The Effect of Activation Method of Rubber on the Performance of Modified Asphalt Binder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Activation of Crumb Rubber
2.3. The Preparation of Rubber-Modified Asphalt Binder
2.4. Test Methods
2.4.1. Characterization
2.4.2. Conventional Physical Properties
2.4.3. Rheological Properties
2.4.4. Storage Stability
3. Results and Discussion
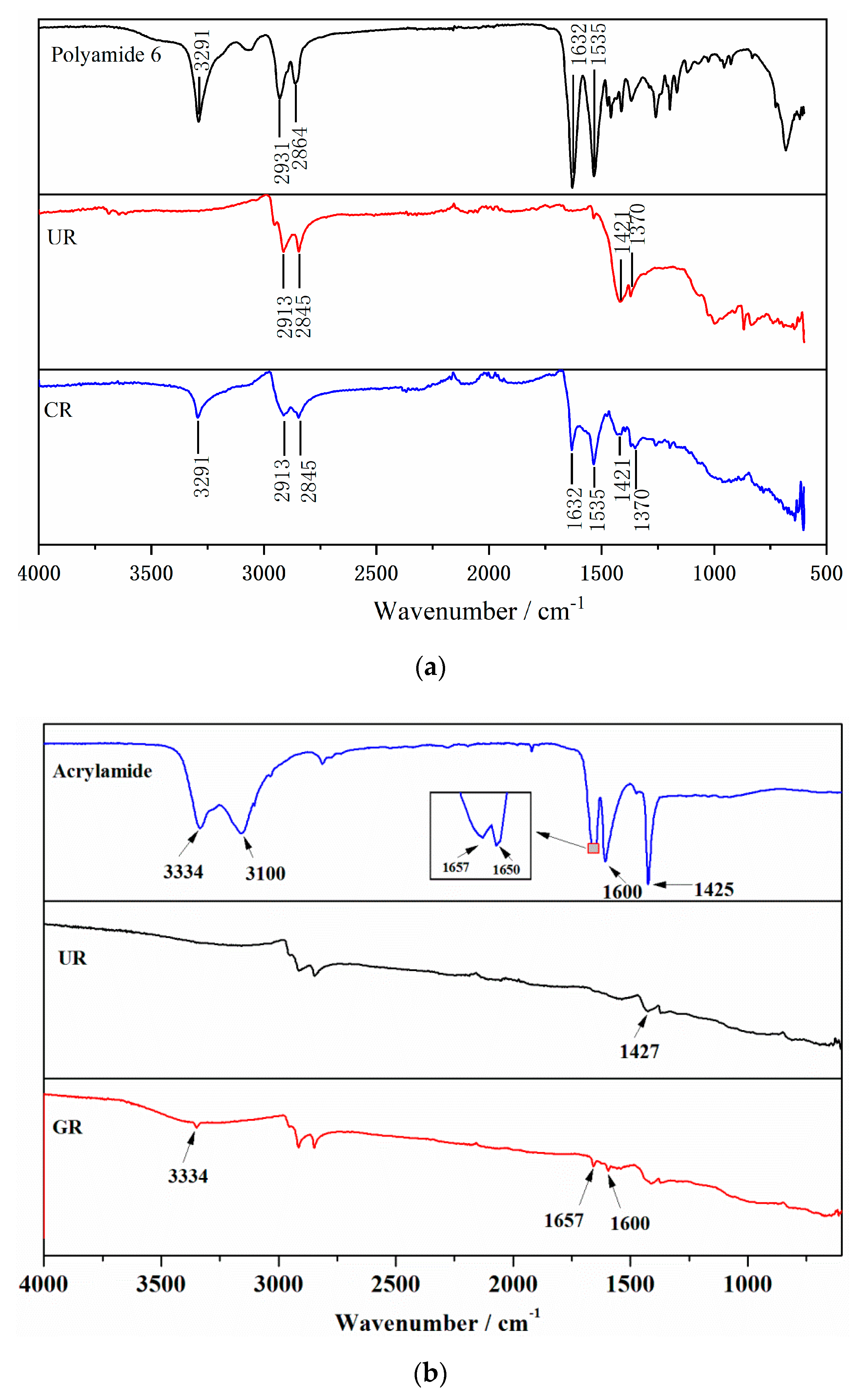
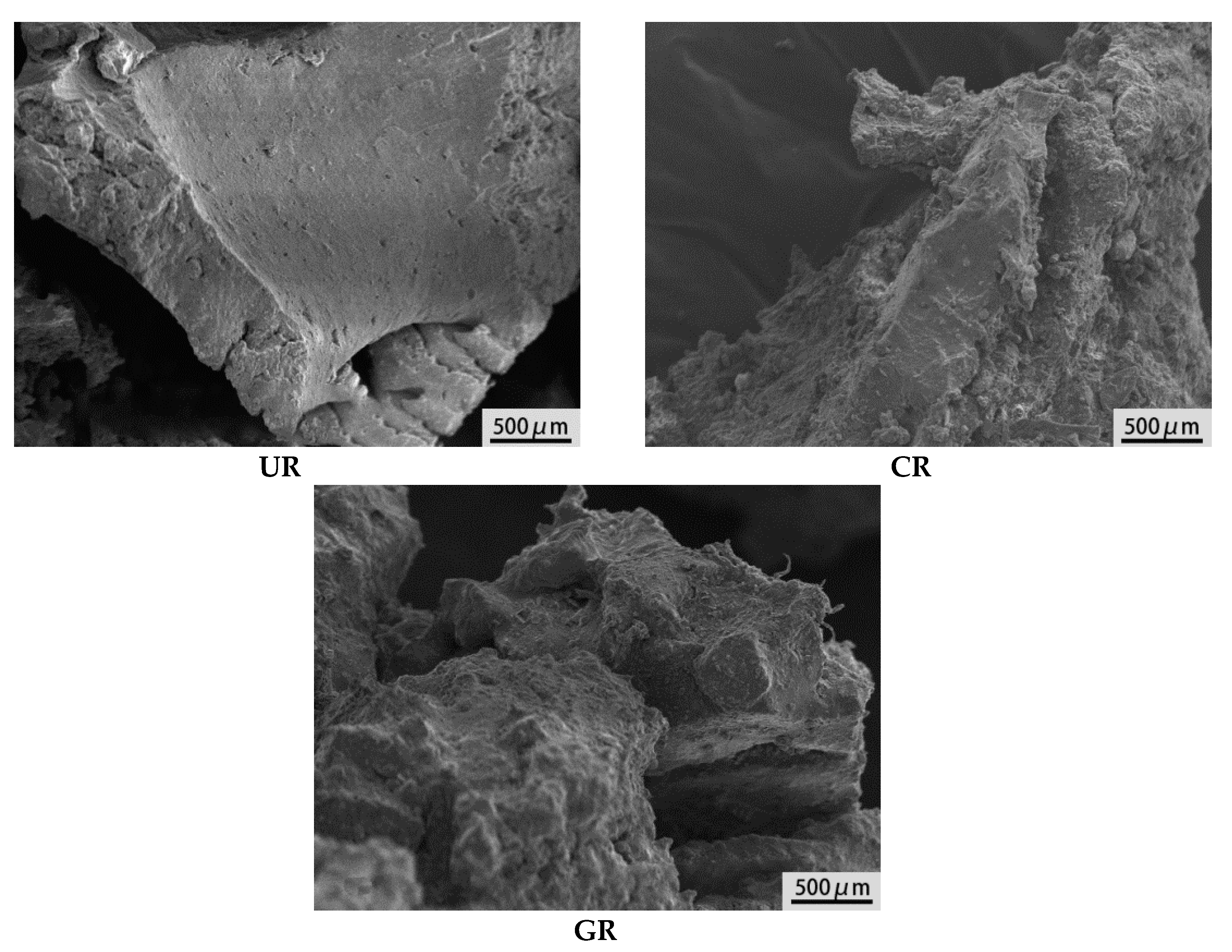
3.1. Characterization of Activated Crumb Rubber
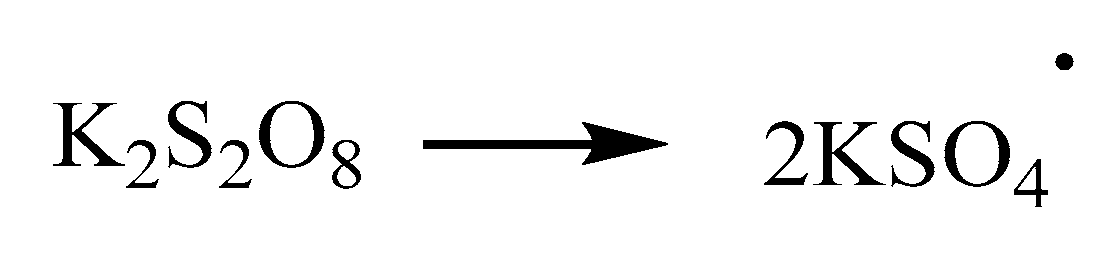
- (1)
- The initiator decomposes into free radicals:
- (2)
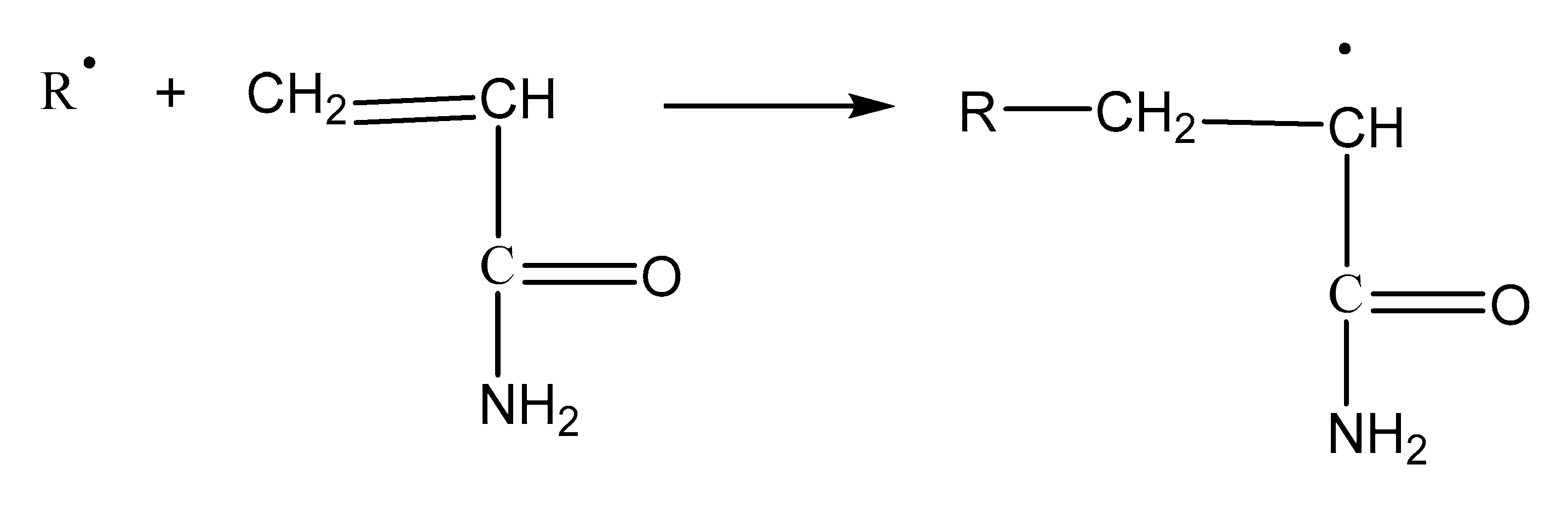
- Rubber hydrocarbon free radical (R.) initiated by free radicals:
- (3)
- Graft reaction:
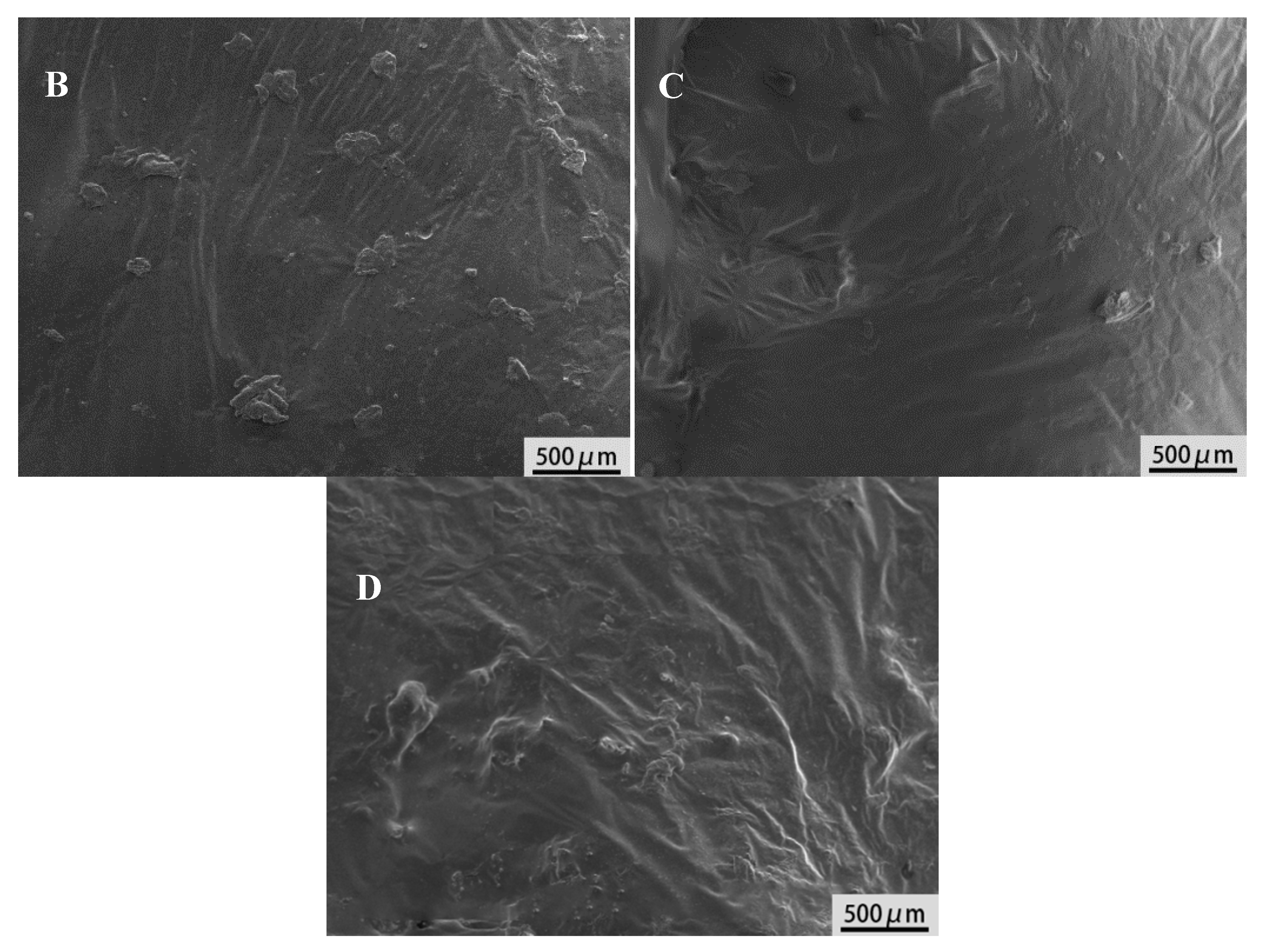
3.2. Characterization of Modified Asphalt Binder
3.3. Conventional Physical Properties of Modified Asphalt Binder
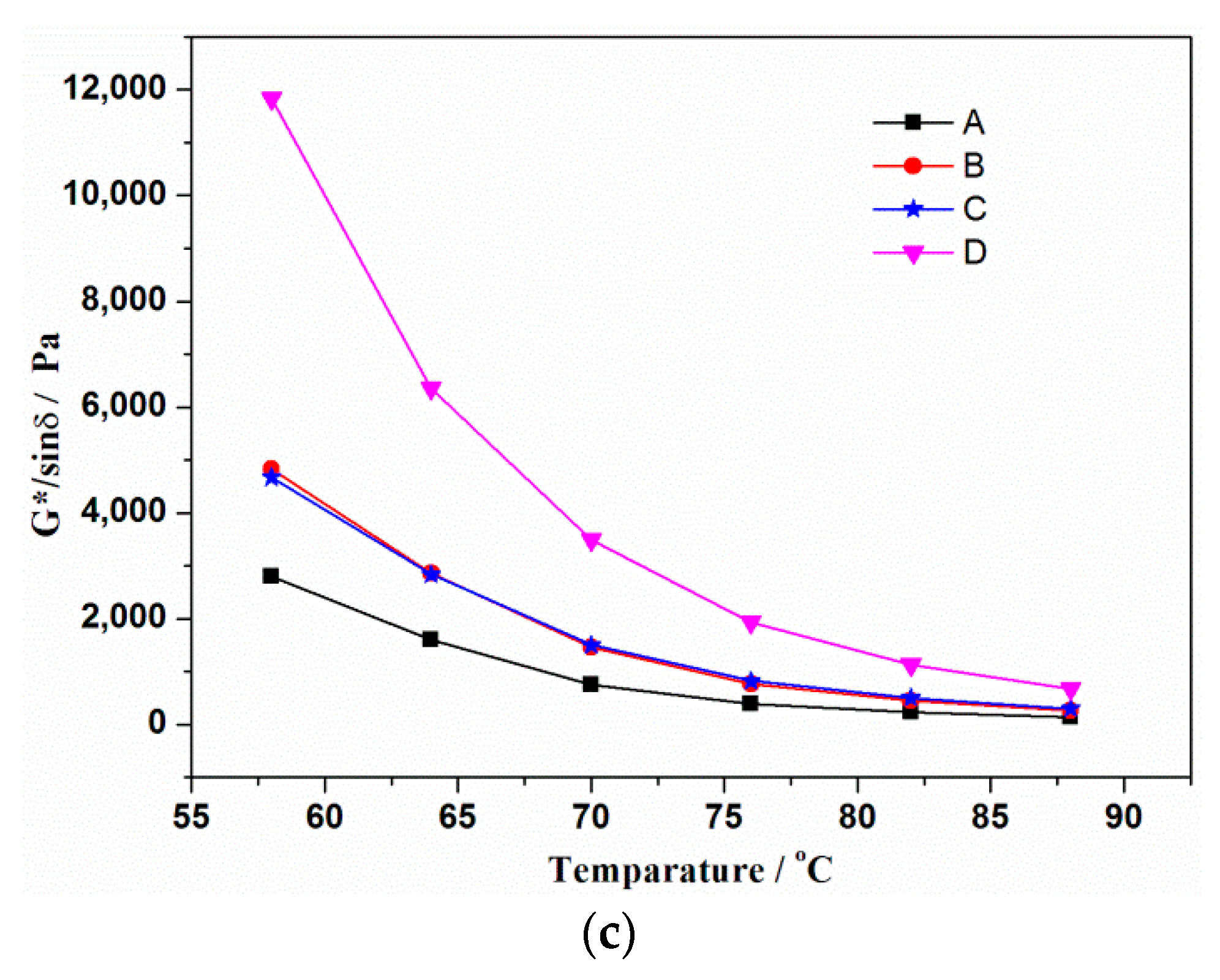
3.4. Rheological Properties of Modified Asphalt Binder
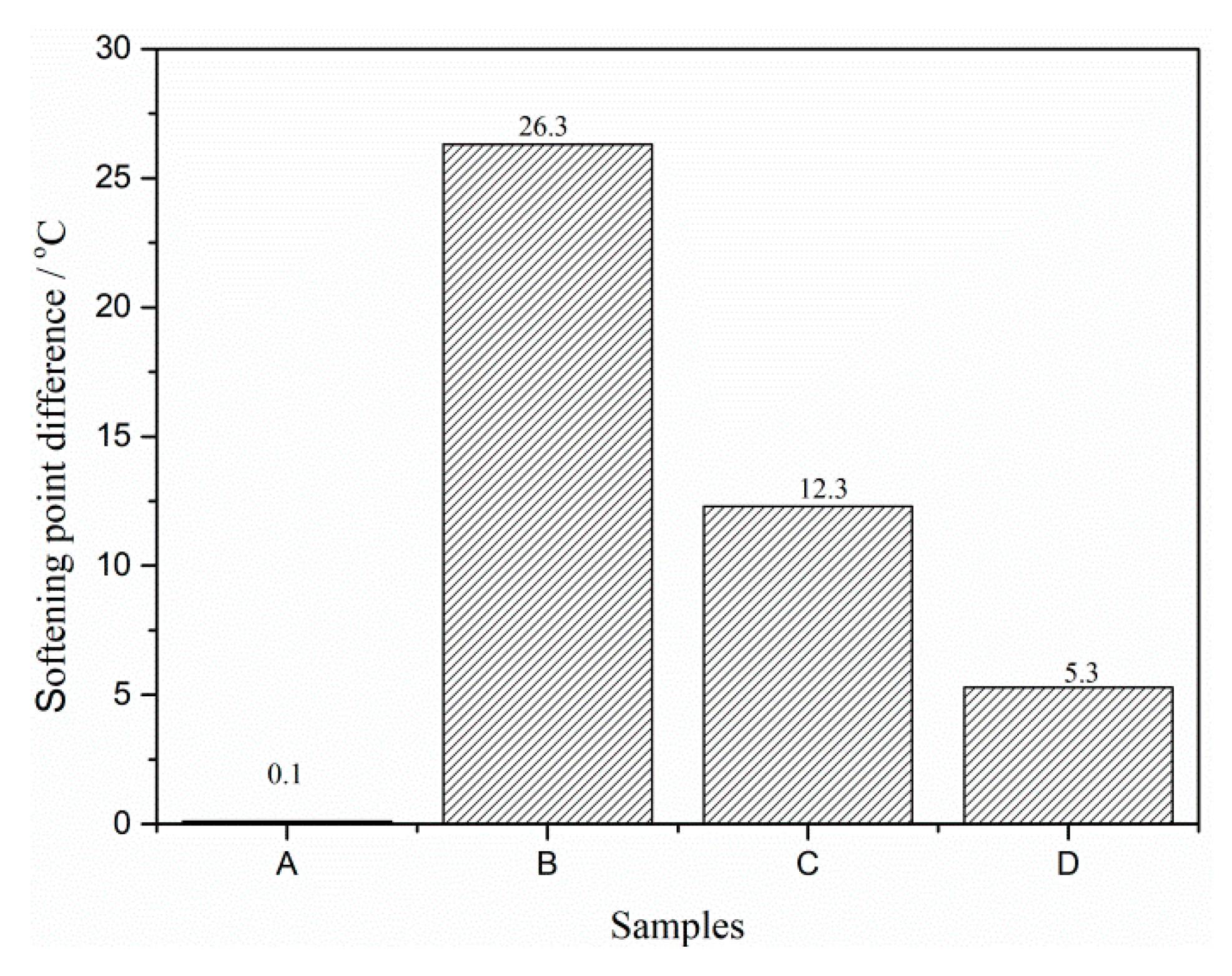
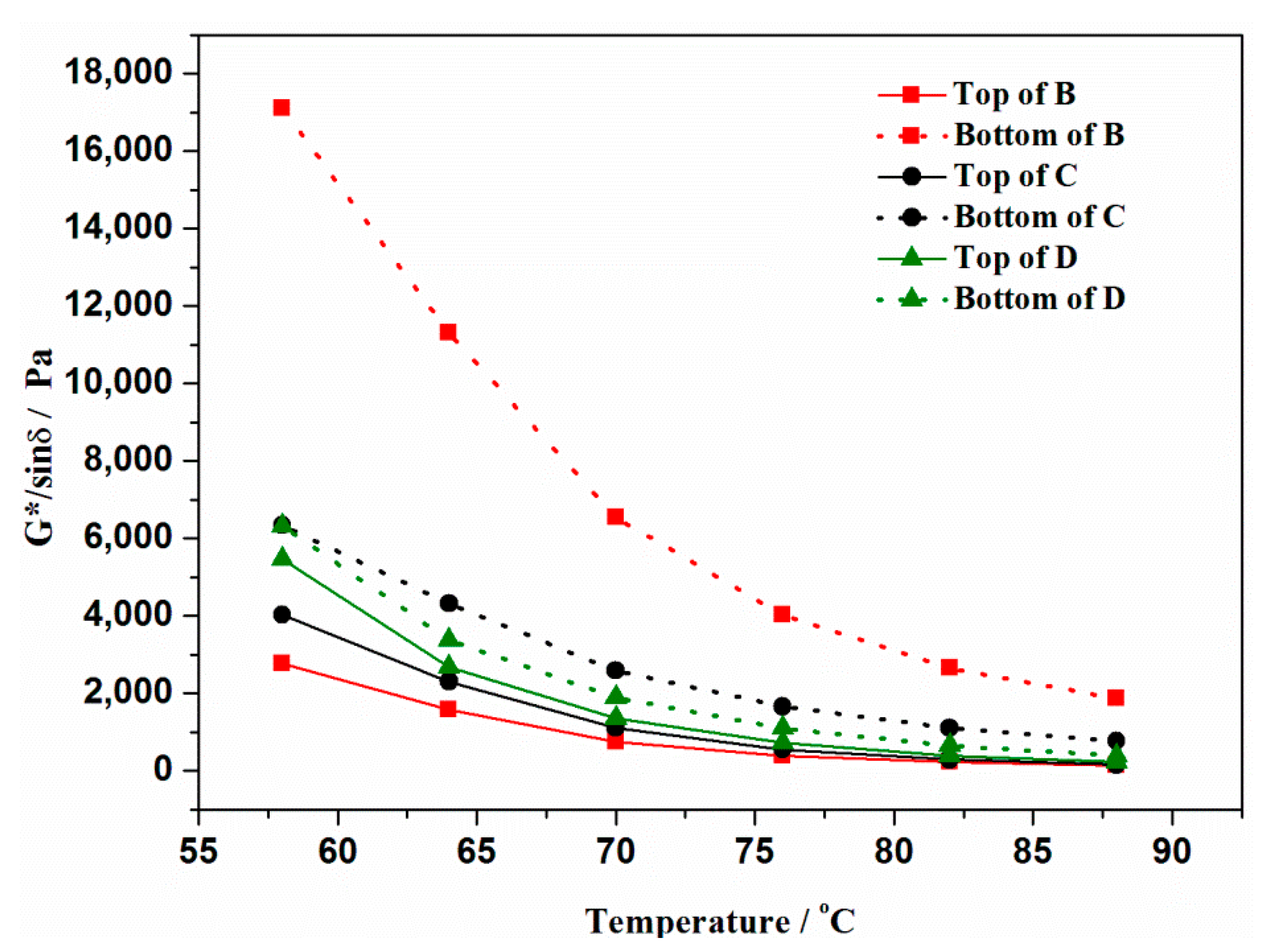
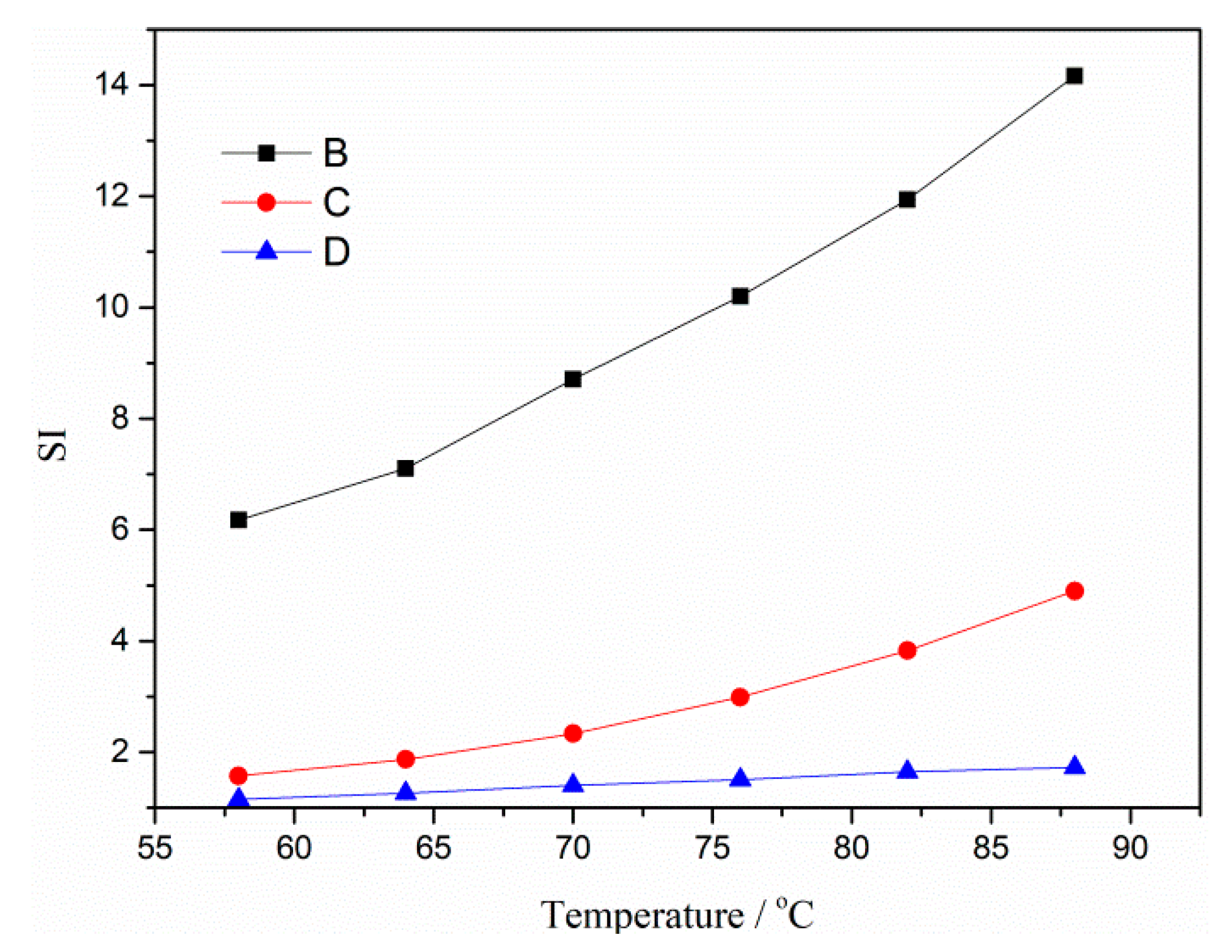
3.5. Storage Stability of Modified Asphalt Binder
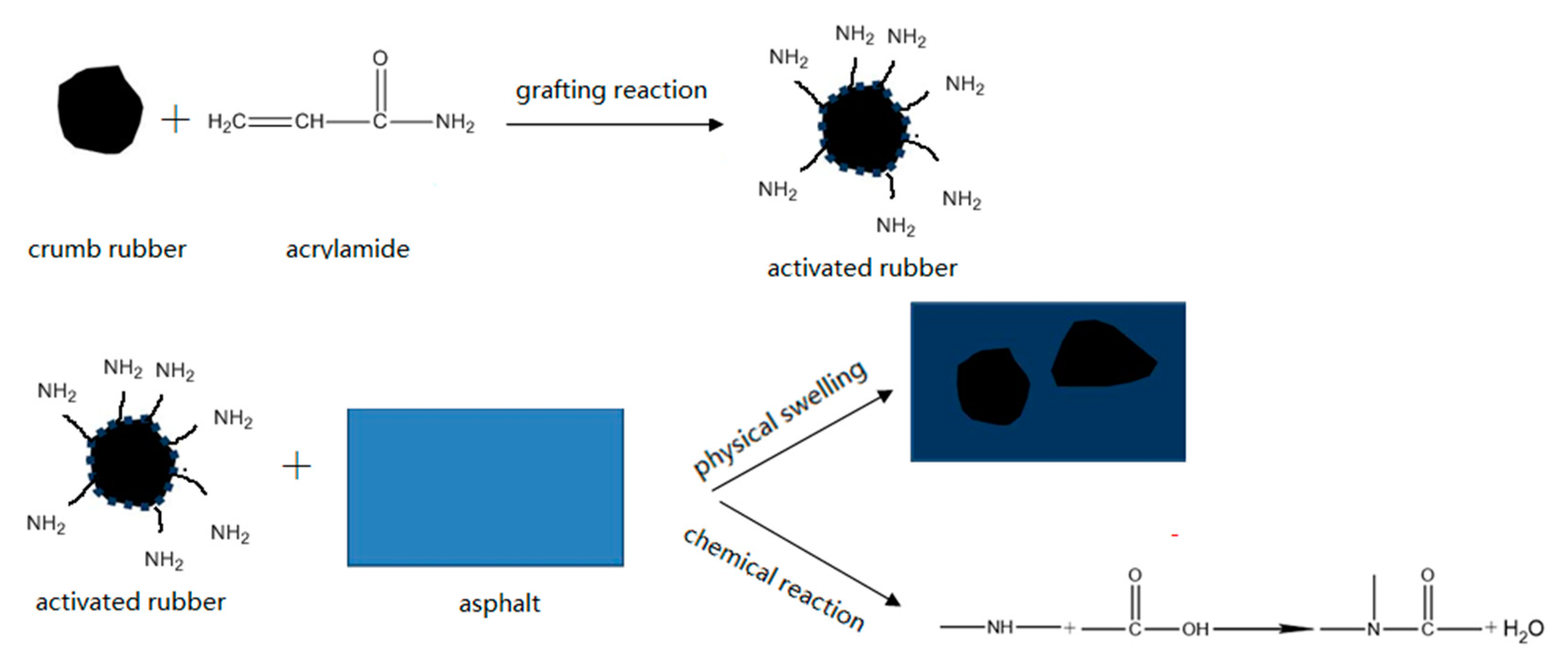
3.6. Modification Mechanism of Asphalt Rubber

4. Conclusions
- (1)
- After being activated, the surface of rubber is porous and rough. Coating activation of rubber with polyamide 6 is a physical process, but chemical reactions occur during grafting activation of rubber with acrylamide.
- (2)
- The penetration, softening point and viscosity results show that the activation of rubber can increase the high temperature properties of modified asphalt binder, and the grafting activation is superior to the coating activation.
- (3)
- All the three types of rubber decrease the ductility of the modified asphalt binder, especially coating-activated rubber. However, according to the results of BBR, the addition of rubber can improves the low temperature, and grafting activated rubber has the largest effect.
- (4)
- Based on the DSR results, it is found that the addition of rubber is beneficial to improving the deformation resistance and rutting factor. The coating activation of rubber has little effect on high temperature rheological properties of asphalt binder. However, grafting activation of rubber has a remarkable effect, which can be attributed to chemical reaction and strong interaction between rubber and asphalt binder.
- (5)
- The storage stability of modified asphalt binder was evaluated by polymer segregation and DSR test. The softening difference of B, C and D were 26.3 °C, 12.3 °C and 5.3 °C, respectively. It proves that both rubber activation methods can promote the interaction between rubber and asphalt binder, and then improve the storage stability of modified asphalt binder.
- (6)
- The modification mechanism of asphalt binder rubber was explored combining microstructure and macroscopic performance. The interaction between inactivated rubber, coating-activated rubber and asphalt binder is mainly swelling. However, there is both physical swelling and chemical action between grafting rubber and asphalt binder.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, J.; Tan, Y.; Liu, R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. Synergy effect of attapulgite, rubber, diatomite on the properties of organic montmorillonite modified asphalt. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2019, 31, 04018388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Abidi, N.; Cabrales, L. Wettability and Surface Free Energy of Graphene Films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11078–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Qi, Z.; Li, R.; Yue, J. Investigation of the effect of aging on the thermodynamic parameters and the intrinsic healing capability of graphene oxide modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Xia, C.; Yang, Q.; Guo, S.; You, L.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J. Improvements on high-temperature stability, rheology, and stiffness of asphalt binder modified with waste crayfish shell powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengoz, B.; Isikyakar, G. Evaluation of the properties and microstructure of SBS and EVA polymer modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Olek, J. Rheological properties of asphalt binders modified with styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), ground tire rubber (GTR), or polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Qi, X.; Duan, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, J. Effect of styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) on the rheological behavior of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Lee, S.-J. Effect of crumb rubber on viscosity of rubberized asphalt binders containing wax additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Presti, D. Recycled Tyre Rubber Modified Bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjegowda, V.H.; Biligiri, K.P. Recyclability of rubber in asphalt roadway systems: A review of applied research and advancement in technology. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitão, S.D.; Neves, J.M.C. Crumb rubber asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Z.; Wang, N.-N.; Tseng, M.-L.; Huang, Y.-M.; Li, N.-L. Waste tire recycling assessment: Road application potential and carbon emissions reduction analysis of crumb rubber modified asphalt in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Rahmani, Z.; Zahedi, M.; Nasrollahi, M. Technical, Economic, and Environmental Investigation of the Effects of Rubber Powder Additive on Asphalt Mixtures. J. Trans. Eng. Part B Pavements 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, T.; Dong, Z. Evaluation of optimum mixing conditions for rubberized asphalt mixture containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.C.; Ruffino, B.; Dalmazzo, D.; Lanotte, M.; Santagata, E. Determination of Crumb Rubber Content of Asphalt Rubber Binders. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Leng, Z.; Dong, Z.; Tan, Z.; Guo, F.; Yan, J. Workability and mechanical property characterization of asphalt rubber mixtures modified with various warm mix asphalt additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.J.; Partal, P.; Martínez-Boza, F.; Gallegos, C. Thermo-rheological behaviour and storage stability of ground tire rubber-modified bitumens. Fuel 2004, 83, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-W.; Luo, J.; Cao, Y.; Yin, X.-C.; He, G.-J.; Peng, X.-F.; Xu, B.-P. Structure and properties of deeply oxidized waster rubber crumb through long time ozonization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, J.; Lo Presti, D.; Santos, C.; Thives, L.; Pereira, P. The effect of prolonged storage time on asphalt rubber binder properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zheng, M.; Wang, C. Current status and development of terminal blend tyre rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, W.; Tang, N.; Hu, J.; Lin, P.; Guan, W.; Xiao, F.; Shan, Z. Evolution of components distribution and its effect on low temperature properties of terminal blend rubberized asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Q. Effect of nano silica and pretreated rubber on the properties of terminal blend crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Hao, P. Investigation of the rheological modification mechanism of crumb rubber modified asphalt (CRMA) containing TOR additive. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Ren, S.; Shi, J.; Luo, H. Thermo-stability and aging performance of modified asphalt with crumb rubber activated by microwave and TOR. Mater. Des. 2017, 127, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, N. Effect of sulfur on the storage stability of tire rubber modified asphalt. World J. Chem. 2008, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, C.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Shan, X. Compatibilizer in waste tire powder and low-density polyethylene blends and the blends modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, C.; Deng, J. Crumb tire rubber and polyethylene mutually stabilized in asphalt by screw extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 131, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinnezhad, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Oldham, D.; Mousavi, M.; Fini, E.H. Surface functionalization of rubber particles to reduce phase separation in rubberized asphalt for sustainable construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.F.; Mousavi, M.; Fini, E.H. Selective adsorption of bio-oils’ molecules onto rubber surface and its effects on stability of rubberized asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Li, J. Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Materials 2019, 12, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Storage, fatigue and low temperature characteristics of plasma treated rubberized binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; Lv, S.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y. Investigation on Preparation Process and Storage Stability of Modified Asphalt Binder by Grafting Activated Crumb Rubber. Materials 2019, 12, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S. Effect of liquid ASAs on the rheological properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zeng, X.; Muhammad, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Meng, F. Preparation of Octadecyl Amine Grafted over Waste Rubber Powder (ODA-WRP) and Properties of its Incorporation in SBS-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2019, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mark, J.E.; Zhu, Y.; Ruoff, R.S.; Schaefer, D.W. Mechanical properties of polybutadiene reinforced with octadecylamine modified graphene oxide. Polymers 2014, 55, 5389–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Pais, J.C.; Pereira, P.A.A.; Trichês, G.; Amorim, S.R. Assessment of the digestion time of asphalt rubber binder based on microscopy analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, M.; Borzędowska-Labuda, K.; Zalewski, S.; Janik, H. The effect of tyre rubber grinding method on the rubber-asphalt binder properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Amirkhanian, S. The influence of crumb rubber modifier (CRM) microstructures on the high temperature properties of CRM binders. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2007, 6, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Fan, W.; Liang, M.; He, Y.; Ren, S.; Lv, X.; Nan, G.; Luo, H. Rheological properties, storage stability and morphology of CR/SBS composite modified asphalt by high-cured method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, C. Investigation on Rheological Properties and Storage Stability of Modified Asphalt Based on the Grafting Activation of Crumb Rubber. Polymers 2019, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donghui, L.; Si, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y. Study on the Elasticity and Crystallization Properties of Copolymer Modified Nylon 6. Mater. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Alloza, A.M.; Gallego, J.; Pérez, I. Study of the effect of four warm mix asphalt additives on bitumen modified with 15% crumb rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifeng, W.; Xie, Y. Crumb Tire Rubber Polyolefin Elastomer Modified Asphalt with Hot Storage Stability. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2015, 32, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q. Investigation on compatibility and microstructure of PCBs-modified asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Units | Test Results | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s) | 0.1 mm | 87 | JTG-T0604-2011 |
| Softening temperature | °C | 47 | JTG-T0606-2011 |
| Ductility (10 °C, 5 cm/min) | cm | >100 | JTG-T0605-2011 |
| Kinematic viscosity (135 °C) | Pa s | 147.3 | JTG-T0625-2011 |
| Density | g/cm3 | 1.009 | JTG-T0603-2011 |
| RTFO treated at 163 °C for 85 min | |||
| Quality change | % | −0.063 | JTG-T0610-1-2011 |
| Residual penetration ratio (25 °C) | % | 59.5 | JTG-T0610-2-2011 |
| Residual ductility (10 °C) | cm | 3.5 | JTG-T0605-2011 |
| Item | Result | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Water content (%) | 1.1 | HG/TXXX-2001 7.2.2 |
| Ash content (%) | 8.9 | GB4498 |
| Acetone extract content (%) | 13.1 | GB/T3516 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.14 | GB/T533 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 15 | GB/T528 |
| Elongation at break (%) | 650 | GB/T52 |
| Sample | Modifier | Content of Modifier (%) |
|---|---|---|
| A | no | 0 |
| B | Unactivated rubber | 20 |
| C | Coating-activated rubber | 20 |
| D | Grafting-activated rubber | 20 |
| Item | Sample | Standard | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||
| Penetration at 25 °C (mm) | 78.1 | 57.3 | 55.2 | 50.9 | JTG-T0604-2011 |
| Softening Point (°C) | 50 | 58.1 | 60.5 | 63.5 | JTG-T0606-2011 |
| Ductility at 5 °C (mm) | 98.5 | 60.6 | 54.5 | 96.8 | JTG-T0605-2011 |
| Viscosity at 175 °C (mPa.s) | 81 | 766 | 1124 | 1580 | JTG-T0625-2011 |
| Simple | −12 °C | −18 °C | −24 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (MPa) | m | S (MPa) | m | S (MPa) | m | |
| A | 131.0 | 0.360 | 325.0 | 0.305 | 615.0 | 0.230 |
| B | 75.6 | 0.396 | 99.0 | 0.320 | 297.3 | 0.296 |
| C | 79.0 | 0.365 | 110 | 0.315 | 295.0 | 0.251 |
| D | 67.3 | 0.422 | 63.4 | 0.368 | 143.3 | 0.309 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, M. The Effect of Activation Method of Rubber on the Performance of Modified Asphalt Binder. Materials 2020, 13, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173679
Xie J, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Ma Y, Li J, Huang M. The Effect of Activation Method of Rubber on the Performance of Modified Asphalt Binder. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173679
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Juan, Yongning Zhang, Yueming Yang, Yunlong Ma, Jing Li, and Menglong Huang. 2020. "The Effect of Activation Method of Rubber on the Performance of Modified Asphalt Binder" Materials 13, no. 17: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173679
APA StyleXie, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Ma, Y., Li, J., & Huang, M. (2020). The Effect of Activation Method of Rubber on the Performance of Modified Asphalt Binder. Materials, 13(17), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173679