Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Mg-Ca-Y Alloys, Morphological and Structural Analysis
2.2. Electrochemical Analysis
2.3. Cytocompatibility Testing
2.3.1. Alloy Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Cell Culture
2.3.3. Cell Viability
2.3.4. Cell Morphology
3. Results and Discussions
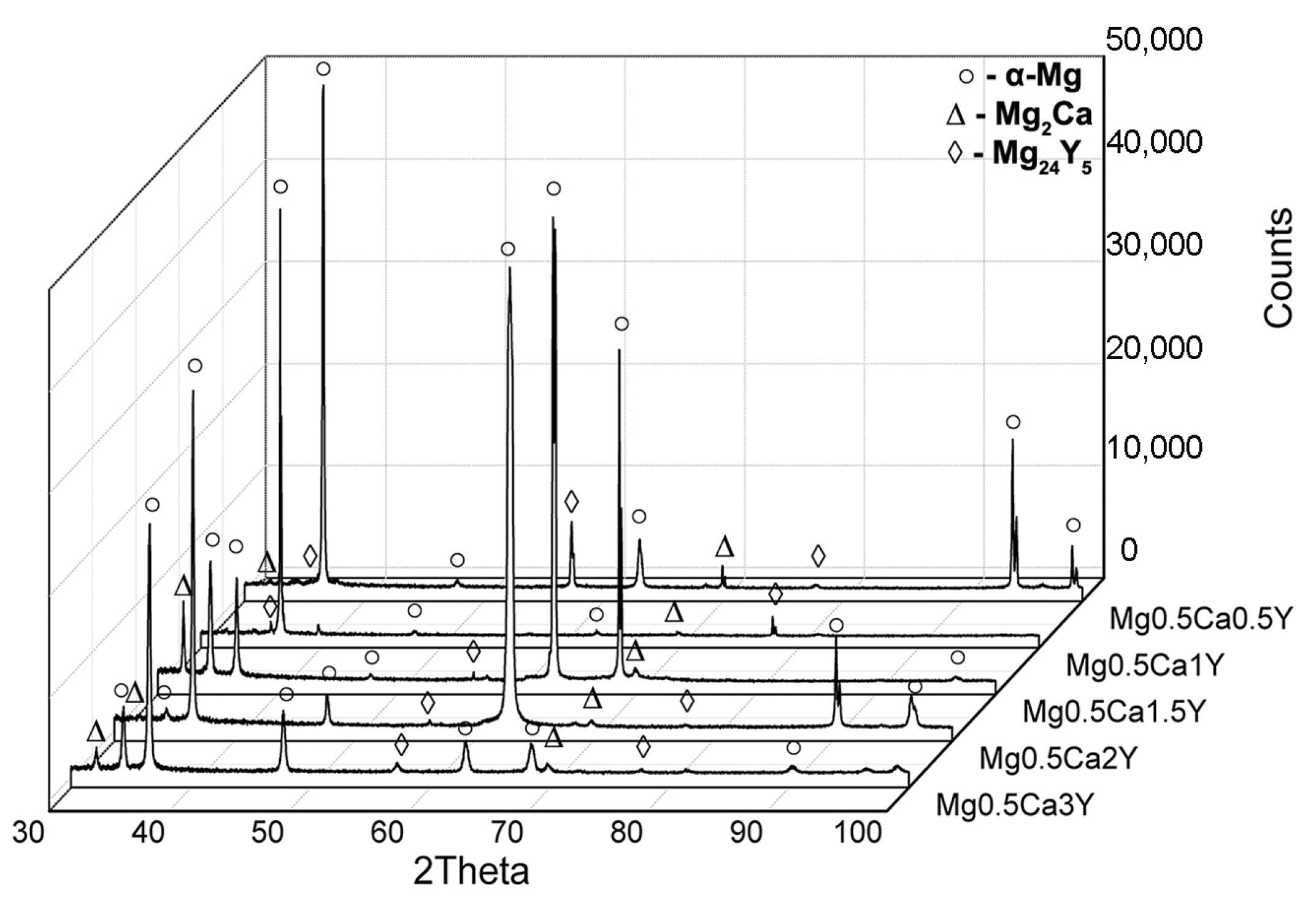
3.1. Structural Characterization
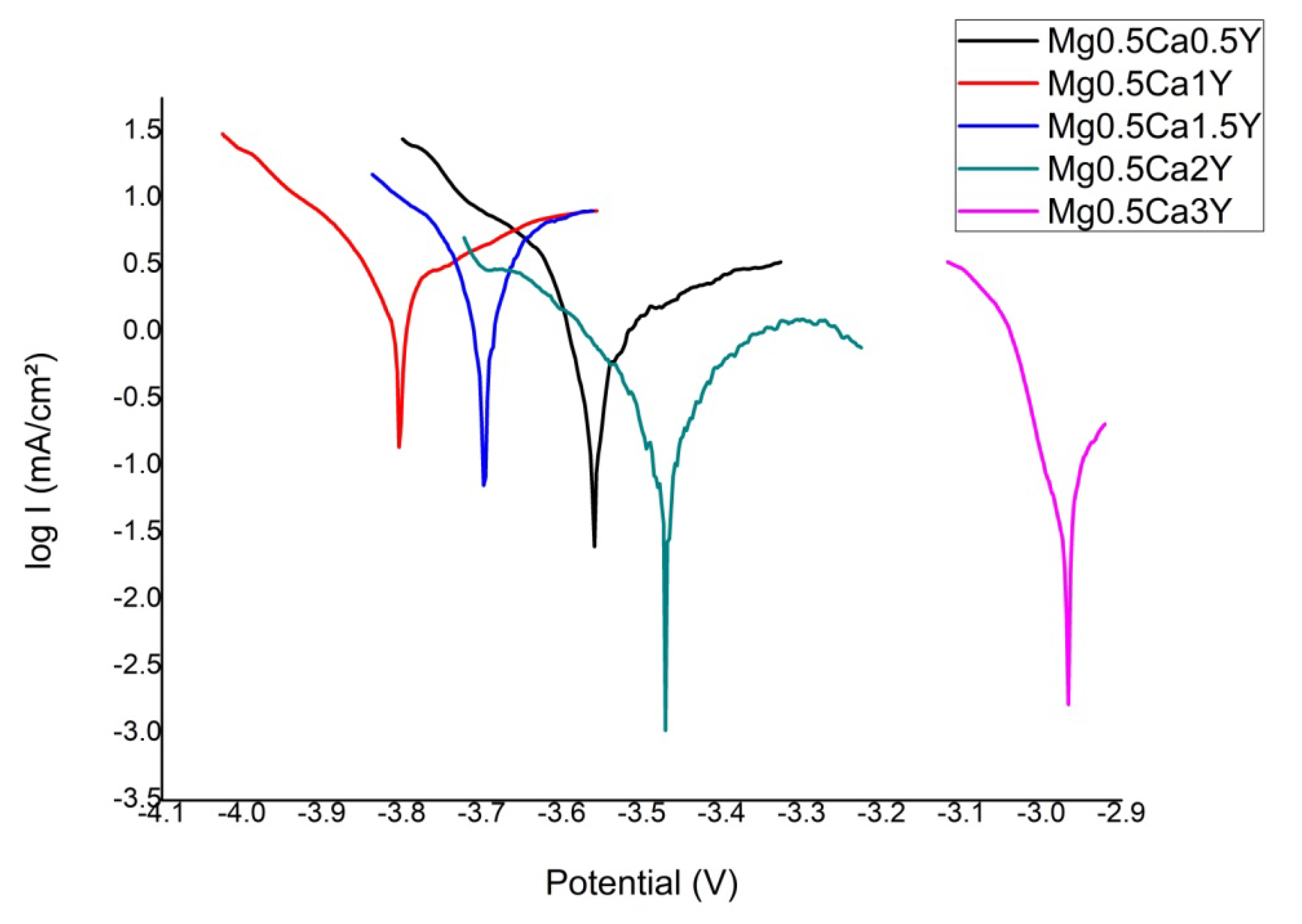
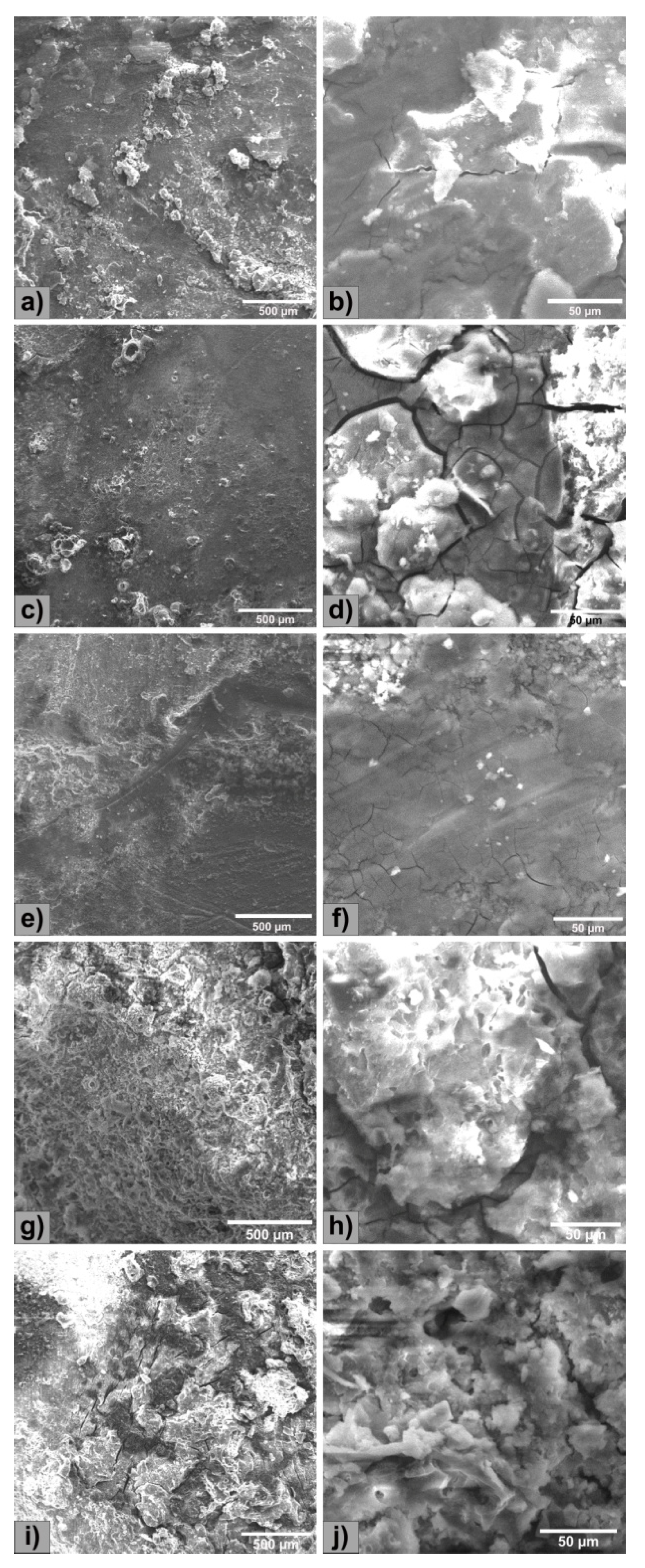
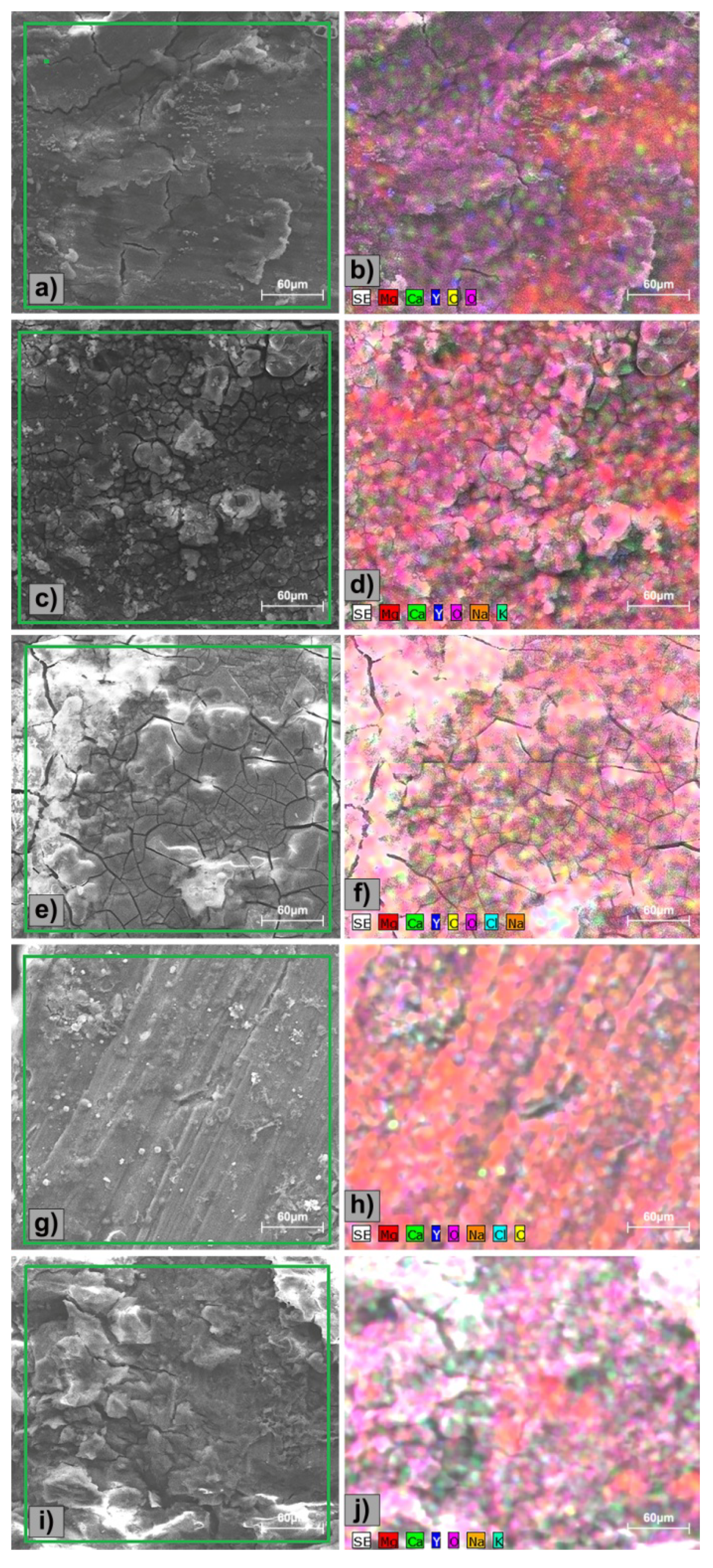
3.2. Electrochemical Evaluation
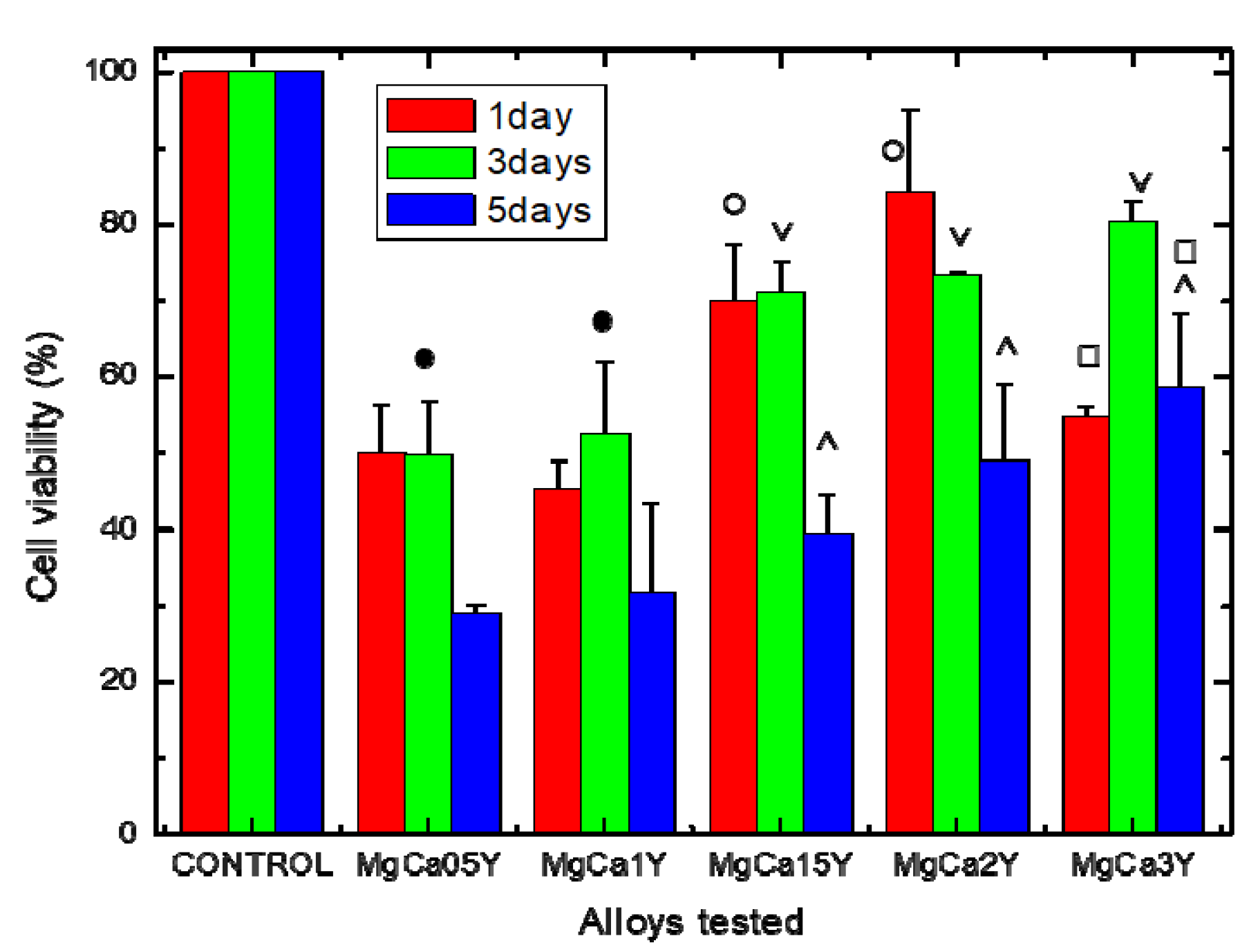
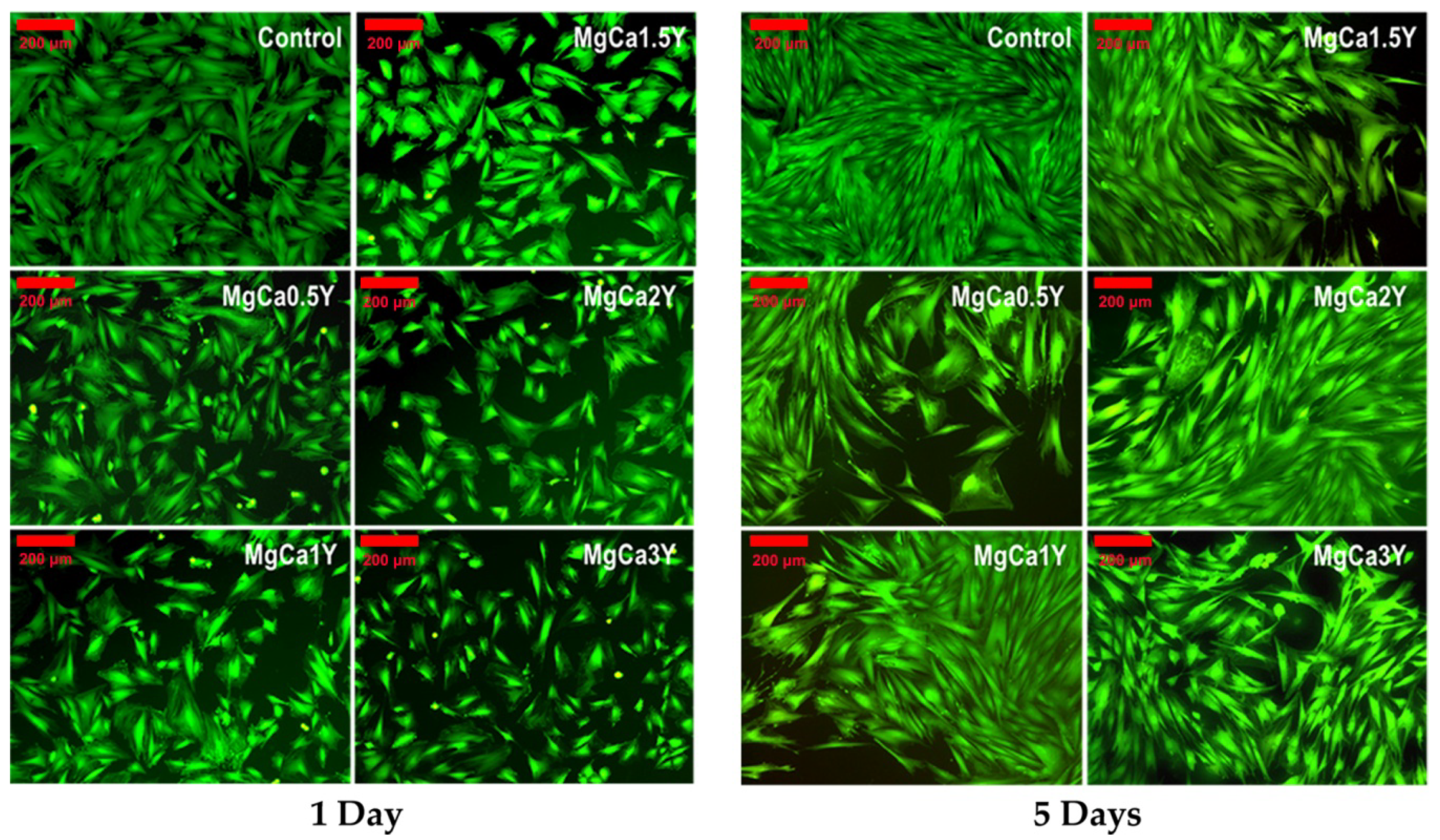
3.3. Cytocompatibility Study
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Addition of Y in the experimental alloys refines the microstructure, resulting in the Mg24Y5 cubic structure compound. Y compounds have a white spherical form in the metallic matrix andtypically a size of 15 µm. Also, Ca forms an eutectic compound—Mg2Ca, founded at the Mg grainsboundary.
- (2)
- The corrosion resistance was performed in SBF solution and presented a generalized type with very few areas not affected by corrosion. Addition of Y leads to an increase in electro-corrosion resistance, especially at alloying percentages greater than 1.0 wt.%. Increasing the content of Y, the immersion and electro-chemical tests show an improved degradation rate as following: 65.7 mm/y (0.5 wt.%) and 10.20 mm/y (3.0 wt.%).
- (3)
- The Mg-0.5Ca-xY alloys have a cytocompatible behavior, i.e., the viability level at 3 days for Mg-Ca-Y alloys with a Y amount of 1.5, 2.0 and 3.0 wt.% was above 70%. The decrease of cell viability level after 5 days at values around 50%, especially in the case of alloys with 1.5 wt.%, 2.0 wt.% and 3.0 wt.% Y, should be attributed to the following factors: change of pH value, ion release from alloys, increasing of osmolarity, and salt precipitation with toxic or inhibitory effect. However, the increase of the Y alloying amount seems to increase the cytocompatibility of these alloys and open the way for future studies concerning alloys with a content higher than 3.0 wt.% Y.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schumann, P.; Lindhorst, D.; Wagner, M.; Schramm, A.; Gellrich, N.C.; Rucker, M. Perspectives on ResorbableOsteosynthesis Materials in Cranio maxilla facial Surgery. Pathobiology 2013, 80, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.I.; Ullah, S.; Mueller, P. Advances and Challenges of Biodegradable Implant Materials with a Focus on Magnesium-Alloys and Bacterial Infections. Metals 2018, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.C.; Al-Saadi, S.; Choudhary, L.; Harandi, S.E.; Singh, R. Magnesium Implants: Prospects and Challenges. Materials 2019, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tune, D. Body-Absorbable Osteosynthesis Devices. Clin. Mater. 1991, 8, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, M.P.; Pietak, A.M.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandu, A.V.; Baltatu, M.S.; Nabialek, M.; Savin, A.; Vizureanu, P. Characterization and Mechanical Proprieties of New TiMo Alloys Used for Medical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltatu, M.S.; Tugui, C.A.; Perju, M.C.; Benchea, M.; Spataru, M.C.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P. Biocompatible Titanium Alloys used in Medical Applications. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S.; Loffredo, S.; Jun, I.; Edwards, J.; Kim, Y.C.; Seok, H.K.; Witte, F.; Mantovani, D.; Glyn-Jones, S. Current status and outlook on the clinical translation of biodegradable metals. Mater. Today 2019, 23, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5 (Suppl. 1), 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Alawi, A.M.; Majoni, S.W.; Falhammar, H. Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W. Opportunities and challenges for the biodegradable magnesium alloys as next-generation biomaterials. Regen. Biomater. 2016, 3, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.; Johnston, S.; Shi, Z.; Dargusch, M.S. Viewpoint—Understanding Mg corrosion in the body for biodegradable medical implants. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Nagasekhar, A.V.; Schmutz, P.; Easton, M.; Song, G.L.; Atrens, A. Calculated phase diagrams and the corrosion of die-cast Mg–Al alloys. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, U.; Shabib, I.; Haider, W. The current trends of Mg alloys in biomedical applications—A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 1970–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Hu, S. Mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and biocompatibilities of degradable Mg-RE alloys: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J.; Seitz, J.M.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Rare Earth Metals as Alloying Components in Magnesium Implants for Orthopaedic Applications. In New Features on Magnesium Alloys; Monteiro, W.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Suzuki, K. Exposure, Metabolism, and Toxicity of Rare Earths and Related Compounds. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, K.T.; Koo, K.H.; Park, J.S. Toxicological Evaluations of Rare Earths and Their Health Impacts to Workers: A Literature Review. Saf. Health Work 2013, 4, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, G.; Guida, M.; Tommasi, F.; Oral, R. Health effects and toxicity mechanisms of rare earth elements—Knowledge gaps and research prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekumalla, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Almajid, A.; Gupta, M. Mechanical Properties of Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloy Systems: A Review. Metals 2015, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hort, N.; Kainer, K.U. Preparation and properties of high purity Mg–Y biomaterials. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Schmutz, P.; Uggowitzer, P.; Song, G.; Atrens, A. The influence of Y (Y) on the corrosion of Mg–Y binary alloys. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3687–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudholz, A.D.; Gusieva, K.; Chen, X.B.; Muddle, B.; Gibson, M.; Birbilis, N. Electrochemical behaviour and corrosion of Mg–Y alloys. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südholz, A.D.; Kirkland, N.T.; Buchheit, R.G.; Birbilis, N. Electrochemical Properties of Intermetallic Phases and Common Impurity Elements in Magnesium Alloys. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2011, 14, C5–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupescu, S.; Munteanu, C.; Istrate, B.; Stanciu, S.; Cimpoesu, N.; Oprisan, B. Microstructural Investigations on Alloy Mg-2Ca-0.2Mn-0.5Zr-1Y. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 209, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Shin, K.S.; Cohen, S. The relation between microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg–Y–RE–Zr alloys. J. Alloys Compounds 2007, 431, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bian, D.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, S. Comparative in vitro study on binary Mg-RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu) alloy systems. Acta Biomater. 2020, 102, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravina, P.; Sayaji, D.; Avinash, M. Calcium and its Role in Human Body. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 4, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Lin, L.; Tang, B. Unraveling the role of Calcium ions in the mechanical properties of individual collagen fibrils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, F.; Chen, N.; Xue, S. Calcium intake, calcium homeostasis and health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Torgersen, J.; Berto, F. Mg and Its Alloys for Biomedical Applications: Exploring Corrosion and Its Interplay with Mechanical Failure. Metals 2017, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.C.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Seok, H.K. Influence of Ca on the corrosion properties of magnesium for biomaterials. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4146–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xiong, G.; Luo, H.; He, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X. Preparation and characterization of a new biomedical magnesium–calcium alloy. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Lou, S.; Zheng, Y. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Der Hoh, N.; Bormann, D.; Lucas, A.; Denkena, B.; Hackenbroich, C.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Influence of different surface machining treatments of magnesium-based resorbable implants on the degradation behavior in rabbits. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, B47–B54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, W.; Hodgson, P.; Wen, C. Biodegradable Mg-Ca and Mg-Ca-Y alloys for Regenerative Medicine. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 654–656, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zeng, R.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, W.J.; Chu, P.K. In vitro corrosion degradation behaviour of Mg–Ca alloy in the presence of albumin. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, N.; Birbilis, N.; Walker, J.; Woodfield, T.; Dias, G.; Staiger, M. In-vitro dissolution of magnesium–calcium binary alloys: Clarifying the unique role of calcium additions in bioresorbable magnesium implant alloys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95B, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; von der Hoh, N.; Bormann, D.; Krause, C.; Bach, F.W.; Windhagen, H.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Degradation behaviour and mechanical properties of magnesium implants in rabbit tibiae. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, N.; Angrisani, N.; Reifenrath, J.; Lucas, A.; Thorey, F.; Bormann, D.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Biomechanical testing and degradation analysis of MgCa0.8 alloy screws: A comparative in vivo study in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harandi, S.E.; Idris, M.H.; Jafari, H. Effect of forging process on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of biodegradable Mg–1Ca alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Guo, Y. Biodegradable Orthopedic Magnesium-Calcium (MgCa) Alloys, Processing, and Corrosion Performance. Materials 2012, 5, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, H.R.B.; Idris, M.H.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Farahany, S. Microstructure analysis and corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–Ca implant alloys. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zheng, Y. Novel Magnesium Alloys Developed for Biomedical Application: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, W.J. Enhancement of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg–Ca alloys through microstructural refinement by indirect extrusion. Corros. Sci. 2014, 82, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, W.J. Development of biodegradable Mg–Ca alloy sheets with enhanced strength and corrosion properties through the refinement and uniform dispersion of the Mg2Ca phase by high-ratio differential speed rolling. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.C.; Qi, W.C.; Cui, H.Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.Q.; Han, E.H. In vitro corrosion of as-extruded Mg–Ca alloys—The influence of Ca concentration. Corros. Sci. 2015, 96, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bita, A.I.; Antoniac, A.; Cotrut, C.; Vasile, E.; Ciuca, I.; Niculescu, M.; Antoniac, I. In Vitro Degradation and Corrosion Evaluation of Mg-Ca Alloys for Biomedical Applications. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2016, 18, 394–398. Available online: https://joam.inoe.ro/articles/in-vitro-degradation-and-corrosion-evaluation-of-mg-ca-alloys-forbiomedical-applications (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Rau, J.V.; Antoniac, I.; Fosca, M.; De Bonis, A.; Blajan, A.I.; Cotrut, C.; Graziani, V.; Curcio, M.; Cricenti, A.; Niculescu, M.; et al. Glass-ceramic coated Mg-Ca alloys for biomedical implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunan High Broad New Material, Co.Ltd. Available online: http://www.hbnewmaterial.com/supplier-129192-master-alloy (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Lupescu, S.; Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Minciuna, M.G.; Focsaneanu, S.; Earar, K. Characterization of Some Master Mg-X System (Ca, Mn, Zr, Y) Alloys Used in Medical Applications. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, F.; Bertocci, U. Electrochemical Corrosion Testing. ASTM STP 1981, 727, 1981–2015. Available online: https://www.astm.org/digital_library/stp/source_pages/stp727.htm (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlad, M.D.; Valle, L.J.; Poeată, I.; Barracó, M.; López, J.; Torres, R.; Fernández, E. Injectable iron-modified apatitic bone cement intended for kyphoplasty: Cytocompatibility study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3575–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlad, M.D.; Valle, L.J.; Poeată, I.; López, J.; Torres, R.; Barracó, M.; Fernández, E. Biphasic calcium sulfate dihydrate/iron-modified alpha-tricalcium phosphate bone cement for spinal applications: In vitro study. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Lupescu, S.; Antoniac, V.I.; Sindilar, E. Structural Characterization of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 782, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrens, A.; Song, G.L.; Cao, F.; Shi, Z.; Bowen, P.K. Advances in Mg corrosion and research suggestions. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2013, 1, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, S.; Chen, M.; Fahlman, B.D.; Liu, D.; Bi, H. In vitro and in vivo corrosion, mechanical properties and biocompatibility evaluation of MgF2-coated Mg-Zn-Zr alloy as cancellous screws. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009—Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. Available online: http://nhiso.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/ISO-10993-5-2009.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Gilles, R.; Belkhir, M.; Compere, P.; Libioulle, C.; Thiry, M. Effect of high osmolarity acclimation on tolerance to hyperosmotic shocks in L929 cultured cells. Tissue Cell 1995, 27, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbele, G.O.; Deloulme, J.C.; Gentil, B.J.; Delphin, C.; Ferro, M.; Garin, J.; Takahashi, M.; Baudier, J. The zinc and calcium-binding S100B interacts and co-localizes with IQGAP1 during dynamic rearrangement of cell membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49998–50007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Hort, N.; Laipple, D.; Höche, D.; Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Element distribution in the corrosion layer and cytotoxicity of alloy Mg–10Dy during in vitro biodegradation. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8475–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J.E.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G.S.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L.G. Fundamentals and advances in magnesium alloy corrosion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 92–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloys | Mg/Ca/Y (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) | Si (wt.%) | Al (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Mg | Mg (99 wt.%) | 0.15–0.2 | 0.17–0.2 | 0.14–0.2 | 0.15–0.2 | 0.16–0.2 |
| Mg15Ca | Ca (15.29 wt.%) | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.011 |
| Mg30Y | Y (28.05 wt.%) | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.011 |
| Sample Code | Mg (g) | Mg-15Ca (g) | Mg-30Y (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-0.5Ca-0.5Y | 21.82 | 0.77 | 0.41 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.0Y | 21.42 | 0.77 | 0.82 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.5Y | 21.00 | 0.77 | 1.23 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-2.0Y | 20.59 | 0.77 | 1.64 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-3.0Y | 19.77 | 0.77 | 2.46 |
| Chemical Composition (Ions) (mmol/dm3) | Na+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Cl− | HCO3− | HPO42− | SO42− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated body fluid | 142 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 147.8 | 4.2 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Human blood plasma | 142 | 5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 103 | 27 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Alloy | Mg (wt.%) | Ca (wt.%) | Y (wt.%) | Si (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-0.5Ca-0.5Y | Average | 97.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Stdev | ±0.4 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.0Y | Average | 97.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Stdev | ±0.5 | ±0.1 | ±0.3 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.2 | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.5Y | Average | 96.6 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Stdev | ±0.2 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-2.0Y | Average | 96.2 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Stdev | ±0.5 | ±0.1 | ±0.3 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.2 | ±0.2 | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-3.0Y | Average | 95.6 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Stdev | ±0.4 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 | ±0.2 |
| Sample | E0 | ba (mV) | bc (mV) | Rp (ohm/cm²) | Jcor (mA/cm²) | Vcor (mm/y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-0.5Ca-0.5Y | −3562.1 | 73.7 | −40.9 | 49.99 | 2.8753 | 65.70 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.0Y | −3801.9 | 479.8 | −237.2 | 13.70 | 2.9812 | 68.12 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.5Y | −3697.5 | 112.1 | −102.8 | 12.95 | 1.5805 | 36.11 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-2.0Y | −3470.8 | 269.3 | −205.6 | 160.31 | 0.3663 | 8.37 |
| Mg-0.5Ca-3.0Y | −2969.2 | 63.4 | −156.6 | 276.38 | 0.4463 | 10.20 |
| Chemical Elements | Mg | Ca | Y | O | Cl | Na | K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | wt.% | wt.% | wt.% | wt.% | wt.% | wt.% | ||
| Mg-0.5Ca-0.5Y | Surface with oxides | 61.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 37.6 | - | - | - |
| Surface without oxides | 96.7 | 1.3 | 2.1 | - | - | - | - | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.0Y | Surface with oxides | 58.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 33.2 | 4.0 | 2.4 | - |
| Surface without oxides | 95.6 | 2.3 | 2.1 | - | - | - | - | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-1.5Y | Surface with oxides | 45.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 46.3 | - | 5.4 | 0.9 |
| Surface without oxides | 90.2 | 3.0 | 6.8 | - | - | - | - | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-2.0Y | Surface with oxides | 44.1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 50.1 | 0.4 | 3.8 | - |
| Surface without oxides | 87.8 | 4.0 | 8.2 | - | - | - | - | |
| Mg-0.5Ca-3.0Y | Surface with oxides | 47.7 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 44.8 | - | 1.8 | 2.9 |
| Surface without oxides | 83.6 | 3.1 | 13.4 | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Istrate, B.; Munteanu, C.; Lupescu, S.; Chelariu, R.; Vlad, M.D.; Vizureanu, P. Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143082
Istrate B, Munteanu C, Lupescu S, Chelariu R, Vlad MD, Vizureanu P. Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143082
Chicago/Turabian StyleIstrate, Bogdan, Corneliu Munteanu, Stefan Lupescu, Romeu Chelariu, Maria Daniela Vlad, and Petrică Vizureanu. 2020. "Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys" Materials 13, no. 14: 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143082
APA StyleIstrate, B., Munteanu, C., Lupescu, S., Chelariu, R., Vlad, M. D., & Vizureanu, P. (2020). Electrochemical Analysis and In Vitro Assay of Mg-0.5Ca-xY Biodegradable Alloys. Materials, 13(14), 3082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143082








