Effect of Phosphate-Based Inhibitor on Corrosion Kinetics and Mechanism for Formation of Passive Film onto the Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Pore Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrochemical Studies
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Electrochemical Studies
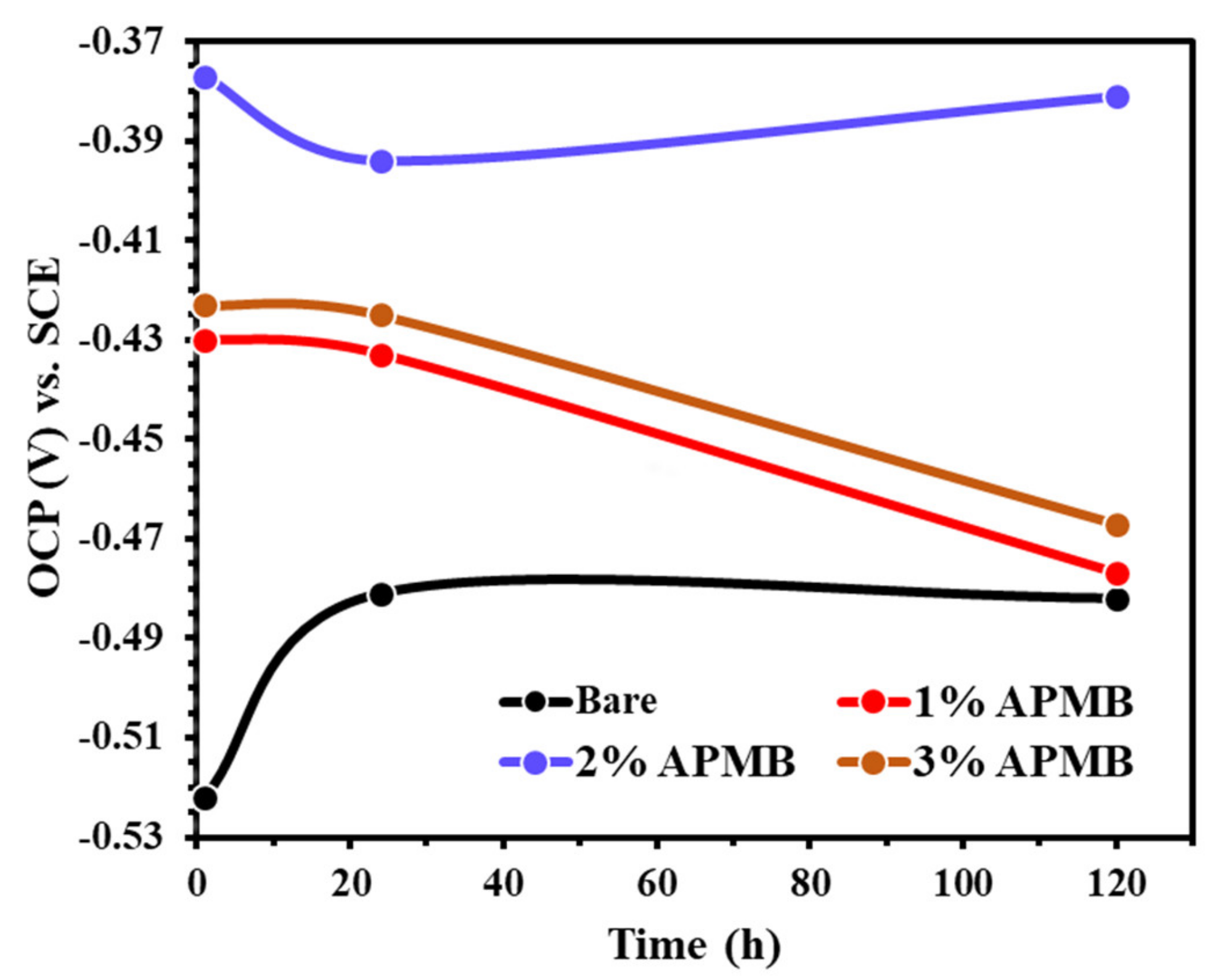
3.1.1. OCP Measurements with Exposure Periods
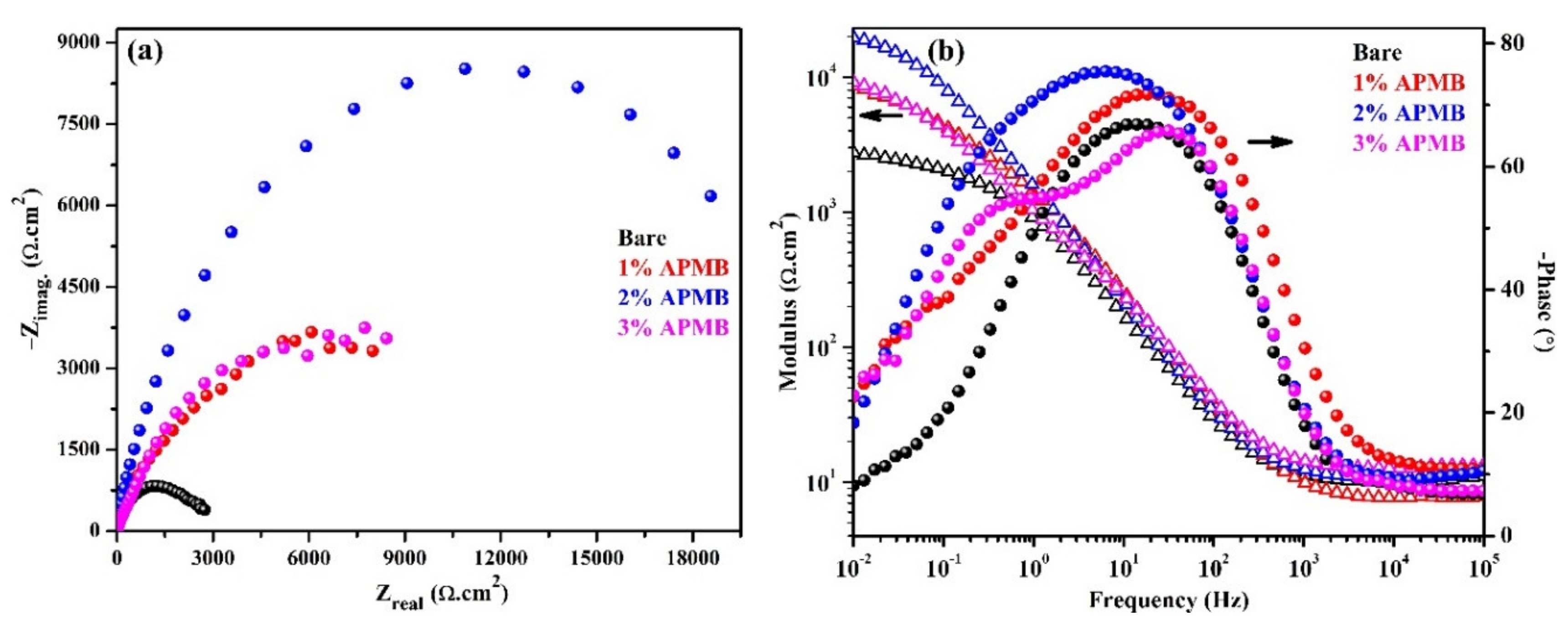
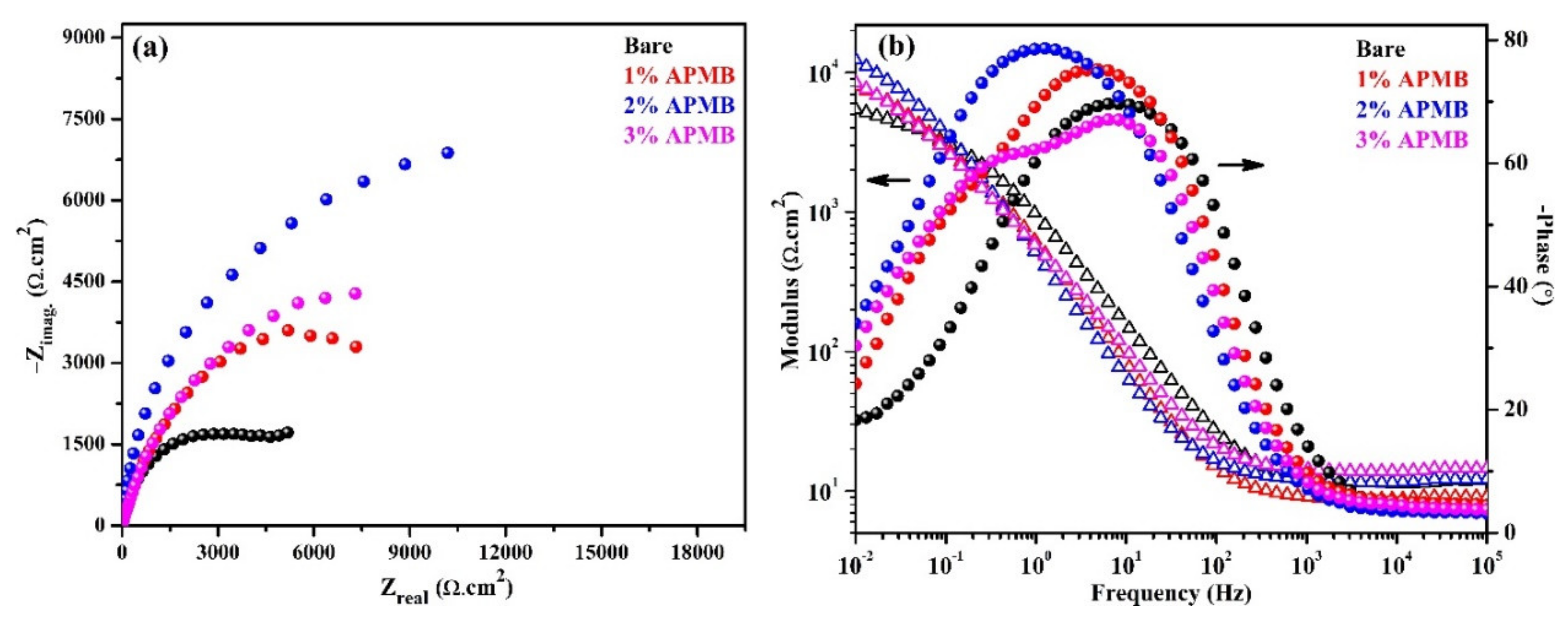
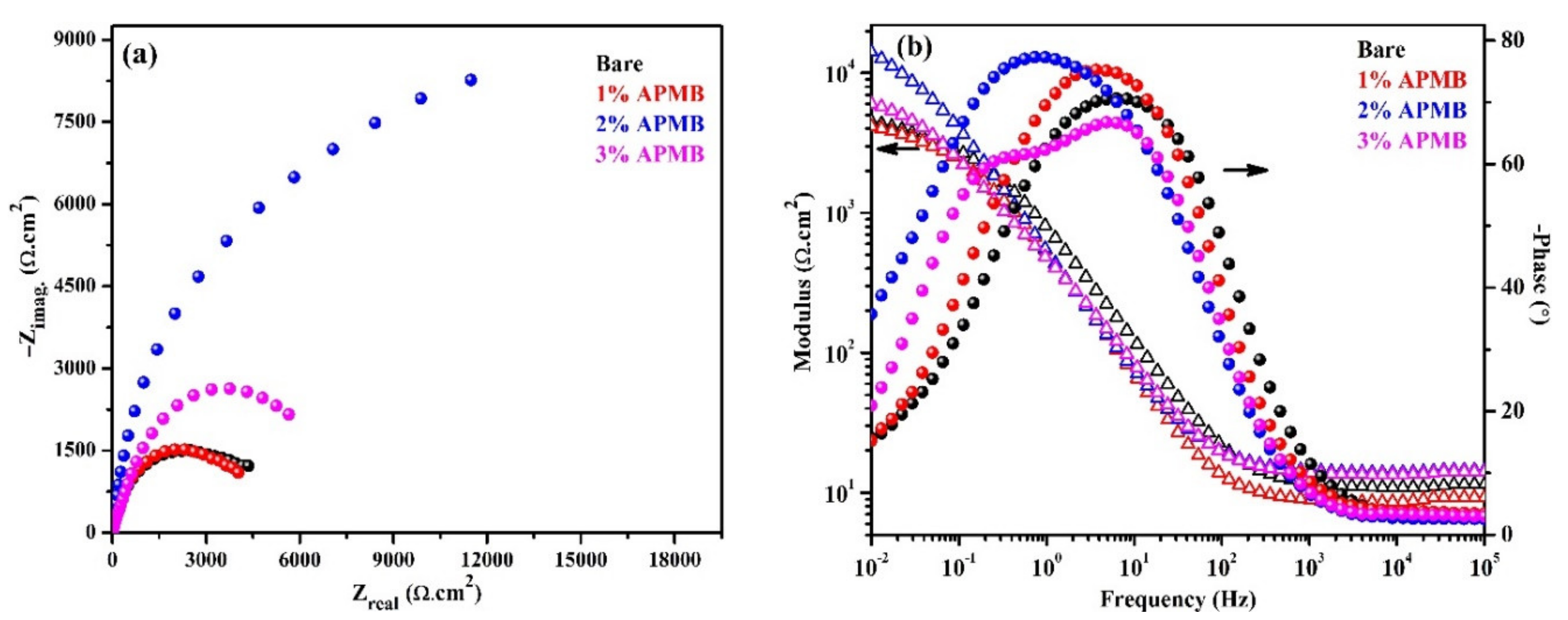
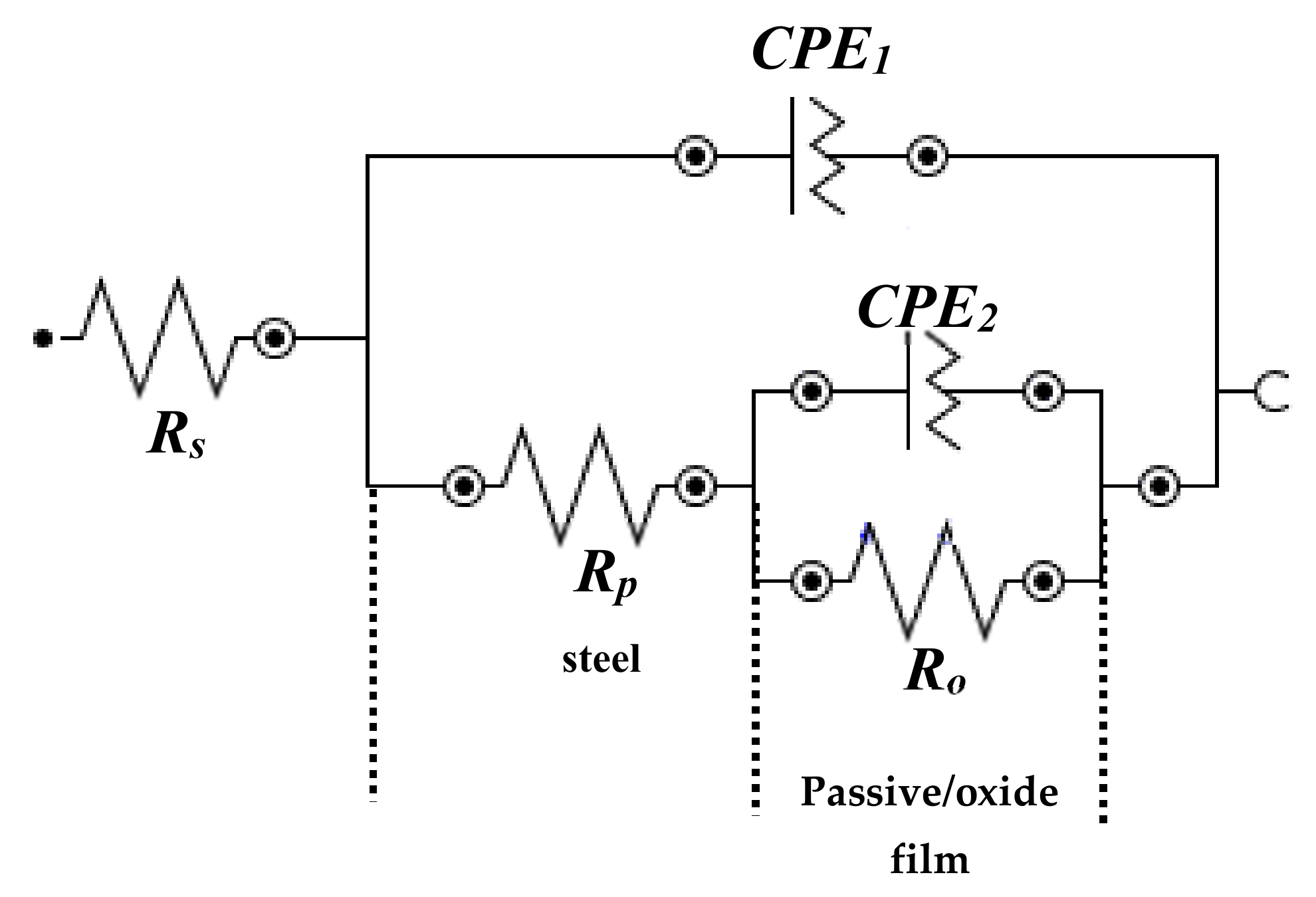
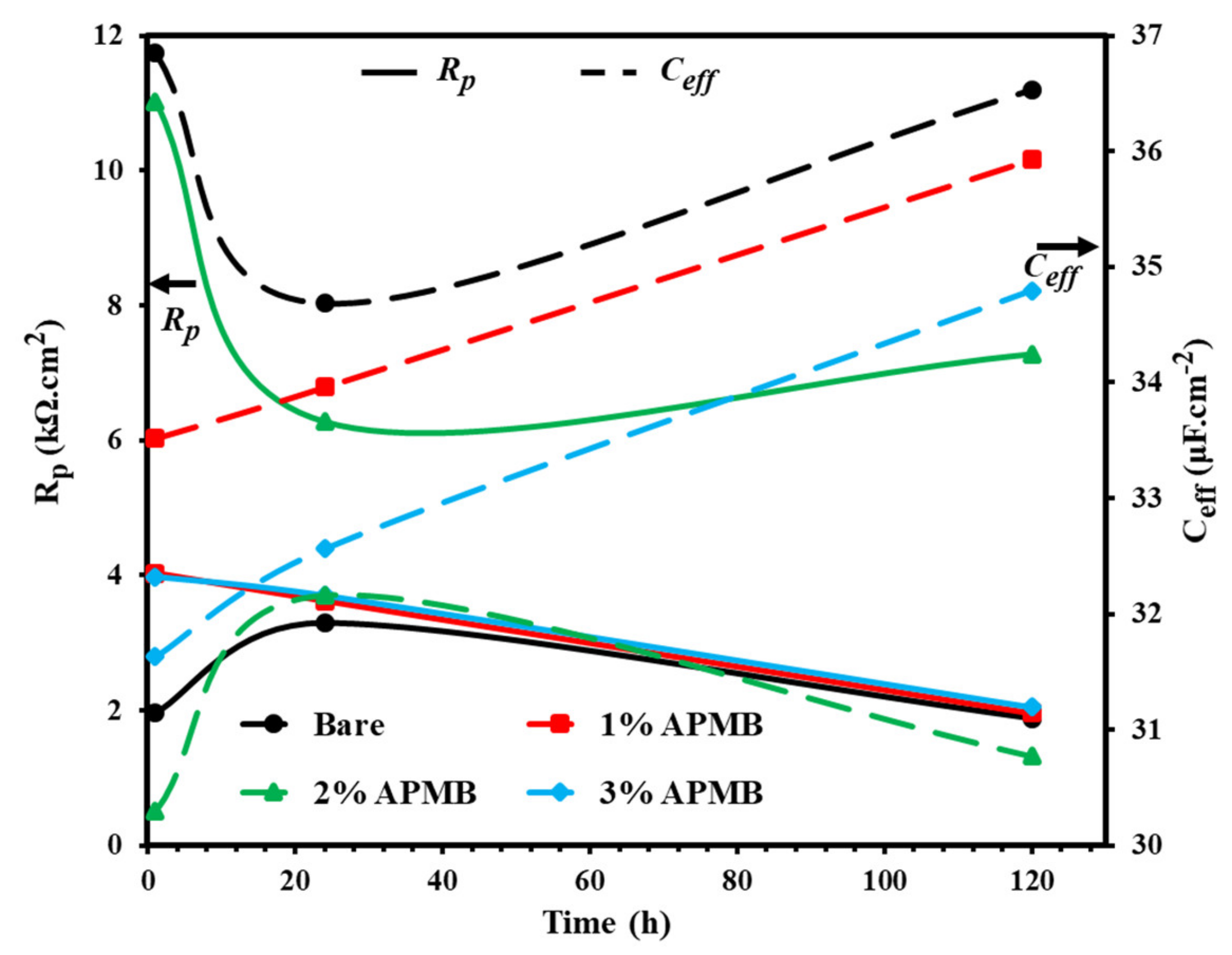
3.1.2. EIS Studies with Exposure Periods
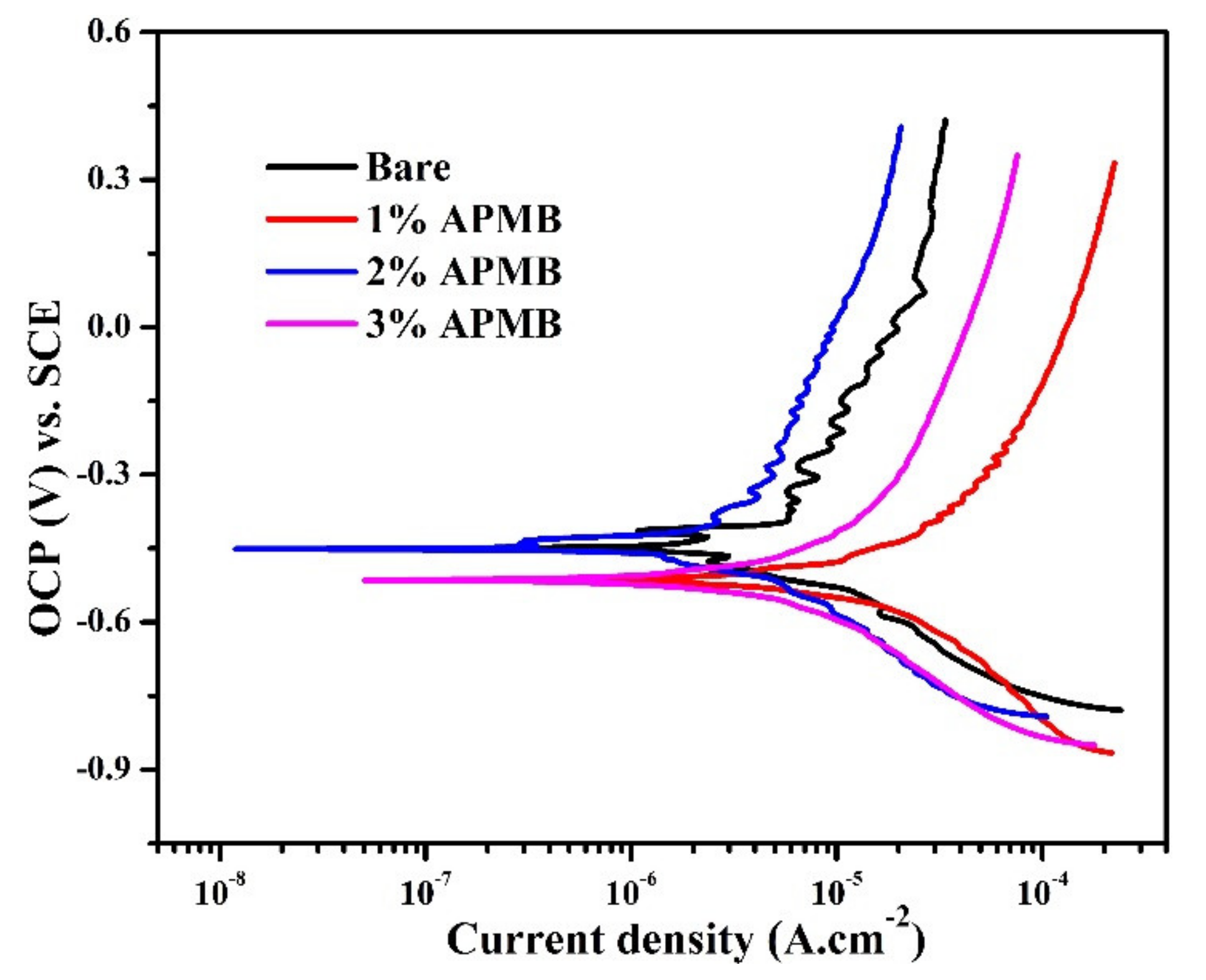
3.1.3. Potentiodynamic Polarization Studies after 120 h of Exposure
3.2. Characterization of Passive/Oxide Film
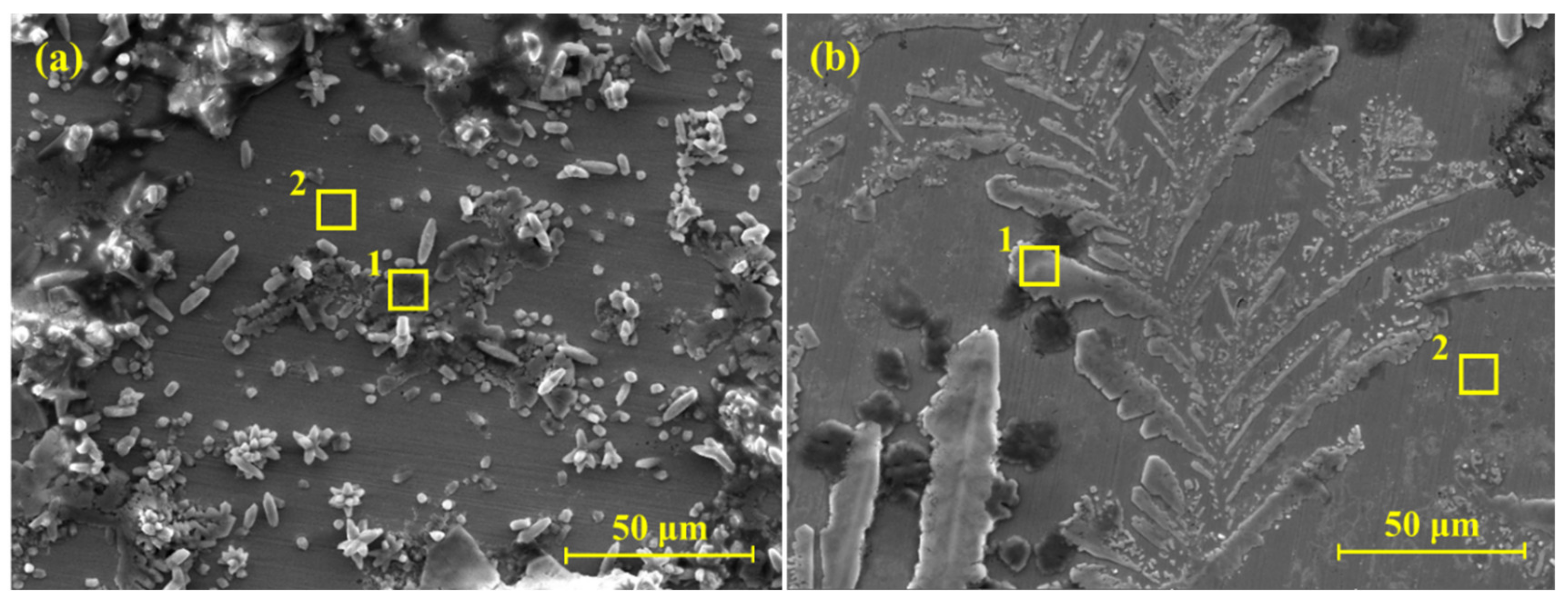
3.2.1. SEM
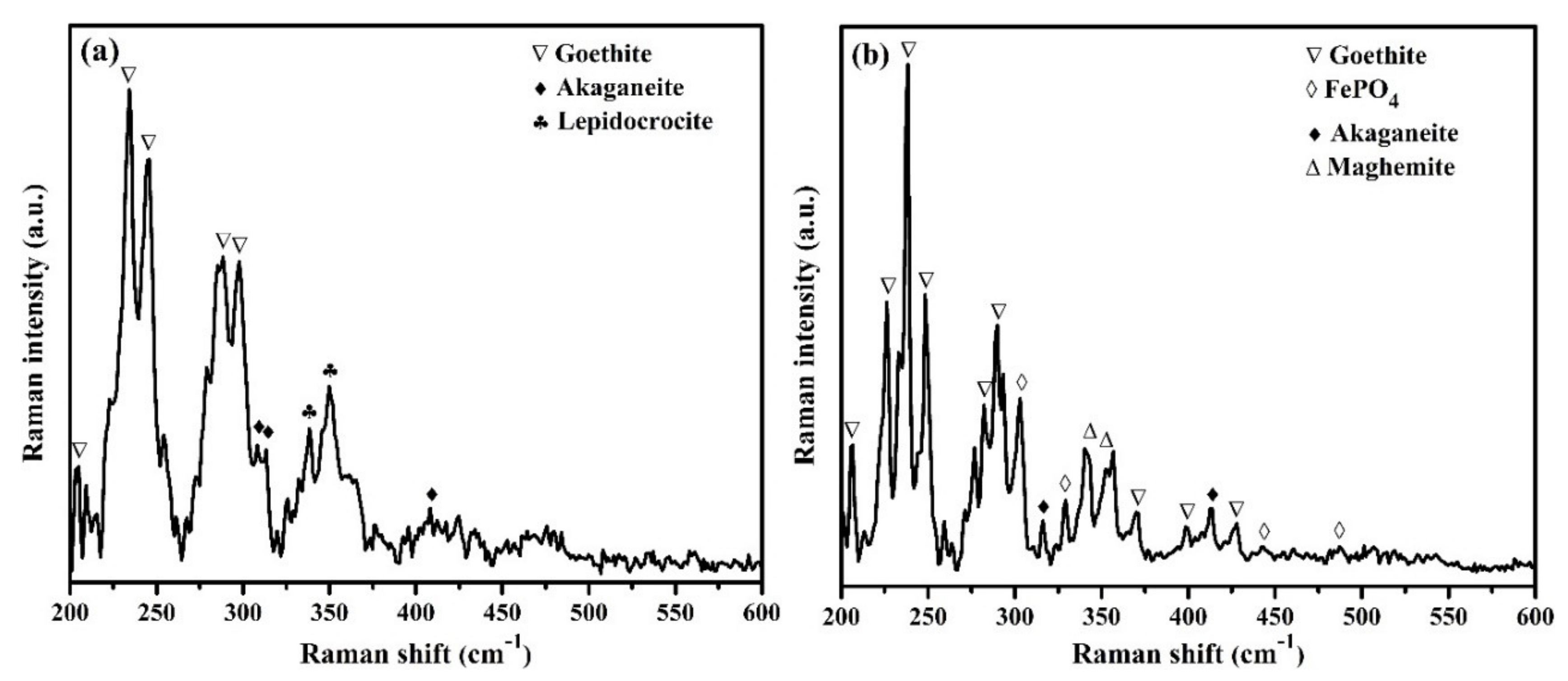
3.2.2. Raman Spectroscopy
3.2.3. XPS Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- EIS results corroborated with the OCP where initially up to 24 h of exposure, Rp and Ro gradually decreased but, once the exposure period reache up to 120 h, their values increased, which revealed the formation of passive film onto the steel rebar in 2% inhibitor-containing solution.
- (2)
- The steel rebar exposed in 2% inhibitor-added SCP + 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution showed 90% inhibition efficiency after 1 h of exposure but its value decreased to 62.48% once the exposure periods were extended up to 120 h.
- (3)
- Potentiodynamic studies revealed that the steel rebar exposed to 2% inhibitor-added solution exhibited lower in cathodic and anodic current density compared to the rebar exposed to bare solution after 120 h of exposure.
- (4)
- SEM results of the steel rebar exposed to 2% inhibitor-containing solution show dendritic growth of the oxides on the surface after 120 h of exposure while the steel rebar exposed to the bare solution exhibited agglomeration of oxide products on the surface.
- (5)
- Raman spectroscopy and XPS confirmed the formation of thermodynamically stable and sparingly soluble goethite, maghemite, and iron phosphate (FePO4) as passive/oxide film onto the surface of steel rebar exposed to 2% inhibitor-containing solution. Thus, corrosion rate reduced at longer duration of exposure in SCP + 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsener, B. Corrosion Inhibitors for Steel in Concrete: State of the Art Report; Maney Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gaidis, J.M. Chemistry of corrosion inhibitors. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, C.M.; Mammoliti, L.; Hope, B.B. Corrosion inhibitors in concrete—Part I: The principles. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.S.; Singh, J.K.; Lee, H.S.; Ismail, M.A.; Park, W.J. Effect of LiNO2 inhibitor on corrosion characteristics of steel rebar in saturated Ca(OH)2 solution containing NaCl: An electrochemical study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, H.E.; Montemor, M.F.; Boulif, R.; Shriri, A.; Ferreira, M.G.S. An electrochemical and analytical approach to the inhibition mechanism of an amino-alcohol-based corrosion inhibitor for reinforced concrete. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 3509–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormellese, M.; Lazzari, L.; Goidanich, S.; Fumagalli, G.; Brenna, A. A study of organic substances as inhibitors for chloride-induced corrosion in concrete. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.S.; Singh, J.K.; Yang, H.M.; Lee, H.S.; Ismail, M.A. Evaluation of corrosion resistance properties of N, N′-Dimethyl ethanolamine corrosion inhibitor in saturated Ca(OH)2 solution with different concentrations of chloride ions by electrochemical experiments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Kong, Q. The performance of a surface-applied corrosion inhibitor for the carbon steel in saturated Ca(OH)2 solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 55, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söylev, T.A.; McNally, C.; Richardson, M. Effectiveness of amino alcohol-based surface-applied corrosion inhibitors in chloride-contaminated concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.S.; Elewady, G.Y.; Shalabi, K.; Abd El-Aziz, H.K. Alcamines as corrosion inhibitors for reinforced steel and their effect on cement based materials and mortar performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36957–36968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.-S.; Singh, J.K.; Lee, H.-S.; Park, W.-J. An Electrochemical Study to Evaluate the Effect of Calcium Nitrite Inhibitor to Mitigate the Corrosion of Reinforcement in Sodium Chloride Contaminated Ca(OH)2 Solution. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, W.; Voshardt, H. Influence of Ca(NO2)2 on Seawater Corrosion of Reinforcing Steel in Concrete, Part 2, Corrosion/81, Publication No. 52; NACE: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Berke, N.S.; Grace, W.R. The Effects of Calcium Nitrite and Mix Design on the Corrosion Resistance of Steel in Concrete, Part 1, Corrosion/85; NACE: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Berke, N.S.; Grace, W.R. The Effects of Calcium Nitrite and Mix Design on the Corrosion Resistance of Steel in Concrete, Part 2, Publ. No. 273, Corrosion/87; NACE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, R.J.; Wood, L.E. Effectiveness of Corrosion Inhibitors and Their Influence on the Physical Properties of Portland Cement Mortars, Highway Research Record No. 328; Highway Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, P.; Elliott, S.; Hristova, R.; Beaudoin, J.J.; Brousseau, R.; Baldock, B. A study of corrosion inhibitor performance in chloride contaminated concrete by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. ACI Mater. J. 1997, 94, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Reou, J.S.; Ann, K.Y. The electrochemical assessment of corrosion inhibition effect of calcium nitrite in blended concretes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 109, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, K.J.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.S.; Moon, H.Y. Effect of calcium nitrite-based corrosion inhibitor in preventing corrosion of embedded steel in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosrra, L.; Youseffi, M.; Ashour, A.F. Effectiveness of calcium nitrite in retarding corrosion of steel in concrete. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2011, 5, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubramanian, M.; Haran, B.S.; Popova, S.; Popov, B.N.; Petrou, M.F.; White, R.E. Inhibiting action of calcium nitrite on carbon steel rebars. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2001, 13, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medford, W. Testing calcium nitrite corrosion inhibitor in concrete. Transp. Res. Rec. 2014, 1795, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormellese, M.; Berra, M.; Bolzoni, F.; Pastore, T. Corrosion inhibitors for chlorides induced corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, P.; Saura, P.; Mendez, A.; Zornoza, E.; Andrade, C. Effect of nitrite in corrosion of reinforcing steel in neutral and acid solutions simulating the electrolytic environments of micropores of concrete in the propagation period. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asipita, S.A.; Ismail, M.; Majid, M.Z.A.; Majid, Z.A.; Abdullah, C.; Mirza, J. Green Bambusa Arundinacea leaves extract as a sustainable corrosion inhibitor in steel reinforced concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarce, M.B.; Vazquez, M. Phosphate ions used as green inhibitor against copper corrosion in tap water. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankara Narayanan, T.S.N. Surface pretreatment by phosphate conversion coatings—A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2005, 9, 130–177. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.-R.; Lee, H.-S.; Jalalzai, P.; Kwon, S.-J.; Singh, J.K.; Hussain, R.R.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Aslam, F. Sodium Phosphate Post-treatment on Al Coating: Morphological and Corrosion Study. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2019, 28, 1511–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Kumar, A.; Mandal, S.; Singh, J.K.; Aslam, F.; Alyousef, R.; Albduljabbar, H. Effect of Sodium Phosphate and Calcium Nitrate Sealing Treatment on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Wire Arc Sprayed Aluminum Coatings. Coatings 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tittarelli, F.; Mobili, A.; Bellezze, T. The use of a Phosphate-based migrating corrosion inhibitor to repair reinforced concrete elements contaminated by chlorides. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 225, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Yang, H.-M.; Singh, J.K.; Prasad, S.K.; Yoo, B. Corrosion mitigation of steel rebars in chloride contaminated concrete pore solution using inhibitor: An electrochemical investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohai, L.; Schreiner, W.; Valcarce, M.B.; Vázquez, M. Inhibiting Steel Corrosion in Simulated Concrete with Low Phosphate to Chloride Ratios. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, C729–C737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohai, L.; Vázquez, M.; Valcarc, M.B. Phosphate ions as corrosion inhibitors for reinforcement steel in chloride-rich environments. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 102, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Shi, R.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, D. The corrosion inhibition efficiency of aluminum tripolyphosphate on carbon steel in carbonated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2017, 124, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohai, L.; Schreiner, W.; Vázquez1, M.; Valcarce, M.B. Phosphate ions as effective inhibitors for carbon steel in carbonated solutions contaminated with chloride ions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 202, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reffass, M.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Berziou, C.; Refait, P. Effects of phosphate species on localised corrosion of steel in NaHCO3+ NaCl electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Haleem, S.M.; Abd El Wanees, S.; Abd El Aal, E.E.; Diab, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel II. Role of some anions in the initiation and inhibition of pitting corrosion of steel in Ca(OH)2 solutions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Sun, W. Effects of phosphate on the chloride-induced corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel in mortars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteyeb, N.; Dhouibi, L.; Takenouti, H.; Alonso, M.C.; Triki, E. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in alkaline chloride media by Na3PO4. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7506–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhouibi, L.; Triki, E.; Raharinaivo, A.; Trabanelli, G.; Zucchi, F. Electrochemical methods for evaluating inhibitors of steel corrosion in concrete. Br. Corros. J. 2000, 35, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Singh, J.K.; Ismail, M.A. An effective and novel pore sealing agent to enhance the corrosion resistance performance of Al coating in artificial ocean water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Singh, J.K. Influence of calcium nitrate on morphology and corrosion characteristics of ammonium phosphate treated Aluminum coating deposited by arc thermal spraying process. Corros. Sci. 2019, 146, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.N.; Ghosh, R. Corrosion resistance performance of fusion bonded epoxy coated rebars used as reinforcement in concrete structures. J. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2003, 45, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, R.; Singh, D.D.N. Kinetics, mechanism and characterisation of passive film formed on hot dip galvanized coating exposed in simulated concrete pore solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7346–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.M.; Criado, M.; La Iglesia, V.M.; Fajardo, S.; Iglesia, A.L.; Bastidas, J.M. Comparative study of three sodium phosphates as corrosion inhibitors for steel reinforcements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 43, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteyeb, N.; Dhouibi, L.; Sanchez, M.; Alonso, C.; Andrade, C.; Triki, E. Electrochemical study of corrosion inhibition of steel reinforcement in alkaline solutions containing phosphates based components. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4721–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Sun, W. Electrochemical and analytical characterization of three corrosion inhibitors of steel in simulated concrete pore solutions. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2012, 19, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahali, H.; Dhouibi, L.; Idrissi, H. Effect of phosphate based inhibitor on the threshold chloride to initiate steel corrosion in saturated hydroxide solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, C.; Frignani, A.; Balbo, A.; Zucchi, F. Influence of two specific inhibitors on steel corrosion in a synthetic solution simulating a carbonated concrete with chlorides. Mater. Corros. 2011, 62, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.E.; Pébère, N.; Tribollet, B. Enhanced graphical representation of electrochemical impedance data. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, B129–B136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brug, G.J.; van den Eeden, A.L.G.; Sluyters-Rehbach, M.; Sluyters, J.H. The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1984, 176, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, V.M.-W.; Vivier, V.; Orazem, M.E.; Pébère, N.; Tribollet, B. The apparent constant-phase-element behavior of a disk electrode with faradaic reactions: A global and local impedance analysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, C99–C107. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschorn, B.; Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B.; Vivier, V.; Frateur, I.; Musiani, M. Determination of effective capacitance and film thickness from constant-phase-element parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6218–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Negheimish, A.-N.; Alhozaimy, A.; Hussain, R.R.; Al-Zaid, R.; Singh, J.K.; Singh, D.D.N. Role of manganese sulfide inclusions in steel rebar in the formation and breakdown of passive films in concrete pore solutions. Corrosion 2014, 70, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simesco, F.; Idrissi, H. Corrosion behavior in alkaline medium of zinc phosphate coated steel obtained by cathodic electrochemical treatment. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Cook, D.C.; Townsend, H.E. Characterization of iron oxides commonly formed as corrosion products on steel. Hyperfine Interact. 1998, 112, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustova, G.N.; Burgina, E.B.; Poryvaev, S.G.; Sadykov, V.A. Vibrational Spectroscopic Investigation of the Goethite Thermal Decomposition Products. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1992, 18, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hihara, L.H. A Micro-Raman Spectroscopic Study of Marine Atmospheric Corrosion of Carbon Steel: The Effect of Akaganeite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, C495–C502. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Dathar, G.K.P.; Sun, C.; Theivanayagam, M.G.; Applestone, D.; Dylla, A.G.; Manthiram, A.; Henkelman, G.; Goodenough, J.B.; Stevenson, K.J. In situ Raman spectroscopy of LiFePO4: Size and morphology dependence during charge and self-discharge. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 424009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaghib, K.; Julien, C.M. Structure and electrochemistry of FePO4.2H2O hydrate. J. Power Sources 2005, 142, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; Brown, J.R.; Bensebaa, F.; Kingston, D. XPS depth profiling study on the passive oxide film of carbon steel in saturatedcalcium hydroxide solution and the effect of chloride on the film properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4669–4677. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Daub, K.; Zhang, X.; Noel, J.J.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Wren, J.C. Oxide formation and conversion on carbon steel in mildly basic solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5727–5738. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, H.; Hostis, V.L.; Miserque, F.; Idrissi, H. Electrochemical behavior of mild steel in concrete: Influence of pH and carbonate content of concrete pore solution. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.G.; Tang, Y.M.; Zuo, Y. Influence of stress on passive behaviour of steel bars in concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, H.A.; Watson, P.R. An XPS study of the adsorption of lead on goethite (α-FeOOH). Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 136, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, F.; Roman, E.; Cristobal, M.J.; Hierro, M.P.; Perez, F.J. Effects of yttrium and erbium ion implantation on the AISI 304 stainless steel passive layer. Thin Solid Films 2002, 414, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Du, R.G.; Hu, R.G.; Shi, H.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Lin, C.J. Correlation between composition of reinforcing steel surface film and steel corrosion behavior in simulated concrete pore solution. Acta Metall. Sin. Chin. Ed. 2011, 47, 735–742. [Google Scholar]
- Carmezim, M.J.; Simoes, A.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Belo, M.D.C. Capacitance behavior of passive films on ferritic and austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Brundle, C.R.; Chuang, T.J.; Wandelt, K. Core and valence level photoemission studies of iron oxide surfaces and the oxidation of iron. Surf. Sci. 1977, 68, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.W.; Wood, P.R. The mechanism of the oxidation and passivation of iron by water vapour-an electron spectroscopic study. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1977, 11, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, N.S. Studies of the oxidation of iron by water vapour using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASESTM. Surf. Sci. 2004, 572, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaux, Y.; Dekiouk, M.; Le Maguer, D.; Gengembre, L.; Huchette, D.; Grimblot, J. Bulk and surface analysis of a Fe-P-O oxydehydrogenation catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1992, 90, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.K.; Singh, D.D.N. The nature of rusts and corrosion characteristics of low alloy and plain carbon steels in three kinds of concrete pore solution with salinity and different pH. Corros. Sci. 2012, 56, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A. About the oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in the air. J. Inorg. Gen. Chem. 1928, 174, 145–160. [Google Scholar]
- Leidheiser, H., Jr.; Czako-Nagy, I. A Mossbauer spectroscopic study of rust formed during simulated atmospheric corrosion. Corros. Sci. 1984, 24, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.; Kuban, B. Infrared spectroscopic analysis of phase transformation process in rust layers formed on weathering steel in bridge spans. Corrosion 1988, 44, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, J.T.; Brown, C.W.; Heidersbach, R.H. Characterization of the passive film formed on weathering steels. Corros. Sci. 1983, 23, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Alhozaimy, A.; Hussain, R.R.; Al-Negheimish, A.; Singh, J.K.; Singh, D.D.N. Protection against Reinforcement Corrosion Using Phosphoric Acid-Based Rust Converter. ACI Mater. J. 2018, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, W. The Phosphating of Metals; Finishing Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]


| Serial No. | Amount of APMB Inhibitor (v/v%) | pH | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.00 | 12.65 | SCP + 3.5 wt% NaCl |
| 2. | 1.00 | 12.65 | SCP + 3.5 wt% NaCl + 1% APMB |
| 3. | 2.00 | 12.67 | SCP + 3.5 wt% NaCl + 2% APMB |
| 4. | 3.00 | 12.68 | SCP + 3.5 wt% NaCl + 3% APMB |
| Time (h) | Sample ID | Electrochemical Parameters | Efficiency (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPE1 | Ro (kΩ·cm2) | CPE2 | |||||
| Q1 (1 × 10−5) (Ω−1·cm−2·sn) | n1 | Q2 (1 × 10−5) (Ω−1·cm−2·sn) | n2 | |||||
| 1 | Bare | 9.96 | 21.0 | 0.78 | 0.87 | 232.8 | 0.70 | - |
| 1% | 9.80 | 14.2 | 0.82 | 4.61 | 54.4 | 0.74 | 81.13 | |
| 2% | 10.09 | 10.2 | 0.85 | 8.71 | 24.5 | 0.80 | 90.01 | |
| 3% | 11.78 | 13.1 | 0.82 | 5.24 | 50.7 | 0.75 | 83.40 | |
| 24 | Bare | 11.48 | 16.6 | 0.80 | 2.16 | 182.4 | 0.73 | - |
| 1% | 9.32 | 15.7 | 0.81 | 4.47 | 55.0 | 0.74 | 51.68 | |
| 2% | 11.64 | 12.3 | 0.83 | 6.45 | 42.4 | 0.78 | 66.51 | |
| 3% | 12.89 | 13.2 | 0.82 | 4.70 | 52.0 | 0.74 | 54.04 | |
| 120 | Bare | 11.12 | 23.8 | 0.76 | 2.66 | 155.7 | 0.73 | - |
| 1% | 10.54 | 22.0 | 0.77 | 2.26 | 175.4 | 0.68 | −17.70 | |
| 2% | 12.59 | 11.7 | 0.83 | 7.09 | 34.8 | 0.79 | 62.48 | |
| 3% | 12.60 | 20.6 | 0.77 | 4.04 | 52.7 | 0.73 | 34.16 | |
| Solution | Figure | Point | Element (wt.%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | N | P | Cl | Na | K | Ca | Fe | |||
| Bare | 8a | 1 | 0.54 (±0.02) | - | - | 40.1 (±2.40) | 55.76 (±1.95) | 1.34 (±0.08) | 0.29 (±0.02) | 1.97 (±0.09) |
| 2 | 2.1 (±0.05) | - | - | 0.18 (±0.01) | 0.35 (±0.02) | 0.24 (±0.02) | 0.23 (±0.02) | 96.90 (±7.27) | ||
| 2% inhibitor | 8b | 1 | 2.37 (±0.10) | 0 | 1.16 (±0.080) | 2.87 (±0.15) | 3.21 (±0.14) | 2.6 (±0.16) | 1.37 (±0.05) | 86.42 (±5.27) |
| 2 | 1.73 (±0.04) | 1.1 (±0.04) | 0.16 (±0.01) | 0.23 (±0.01) | 0.48 (±0.013) | 0.22 (±0.01) | 0.2 (±0.01) | 95.88 (±4.99) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandal, S.; Singh, J.K.; Lee, D.-E.; Park, T. Effect of Phosphate-Based Inhibitor on Corrosion Kinetics and Mechanism for Formation of Passive Film onto the Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Pore Solution. Materials 2020, 13, 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163642
Mandal S, Singh JK, Lee D-E, Park T. Effect of Phosphate-Based Inhibitor on Corrosion Kinetics and Mechanism for Formation of Passive Film onto the Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Pore Solution. Materials. 2020; 13(16):3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163642
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandal, Soumen, Jitendra Kumar Singh, Dong-Eun Lee, and Taejoon Park. 2020. "Effect of Phosphate-Based Inhibitor on Corrosion Kinetics and Mechanism for Formation of Passive Film onto the Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Pore Solution" Materials 13, no. 16: 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163642
APA StyleMandal, S., Singh, J. K., Lee, D.-E., & Park, T. (2020). Effect of Phosphate-Based Inhibitor on Corrosion Kinetics and Mechanism for Formation of Passive Film onto the Steel Rebar in Chloride-Containing Pore Solution. Materials, 13(16), 3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163642








