A Prediction Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture and Its Parameters
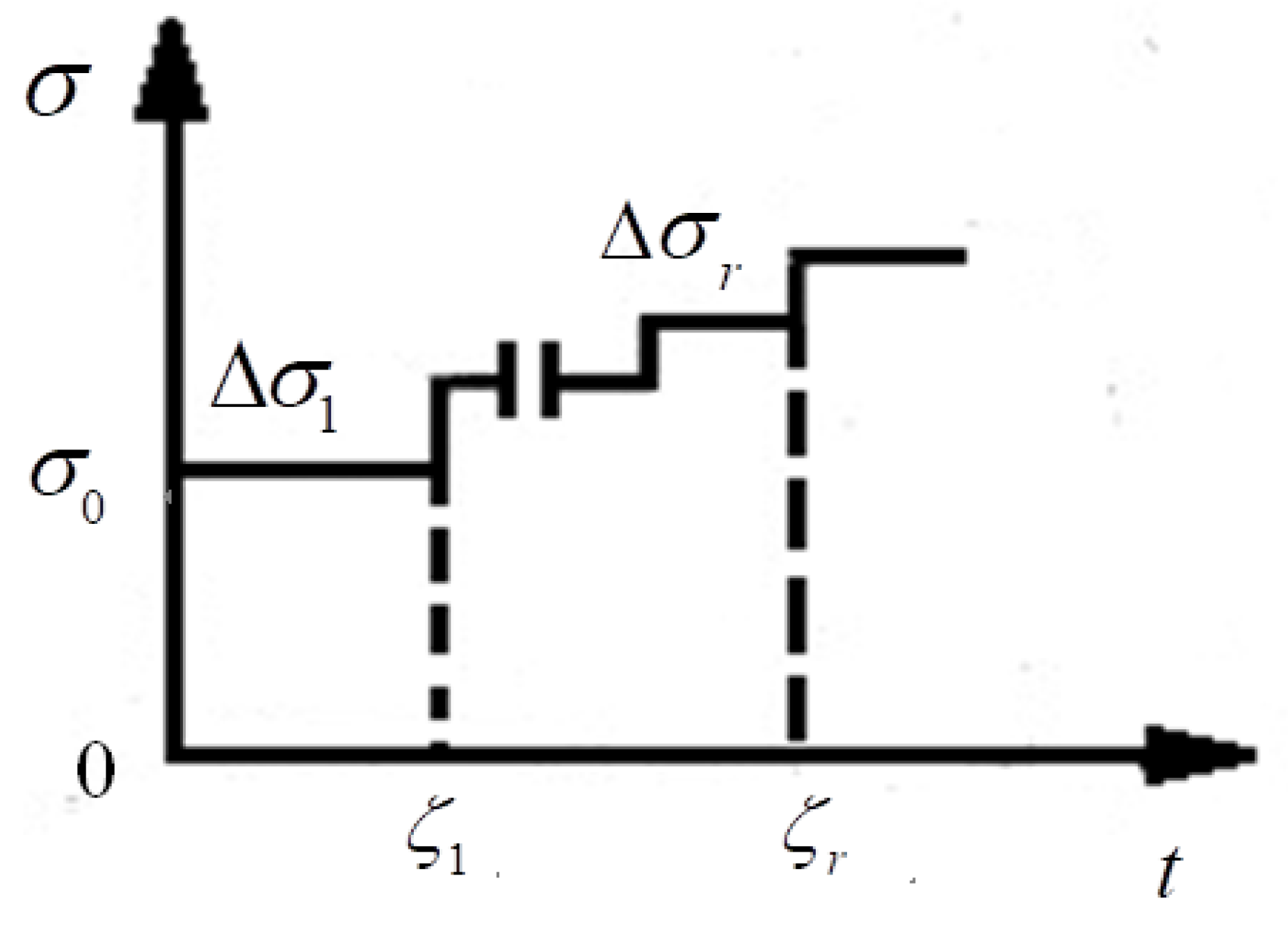
2.1. Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture
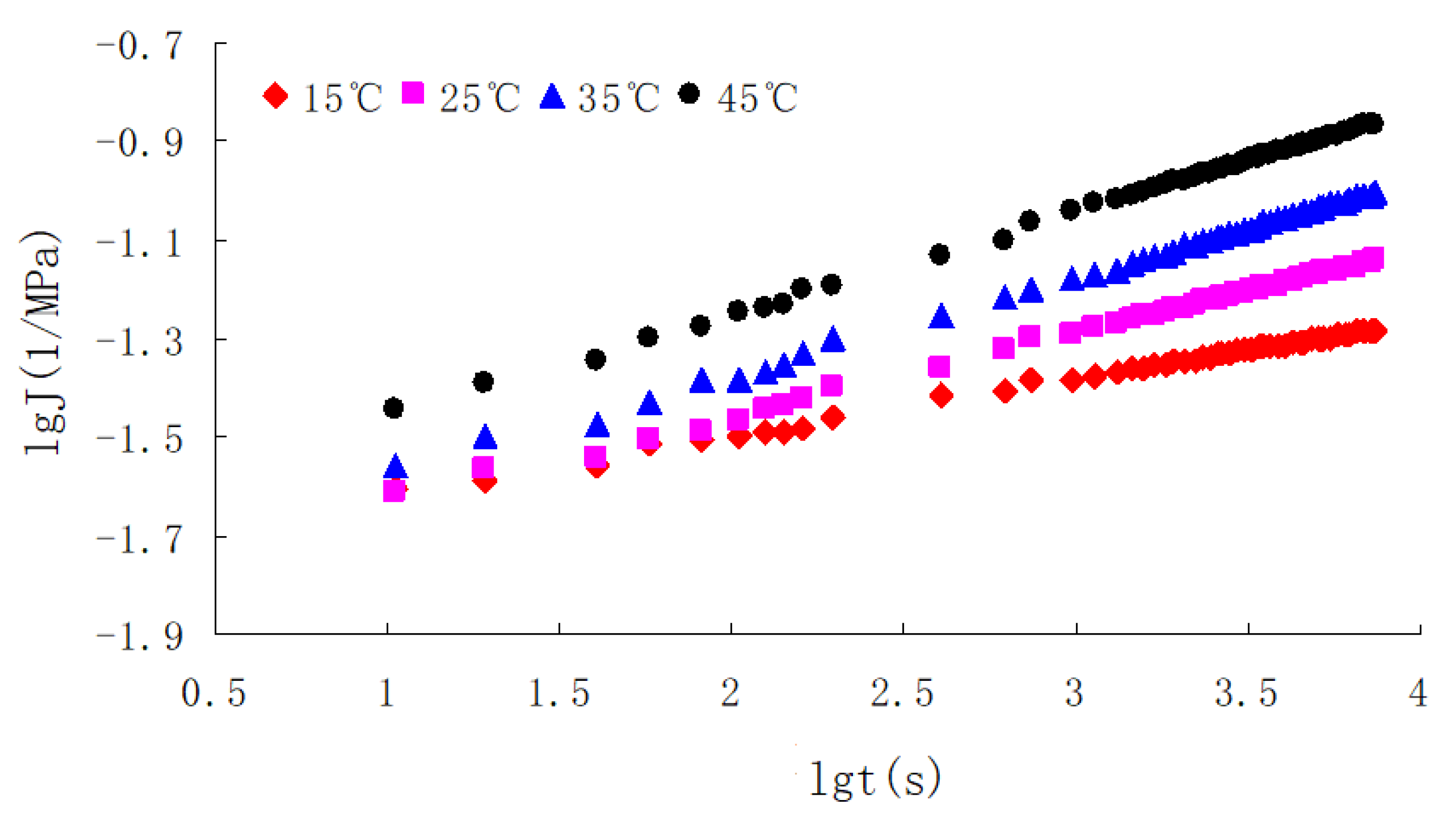
2.2. Model Parameters
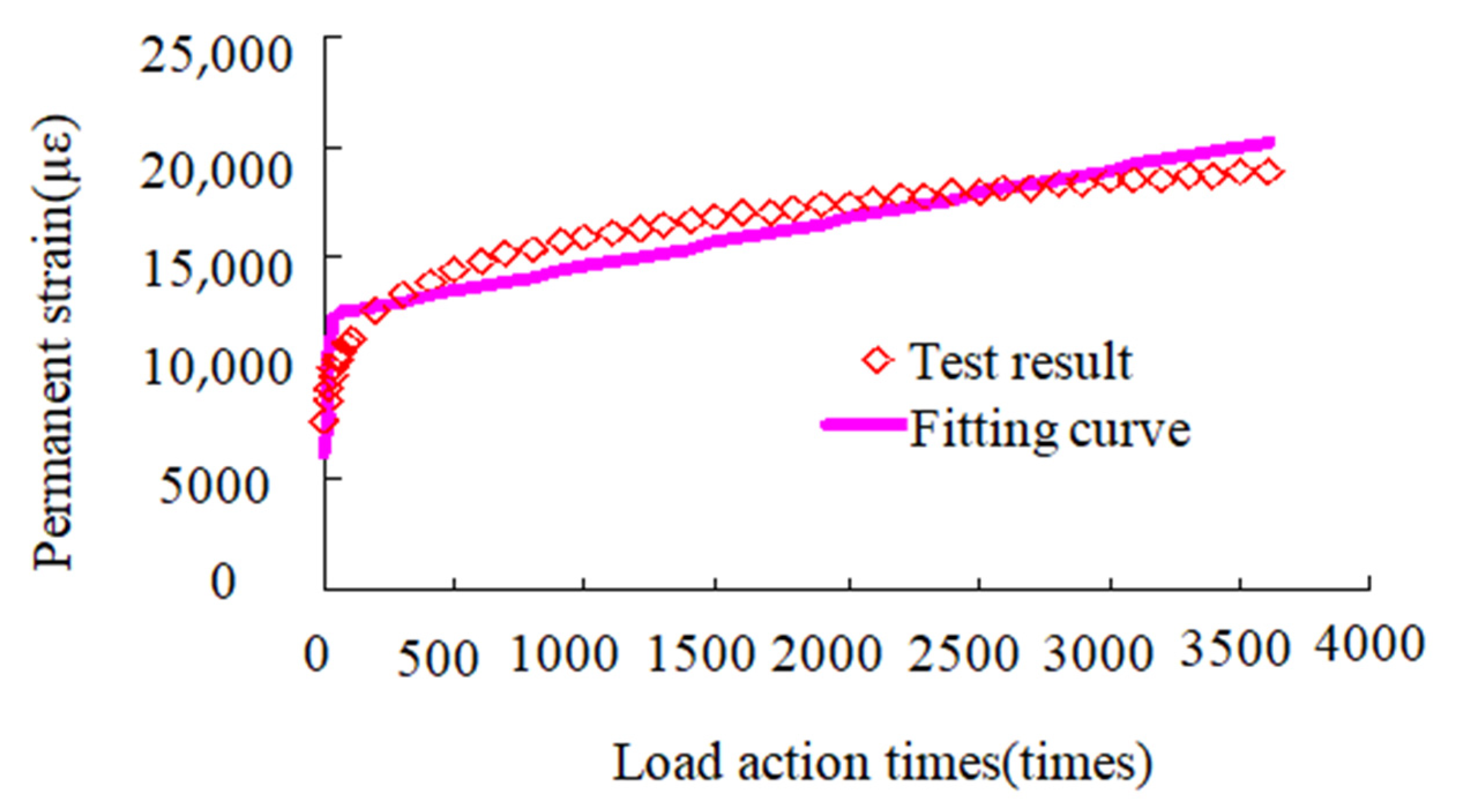
3. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A viscoelastic fatigue damage prediction model for asphalt mixtures considering the combined effects of creep damage and fatigue damage is proposed, using Burgers’ model, the WLF equation and Boltzmann’s superposition principles, based on bending fatigue and dynamic creep testing, and theoretic analysis and testing demonstrated that it is reasonable.
- (2)
- The proposed model on viscoelastic fatigue damage of asphalt mixtures can consider the influences of aging, temperature, loading frequency and stress on the fatigue failure of asphalt mixtures by introducing the parameter β and shift factor, and it can embody the essence of viscoelastic fatigue damage of asphalt mixtures.
- (3)
- To bring the model to asphalt pavement design in the future, problems such as the equivalent fatigue temperature based on fatigue damage and the field correction coefficient considering the difference between indoor testing and actual pavements should be further investigated systematically.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Basyouny, M.M.; Witczak, M. Calibration of alligator fatigue cracking model for 2002 design guide. In Proceedings of the Meeting of the Transportation-Research-Board, Washington, DC, USA, 9–13 January 2005; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Masoud, K.; Rashid, K.; Abu, A.; Eyad, A.; Dallas, N. Constitutive modeling of fatigue damage response of asphalt concrete materials. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2373, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Shen, S.; You, Z. Evaluation of fatigue models of hot-mix asphalt through laboratory testing. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2127, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, A.; Gajewski, M.; Bańkowski, W. Application of a material fatigue damage model in 4PB tests. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, A.; Gajewski, M.; Bańkowski, W. Processing of four point bending test results for visco-elasticity and fatigue models. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mohammad, L.; Barghabany, P. Use of viscoelastic continuum damage theory to correlate fatigue resistance of asphalt binders and mixtures. Int. J. Geomech. 2018, 18, 04018151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; West, R.C. Application of the Viscoelastic Continuum Damage Model to the Indirect Tension Test at a Single Temperature. J. Eng. Mech. 2010, 136, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.; Farias, M.M.D.; Kaloush, K.E. Using damage theory to analyze fatigue of asphalt mixtures on flexural tests. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Yu, B.; Gu, X.; Xu, K. Characterization of Fatigue Damage of Hot Mix Asphalt Based on Residual Strength. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Shams, N.; Mohammad, M.; Mohammad, H. A study on fatigue modeling of hot mix asphalt mixtures based on the viscoelastic continuum damage properties of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Xia, C.; Zheng, J.; Lv, S. Nonlinear fatigue damage model of asphalt mixture based on dynamic modulus and residual strength decay. Materials 2019, 12, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Sanchez, J.A. Estimation of asphalt concrete fatigue curves—A damage theory approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, H.; Tang, B. Damage model of interaction between fatigue and creep for asphalt mixture. China J. Highw. Transp. 2011, 24, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Lv, S. Nonlinear fatigue damage model for asphalt mixtures. China J. Highw. Transp. 2009, 22, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Fang, C.; Fan, D.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X. A research on fatigue damage constitutive equation of asphalt mixture. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. A Research on Damage Model of Interation between Fatigue and Creep of Asphalt Mixture. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, S.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, H. Analysis on fatigue life predicted model of aged asphalt based on dissipation energy. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2019, 36, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.A. Research on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage Model of Asphalt Mixture. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Rong, L. Development of failure criterion and fatigue model to characterize the fatigue resistance of asphalt binders under controlled-stress time sweep tests. Mater. Struct. 2019, 53, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y. Fatigue damage evolution model of asphalt mixture considering influence of loading frequency. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Ma, T. Damage-creep characteristics and model of asphalt mixture. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2008, 30, 867–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Rabotnov, Y.N. On the equations of state for creep. Prog. Appl. Mech. 1963, 178, 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H. Study on Fatigue Performances and Design Method of Flexible Base Asphalt Pavement. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Ren, R. Mechanics of Layered Viscoelastic System; Harbin Institute of Technology Press: Harbin, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Application of burgers model to the analysis of fatigue characteristic of bituminous mixtures. J. Changsha Commun. Inst. 1995, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Ma, J.; Lu, S.; Qian, G.; Tian, X. Research on viscoelastic fatigue damage model of aging asphalt mixtures. Eng. Mech. 2010, 27, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Safaei, F.; Cassie, C.; Kim, Y. Linking asphalt binder fatigue to mixture fatigue performance using viscoelastic continuum asphalt damage modeling. Mech. Time Depend. Mater. 2016, 20, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lv, S.; Tian, X. Viscoelastic damage characteristics of asphalt based on creep test. Eng. Mech. 2008, 25, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C. Face Stability Analysis for a Shield Tunnel in Anisotropic Sands. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X. Viscoelastic mechanical model of permanent deformation of asphalt mixtures under repeated load. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2008, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Feng, X. Damage Mechanics; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- China Ministry of Transport. JTG E20-2011 Specifications and Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- China Ministry of Transport. JTGE42-2005 Test Methods of Aggregate for Highway Engineering; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
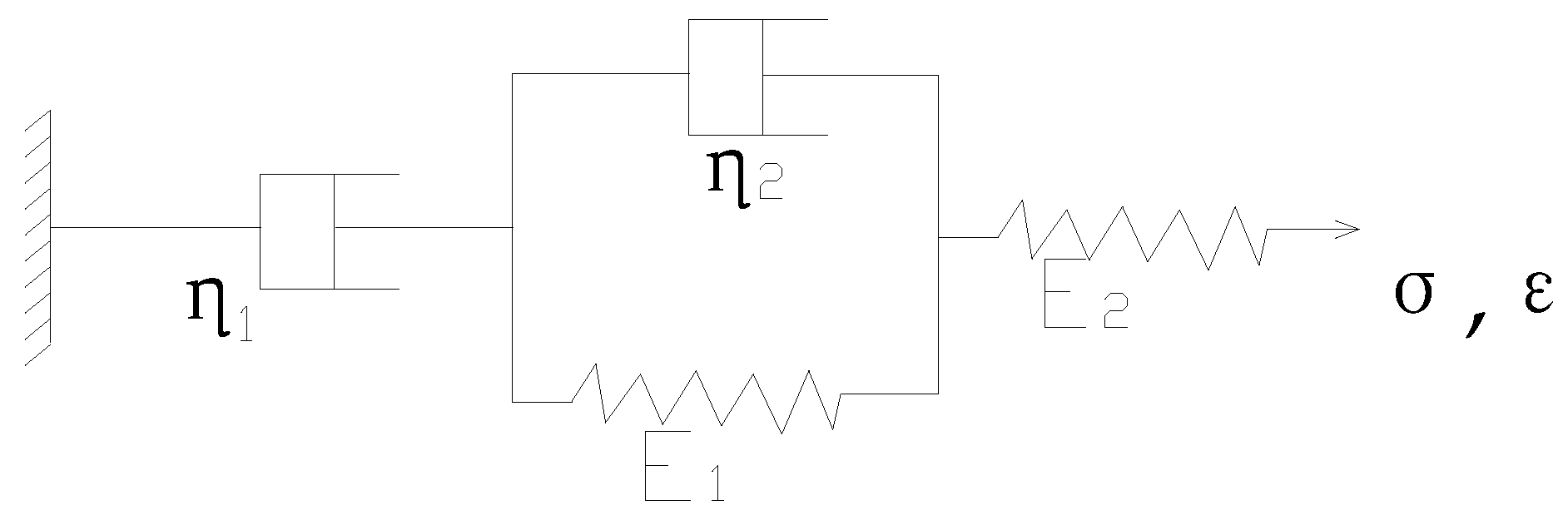
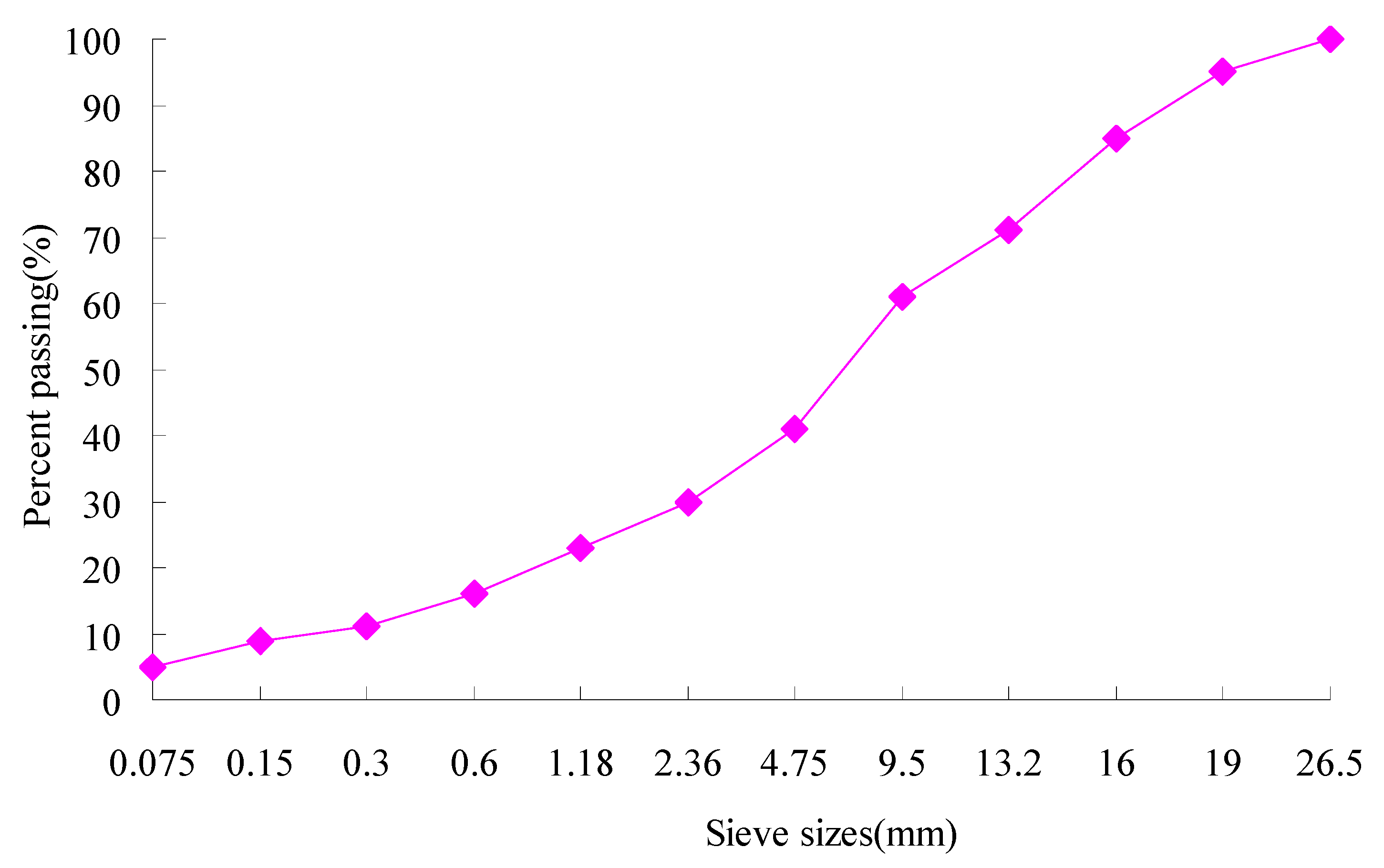



| Properties | Criteria | Zhonghai AH-70 | Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ductility at 15 °C (cm) | ≥100 | 135 | T0605-2011 [32] | |
| Penetration degree at 25 °C (0.1 mm) | 60~80 | 70 | T0604-2011 [32] | |
| Softening point (°C) | ≥46 | 51 | T0606-2011 [32] | |
| Dynamic viscosity at 60 °C (Pa·s) | ≥180 | 217 | T0620-2000 [32] | |
| After the rolling thin film oven (TFOT) (163 °C, 5 h) | Mass loss (%) | −0.36 | −0.15 | T0609-2011 [32] |
| Ductility at 15 °C (cm) | 16.2 | 21.2 | T0605-2011 [32] | |
| Ductility at 10 °C (cm) | ≥6 | 9.1 | T0605-2011 [32] | |
| Penetration degree ratio at 25 °C (%) | −61.5 | 65 | T0604-2011 [32] | |
| Technical Indexes | Results | Criteria | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crush value (%) | 16.4 | ≤26 | T0316-2005 [33] |
| Content of acicular and flaky shape particles (%) | 9.4 | ≤15 | T0312-2005 [33] |
| Losses of Los Angeles Abrasion Test (%) | 21.5 | ≤28 | T0317-2005 [33] |
| Water absorption (%) | 0.32 | ≤2 | T0307-2005 [33] |
| Asphalt adhesion (graduation) | 5 | ≥4 | T0616-1993 [32] |
| Impact value (%) | 18 | ≤30 | T0322-2005 [33] |
| Firmness (%) | 4.3 | ≤12 | T0314-2005 [33] |
| Mud content (%) | 0.7 | ≤1 | T0310-2005 [33] |
| Optimum Asphalt Content (%) | Bulk Volume Relative Density (g·cm−3) | Volume of Air Voids (%) | Voids Filled with Asphalt (%) | Voids in Mineral Aggregate (%) | Flow Value (0.1 mm) | Marshall Stability (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.2 | 2.44 | 4.2 | 68.5 | 13.8 | 38.2 | 11.1 |
| Specification Requirement [32] | - | 3–6 | 55–70 | >12.5 | 15–40 | >8 |
| Stress Ratio | Stress (MPa) | Value of M | Test Value of Fatigue Life (Times) | Predicted Value of Fatigue Life (Times) | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 0.52 | 0.00740727 | 2858 | 3227 | 0.13 |
| 0.45 | 0.59 | 0.00514394 | 5752 | 6627 | 0.15 |
| 0.5 | 0.65 | 0.00423812 | 8955 | 9711 | 0.08 |
| 0.6 | 0.78 | 0.00329212 | 16,819 | 15,986 | −0.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Y.; Yan, H. A Prediction Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2020, 13, 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173782
Li L, Jiang X, Lin Y, Yan H. A Prediction Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173782
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Limin, Xiaoling Jiang, Yuliang Lin, and Heng Yan. 2020. "A Prediction Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture" Materials 13, no. 17: 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173782
APA StyleLi, L., Jiang, X., Lin, Y., & Yan, H. (2020). A Prediction Model on Viscoelastic Fatigue Damage of Asphalt Mixture. Materials, 13(17), 3782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173782





