Form-Stable Phase Change Materials Based on SEBS and Paraffin: Influence of Molecular Parameters of Styrene-b-(Ethylene-co-Butylene)-b-Styrene on Shape Stability and Retention Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.3.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.3.5. Rheology Measurement
2.3.6. Leakage Test
3. Results and Discussion
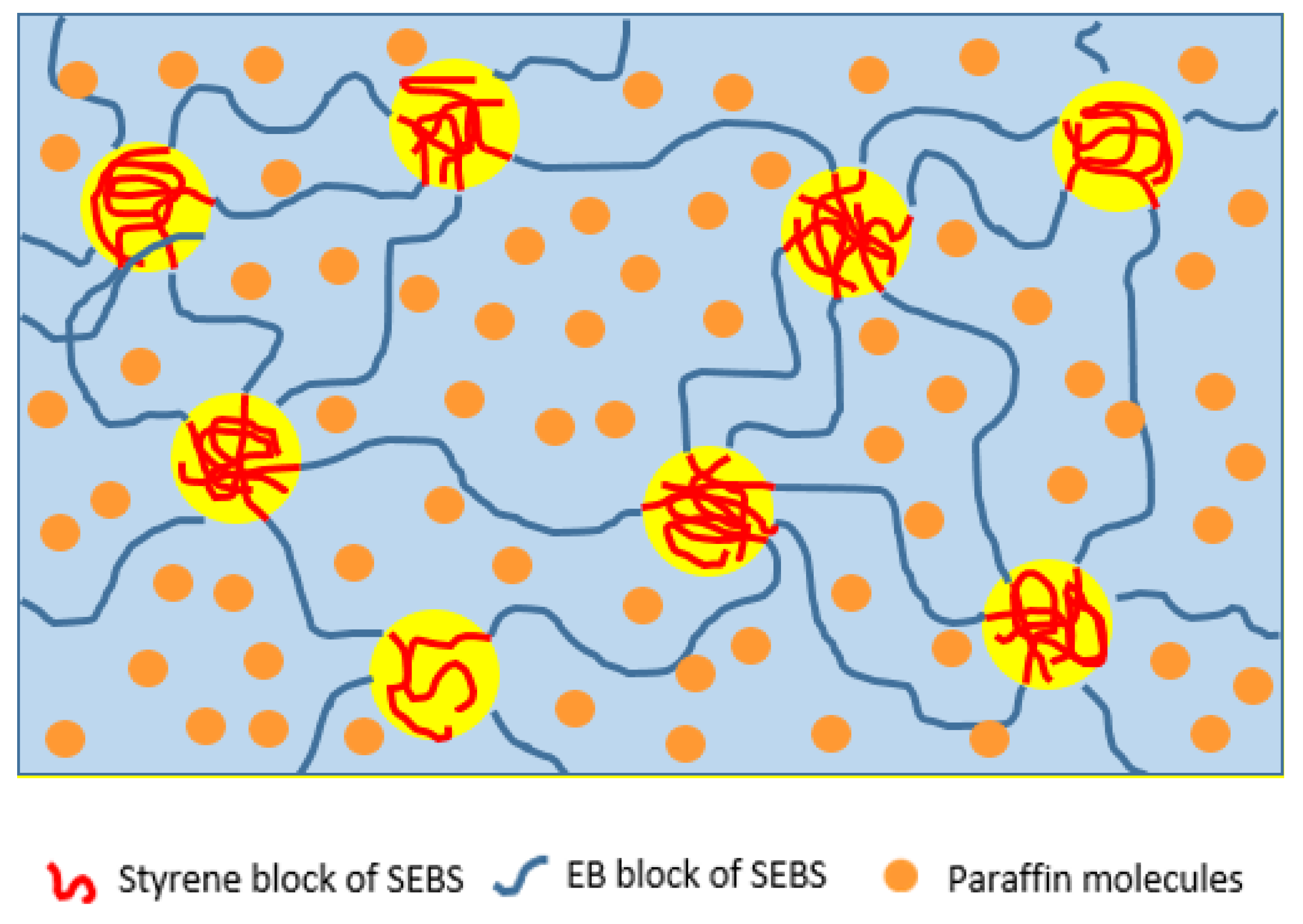
3.1. Chemical Analysis of SEBS Types
3.2. Thermal Properties of SEBS/Paraffin FSPCMs
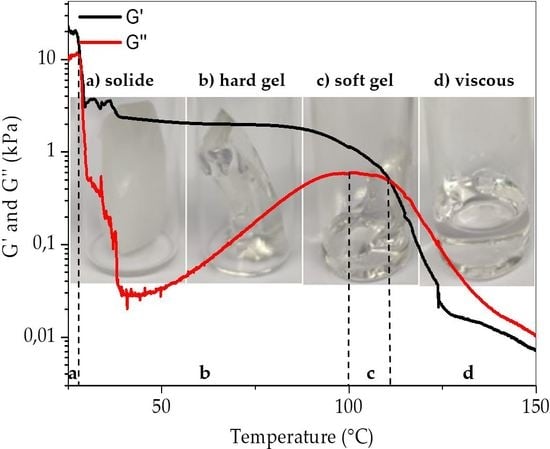
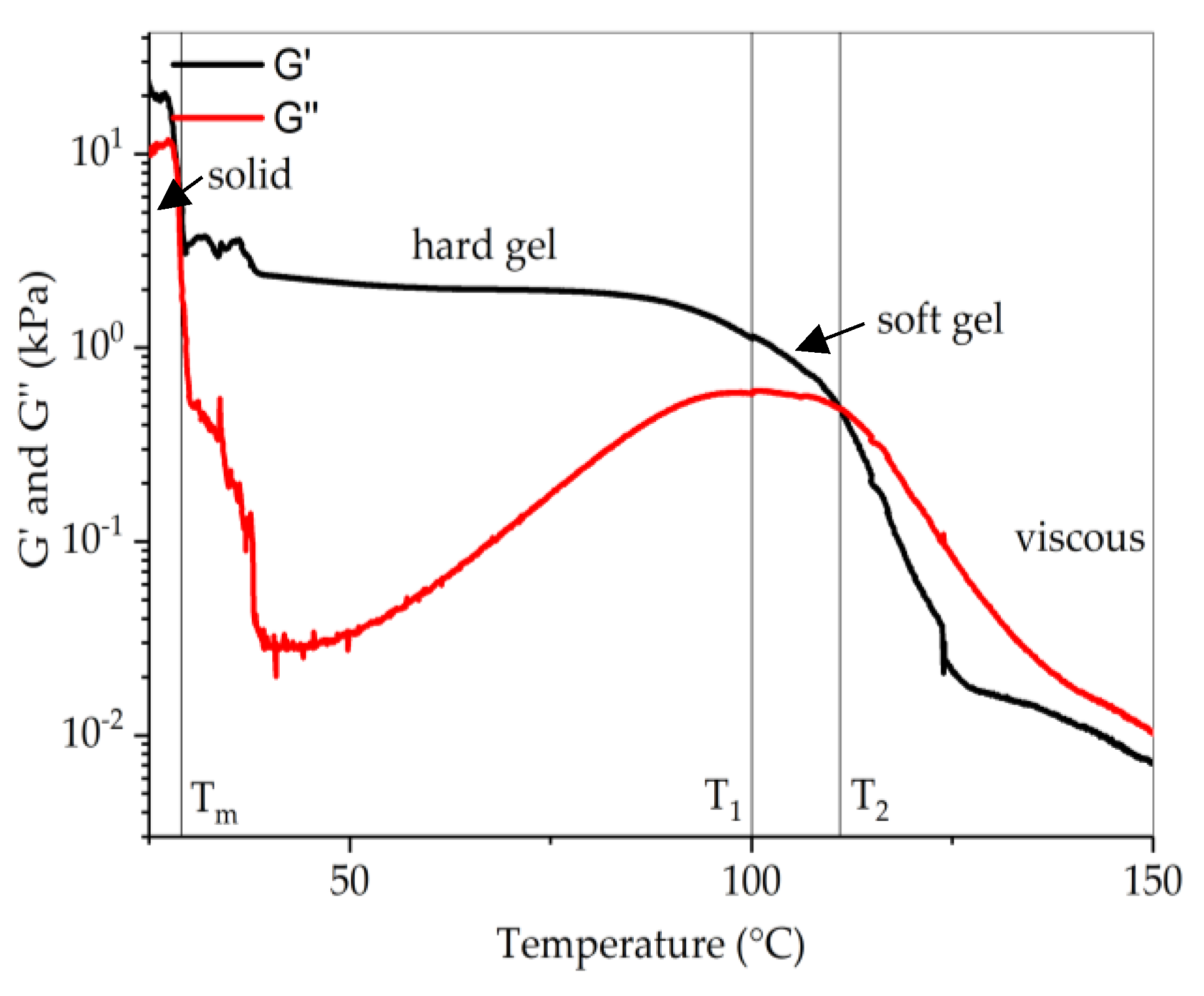
3.3. Rheology
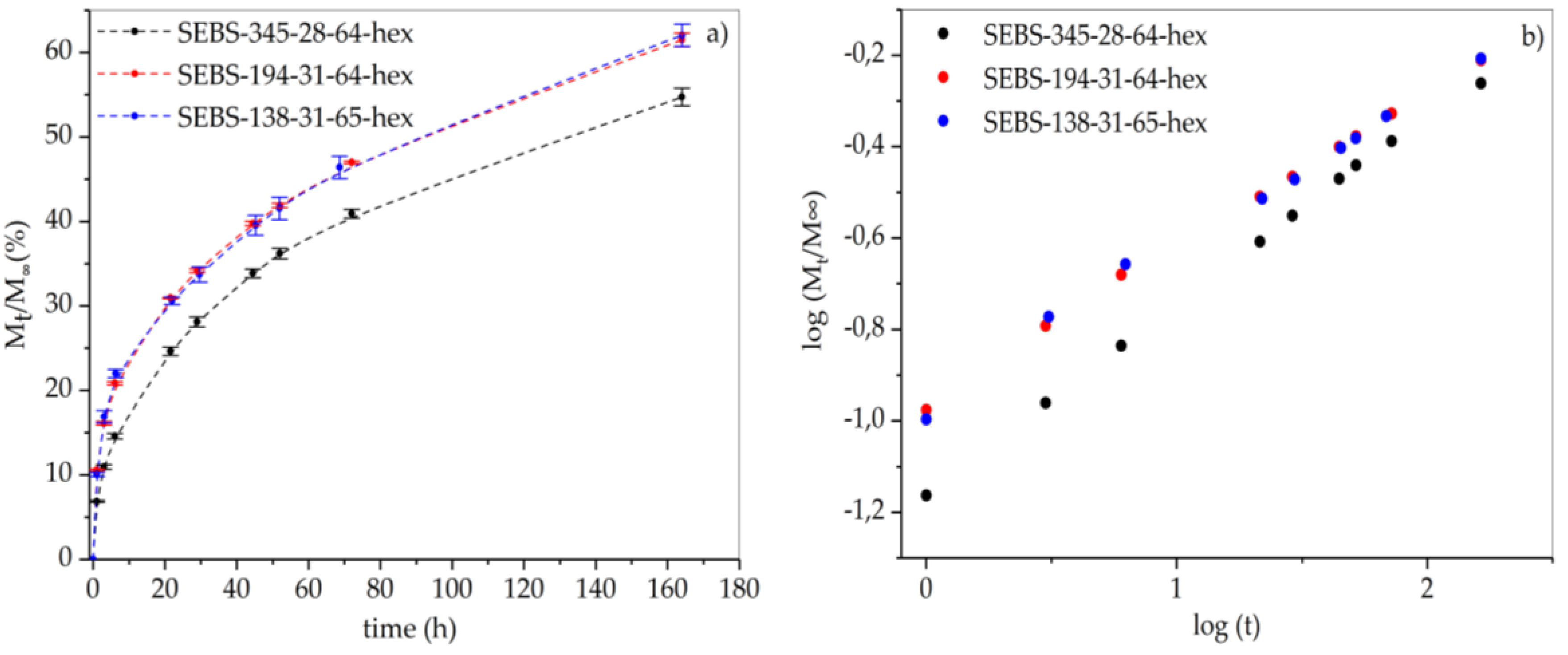
3.4. Leakage Behavior of Hexadecane in FSPCM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Metal foam embedded in SEBS/paraffin/HDPE form-stable PCMs for thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 149, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenisarin, M.M.; Kenisarina, K.M. Form-stable phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1999–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tyagi, V.; Chen, C.; Buddhi, D. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 318–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.; Gustavsen, A. Phase change materials for building applications: A state-of-the-art review. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Castell, A.; Barreneche, C.; De Gracia, A.; Fernandez, A.I. Materials used as PCM in thermal energy storage in buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousksou, T.; Jamil, A.; El Rhafiki, T.; Zeraouli, Y. Paraffin wax mixtures as phase change materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Khan, Z.; Ghafoor, A. A review of performance enhancement of PCM based latent heat storage system within the context of materials, thermal stability and compatibility. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J. Systematic investigation on shape stability of high-efficiency SEBS/paraffin form-stable phase change materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 118, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Sari, A. Fatty acid/poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) blends as form-stable phase change materials for latent heat thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Zhao, T.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J. Low cracking ratio of paraffin microcapsules shelled by hydroxyl terminated polydimethylsiloxane modified melamine-formaldehyde resin. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, C.; Lin, Y.; Fang, G. Thermal properties and applications of microencapsulated PCM for thermal energy storage: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 147, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamekhorshid, A.; Sadrameli, S.; Farid, M. A review of microencapsulation methods of phase change materials (PCMs) as a thermal energy storage (TES) medium. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Castellón, C.; Nogués, M.; Medrano, M.; Leppers, R.; Zubillaga, O. Use of microencapsulated PCM in concrete walls for energy savings. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Lazaro, A.; Mazo, J.; Zalba, B. Review on phase change material emulsions and microencapsulated phase change material slurries: Materials, heat transfer studies and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadiran, T.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z.; Rusli, R. Encapsulation techniques for organic phase change materials as thermal energy storage medium: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 143, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmet, S. Form-stable paraffin/high density polyethylene composites as solid–liquid phase change material for thermal energy storage: Preparation and thermal properties. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, C.; Kaya, K.; Sarı, A. Preparation, thermal properties and thermal reliability of form-stable paraffin/polypropylene composite for thermal energy storage. J. Polym. Environ. 2009, 17, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Bo, F.; Kecheng, G. Preparation and performance of shape stabilized phase change thermal storage materials with high thermal conductivity. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurer, J.H.; Bukovnik, R.; Spontak, R.J. Morphological characteristics of SEBS thermoplastic elastomer Gels. Macromol. 1996, 29, 5760–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Feng, J.; Wu, P. A new strategy to prepare polymer-based shape memory elastomers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ni, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H. Preparation and characterization of side-chain liquid crystal polymer/paraffin composites as form-stable phase change materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9645–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wolcott, M.P. Polyethylene/paraffin binary composites for phase change material energy storage in building: A morphology, thermal properties, and paraffin leakage study. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 137, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcke, A.I.V.D.; Bogdanov, B.; De Rooze, N.; Schacht, E.H.; Cornelissen, M.; Berghmans, H. Structural and rheological properties of methacrylamide modified gelatin hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudy, P.; Camberlain, Y.; Pascault, J.P. Glass transition of polystyrene versus molecular weight. Polym. Bull. 1983, 9, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBenedetto, A.T.; Di Landro, L.A. Correlation of glass transition temperature and molecular weight: A model based on the principle of corresponding states. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 1989, 27, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, L.; Richardson, M. The glass transition behaviour and thermodynamic properties of amorphous polystyrene. Polymer 1989, 30, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, S.; Feng, J.; Wu, P. A new strategy to prepare polymer composites with versatile shape memory properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taimoori, M.; Modarress, H.; Mansoori, G.A. Generalized Flory-Huggins model for heat-of-mixing and phase-behavior calculations of polymer-polymer mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 1328–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovejero, G.; Pérez, P.; Romero, M.; Diaz, I.; Diez, E. SEBS triblock copolymer–solvent interaction parameters from inverse gas chromatography measurements. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Sahm, P.R. Eigenschaften und anwendungen von in-situ-verbundwerkstoffen. In Gerichtet Erstarrte Eutektische Werkstoffe, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1975; pp. 203–299. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, M. Diffusion in polymer solids and solutions. In Mass Transfer in Chemical Engineering Processes; Jozef Markoš, IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 17–40. [Google Scholar]
- Güreş, S. Experimentelle Untersuchungen und Mathematisch-Theoretische Vorhersagen des Freisetzungsverhaltens aus ext. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.K. Crystalline morphology in high-density polyethylene/paraffin blend for thermal energy storage. Polym. Compos. 1998, 19, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Polymer | Molecular Weight (kg/mol) | Styrene Content (wt.%) | Molar Mass Styrene Block (kg/mol) | Ethylene Content in E/B Phase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEBS-345-28-64 | 345 | 28 | 48.3 | 64 |
| SEBS-194-31-65 | 194 | 31 | 30.1 | 65 |
| SEBS-138-31-65 | 138 | 31 | 21.4 | 65 |
| SEBS-080-29-66 | 80 | 29 | 11.7 | 66 |
| SEBS-065-30-67 | 65 | 30 | 9.7 | 67 |
| Polymer | Molecular Weight (kg/mol) | Styrene Content (wt.%) | Molar Mass Styrene Block (kg/mol) | Ethylene Content in E/B Phase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEBS-080-29-66 | 80 | 29 | 11.7 | 66 |
| SEBS-085-18-52 | 85 | 18 | 7.7 | 52 |
| SEBS-065-41-66 | 65 | 41 | 13.3 | 66 |
| SEBS-065-30-67 | 65 | 30 | 9.7 | 64 |
| Polymer | Molecular Weight (kg/mol) | Styrene Content (wt.%) | Molar Mass Styrene Block (kg/mol) | Ethylene Content in E/B Phase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEBS-087-18-27 | 87 | 18 | 7.8 | 27 |
| SEBS-085-18-52 | 85 | 18 | 7.7 | 52 |
| Polymer | T99% (°C) | T15% (°C) | ∆Hc (J/g) | Tc1 (°C) | Tc2 (°C) | ∆Tc (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEBS-345-28-64-hex | 115 | 220 | 191 | 14.4 | 4.3 | 10.1 |
| SEBS-194-31-64-hex | 115 | 214 | 191 | 15.3 | 6.9 | 8.4 |
| SEBS-138-31-65-hex | 117 | 212 | 194 | 14.2 | 5.6 | 8.6 |
| SEBS-065-41-66-hex | 115 | 211 | 187 | 14.9 | 8.4 | 6.5 |
| SEBS-080-29-66-hex | 116 | 211 | 192 | 14.6 | 7.2 | 7.4 |
| SEBS-065-30-67-hex | 116 | 212 | 192 | 14.6 | 9.8 | 4.8 |
| SEBS-087-18-27-hex | 114 | 211 | 189 | 15.6 | 10.8 | 4.8 |
| SEBS-085-18-52-hex | 113 | 210 | 190 | 15.5 | 11.0 | 4.5 |
| SEBS-118-12-26-hex | 115 | 212 | 193 | 15.4 | 10.9 | 4.5 |
| Hexadecane (hex) | 115 | 206 | 235 | 16.0 | 12.1 | 3.9 |
| Polymer | Molecular Weight of Styrene Block | Transition Temperature | Tg of PS End Block | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mw (kg/mol) | T1 (°C) | T2 (°C) | Tg (°C) | |
| SEBS-345-28-64-hex | 48.3 | 161 * | 179 * | 104 |
| SEBS-194-31-64-hex | 30.1 | 126 | 142 | 102 |
| SEBS-138-31-65-hex | 21.4 | 100 | 111 | 99 |
| SEBS-065-41-66-hex | 13.3 | 65 | 67 | 94 |
| SEBS-080-29-66-hex | 11.7 | 70 | 73 | 92 |
| SEBS-065-30-67-hex | 9.7 | 51 | 52 | 89 |
| SEBS-087-18-27-hex | 7.8 | – | 42 | 85 |
| SEBS-085-18-52-hex | 7.7 | – | 43 | 85 |
| SEBS-118-12-26-hex | 7.1 | – | – | 83 |
| Matrix | Equation of Line | n | k |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEBS-345-28-64-hex | y = 0.41 × – 1.16 | 0.41 | 0.07 |
| SEBS-138-31-65-hex | y = 0.34 × – 0.96 | 0.34 | 0.11 |
| SEBS-194-31-64-hex | y = 0.34 × – 0.96 | 0.34 | 0.11 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rickert, R.; Klein, R.; Schönberger, F. Form-Stable Phase Change Materials Based on SEBS and Paraffin: Influence of Molecular Parameters of Styrene-b-(Ethylene-co-Butylene)-b-Styrene on Shape Stability and Retention Behavior. Materials 2020, 13, 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153285
Rickert R, Klein R, Schönberger F. Form-Stable Phase Change Materials Based on SEBS and Paraffin: Influence of Molecular Parameters of Styrene-b-(Ethylene-co-Butylene)-b-Styrene on Shape Stability and Retention Behavior. Materials. 2020; 13(15):3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153285
Chicago/Turabian StyleRickert, Ralf, Roland Klein, and Frank Schönberger. 2020. "Form-Stable Phase Change Materials Based on SEBS and Paraffin: Influence of Molecular Parameters of Styrene-b-(Ethylene-co-Butylene)-b-Styrene on Shape Stability and Retention Behavior" Materials 13, no. 15: 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153285
APA StyleRickert, R., Klein, R., & Schönberger, F. (2020). Form-Stable Phase Change Materials Based on SEBS and Paraffin: Influence of Molecular Parameters of Styrene-b-(Ethylene-co-Butylene)-b-Styrene on Shape Stability and Retention Behavior. Materials, 13(15), 3285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153285