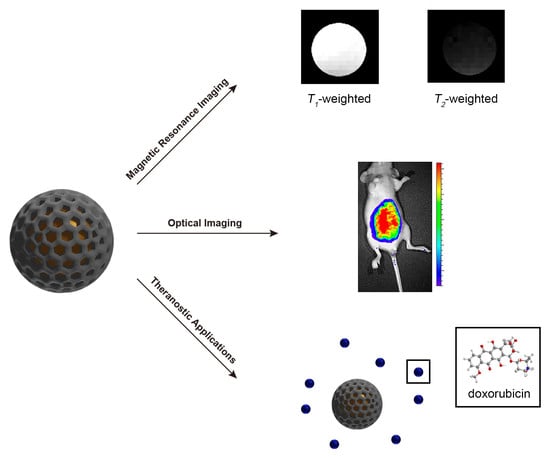
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Bioimaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis
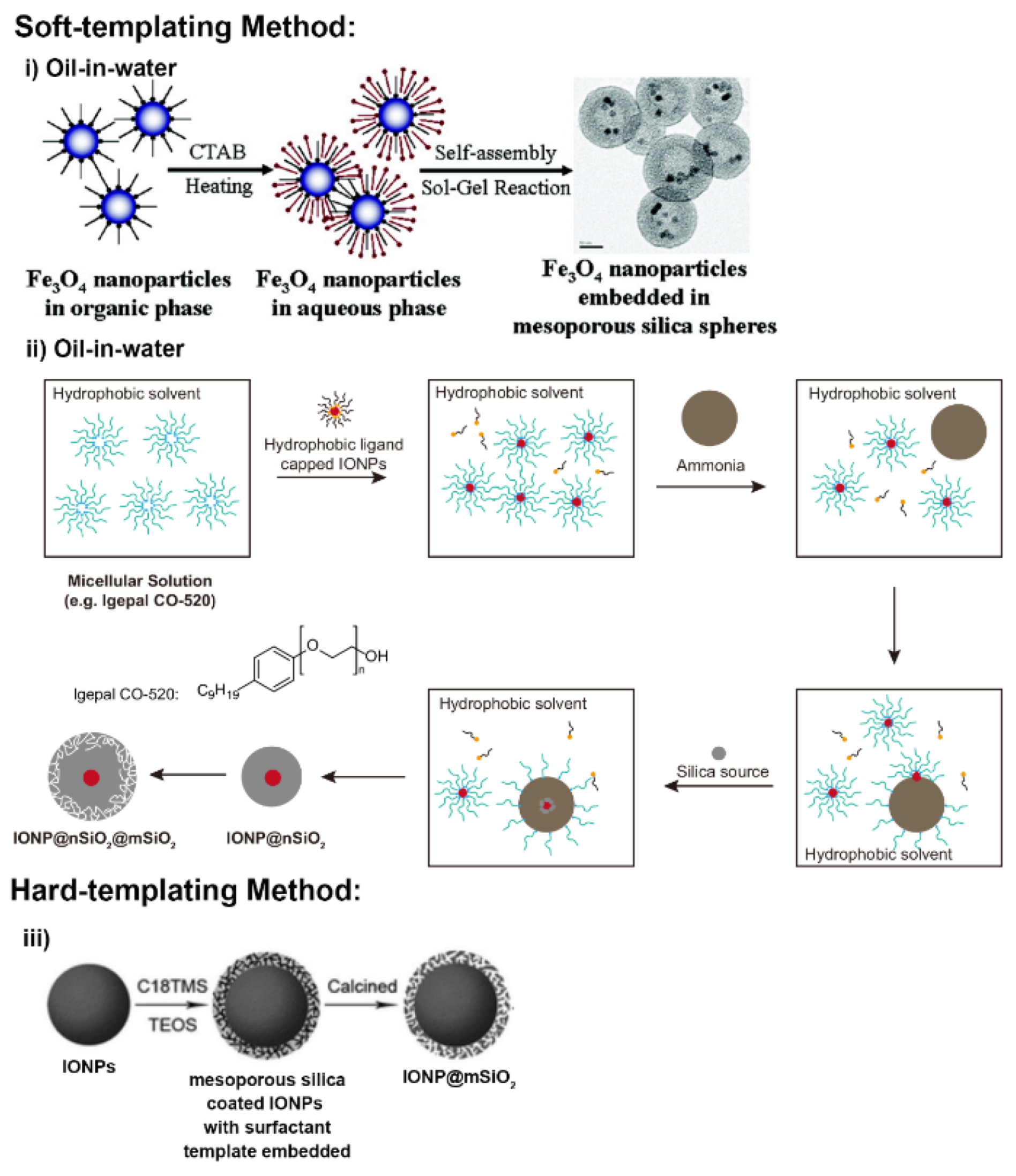
2.1. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles by Sol–Gel Chemistry
2.2. Synthesis of Hollow MSNs and Core–Shell Structured MSNs
2.3. Functionalisation of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.1. Paramagnetically Doped MSNs
3.1.1. Targeting MSNs
3.1.2. Environmentally Responsive MSNs
3.2. Core–Shell Hybrid Nanoparticles
4. Optical Imaging
4.1. Luminescent MSNs
4.1.1. Organic Fluorophore-Incorporated MSNs
4.1.2. Luminescent Inorganic-Composite MSNs
4.2. Luminescent Core–Shell MSNs
5. Other Imaging Modes and Multi-Modal Imaging
5.1. Other Imaging Modalities
5.1.1. Positron Emission Tomography
5.1.2. Computed Tomography
5.2. Multi-Modal Imaging
5.2.1. Functional Moiety Incorporated MSNs
5.2.2. Core–Shell Structured MSNs
6. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Teh, C.; Ang, C.Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Korzh, V.; Zhao, Y. Responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for sensing of hydrogen peroxide and simultaneous treatment toward heart failure. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, S.-T.; Lai, J.-Y.; Wu, K.C.W. Gelatin-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles with sustained release properties for intracameral pharmacotherapy of glaucoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7008–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Self-Regulated Carboxyphenylboronic Acid-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with “Touch Switch” Releasing Property for Insulin Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21927–21938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert-Garzaran, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Complex Bone Diseases: Bone Cancer, Bone Infection and Osteoporosis. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Patel, K.D.; Leong, K.W.; Kim, H.-W. Progress in Nanotheranostics Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanomaterial Platforms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10309–10337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Dutta, S.; Zboril, R.; Gawande, M.B. Silica-nanosphere-based organic–inorganic hybrid nanomaterials: Synthesis, functionalization and applications in catalysis. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3207–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, T.L.; Burda, C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoprobes: Material Chemistry–Based Fabrication and Bio-Imaging Functionality. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1800078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanomaterials for in vivo Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torney, F.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.Y.; Wang, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9972–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyo, C.; Weiss, V.; Bräuchle, C.; Bein, T. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Universal Platform for Drug Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekaru, H.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F. Development of mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release capability for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 95, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z. Mesoporous silica-based nanodevices for biological applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18961–18980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Margolese, D.I.; Stucky, G.D. Surfactant Control of Phases in the Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Schumacher, K.; du Fresne von Hohenesche, C.; Grün, M.; Unger, K.K. MCM-41, MCM-48 and related mesoporous adsorbents: Their synthesis and characterisation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 187–188, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Leon, R.; Petroff, P.M.; Stucky, G.D. Mesostructure Design with Gemini Surfactants: Supercage Formation in a Three-Dimensional Hexagonal Array. Science 1995, 268, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Melde, B.J.; Schroden, R.C. Hybrid Inorganic–Organic Mesoporous Silicates—Nanoscopic Reactors Coming of Age. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luz, Z.; Goldfarb, D. EPR Studies of the Formation Mechanism of the Mesoporous Materials MCM-41 and MCM-50. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 7087–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbia, M.; Salehi, S. Removal of acid dyes from aqueous media by adsorption onto amino-functionalized nanoporous silica SBA-3. Dye. Pigment. 2012, 94, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Ko, C.H.; Ryoo, R. Characterization of the Porous Structure of SBA-15. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Stucky, G.D. Morphological Control of Highly Ordered Mesoporous Silica SBA-15. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Schüth, F. Ordered mesoporous materials in catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 77, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitz, F.; Liu, D.; Anilkumar, G.M.; Park, I.-S.; Solovyov, L.A.; Shmakov, A.N.; Ryoo, R. Large Cage Face-Centered-Cubic Fm3m Mesoporous Silica: Synthesis and Structure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 14296–14300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javad Kalbasi, R.; Zirakbash, A. Synthesis, characterization and drug release studies of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)/KIT-5 nanocomposite as an innovative organic–inorganic hybrid carrier system. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12463–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, F.; Lei, J.; Tian, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, Q.; Tu, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, D. Cubic Mesoporous Silica with Large Controllable Entrance Sizes and Advanced Adsorption Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3146–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, C.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Tu, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, D. Low-Temperature Strategy to Synthesize Highly Ordered Mesoporous Silicas with Very Large Pores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10794–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Lauer, I.; Unger, K.K. The synthesis of micrometer- and submicrometer-size spheres of ordered mesoporous oxide MCM-41. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollamby, M.J.; Borisova, D.; Brown, P.; Eastoe, J.; Grillo, I.; Shchukin, D. Growth of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Monitored by Time-Resolved Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-P.; Mou, C.-Y. Structural and Morphological Control of Cationic Surfactant-Templated Mesoporous Silica. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zhao, D. On the Controllable Soft-Templating Approach to Mesoporous Silicates. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2821–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, F.; Testa, F.; Chen, J.D.; Cambon, H.; Galarneau, A.; Plee, D.; Fajula, F. Textural control of micelle-templated mesoporous silicates: The effects of co-surfactants and alkalinity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Di, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Hyaluronic acid and carbon dots-gated hollow mesoporous silica for redox and enzyme-triggered targeted drug delivery and bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dineshkumar, S.; Raj, A.; Srivastava, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Pasha, S.S.; Kachwal, V.; Fageria, L.; Chowdhury, R.; Laskar, I.R. Facile Incorporation of “Aggregation-Induced Emission”-Active Conjugated Polymer into Mesoporous Silica Hollow Nanospheres: Synthesis, Characterization, Photophysical Studies, and Application in Bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31270–31282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochert, A.; Vernikouskaya, I.; Pascher, F.; Rasche, V.; Lindén, M. Cargo-influences on the biodistribution of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as studied by quantitative 19F-magnetic resonance imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Lai, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Ren, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, R.; Ma, G.; et al. Multi-shelled hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6749–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, J. Hollow-Structured Mesoporous Materials: Chemical Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3176–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hsu, B.Y.W.; Ren, C.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Silica-based nanocapsules: Synthesis, structure control and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ge, J.; Yin, Y. Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2867–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.-R.; Shi, J.-L. Construction of Homogenous/Heterogeneous Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanostructures by Silica-Etching Chemistry: Principles, Synthesis, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.K.; Lee, S.S.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Ying, J.Y. Nanoparticle Architectures Templated by SiO2/Fe2O3 Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.; Yu, J.H.; Kim, B.C.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Shin, C.-H.; Park, J.-G.; Kim, J.; et al. Magnetic Fluorescent Delivery Vehicle Using Uniform Mesoporous Silica Spheres Embedded with Monodisperse Magnetic and Semiconductor Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 688–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, S.C.; Li, G.H. Fe3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell Nanoparticles: The Silica Coating Regulations with a Single Core for Different Core Sizes and Shell Thicknesses. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4572–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lang, M.; Shi, J. Uniform Rattle-type Hollow Magnetic Mesoporous Spheres as Drug Delivery Carriers and their Sustained-Release Property. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, J. Fabrication of uniform hollow mesoporous silica spheres and ellipsoids of tunable size through a facile hard-templating route. J. Mater. Chem 2009, 19, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, A.; Aznar, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. New Advances in in vivo Applications of Gated Mesoporous Silica as Drug Delivery Nanocarriers. Small 2020, 16, 1902242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brühwiler, D. Postsynthetic functionalization of mesoporous silica. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.H.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Reactive Vinyl-Functionalized MCM-41: Probing the Internal Pore Structure by a Bromination Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 4090–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macquarrie, D.J. Direct preparation of organically modified MCM-type materials. Preparation and characterisation of aminopropyl–MCM and 2-cyanoethyl–MCM. Chem. Commun. 1996, 16, 1961–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauvel, A.; Renard, G.; Brunel, D. Monoglyceride Synthesis by Heterogeneous Catalysis Using MCM-41 Type Silicas Functionalized with Amino Groups. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, R.; Xiao, F. Distinguishing the Silanol Groups in the Mesoporous Molecular Sieve MCM-41. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 34, 2694–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, N.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, Y. Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 2003, 421, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, N.; Serrano, E.; Rico, M.; Balu, A.M.; Losada, E.; Luque, R.; Garcia-Martinez, J. Incorporation of chemical functionalities in the framework of mesoporous silica. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9024–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Landry, C.C. Diffusion-Based Deprotection in Mesoporous Materials: A Strategy for Differential Functionalization of Porous Silica Particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9674–9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.D.; Seki, T.; Goldston, J.F.; Pruski, M.; Crudden, C.M. Selective functionalization of the mesopores of SBA-15. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Fröba, M. Silica-Based Mesoporous Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Inagaki, S. Self-Organization of Organosilica Solids with Molecular-Scale and Mesoscale Periodicities. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, K.J.; Loy, D.A. Bridged Polysilsesquioxanes. Molecular-Engineered Hybrid Organic−Inorganic Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3306–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoshita, N.; Tani, T.; Inagaki, S. Syntheses, properties and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilicas prepared from bridged organosilane precursors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, A.; Esquivel, D.; Arce, L.; Romero-Salguero, F.J.; Van Der Voort, P.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Válcarcel, M. Evaluation of phenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica as a stationary phase for solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1370, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Bu, W.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Cai, W.; Shi, J. Engineering of inorganic nanoparticles as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7438–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, X. Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, T.-H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Cheon, J. Recent advances in magnetic nanoparticle-based multi-modal imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4501–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.M.L.; Kim, J.S.; Rieter, W.J.; An, H.; Lin, W.; Lin, W. Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres as Highly Efficient MRI Contrast Agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2154–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Huang, W.-Y.; Davies, G.-L. Location-tuned relaxivity in Gd-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22848–22850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, H. Core–Shell-Type Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites for Bioimaging and Therapeutic Agent Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Ai, H.; Gao, J. Geometrically confined ultrasmall gadolinium oxide nanoparticles boost the T1 contrast ability. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3768–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellico, J.; Ellis, C.M.; Davis, J.J. Nanoparticle-Based Paramagnetic Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 1845637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillet-Nicolas, R.; Laprise-Pelletier, M.; Nair, M.M.; Chevallier, P.; Lagueux, J.; Gossuin, Y.; Laurent, S.; Kleitz, F.; Fortin, M.A. Manganese-impregnated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for signal enhancement in MRI cell labelling studies. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11499–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-Y.; Pellico, J.; Khrapitchev, A.A.; Sibson, N.R.; Davis, J.J. Dy-DOTA integrated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as promising ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21041–21045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xu, F.; Qu, H.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Shao, Y. Dysprosium-doped iron oxide nanoparticles boosting spin–spin relaxation: A computational and experimental study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 11883–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Arena, F.; Gianolio, E.; Boffa, C.; Di Gregorio, E.; Stefania, R.; Orio, L.; Baroni, S.; Aime, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with fluorescent and MRI reporters for the visualization of murine tumors overexpressing αvβ3 receptors. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7094–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, N.; Wang, R.; Huang, G.; Zhu, J.; He, D. A versatile theranostic nanoplatform based on mesoporous silica. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.-H.; Lin, H.-M. Preparation and identification of multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo dual-mode imaging, theranostics, and targeted tracking. Biomaterials 2015, 46, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoucha, M.; Béliveau, É.; Kleitz, F.; Calon, F.; Fortin, M.-A. Antibody-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for brain microvessel endothelial cell targeting. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7721–7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.M.; Pellico, J.; Davis, J.J. Magnetic Nanoparticles Supporting Bio-responsive T1/T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Materials 2019, 12, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Yin, Q.; Lu, L. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cai, Z.; Liao, N.; Lan, S.; Wu, M.; Sun, H.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X. pH/hypoxia programmable triggered cancer photo-chemotherapy based on a semiconducting polymer dot hybridized mesoporous silica framework. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7390–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Y. pH-Responsive polyelectrolyte coated gadolinium oxide-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Gd2O3@MSNs) for synergistic drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6840–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellico, J.; Ellis, C.M.; Miller, J.; Davis, J.J. Water gated contrast switching with polymer–silica hybrid nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8540–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, G.; Si, Y.; Yang, H.; Bai, G.; Yang, C.; Zhong, K.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; et al. Effective pH-Activated Theranostic Platform for Synchronous Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnosis and Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31114–31123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, G.-L.; Kramberger, I.; Davis, J.J. Environmentally responsive MRI contrast agents. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9704–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.H.; Zink, J.I. A Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Platform for Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound-Stimulated Cargo Delivery with Controllable Location, Time, and Dose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17670–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, K.; Bhattacharya, K.; Sen, D.; Kaushik, S.D.; Biswas, J.; Lodha, S.; Gogoi, B.; Buragohain, A.K.; Kockenberger, W.; Deb, P. Solvent evaporation driven entrapment of magnetic nanoparticles in mesoporous frame for designing a highly efficient MRI contrast probe. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, D.; Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Chemical Synthesis and Assembly of Uniformly Sized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Medical Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, K.R.; Ring, H.L.; Etheridge, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Shao, Q.; Klein, N.D.; Szlag, V.M.; Chung, C.; Reineke, T.M.; et al. Predictable Heating and Positive MRI Contrast from a Mesoporous Silica-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticle. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2172–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zeng, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, F.; Feng, J.; Shi, J. Core/Shell Structured Hollow Mesoporous Nanocapsules: A Potential Platform for Simultaneous Cell Imaging and Anticancer Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6001–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, M.; Meyer, F.; Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, C.; Rabineau, M.; Adam, A.; Ramirez, P.D.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Mertz, D. Design of hybrid protein-coated magnetic core-mesoporous silica shell nanocomposites for MRI and drug release assessed in a 3D tumor cell model. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 174001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.; Lu, M.; Shao, D.; Yue, J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Li, M.; He, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Shape-controlled magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for magnetically-mediated suicide gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials 2018, 154, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, F.; Grisendi, G.; Spano, C.; Golinelli, G.; Recchia, A.; Rovesti, G.; Orsi, G.; Veronesi, E.; Horwitz, E.M.; Dominici, M. Inducible Caspase9-mediated suicide gene for MSC-based cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaranti, M.; Cojocaru, E.; Banerjee, S.; Banerji, U. Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Q. A theranostic nanocomposite system based on radial mesoporous silica hybridized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted magnetic field responsive chemotherapy of breast cancer. Rsc Adv. 2018, 8, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, W. VHPKQHR peptide modified magnetic mesoporous nanoparticles for MRI detection of atherosclerosis lesions. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.; Devi, K.S.P.; Dutta, S.; Maiti, T.K.; Pramanik, P.; Dhara, D. Biocompatible mesoporous silica-coated superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and MR imaging applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Wang, P.; Kou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C. Gadolinium(III)-Chelated Silica Nanospheres Integrating Chemotherapy and Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Treatment and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25014–25023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Momin, E.; Choi, J.; Yuan, K.; Zaidi, H.; Kim, J.; Park, M.; Lee, N.; McMahon, M.T.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; et al. Mesoporous Silica-Coated Hollow Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles as Positive T1 Contrast Agents for Labeling and MRI Tracking of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Fu, H.-J.; Ren, W.-w.; Li, X.-L.; Guo, L.-H. PSA targeted dual-modality manganese oxide–mesoporous silica nanoparticles for prostate cancer imaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Deng, G.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J. Fe3O4@mSiO2-FA-CuS-PEG nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and targeted chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of cancer cells. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 13456–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Deng, G.; Ge, R.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Lu, J. Tumor environment responsive degradable CuS@mSiO2@MnO2/DOX for MRI guided synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy and chemodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ge, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, P.; Shi, L.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Double-mesoporous core–shell nanosystems based on platinum nanoparticles functionalized with lanthanide complexes for in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 16012–16023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Hu, X.-X.; Zhang, X.-B. Dye-doped fluorescent silica nanoparticles for live cell and in vivo Bioimaging. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, B.G.; Kim, J. Functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bio-imaging applications. Wires Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ogawa, M.; Alford, R.; Choyke, P.L.; Urano, Y. New Strategies for Fluorescent Probe Design in Medical Diagnostic Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2620–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suratwala, T.; Gardlund, Z.; Davidson, K.; Uhlmann, D.R.; Watson, J.; Bonilla, S.; Peyghambarian, N. Silylated Coumarin Dyes in Sol−Gel Hosts. 2. Photostability and Sol−Gel Processing. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, J.W.; Yokoyama, K.; Yip, W.T. Solvent Effect on Mobility and Photostability of Organic Dyes Embedded inside Silica Sol−Gel Thin Films. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 6702–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-A.; Choi, S.; Jeon, S.M.; Yu, J. Silica nanoparticle stability in biological media revisited. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Li, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Biocompatibility, Biodistribution, and Drug-Delivery Efficiency of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy in Animals. Small 2010, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Hao, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The Shape Effect of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles on Biodistribution, Clearance, and Biocompatibility in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Ma, K.; Li, B.; Shen, S.; Jin, Y. A multifunctional mesoporous silica nanocomposite for targeted delivery, controlled release of doxorubicin and bioimaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 110, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidegger, S.; Gößl, D.; Schmidt, A.; Niedermayer, S.; Argyo, C.; Endres, S.; Bein, T.; Bourquin, C. Immune response to functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Li, D.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jin, J.; Yu, J. AIE Luminogen-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 3681–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreejith, S.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Graphene Oxide Wrapping on Squaraine-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17346–17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Dong, H.; Yin, K.; Huang, W.T.; Yang, R. In vivo Imaging of Hypoxia Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease by a Cytoplasmic Protein-Powered Fluorescence Cascade Amplifier. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5787–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Fluorescent Protein Capped Mesoporous Nanoparticles for Intracellular Drug Delivery and Imaging. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15378–15383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Chitosan-Gated Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for the Real-Time Monitoring of Drug Release. Langmuir 2020, 36, 6749–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress of Rare-Earth Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Optimization, and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-K.; Wang, H.-F.; Yan, X.-P. Engineering Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles for Biological Applications: From Biosensing/Bioimaging to Theranostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.G.; Sahu, S.; Yang, S.-T.; Sonkar, S.K.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; LeCroy, G.E.; Cao, L.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon “quantum” dots for optical bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhen, Z.; Tang, W.; Todd, T.; Chuang, Y.-J.; Wang, L.; Pan, Z.; Xie, J. Label-Free Luminescent Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Imaging and Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2013, 3, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Singh, R.K.; Kim, T.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Patel, K.D.; Kim, H.-W. Optical imaging and anticancer chemotherapy through carbon dot created hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Yang, L.; Lu, D.; Yan, X.; Cheng, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Carbon Dot-Incorporated PMO Nanoparticles as Versatile Platforms for the Design of Ratiometric Sensors, Multichannel Traceable Drug Delivery Vehicles, and Efficient Photocatalysts. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.-X.; Ge, X.; Shi, L.; Huang, W. Multicolor (Vis-NIR) mesoporous silica nanospheres linked with lanthanide complexes using 2-(5-bromothiophen)imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline for in vitro bioimaging. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, P.P.; Yang, X.X.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.Z. Real-time imaging of intracellular drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, N.; Umehara, Y.; Son, A.; Kondo, T.; Tanabe, K. Confinement of Singlet Oxygen Generated from Ruthenium Complex-Based Oxygen Sensor in the Pores of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 4168–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L. Recent Advances of Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles in Bioapplications. Nano Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan-Jun, L.; Hong-Wu, Z.; Meng, S.; Jiang-Shan, S.; Hai-Xia, F. A facile and effective method to prepare long-persistent phosphorescent nanospheres and its potential application for in vivo imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24713–24720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Maudgal, R.; Zhang, H.; Han, G. In vivo Repeatedly Charging Near-Infrared-Emitting Mesoporous SiO2/ZnGa2O4:Cr3+ Persistent Luminescence Nanocomposites. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Sun, W.; Qin, R.; Li, D.; Feng, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. X-Ray-Induced Persistent Luminescence Promotes Ultrasensitive Imaging and Effective Inhibition of Orthotopic Hepatic Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Toni, A.M.; Habila, M.A.; Labis, J.P.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alhoshan, M.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Zhang, F. Design, synthesis and applications of core–shell, hollow core, and nanorattle multifunctional nanostructures. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2510–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wan, D.; Gong, J. PEGylated liposome coated QDs/mesoporous silica core-shell nanoparticles for molecular imaging. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3442–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Di, W.; Qin, W. Synthesis of mesoporous-silica-coated Gd2O3:Eu@silica particles as cell imaging and drug delivery agents. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 7443–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bu, W.; Pan, L.; Shi, J. NIR-Triggered Anticancer Drug Delivery by Upconverting Nanoparticles with Integrated Azobenzene-Modified Mesoporous Silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4375–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Shah, B.P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Lee, K.-B. Real-Time Monitoring of ATP-Responsive Drug Release Using Mesoporous-Silica-Coated Multicolor Upconversion Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5234–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-M.; Zhang, D.-D.; Fang, G.-Z.; Wang, S. Erythrocyte membrane bioinspired near-infrared persistent luminescence nanocarriers for in vivo long-circulating bioimaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 2018, 165, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Liu, J.-M.; Li, C.-Y.; Wang, D.; Lv, H.; Lv, S.-W.; Zhao, N.; Ma, H.; Wang, S. Bacterial Biofilm Bioinspired Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles with Gut-Oriented Drug Delivery for Colorectal Cancer Imaging and Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 36409–36419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, L.-J.; Yang, C.-X.; Yan, X.-P. pH-Driven Targeting Nanoprobe with Dual-Responsive Drug Release for Persistent Luminescence Imaging and Chemotherapy of Tumor. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; England, C.G.; Chen, F.; Cai, W. Positron emission tomography and nanotechnology: A dynamic duo for cancer theranostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 113, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, P.A.; Chen, F.; Goel, S.; Barnhart, T.E.; Nickles, R.J.; DeJesus, O.T.; Cai, W. Intrinsic and Stable Conjugation of Thiolated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Radioarsenic. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6772–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Chen, F.; Luan, S.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Shi, S.; Graves, S.A.; Ai, F.; Barnhart, T.E.; Theuer, C.P.; Cai, W. Engineering Intrinsically Zirconium-89 Radiolabeled Self-Destructing Mesoporous Silica Nanostructures for in vivo Biodistribution and Tumor Targeting Studies. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Nam, J.; Hong, H.; Xu, Y.; Moon, J.J. Positron Emission Tomography-Guided Photodynamic Therapy with Biodegradable Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12148–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, R.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, M.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lim, J.W.; Do, S.H.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Macrophage cell tracking PET imaging using mesoporous silica nanoparticles via in vivo bioorthogonal F-18 labeling. Biomaterials 2019, 199, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.O.; Kim, T.J.; Yu, J.H.; Rhee, S.; Zhao, W.; Ha, B.; Red-Horse, K.; Gambhir, S.S.; Pratx, G. Whole-body tracking of single cells via positron emission tomography. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T. Nano-Sized CT Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2641–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Xu, K.; Taratula, O.; Farsad, K. Applications of nanoparticles in biomedical imaging. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Nguyen, Q.T. Molecular imaging for cancer diagnosis and surgery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Singh, R.K.; Kim, T.-H.; Seo, J.-W.; Shin, U.S.; Chrzanowski, W.; Kim, H.-W. Triple Hit with Drug Carriers: pH- and Temperature-Responsive Theranostics for Multimodal Chemo- and Photothermal Therapy and Diagnostic Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8967–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, D.; Chang, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yue, J.; Yang, D.; Li, M.; Xu, Q.; Dong, W.-f. Janus Gold Nanoplatform for Synergetic Chemoradiotherapy and Computed Tomography Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12732–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfi-Sadabad, R.; Gonzalez-Fajardo, L.; Hargrove, D.; Ahmadi, B.; Munteanu, D.; Shahbazmohamadi, S.; Jay, M.; Lu, X. Contrast Agents: Engineering Multifunctional Gold Decorated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica/Tantalum Oxide Nanoparticles for Intraperitoneal Tumor-Specific Delivery (Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 4/2019). Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1970010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, M.; Xia, H.; Han, G. Enhancing Osteosarcoma Killing and CT Imaging Using Ultrahigh Drug Loading and NIR-Responsive Bismuth Sulfide@Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, C.; Bettoschi, A.; Garau, A.; Montis, R. Silica-based nanoparticles: A versatile tool for the development of efficient imaging agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4645–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Huxford-Phillips, R.C.; Lin, W. Silica-based nanoprobes for biomedical imaging and theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2673–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; You, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, F.; Li, N. Theranostic Nanoplatform: Triple-Modal Imaging-Guided Synergistic Cancer Therapy Based on Liposome-Conjugated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1963–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carniato, F.; Alberti, D.; Lapadula, A.; Martinelli, J.; Isidoro, C.; Geninatti Crich, S.; Tei, L. Multifunctional Gd-based mesoporous silica nanotheranostic for anticancer drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Sun, S.; Li, C.; Wu, L.; Hou, X.; Wu, P. Enriching Mn-Doped ZnSe Quantum Dots onto Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Enhanced Fluorescence/Magnetic Resonance Imaging Dual-Modal Bio-Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34060–34067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Niu, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Gu, B.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. 99mTc-conjugated manganese-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles for SPECT, pH-responsive MRI and anti-cancer drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19573–19580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Das, G.K.; Yang Tan, T.T. Engineering lanthanide-based materials for nanomedicine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2014, 20, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ma, P.a.; Hou, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Current advances in lanthanide ion (Ln3+)-based upconversion nanomaterials for drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1416–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shen, B.; Bu, W.; Chen, F.; He, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Peng, W.; Xiao, Q.; et al. A smart upconversion-based mesoporous silica nanotheranostic system for synergetic chemo-/radio-/photodynamic therapy and simultaneous MR/UCL imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8992–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Cui, Z.; Yang, S.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Han, X.; Fan, Q.; Qin, A.; Wang, T.; et al. Targeting Osteocytes to Attenuate Early Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis by Theranostic Upconversion Nanoparticles with Responsive Plumbagin Release. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7259–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Chan, H.-N.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.-W.; Wong, M.S. Amyloid-β Oligomer-Targeted Gadolinium-Based NIR/MR Dual-Modal Theranostic Nanoprobe for Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, L.; Ma, B.; Jin, D.; Dong, L.; Shi, L.; Li, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, W. Simultaneous realization of Hg2+ sensing, magnetic resonance imaging and upconversion luminescence in vitro and in vivo bioimaging based on hollow mesoporous silica coated UCNPs and ruthenium complex. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13877–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Yang, P.; He, F.; Gai, S.; Li, C.; Dai, Y.; Yang, G.; Lin, J. A Yolk-like Multifunctional Platform for Multimodal Imaging and Synergistic Therapy Triggered by a Single Near-Infrared Light. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, R.; Gong, S.; Shi, J.; Jiao, J.; Wong, K.-L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Su, Q. Magnetic-NIR Persistent Luminescent Dual-Modal ZGOCS@MSNs@Gd2O3 Core–Shell Nanoprobes For In vivo Imaging. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perton, F.; Tasso, M.; Muñoz Medina, G.A.; Ménard, M.; Blanco-Andujar, C.; Portiansky, E.; van Raap, M.B.F.; Bégin, D.; Meyer, F.; Begin-Colin, S.; et al. Fluorescent and magnetic stellate mesoporous silica for bimodal imaging and magnetic hyperthermia. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 16, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-J.; Chou, S.-W.; Shyue, J.-J.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hsiao, J.-K.; Chou, P.-T. A Versatile Theranostic Delivery Platform Integrating Magnetic Resonance Imaging/Computed Tomography, pH/cis-Diol Controlled Release, and Targeted Therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5809–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-G.; Han, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.-T.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Rerouting engineered metal-dependent shapes of mesoporous silica nanocontainers to biodegradable Janus-type (sphero-ellipsoid) nanoreactors for chemodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Ovejero Paredes, K.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Martínez-Ruíz, P.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Villalonga, R.; Filice, M. Hybrid Decorated Core@Shell Janus Nanoparticles as a Flexible Platform for Targeted Multimodal Molecular Bioimaging of Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31032–31043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-T.; Yang, X.-Q.; Zhang, X.-S.; Yan, D.-M.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-D. Facile Synthesis of Gold Nanospheres Modified by Positively Charged Mesoporous Silica, Loaded with Near-Infrared Fluorescent Dye, for in vivo X-ray Computed Tomography and Fluorescence Dual Mode Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17287–17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Hix, J.M.L.; Wiewiora, K.A.; Volk, M.C.; Kenyon, E.; Shuboni-Mulligan, D.D.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Kiupel, M.; Thomas, J.; Sempere, L.F.; et al. Tantalum oxide nanoparticles as versatile contrast agents for X-ray computed tomography. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 7720–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; Tao, Z. Biocompatibility of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2265–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Biocompatibility and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In vivo Bio-Safety Evaluations and Diagnostic/Therapeutic Applications of Chemically Designed Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarn, D.; Ashley, C.E.; Xue, M.; Carnes, E.C.; Zink, J.I.; Brinker, C.J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Nanocarriers: Biofunctionality and Biocompatibility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| MSNs Type | Morphological Structure | Pore Size (nm) | Surfactant in Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 2D hexagonal p6mm | 1.5–8 | CnTMA+ (n = 12–18) a | [19,20,21] |
| MCM-48 | 3D cubic Ia3d | 2–5 | CnTMA+ (n = 16) C16-12-16 | [22,23] |
| MCM-50 | Lamellar p2 | 2–5 | CnTMA+ (n = 16) | [19,24] |
| SBA-3 | 2D hexagonal p6mm | 2–4 | CnTMA+ (n = 14–18) | [19,25] |
| SBA-15 | 2D hexagonal p6mm | 5–10 | Gemini surfactants b | [26,27,28] |
| KIT-5 | Cubic Fm3m | ∼9.3 | F–127 c | [29,30] |
| FDU-12 | Cubic Fm3m | 10–27 | F–127 | [31,32] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, D.; Ellis, C.M.; Davis, J.J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Bioimaging. Materials 2020, 13, 3795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173795
Yuan D, Ellis CM, Davis JJ. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Bioimaging. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173795
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Daohe, Connor M. Ellis, and Jason J. Davis. 2020. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Bioimaging" Materials 13, no. 17: 3795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173795
APA StyleYuan, D., Ellis, C. M., & Davis, J. J. (2020). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Bioimaging. Materials, 13(17), 3795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173795