Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ACRM Asphalt
2.3. Characterization of Microscopic Properties of Crumb Rubber
2.4. ACRM Asphalt Viscoelastic Test
3. Results and Discussion
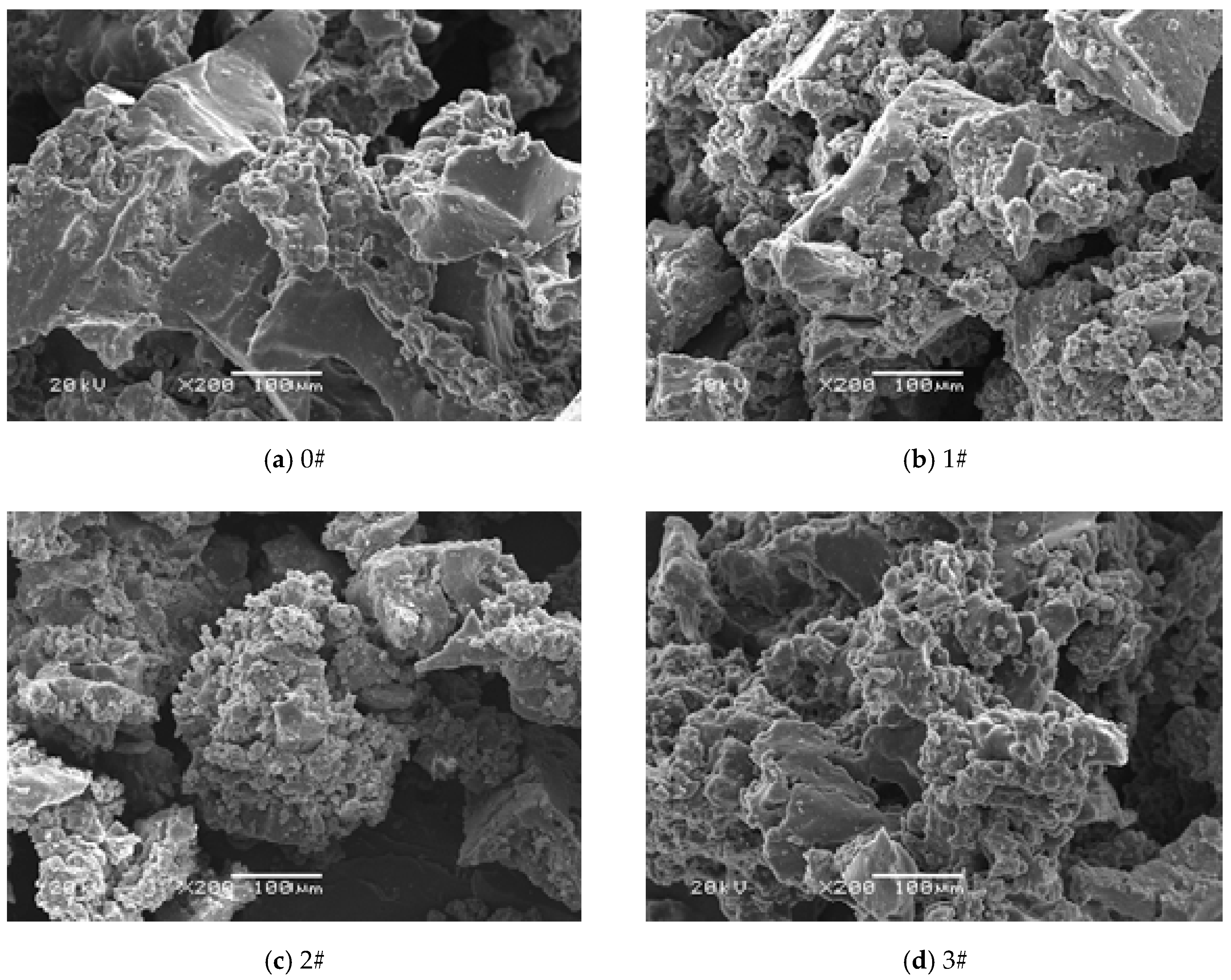
3.1. Microscopic Morphology of Crumb Rubber
3.2. Pore Structure of Crumb Rubber Activated by H2O2
3.3. ACRM Asphalt Viscoelastic
3.4. Creep Recovery Performance of ACRM Asphalt
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Presti, D.L. Recycled tyre rubber modified bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, J.; Xie, Z. Influence of trans-polyoctenamer on rheological properties of rubberised asphalt binders after short term aging procedures. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 5, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, J.; Cao, G.; Wang, C.; Yang, X. Influence mechanism of crumb rubber characteristics on high-temperature performance for rubber modified asphalt binder. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Behnood, A.; Olek, J. Rheological properties of asphalt binders modified with styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), ground tire rubber (GTR), or polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Olek, J. Stress-dependent behavior and rutting resistance of modified asphalt binders: An MSCR approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhy, A.; Presti, D.L.; Airey, G. An investigation on using pre-treated tyre rubber as a replacement of synthetic polymers for bitumen modification. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, O.; Xiao, F.; Han, S. High temperature rheological properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt binders with various modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Tan, Y.; Yang, L. Evaluation of performance on crumb-rubber-modified asphalt mixture. J. Test. Eval. 2012, 40, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; You, Z. Analysis of the low-temperature rheological properties of rubberized warm mix asphalt binders. J. Test. Eval. 2012, 40, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, F.M. Noise abatement of rubberized hot mix asphalt: A brief review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2015, 8, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.J.; Yun, Y.B.; Kim, K.W. The use of CRM-modified asphalt mixtures in Korea: Evaluation of high and ambient temperature performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.T.; Duhovny, G.S.; Sachkova, A.V. Comparison of bitumen–rubber use in extreme conditions in Russia and South Africa. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venudharan, V.; Biligiri, K.P.; Sousa, J.B.; Way, G.B. Asphalt-rubber gap-graded mixture design practices: A state-of-the-art research review and future perspective. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 730–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, H.; Geng, J. Production and Performance of Desulfurized Rubber Asphalt Binder. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, Y. Experimental study on storage stability of crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Southeast Univ. 2011, 41, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Shen, B.; Zhang, J. A Study on the Performance and Storage Stability of Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalts. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.J. Laboratory Investigation of Different Standards of Phase Separation in Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatanawi, K.; Biro, S.; Thodesen, C.; Amirkhanian, S. Effects of water activation of crumb rubber on the properties of crumb rubber-modified binders. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2009, 10, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Duan, W. Novel method to prepare activated crumb rubber used for synthesis of activated crumb rubber modified asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 5, 04014173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y. Effect of Short-Term Aging on Asphalt Modified Using Microwave Activation Crumb Rubber. Materials 2019, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Ren, S.; Shi, J.; Luo, H. Thermo-stability and aging performance of modified asphalt with crumb rubber activated by microwave and TOR. Mater. Des. 2017, 127, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. Crumb rubber-modified asphalt: Microwave treatment effects. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocevski, S.; Yagneswaran, S.; Xiao, F.; Punith, V.S.; Smith, D.W., Jr.; Amirkhanian, S. Surface modified ground rubber tire by grafting acrylic acid for paving applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H. Influence of sodium hypochlorite oxidization of crumb tire rubber on performance of modified bitumen. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Qiao, Y.Y.; Song, L.F. Benzoyl peroxide oxidization of crumb tire rubber and its application in rubber Asphalt. Chem. Res. Appl. 2017, 29, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Shen, A.; Guo, Y.; Lv, Z. Effect of process parameters on the high temperature performance and reaction mechanism of CRMA. Petroleum Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; You, Z.; Mills-Beale, J.; Hao, P. Laboratory evaluation on high temperature viscosity and low temperature stiffness of asphalt binder with high percent scrap tire rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Shu, X.; Cao, J. A two-staged surface activation to improve properties of rubber modified cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Amirkhanian, S. The influence of crumb rubber modifier (CRM) microstructures on the high temperature properties of CRM binders. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2005, 6, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.R.; Gareth, R.; Marc, B.R.; Power, I.M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses: Examples from the barnett, woodford, haynesville, marcellus, and doig units. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wang, H.; Hao, P. Rheological property investigations for polymer and polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt binders at high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Qiang, Z. Application of two phase model to linear dynamic rheology of filled polymer melts. Polymer 2011, 52, 6173–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y. Effect of hydrogen peroxide treated rubber powder on viscoelasticity of rubber modified asphalt. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2019, 36, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Bahia, H.; Tabatabaee, N.; Clopotel, C.; Golalipour, A. Evaluation of the MSCR test for modified binder specification. In Proceedings of the Fifty–sixth Annual Conference of the Canadian Technical Asphalt Association, Québec City, QC, Canada, November 2011; Volume 11, pp. 61–82. [Google Scholar]










| Test Properties | Specification | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s)/0.1 mm | 80–100 | 92.0 | |
| Softening point/°C | ≥42 | 46.2 | |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 10 °C)/cm | ≥100 | >100 | |
| RTFOT (163 °C, 85 min) | Loss of quality/% | ≤ ±0.8 | 0.07 |
| Penetration ratio/% | ≥54 | 70 | |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 10 °C)/cm | ≥6 | 9.0 | |
| Test Properties | Bulk Density/(kg/m3) | Moisture Content/% | Metal Content/% | Fiber Content/% | Ash Content/% | Acetone Extract/% | Carbon Black Content/% | Rubber Hydrocarbon Content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical indexes | 260–460 | <1 | <0.03 | <1 | ≤8 | ≤22 | ≥28 | ≥42 |
| Test results | 302.5 | 0.0 | 0.009 | 0.065 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 30 | 52 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Li, J. Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Materials 2019, 12, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091434
Li B, Li H, Wei Y, Zhang X, Wei D, Li J. Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091434
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Hao Li, Yongzheng Wei, Xingjun Zhang, Dingbang Wei, and Jia Li. 2019. "Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt" Materials 12, no. 9: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091434
APA StyleLi, B., Li, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, X., Wei, D., & Li, J. (2019). Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Materials, 12(9), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091434





