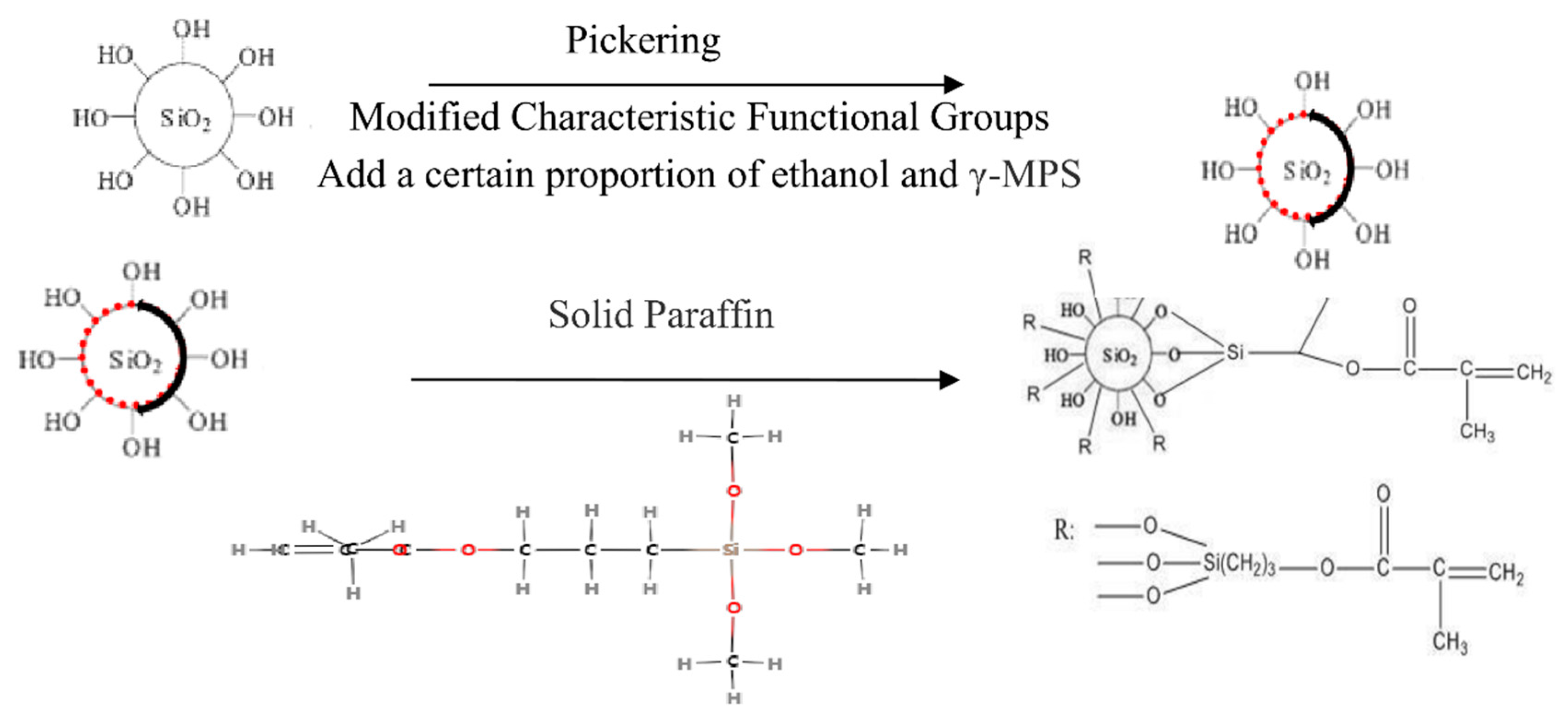
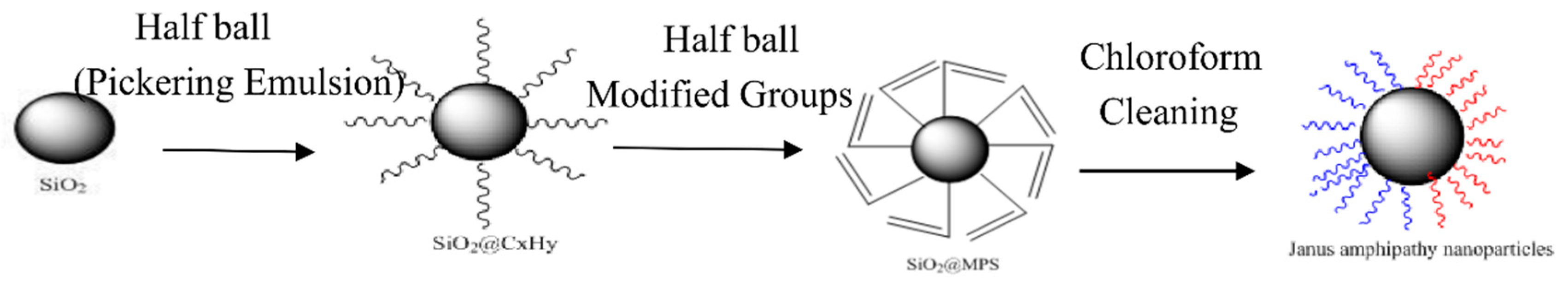
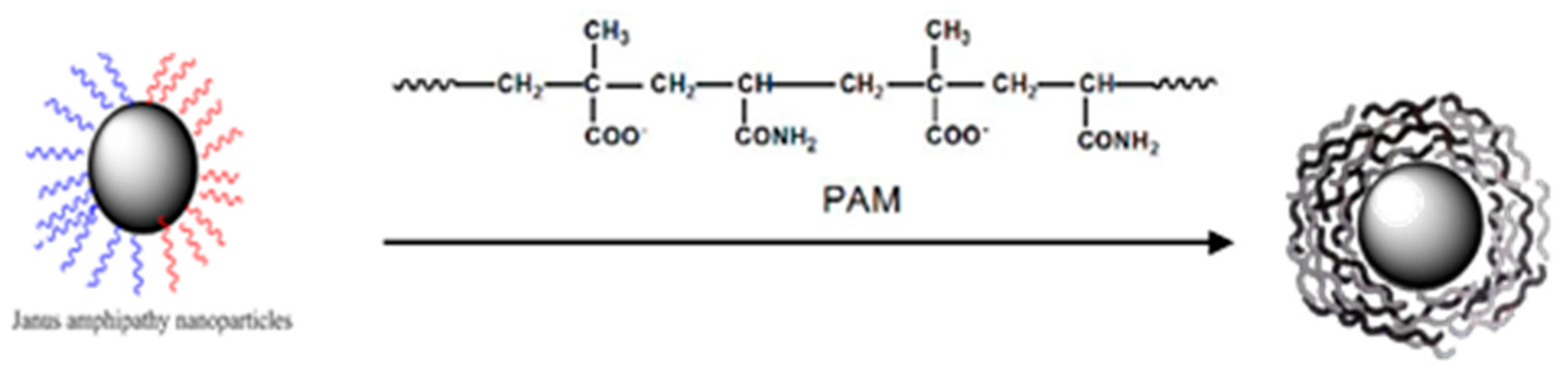
2.2. Preparation of Asymmetric Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
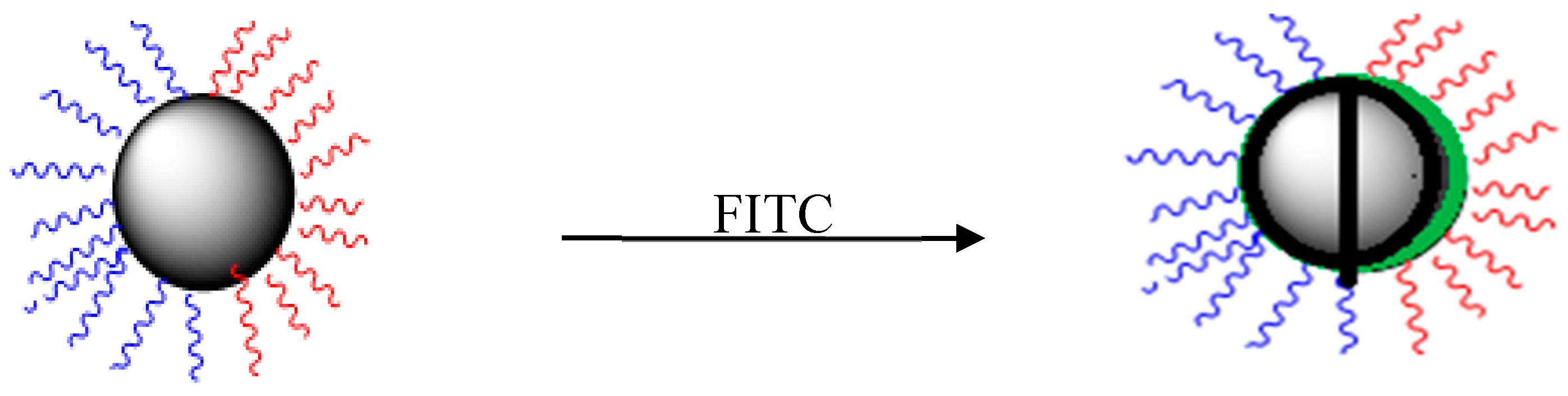
2.3. Preparation of Fluorescent Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
2.4. Interface Properties of Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
2.4.1. Types of Surfactants
2.4.2. Surfactant Hydrophobic Group
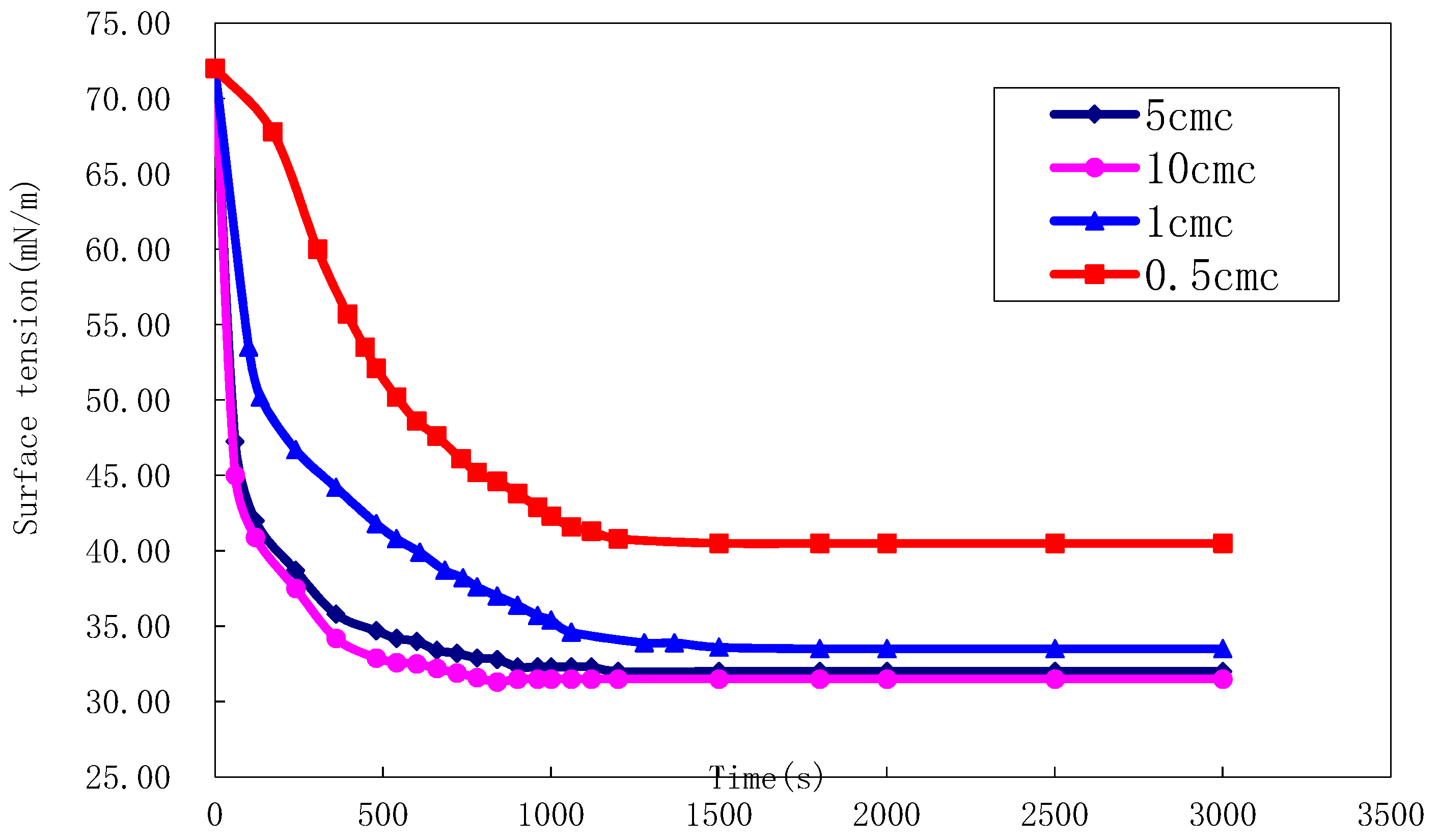
2.4.3. Effect of Salt Water on Surface Tension of Surfactants
2.4.4. Effect of Temperature on Surface Tension of Surfactants
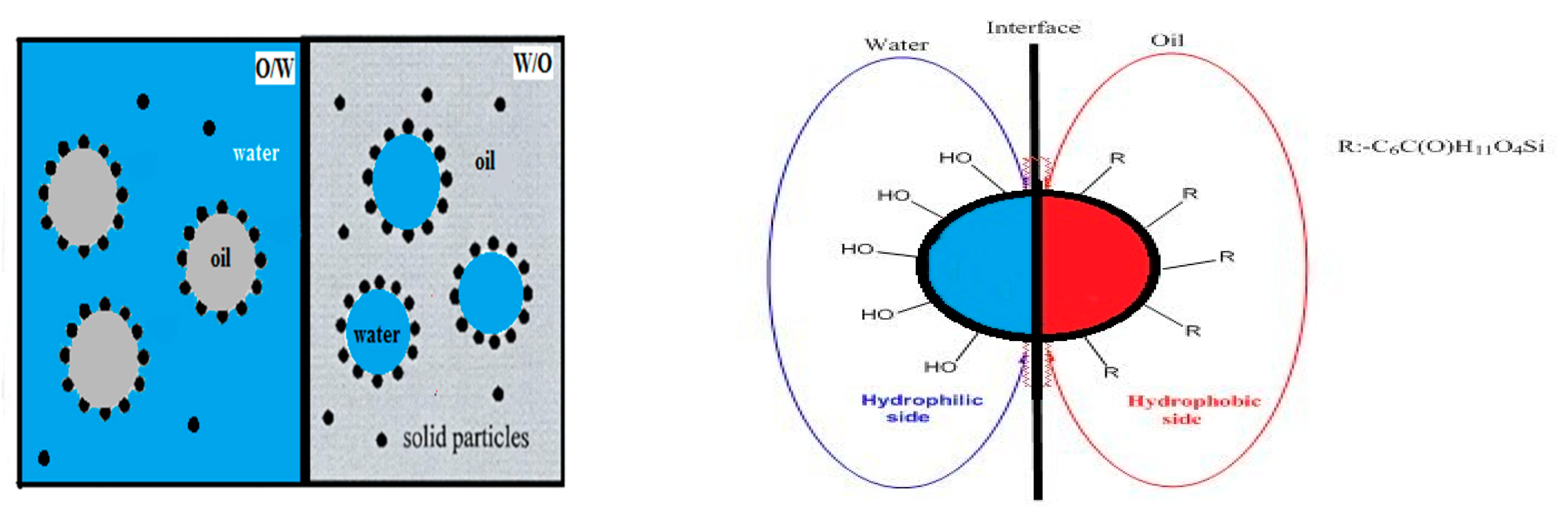
2.4.5. Emulsification Mechanism of Asymmetric Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
2.5. Characterization of the Modified Nanoparticles
2.6. Assembly of Smart Microcapsules
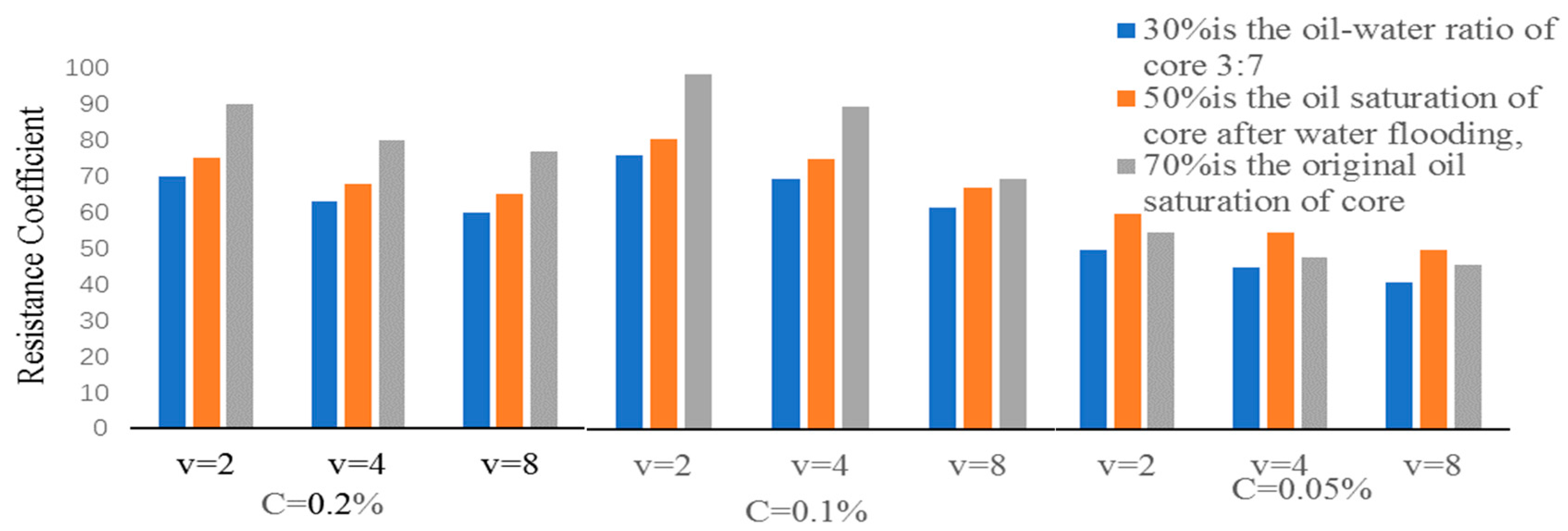
2.7. Determination of Emulsified Resistance Coefficient
2.8. Adaptability Assessment
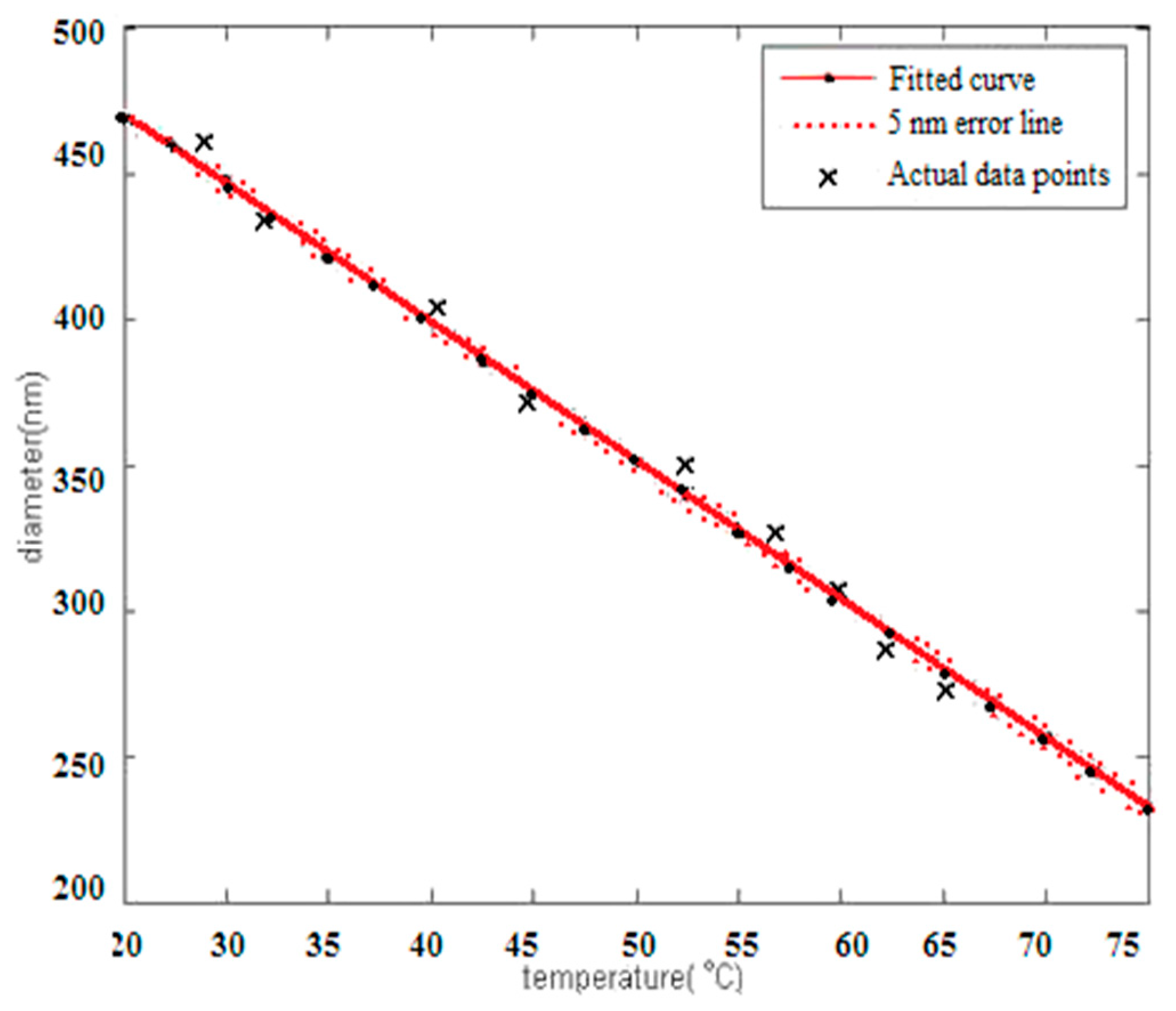
2.9. Release Mechanism
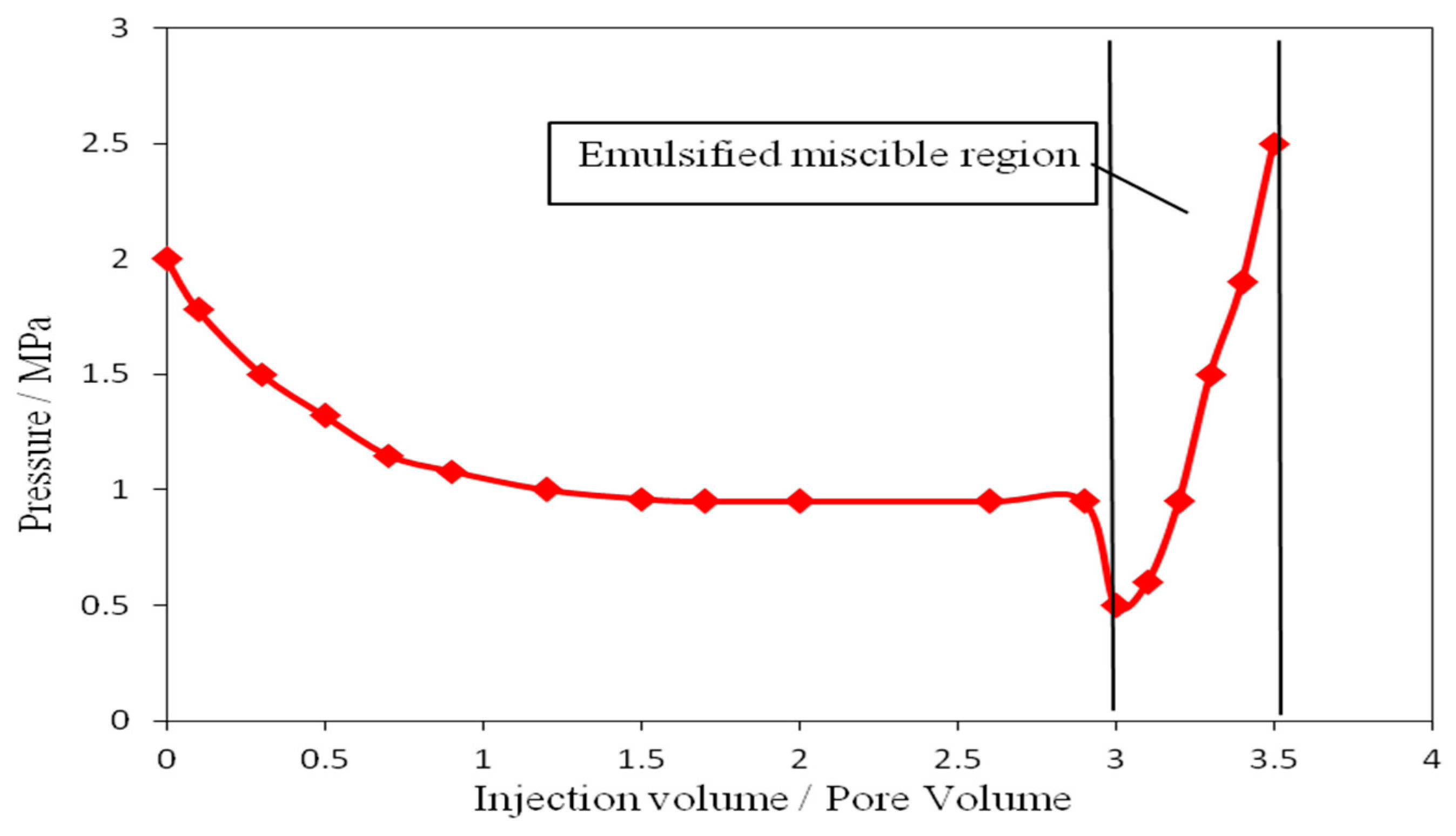
2.10. Reducing Displacement Pressure Experiment
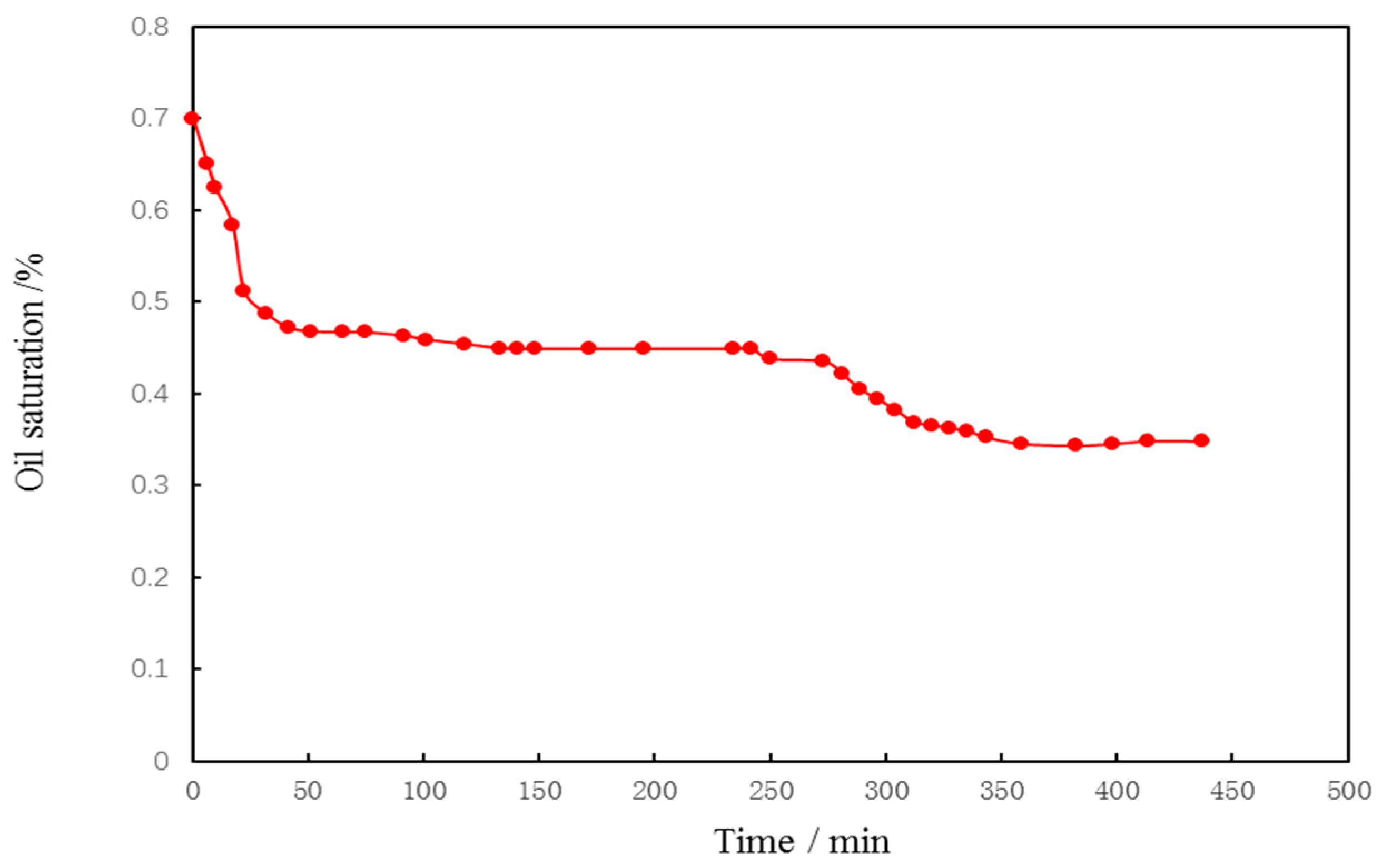
2.11. The Relationship between Oil Saturation of Core 2 and Time
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Asymmetric Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
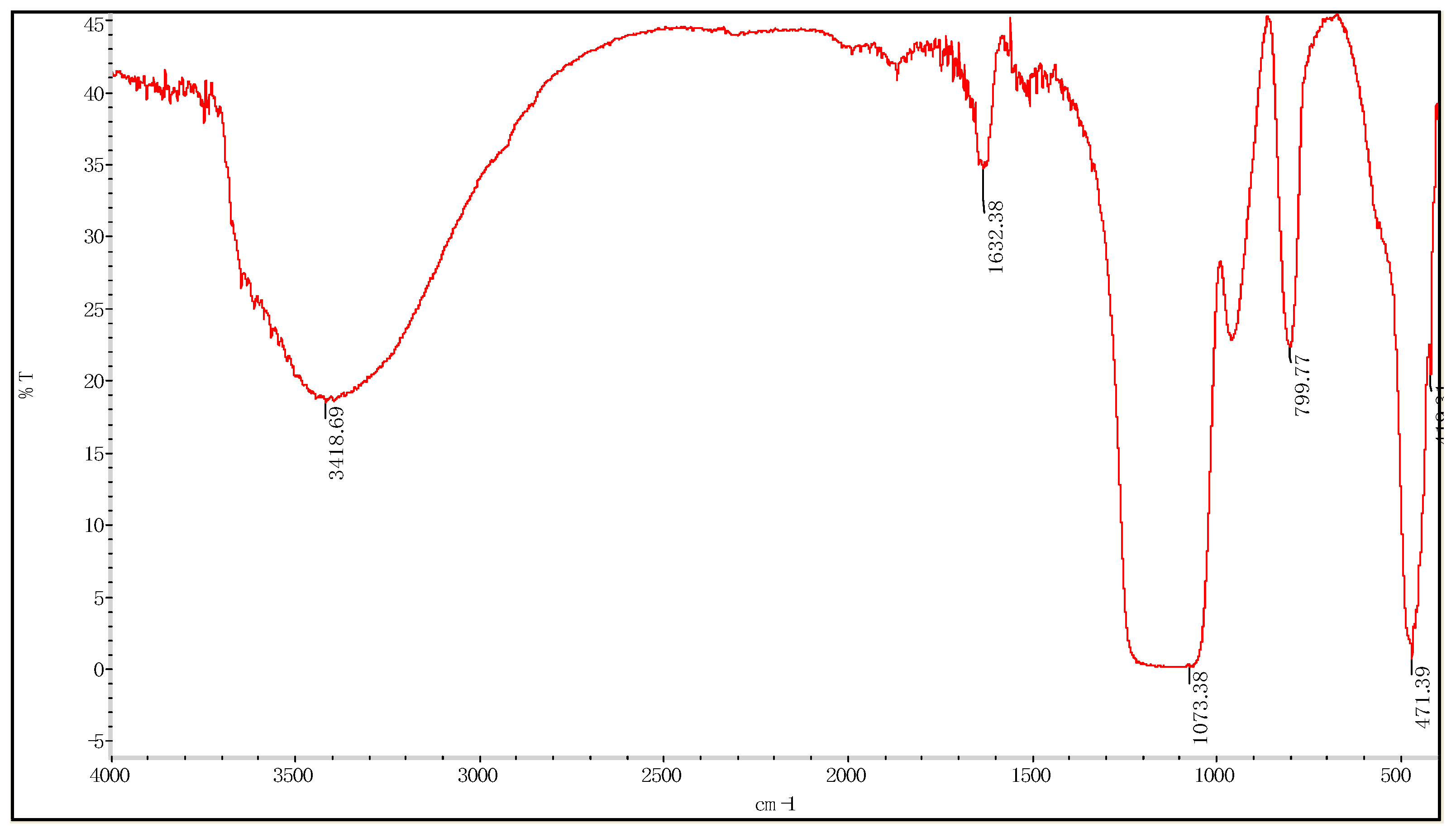
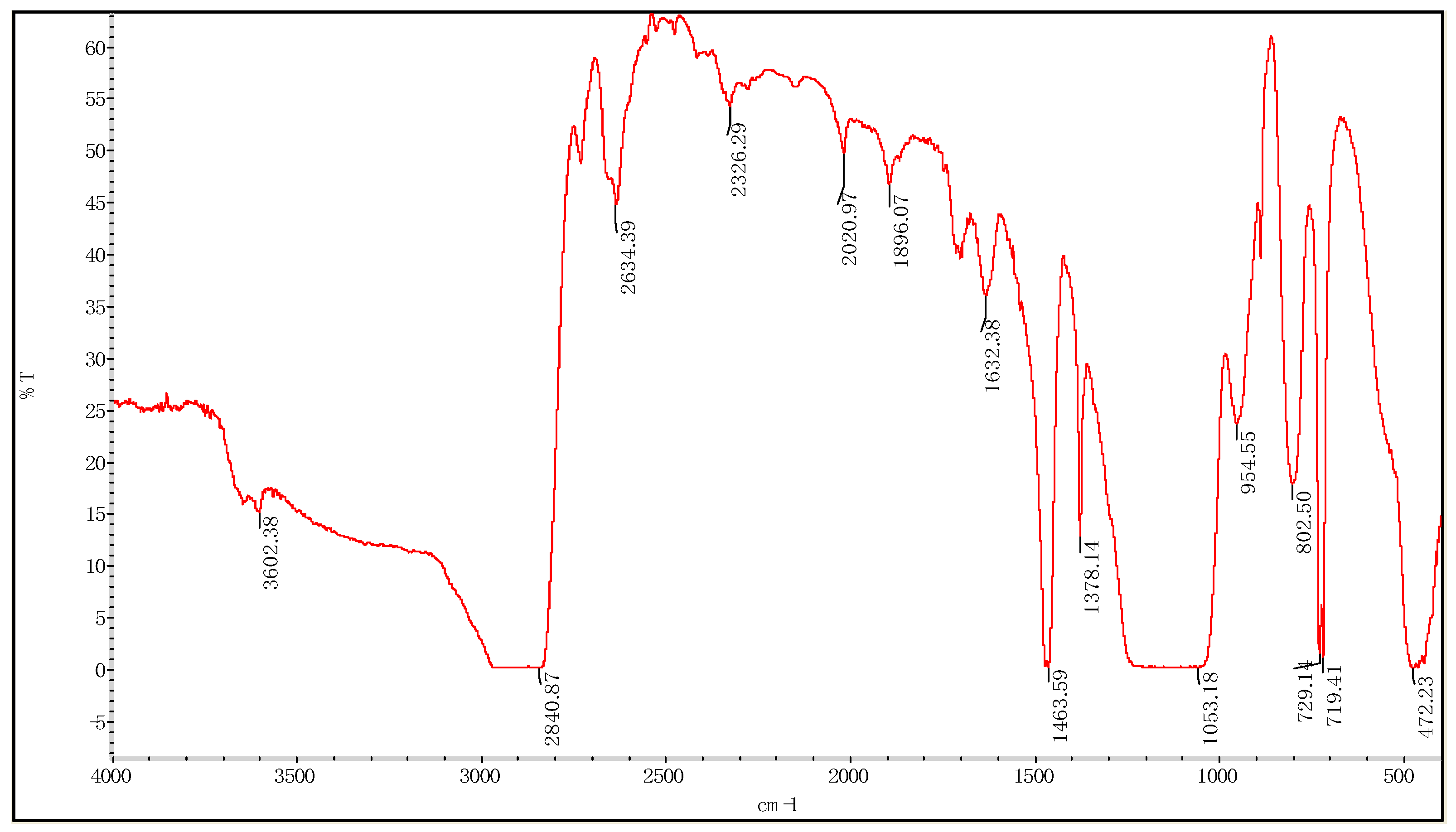
3.1.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Diffraction Spectrum
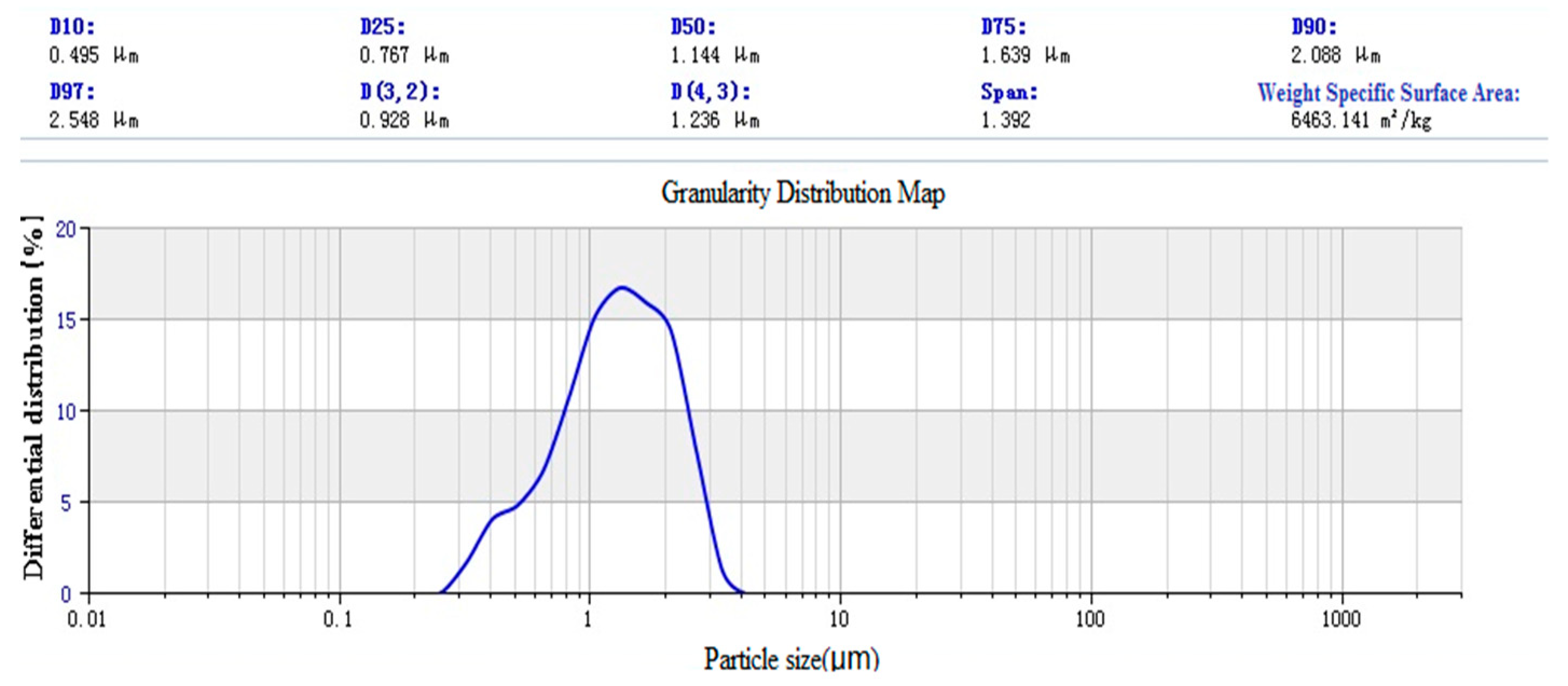
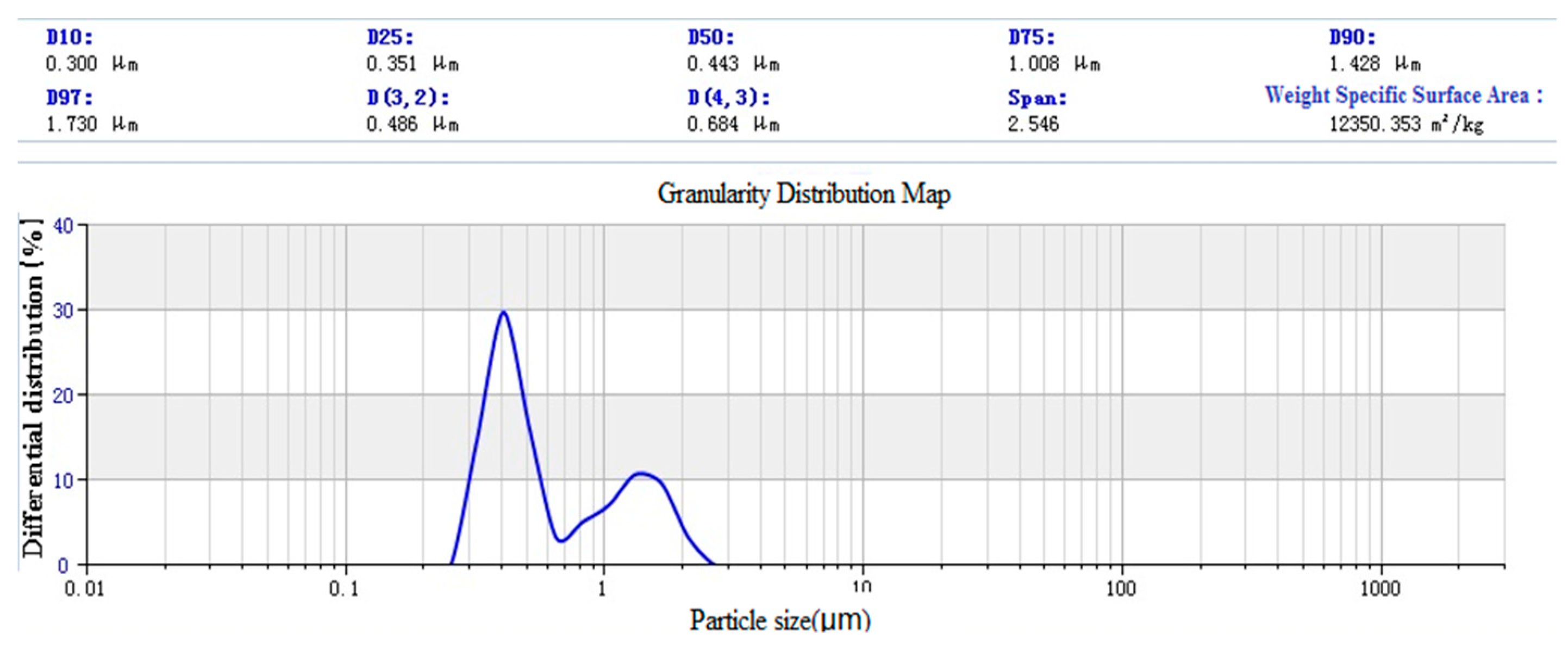
3.1.3. Laser Particle Size Distribution
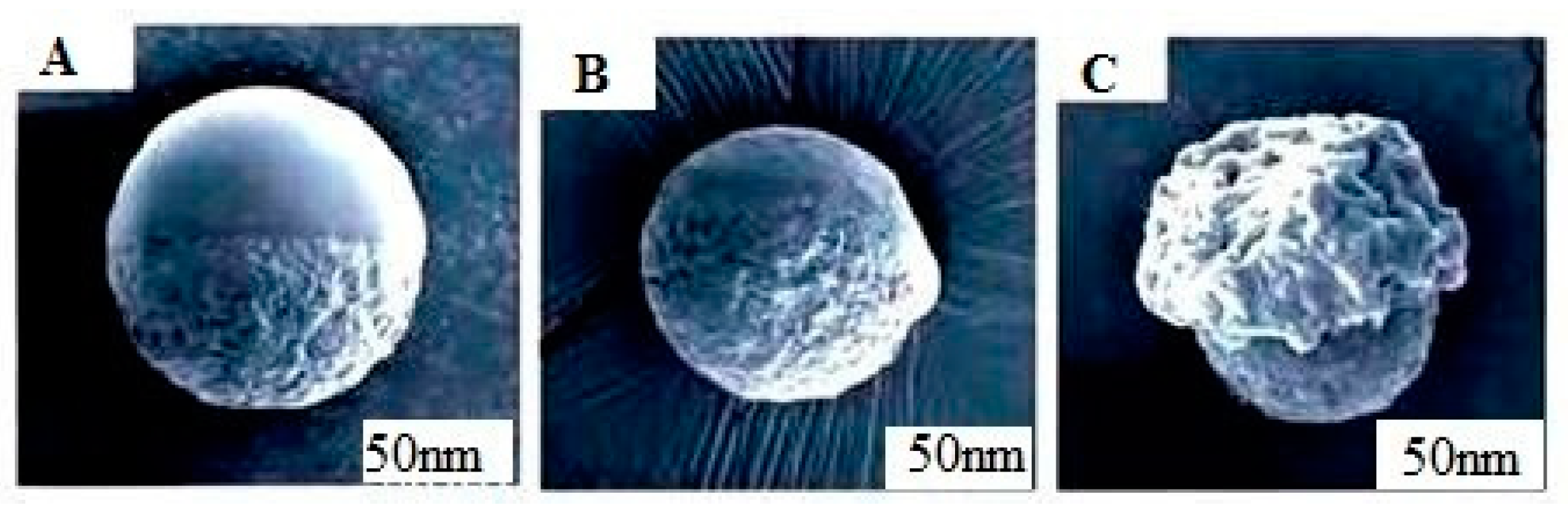
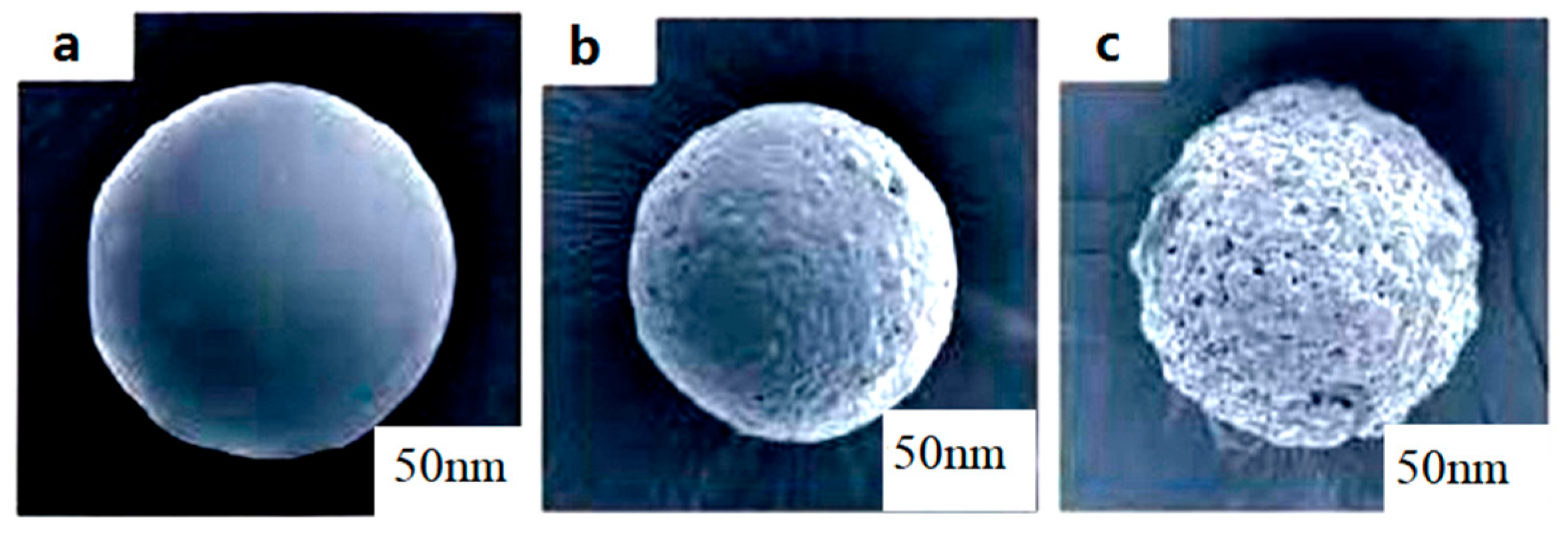
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscope
3.2. Interface Properties of Amphiphilic Nanoparticles
3.3. Emulsifying Ability
3.4. Determination of Emulsified Resistance Coefficient of Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles System
4. Discussion
4.1. Preparation of Amphiphilic Asymmetric Nanoparticles
4.2. Interfacial Activity and Emulsifying Ability of Amphiphilic Asymmetric Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finkle, P.; Draper, H.D.; Hildebrand, J.H. The theory of emulsification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1923, 45, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, R.; Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 503–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, N.; Adams, D.J.; Böker, A.; Krausch, G. Janus particles at liquid-liquid interfaces. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5227–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, K.H.; Martin, D.C.; Lahann, J. Biphasic Janus particles with nanoscale anisotropy. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Solid wettability from surface energy components: Relevance to Pickering emulsions. Langmuir 2002, 18, 1270–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blute, I.; Pugh, R.J.; van de Pas, J.; Callaghan, I. Silica nanoparticle sols: 1. Surface chemical characterization and evaluation of the foam generation (foamability). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.S.; Ettelaie, R. Foam stability: Proteins and nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, R.J. Foaming in chemical surfactant free aqueous dispersions of anatase(titanium dioxide) particles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7972–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthen, A.J.; Bagaria, H.G.; Chen, Y.; Bryant, S.L.; Huh, C.; Johnston, K.P. Nanoparticle-stabilized carbondioxide-in-water foams with fine texture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 391, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignati, E.; Piazza, R.; Lockhart, T.P. Pickering emulsions: Interfacial tension, colloidal layer morphology, and trapped-particle motion. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6650–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, W. Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and suspensions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1904, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. Utilization of surfactant-stabilized foam for enhanced oil recovery by adding nanoparticles. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synytska, A.; Khanum, R.; Ionov, L.; Cherif, C.; Bellmann, C. Water-repellent textile via decorating fibers with amphiphilic janus particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhland, T.M.; Gröschel, A.H.; Ballard, N.; Skelhon, T.S.; Walther, A.; Müller, A.H.; Bon, S.A. Influence of Janus particle shape on their interfacial behavior at liquid–liquid interfaces. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Reilly, R.K. Anisotropic particles with patchy, multicompartment and Janus architectures: Preparation and application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennes, P.G. Soft matter. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wei, W.; Qu, X.; Yang, Z. Janus colloids formed by biphasic grafting at a Pickering emulsion interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 120, 4037–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Erhardt, R.; Abetz, V.; Müller, A.H.; Goedel, W.A. Janus micelles at the air/water interface. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6787–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z. Janus hollow spheres by emulsion interfacial self-assembled sol-gel process. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Müller, A.H.E. Janus particles: Synthesis, self-assembly, physicalproperties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5194–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsaneha, C.; Tangboriboonrat, P.; Polpanich, D.; Eissa, M.; Elaissari, A. Preparation of Januscolloidal particles via Pickering emulsion: An overview. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perro, A.; Reculusa, S.; Ravaine, S.; Bourgeat-Lami, E.; Duguet, E. Design and synthesis of Janus micro-and nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3745–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Garcia, M.A.; Frey Huls, N.A.; Sun, S. Synthetic tuning of the catalyticproperties of Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 122, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perro, A.; Meunier, F.; Schmitt, V.; Ravaine, S. Production of large quantities of “Janus”nanoparticles using wax-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 332, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.Y.; Phang, I.Y.; Acikgoz, C.; Yilmaz, M.D.; Hempenius, M.A.; Vancso, G.J.; Huskens, J. Janus particles with controllable patchiness and their chemical functionalization and supramolecular assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7677–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Liao, C.W.; Chao, Y.C.; Kuo, C. Fabrication and characterization of asymmetric Janus and ternary particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3185–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayre, O.; Paunov, V.N.; Velev, O.D. Fabrication of dipolar colloid particles by microcontact printing. Chem. Commun. 2003, 2296–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Growth of lightly crosslinked PHEMA brushes and capsule formation using pickering emulsion interface-initiated ATRP. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardhy, N.P.; Budhlall, B.M. Pickering emulsion as a template to synthesize Janus colloids with anisotropy in the surface potential. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13130–13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yi, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. Janus graphene oxide nanosheets prepared via Pickering emulsion template. Carbon, 2015; 93, 473–483. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, D.; Tsuji, S.; Kawaguchi, H. Janus microgels prepared by surfactant-freepickering emulsion-based modification and their self-assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8088–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Jiang, S.; Granick, S. Simple method to produce Janus colloidal particles in large quantity. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9495–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalland, M.; Hanssen, J.E.; Kristiansen, T.S. Oil interaction with foams under static and flowing conditions in porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 82, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, G.; Meissner, E.; Milchert, E. Special applications of fluorinated organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binks, B.P.; Tyowua, A.T. Influence of the degree of fluorination on the behaviour of silica particles at air-oil surfaces. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, P.; Ding, B.; Zeng, M.; Cheng, Z. A review of nanomaterials for nanofluid enhanced oil recovery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32246–32254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Oil Displacement System | Composition (w t%) |
|---|---|
| Surfactant (sodium heavy alkylbenzene sulfonate) | 0.3 |
| Uniform Modified Nanoparticles | 0.3 |
| Asymmetric Modified Nanoparticles | 0.3 |
| Uniform modified nanoparticle microcapsules | 0.3 |
| Asymmetric amphiphilic nanoparticles microcapsules | 0.3 |
| Parameters | Core Type | |
|---|---|---|
| Low Permeability Core L1 | Low Permeability Core L2 | |
| Core length (cm) Core diameter(cm) | 9.80 | 9.81 |
| 2.5 | 2.5 | |
| Water permeability measurements(10−3μm2) | 51.6 | 53.1 |
| Pore volume(cm3) | 6.3 | 6.5 |
| Porosity (%) | 13.1 | 13.5 |
| Oil Displacement Agent | Pore Volume Multiple of Water Flooding | Pressure at the End of Water Flooding (M·Pa) | Follow-Up Water Drive Pressure after Displacement by Oil Displacement Agent (M·Pa) | Pressure Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Heavy Alkylbenzene Sulfonate | 3.76 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 49.1 |
| Uniform Modified Nanoparticles | 2.87 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 56.6 |
| Asymmetric Modified Nanoparticles | 2.98 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 60.4 |
| Uniform modified nanoparticle microcapsules | 3.18 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 60.4 |
| JANUS Nanoparticle microcapsules | 3.26 | 0.53 | 0.18 | 66.0 |
| JPs (wt%) | Surface Tension (m N/m) | Interfacial Tension (m N/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 72.0 | 10 |
| 0.05 | 45.3 | 1.5 × 10−1 |
| 0.1 | 40.2 | 5.1 × 10−2 |
| 0.2 | 37.9 | 8.4 × 10−3 |
| 0.4 | 33.5 | 2.3 × 10−3 |
| 0.8 | 31.0 | 3.3 × 10−4 |
| Sodium Heavy Alkylbenzene Sulfonate (mol/mL) | Volume of Emulsified Layer (mL) | |||
| 0 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| 0.4 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| 0.6 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 |
| 0.8 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.5 |
| 1 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 5.0 |
| 1.2 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 |
| Modified nanoparticles (mol/mL) | Volume of emulsified layer (mL) | |||
| 0 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| 0.4 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| 0.6 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| 0.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
| 1 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| 1.2 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| Asymmetric Modified nanoparticles (mol/mL) | Volume of emulsified layer (mL) | |||
| 0 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| 0.4 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| 0.6 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| 0.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
| 1 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| 1.2 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 |
| Considerations | Range of Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| oil saturation (%) | 30 | 50 | 70 |
| Surfactant Concentration (%) <interfacial tension (mN/m)> | 0.05 (1.5 × 10−1) | 0.1 (5.1 × 10−2) | 0.2 (8.4 × 10−3) |
| Velocity of flow (m/d) | 2 | 4 | 8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, F.; Wu, J.; Zhao, B. Preparation and Investigation of Intelligent Polymeric Nanocapsule for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Materials 2019, 12, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071093
Shi F, Wu J, Zhao B. Preparation and Investigation of Intelligent Polymeric Nanocapsule for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071093
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Fang, Jingchun Wu, and Bo Zhao. 2019. "Preparation and Investigation of Intelligent Polymeric Nanocapsule for Enhanced Oil Recovery" Materials 12, no. 7: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071093
APA StyleShi, F., Wu, J., & Zhao, B. (2019). Preparation and Investigation of Intelligent Polymeric Nanocapsule for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Materials, 12(7), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071093





