Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC in Cement Mortar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of HPMC Aqueous Solution
2.2.2. Sample Preparation of HPMC Sand Mixture
2.2.3. Preparation of Cement Mortar Samples
2.2.4. Preparation of Cement Paste Samples
2.2.5. Testing Method for Plastic Viscosity of Cement Mortar
2.2.6. Thermal Analysis
2.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.8. Water Retention Tests
2.2.9. Measurement of Viscosity and Total Organic Carbon (TOC) of Interstitial Solution
3. Results and Discussion
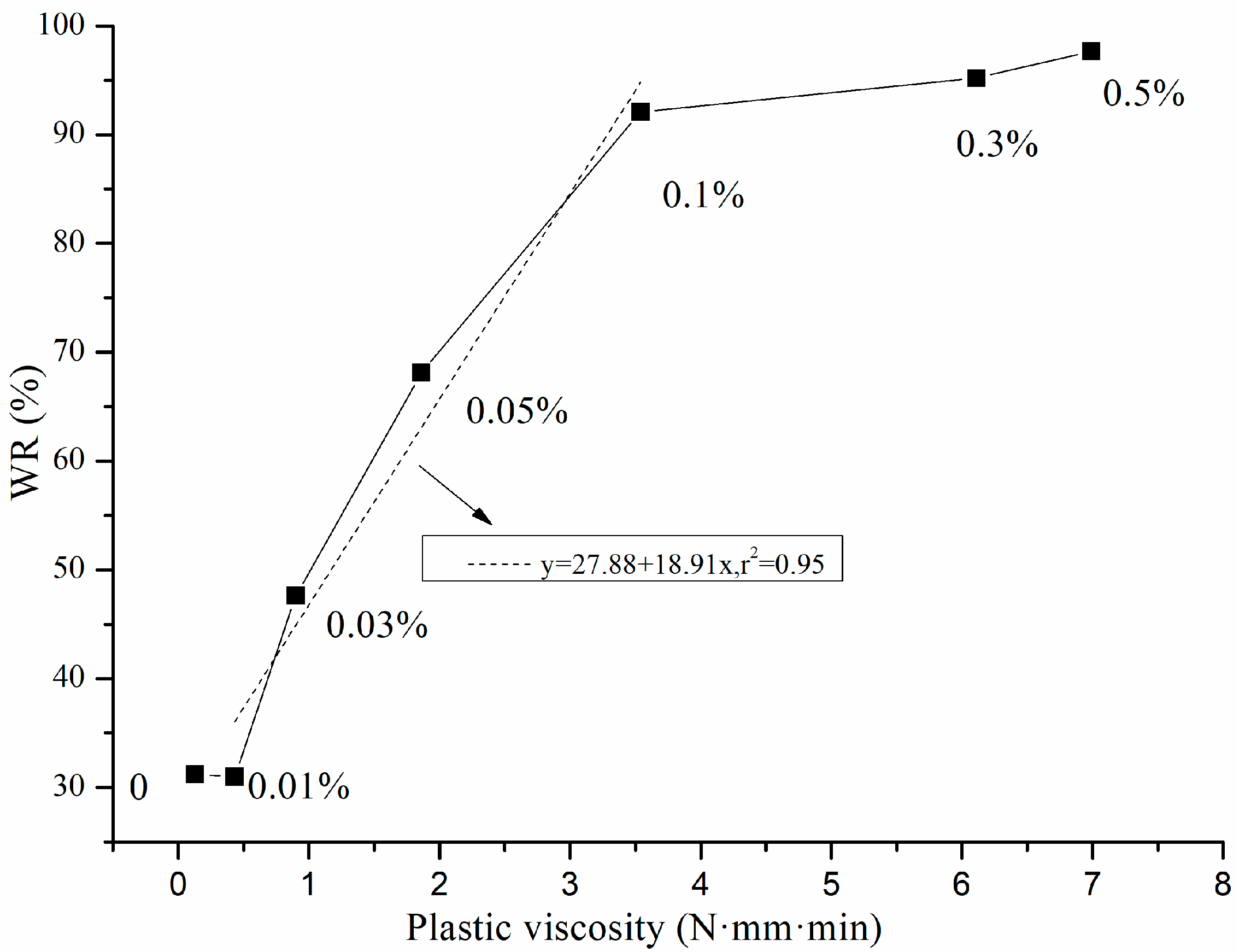
3.1. Water Retention and Plastic Viscosity
3.2. Effect of HPMC on the Interstitial Solution of Cement Mortar
3.3. Effect of HPMC on Hydration of Cement
3.4. The Interaction between HPMC and Cement Mortar
3.4.1. Early Distribution of HPMC in Water
3.4.2. The Interaction between HPMC and Sand
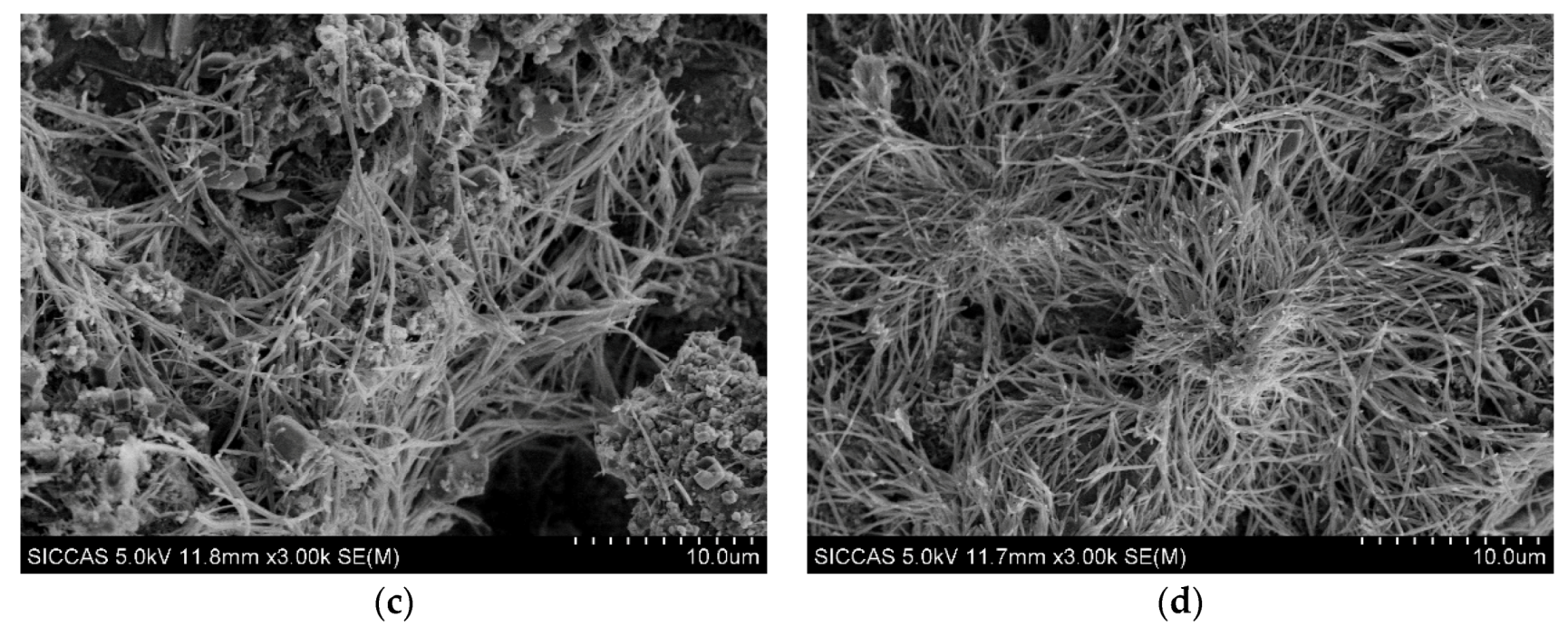
3.4.3. Interaction between HPMC and Cement Mortar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pourchez, J.; Peschard, A.; Grosseau, P.; Guyonnet, R.; Guilhot, B.; Vallée, F. HPMC and HEMC influence on cement hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patural, L.; Marchal, P.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. Cellulose ethers influence on water retention and consistency in cement-based mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bülichen, D.; Plank, J. Water retention capacity and working mechanism of methyl hydroxypropyl cellulose (MHPC) in gypsum plaster—Which impact has sulfate? Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 46, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govin, A.; Bartholin, M.-C.; Biasotti, B.; Giudici, M.; Langella, V.; Grosseau, P. Modification of water retention and rheological properties of fresh state cement-based mortars by guar gum derivatives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, R.; Lu, X.; Wang, P. Early hydration of calcium sulfoaluminate cement in the presence of hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbrières, J. Cement cake properties in static filtration. Influence of polymeric additives on cement filter cake permeability. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlière, C.; Mabrouk, E.; Lamblet, M.; Coussot, P. How water retention in porous media with cellulose ethers works. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B. Current understanding of cellulose ethers impact on the hydration of C3A and C3A-sulphate systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B. Changes in C3S hydration in the presence of cellulose ethers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brumaud, C.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Mohler, C.; Baumann, R.; Schmitz, M.; Radler, M.; Roussel, N. Cellulose ethers and water retention. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumaud, C.; Baumann, R.; Schmitz, M.; Radler, M.; Roussel, N. Cellulose ethers and yield stress of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 55, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, H.; Müller, I.; Schmitt, B.; Bosbach, D.; Putnis, A. Time-resolved monitoring of cement hydration: Influence of cellulose ethers on hydration kinetics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater At. 2005, 238, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Korb, J.-P.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion investigations of water retention mechanism by cellulose ethers in mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messan, A.; Ienny, P.; Nectoux, D. Free and restrained early-age shrinkage of mortar: Influence of glass fiber, cellulose ether and EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Peng, Y.; Tan, H.; Jian, S.; Zhi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, T.; He, X. Effect of hydroxypropyl-methyl cellulose ether on rheology of cement paste plasticized by polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betioli, A.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Silva, D.; John, V.M.; Pileggi, R.G. Effect of HMEC on the consolidation of cement pastes: Isothermal calorimetry versus oscillatory rheometry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapen, E.; Van Gemert, D. Cement hydration and microstructure formation in the presence of water-soluble polymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.-Y.; Wirquin, E. Evaluation of various cellulose ethers performance in ceramic tile adhesive mortars. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 40, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülichen, D.; Kainz, J.; Plank, J. Working mechanism of methyl hydroxyethyl cellulose (MHEC) as water retention agent. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinot, T.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P. Impact of hydroxypropylguars on the early age hydration of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 44, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurnaus, T.; Plank, J. Adsorption of non-ionic cellulose ethers on cement revisited. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 195, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Devlin, L.P.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C.C. Impact of water-soluble cellulose ethers on polymer-modified mortars. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 49, 923–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, N.; Pooja, K.; Khan, R. Preparation and applications of hydrophobic multicomponent based redispersible polymer powder: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Chemical Composition (wt.%) | Physical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.68 | Fineness (80 μm sieve residue)/% | 6.2 |
| Al2O3 | 5.20 | Specific surface area (m2/kg) | 362 |
| Fe2O3 | 2.59 | Water requirement of normal consistency/% | 26.8 |
| CaO | 62.94 | Initial setting/min | 135 |
| Na2O | 0.53 | Final setting/min | 170 |
| MgO | 1.56 | 3 d flexural strength/MPa | 7.9 |
| SO3 | 2.39 | 28 d flexural strength/MPa | 11.6 |
| Loss | 1.58 | 2 d compressive strength/MPa | 39.0 |
| f-CaO | 1.58 | 28 d compressive strength/MPa | 64.7 |
| Specimen | Cement (g) | Sand (g) | HPMC (g) | H2O (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW1 | 0.5 | 99.5 | ||
| HW2 | 1.5 | 98.5 |
| Cement | HPMC | H2O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 300 | 156 | |
| C2 | 300 | 0.03 | 156 |
| C3 | 300 | 0.09 | 156 |
| C4 | 300 | 0.15 | 156 |
| C5 | 300 | 0.3 | 156 |
| C6 | 300 | 0.9 | 156 |
| C7 | 300 | 1.5 | 157 |
| C8 | 300 | 3 | 157 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, N.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, G. Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC in Cement Mortar. Materials 2020, 13, 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132918
Chen N, Wang P, Zhao L, Zhang G. Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC in Cement Mortar. Materials. 2020; 13(13):2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132918
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ning, Peiming Wang, Liqun Zhao, and Guofang Zhang. 2020. "Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC in Cement Mortar" Materials 13, no. 13: 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132918
APA StyleChen, N., Wang, P., Zhao, L., & Zhang, G. (2020). Water Retention Mechanism of HPMC in Cement Mortar. Materials, 13(13), 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132918




