Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibril-Based Silane Cellulose Aerogel: Fabrication and Oil Absorbent Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
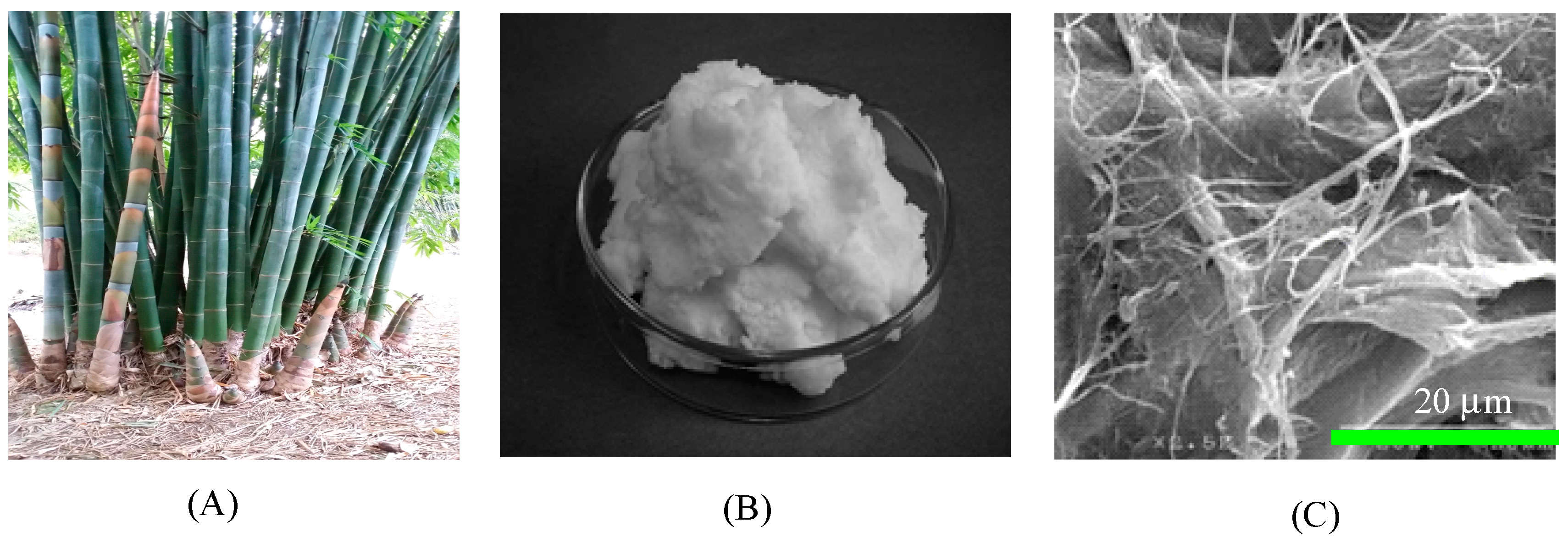
2.2. Preparation of Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibrils
2.3. Preparation of Cellulose Aerogel
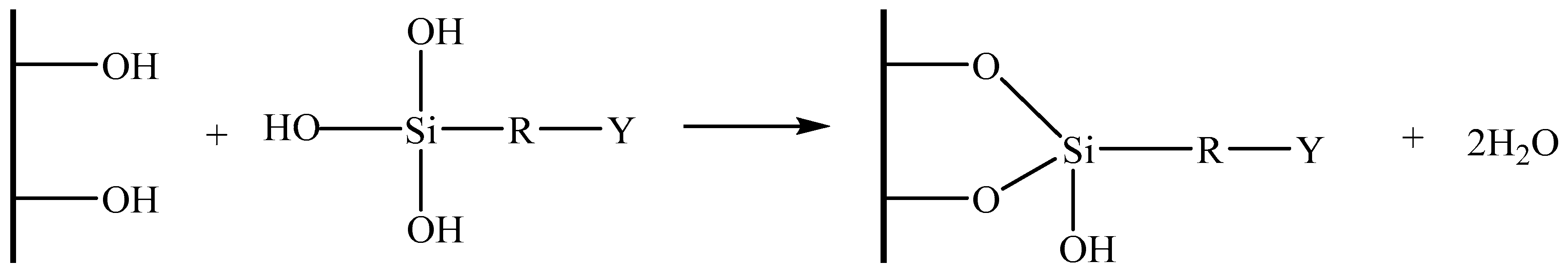
2.4. Fabrication of Silane Treated Cellulose Aerogel
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Oil/Solvent Absorption Capacity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
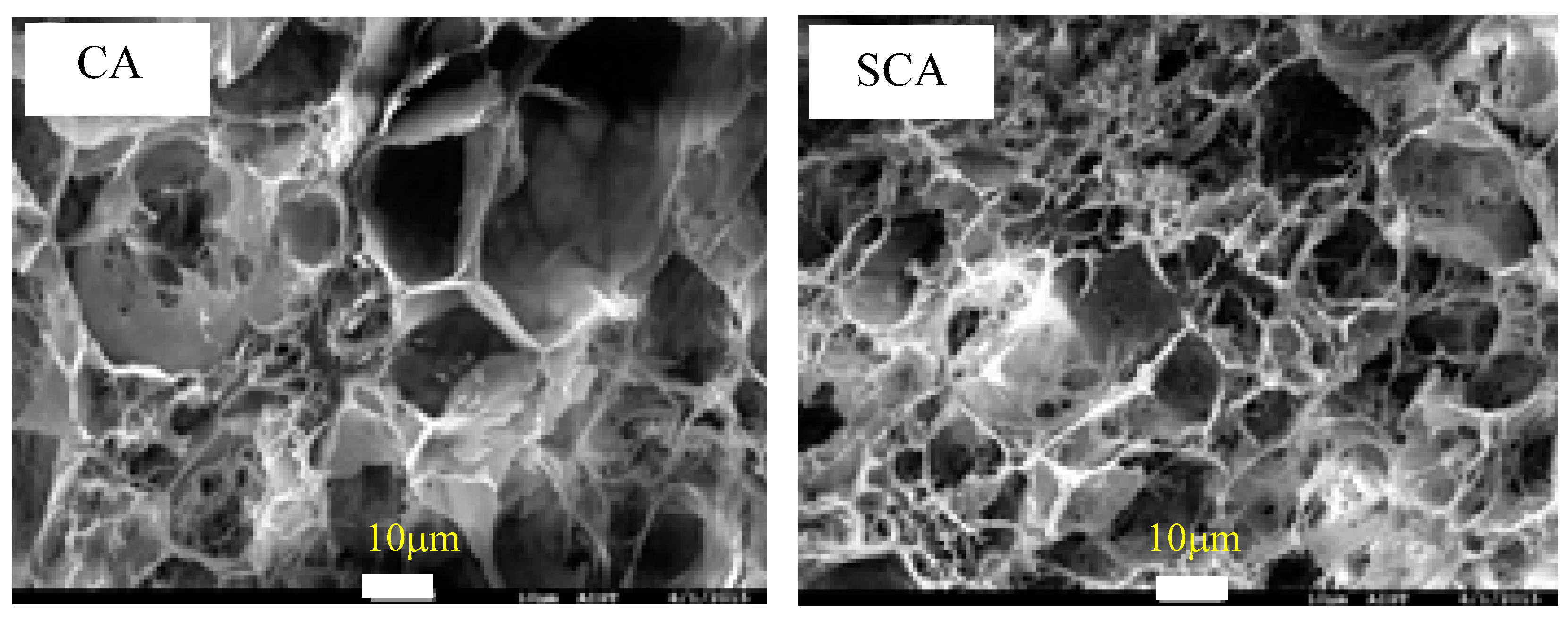
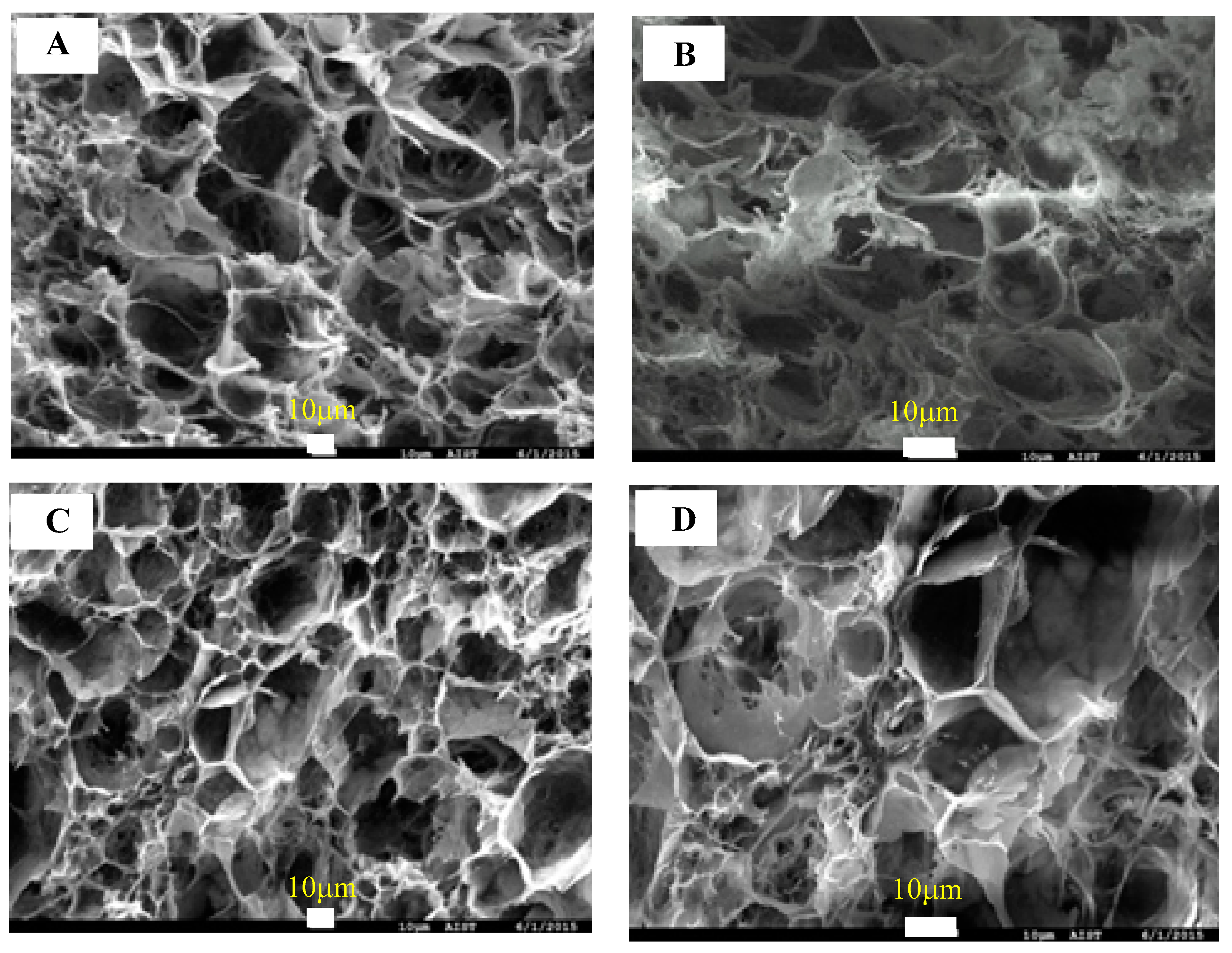
3.1. Cellulose Aerogel Characteristics
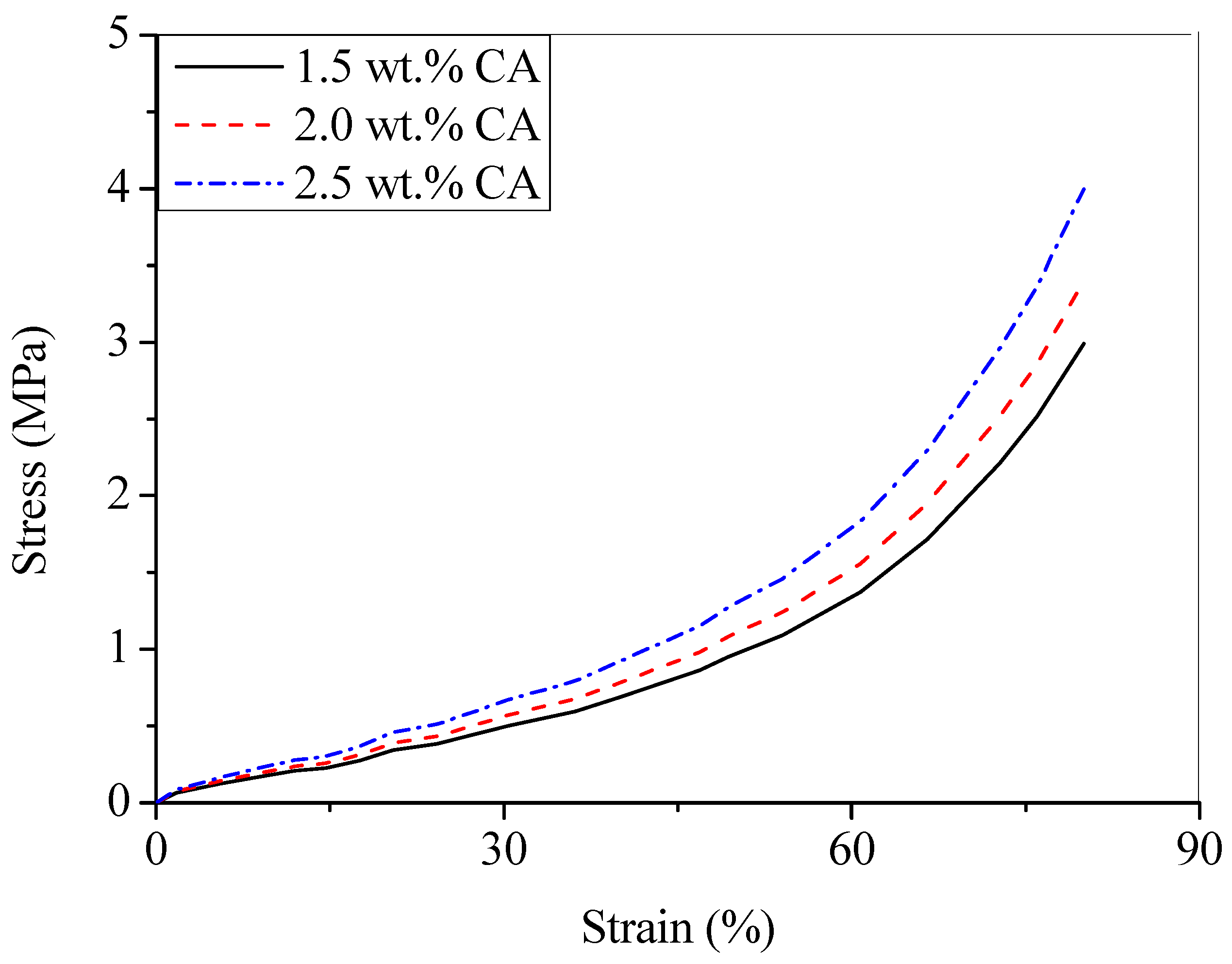
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Aerogel
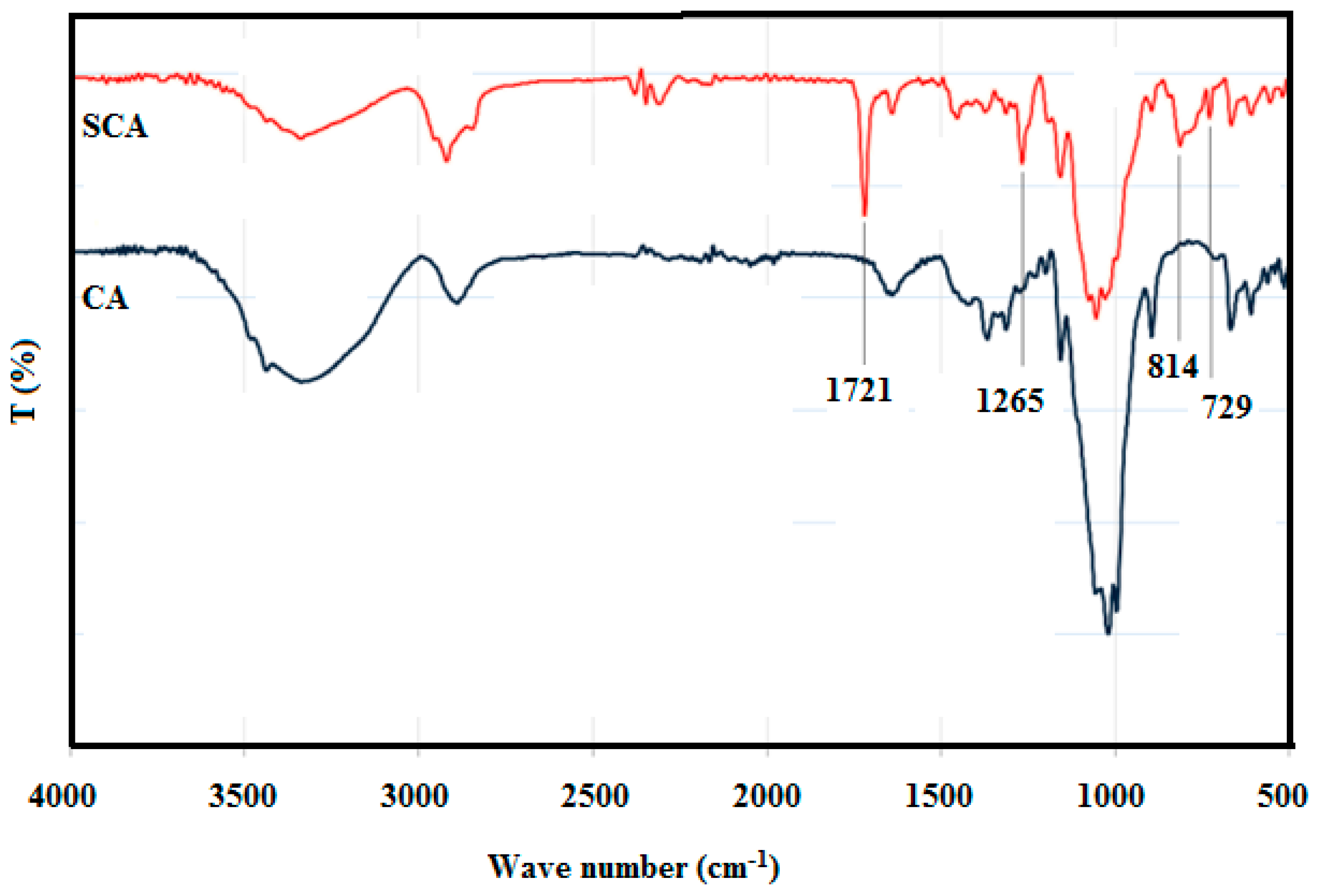
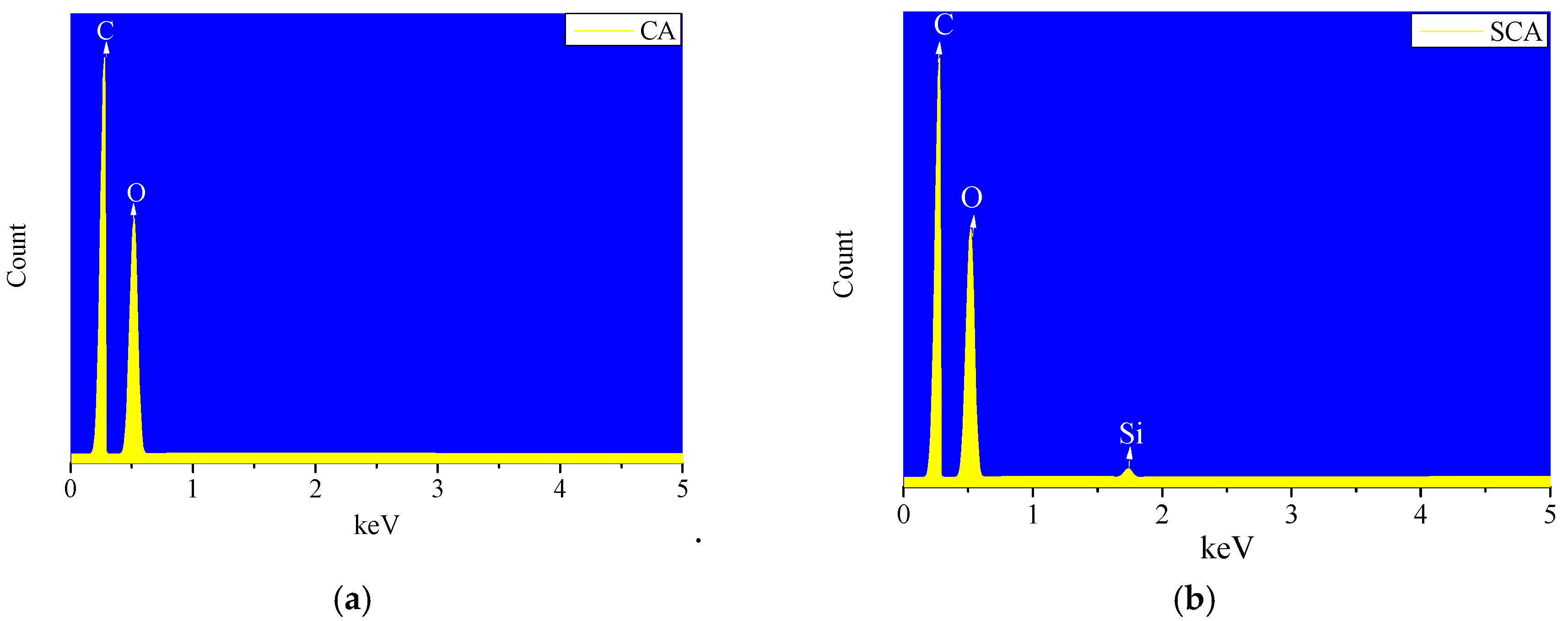
3.3. Silane Modification of Cellulose Aerogel
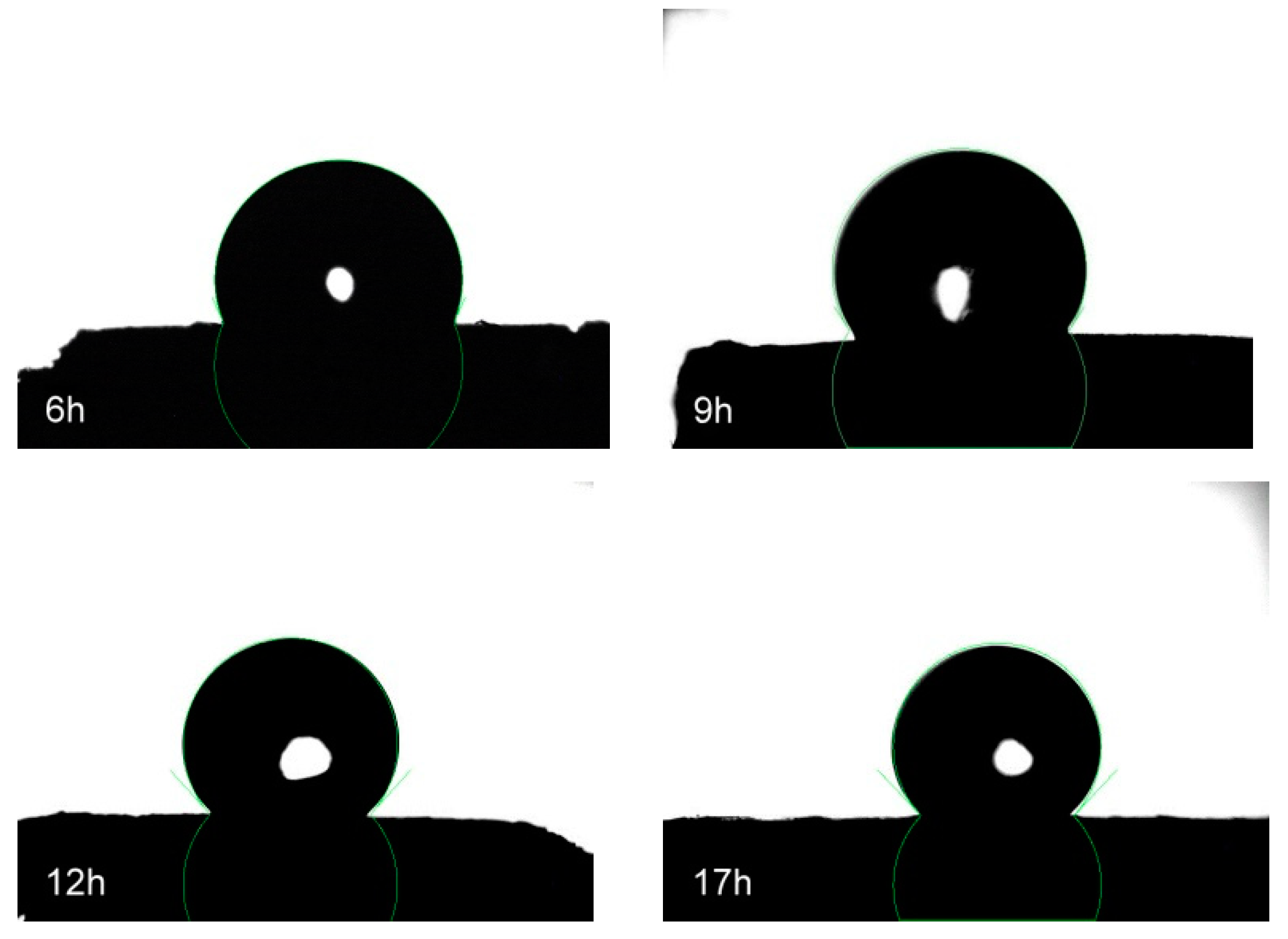
3.4. Surface Wettability of Silane-coated cellulose aerogel
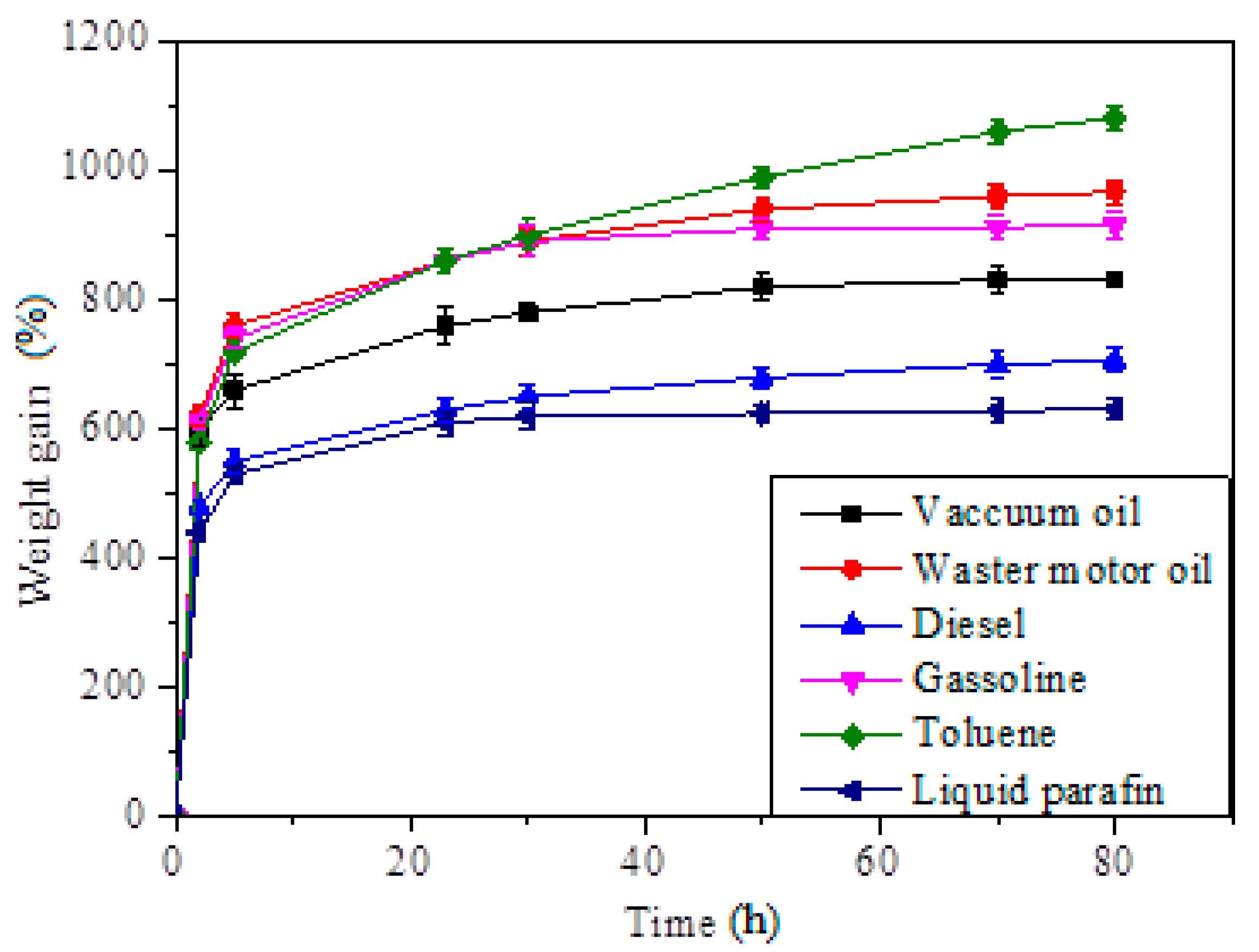
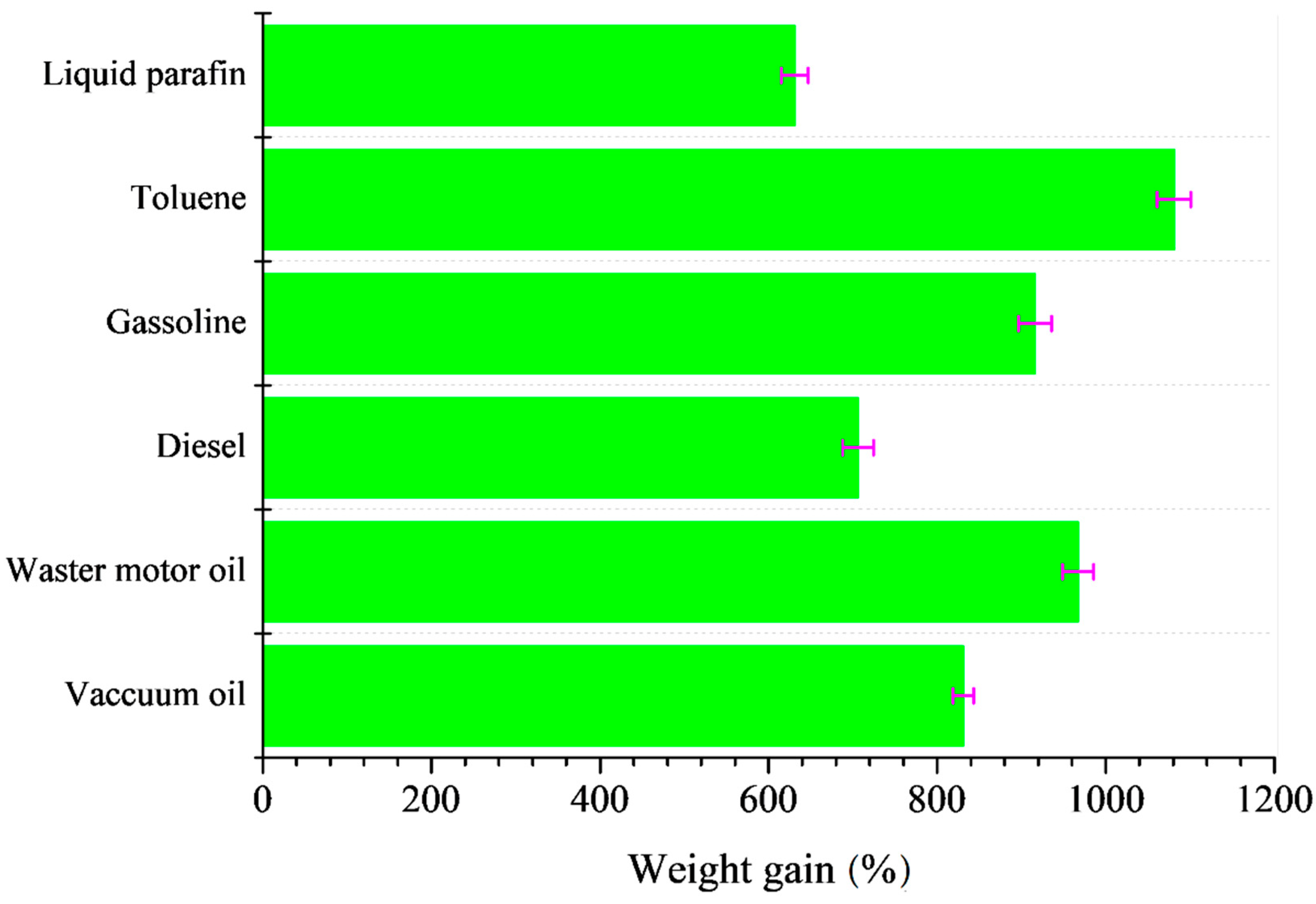
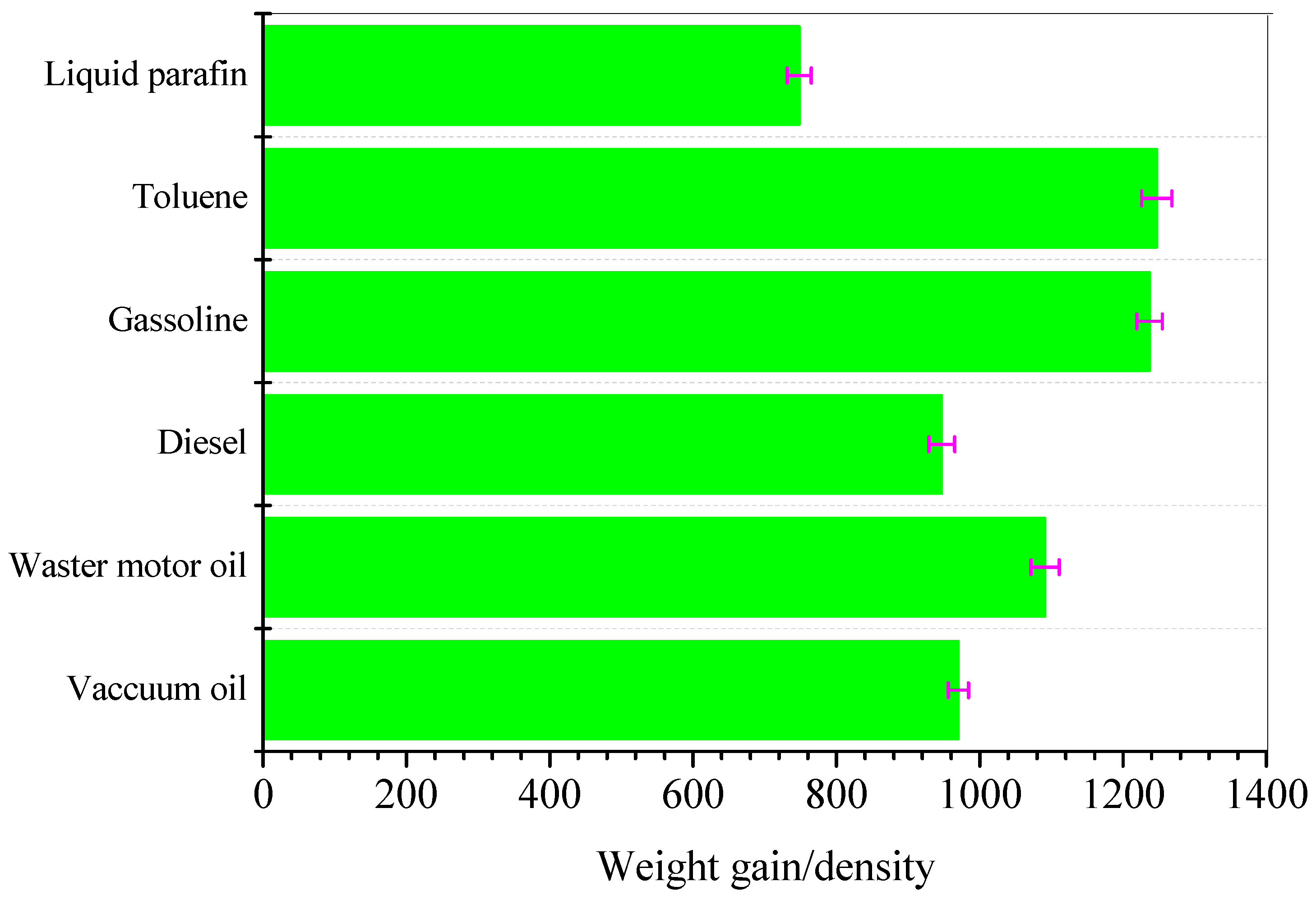
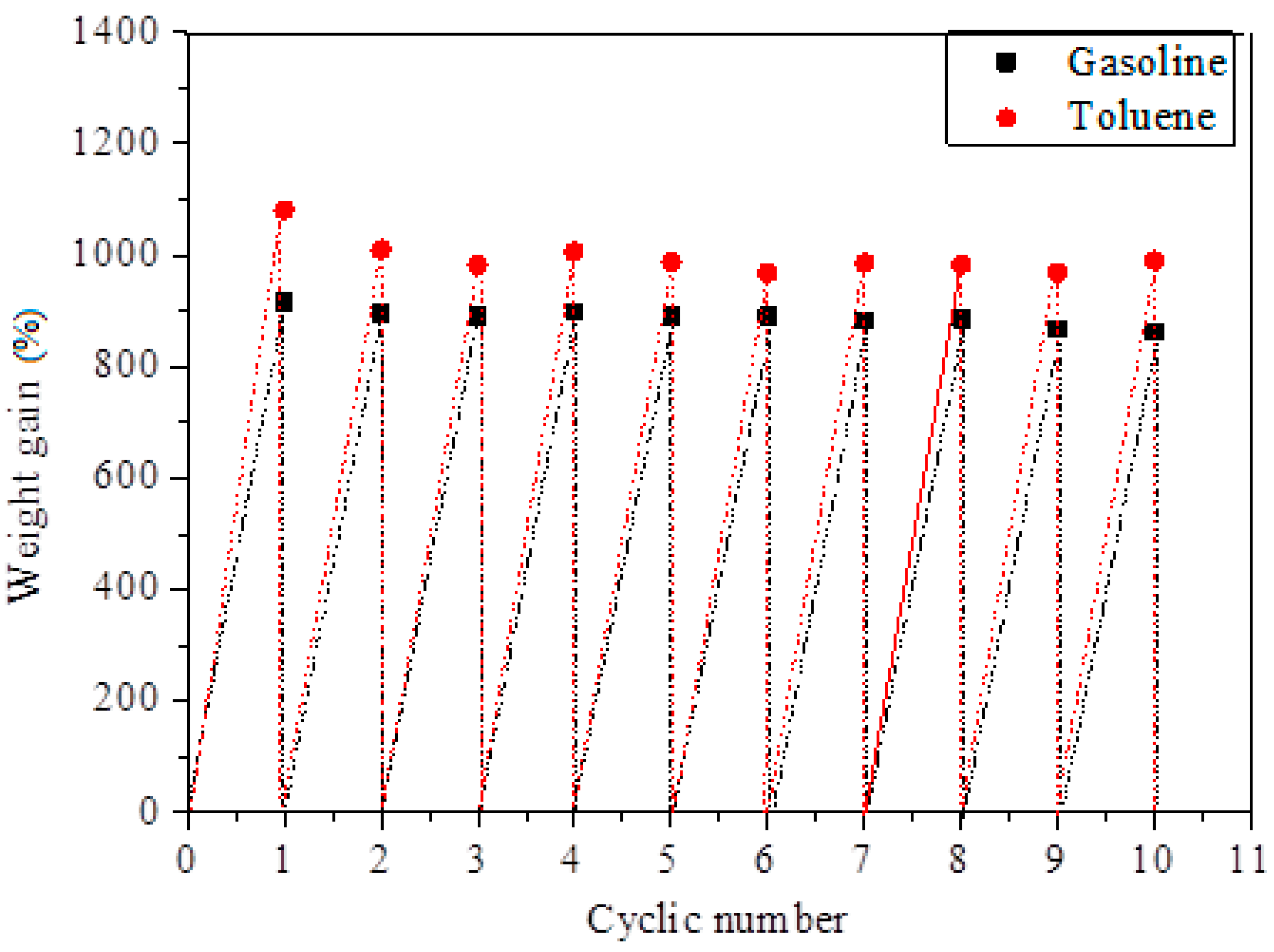
3.5. Oil/Solvent Absorption Capacity of SCA and Its Recycleability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, P.C.; Tan, L.; Liu, J.M.; Tan, B.; Yang, X.L.; Xu, H.B. Triptycene-Based Hyper-Cross-Linked Polymer Sponge for Gas Storage and Water Treatment. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8509–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Metal-organic frameworks for applications in remediation of oxyanion/cation-contaminated water. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2015, 17, 7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Mena, E.; Ch´avez, A.M.; Beltran, F.J.; Medina, F. Influence of structural properties on the activity of WO3catalysts for visible light photocatalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 126, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; You, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Switchable and simultaneous oil/water separation induced by prewetting with a superamphiphilic self-cleaning mesh. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.Y.; Lyu, S.S.; Fu, Y.X.; Heng, Y.; Mo, D.C. The Janus effect on superhydrophilic Cu mesh decorated with Ni-NiO/Ni(OH)2 core-shell nanoparticles for oil/water separation. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2017, 409, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Mi, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, D.; Li, N. A facile method to fabricate the superhydrophobic magnetic sponge for oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanalizadeh, H.; Manteghi, F. Design and development of a novel BiFeO3/CuWO4 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic performance for the degradation of organic dyes. J. Photochem. Photobio A Chem. 2017, 338, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Xie, Y.; Fang, J.; Ling, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, D. CdS quantum dots confined in mesoporous TiO2 with exceptional photocatalytic performance for degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunaseth, M.; Poldorn, P.; Junkeaw, A.; Meeprasert, J.; Rungnim, C.; Namuangruk, S.; Kungwan, N.; Inntam, C. A DFT study of volatile organic compounds adsorption on transition metal deposited graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. LSER model for organic compounds adsorption by single-walled carbon nanotubes: Comparison with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and activated carbon. Environ. Pollul. 2015, 206, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, B.; Repo, E.; Heiskanen, J.P.; Sirviö, J.A.; Sillanpää, M. Effectiveness of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan on destabilization of Marine Diesel, Diesel and Marine-2T oil for oil spill treatment. Carbohy. Polym. 2017, 167, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Carmody, O.; Kokot, S. Porous Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup: A Review of Synthesis and Absorbing Properties. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahi, R.; Chuah, L.A.; Choong, T.S.; Ngaini, Z.; Nourouzi, M.M. Oil removal from aqueous state by natural fibrous sorbent: An overview. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.F.; Lim, T.T. Perfomance and mechanism of a hydrophobic-oleophilic kapok filter for oil/water separation. Desalination 2006, 190, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Investigation of acetylated kapok fibers on the sorption of oil in water. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, G.; Caruel, H.; Borredon, M.E.; Bonnin, C.; Vignoles, C. Oil Removal from water by selective sorption on hydrophobic cotton fibers. 1. Study of sorption properties and comparison with other cotton fiber-based sorbents. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2003, 37, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakovic, V.; Aleksic, G.; Radetic, M.; Rajakovic, L. Efficiency of oil removal from real wastewater with different sorbent materials. J. Hazar. Mater. 2007, 143, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.M.; Cloud, R.M. Natural sorbents in oil spill cleanup. Environ. Sci. Tech. 1992, 26, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunciado, T.R.; Sydenstricker, T.H.D.; Amico, S.C. Experimental investigation of various vegetable fibers as sorbent materials for oil spills. Marin. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegerter, M.A.; Leventis, N.; Koebel, M.M. Aerogel Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Tao, W.Q. Numerical predictions of thermal conductivities for the silica aerogel and its composites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 115, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeran, N.; Moghaddas, J. Synthesis and characterization of silica aerogel reinforced rigid polyurethane foam for thermal insulation application. J. Non-Crystall. Solid 2017, 461, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobach, E.; Bhatia, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, E.N. High temperature annealing for structural optimization of silica aerogels in solar thermal applications. J. Non-Crystall. Solid 2017, 462, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Shao, G.; Shen, X.; Cui, S.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X. Investigation on textural and structural evolution of the novel crack-free equimolar Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2 ternary aerogel during thermal treatment. Ceramic. Inter. 2017, 43, 4188–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Cai, Z.; Gong, S. Green synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofibril (CNF) hybrid aerogels and their use as superabsorbents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Parsons, G.N.; Khan, S.A.; Rojas, O.J. Synthesis of organic aerogels with tailorable morphology and strength by controlled solvent swelling following Hansen solubility. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Meador, M.A.B.; McCorkle, L.; Quade, D.J.; Guo, J.; Hamilton, B.; Cakmak, M.; Sprowl, G. Polyimide Aerogels Cross-Linked through Amine Functionalized Polyoligomeric Silsesquioxane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Du, D.; Feng, J. Study on Thermal Conductivities of Aromatic Polyimide Aerogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12992–12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, M.; Lin, X.; Ren, X.; Huang, T.S.; Kim, I.S. Functional Nanocomposite Aerogels Based on Nanocrystalline Cellulose for Selective Oil/Water Separation and Antibacterial Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Li, Z. Hybrid aerogels derived from banana peel and waste paper for efficient oil absorption and emulsion separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, O.; Frost, R.; Xi, Y.; Kokot, S. Surface characterisation of selected sorbent materials for common hydrocarbon fuels. Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, T.C.F.; Habibi, Y.; Colodette, J.L.; Elder, T.; Lucia, L.A. A fundamental investigation of the microarchitecture and mechanical properties of tempo-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC)-based aerogels. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, H.; Xing, L.; Xiang, J.; Cui, L.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, C.; Lia, Z.; Lia, F. Flexible aerogels based on an interpenetrating network of bacterial cellulose and silica by a non-supercritical drying process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7963–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M.; Kuga, S.; Zhang, L. Cellulose Aerogels from Aqueous Alkali Hydroxide–Urea Solution. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2008, 1, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervin, N.T.; Aulin, C.; Larsson, P.T.; Wagberg, L. Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 2012, 19, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Fan, Z.; Duong, H.M. Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Q. Fabrication of cellulose-based aerogels from waste newspaper without any pretreatment and their use for absorbents. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 123, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalder, A.F.; Melchior, T.; Müller, M.; Sage, D.; Blu, T.; Unser, M. Low-bond axisymmetric drop shape analysis for surface tension and contact angle measurements of sessile drops. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 364, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Yoon, B.; Chen, L.; Ci, L.; Nam, J.D.; Chen, X.; Suhr, J. Hierarchical porous chitosan sponges as robust and recyclable adsorbents for anionic dye adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | Cellulose Content (%) | Coagulation Solution | Density (g/cm3) | Porosity (%) | Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose aerogel | 1.5 | Ethanol | 0.085 | 94.46 | – |
| Sulfuric acid | 0.116 | 92.42 | 13.419 | ||
| 2 | Ethanol | 0.131 | 91.41 | – | |
| Sulfuric acid | 0.135 | 91.19 | 9.046 | ||
| 2.5 | Ethanol | 0.144 | 90.58 | 8.155 |
| Silanization Time (h) | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| 6 | 114.1 ± 5.26 |
| 9 | 125.5 ± 4.68 |
| 12 | 132.3 ± 6.92 |
| 17 | 131.8 ± 5.18 |
| Adsorbate | Maximum Absorption Capacity | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (%) | k1 | R2 | k2 | R2 | |
| Vacuum oil | 831 ± 12.2 | 0.0874 | 0.9921 | 1.27 × 10−5 | 0.994 |
| Waste motor oil | 968 ± 18.6 | 0.0707 | 0.9956 | 8.99 × 10−5 | 0.9815 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, D.D.; Vu, C.M.; Vu, H.T.; Choi, H.J. Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibril-Based Silane Cellulose Aerogel: Fabrication and Oil Absorbent Characteristics. Materials 2019, 12, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091407
Nguyen DD, Vu CM, Vu HT, Choi HJ. Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibril-Based Silane Cellulose Aerogel: Fabrication and Oil Absorbent Characteristics. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091407
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Dinh Duc, Cuong Manh Vu, Huong Thi Vu, and Hyoung Jin Choi. 2019. "Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibril-Based Silane Cellulose Aerogel: Fabrication and Oil Absorbent Characteristics" Materials 12, no. 9: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091407
APA StyleNguyen, D. D., Vu, C. M., Vu, H. T., & Choi, H. J. (2019). Micron-Size White Bamboo Fibril-Based Silane Cellulose Aerogel: Fabrication and Oil Absorbent Characteristics. Materials, 12(9), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091407





