Comparison of Test Setups for the Experimental Evaluation of the Primary Fixation Stability of Acetabular Cups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
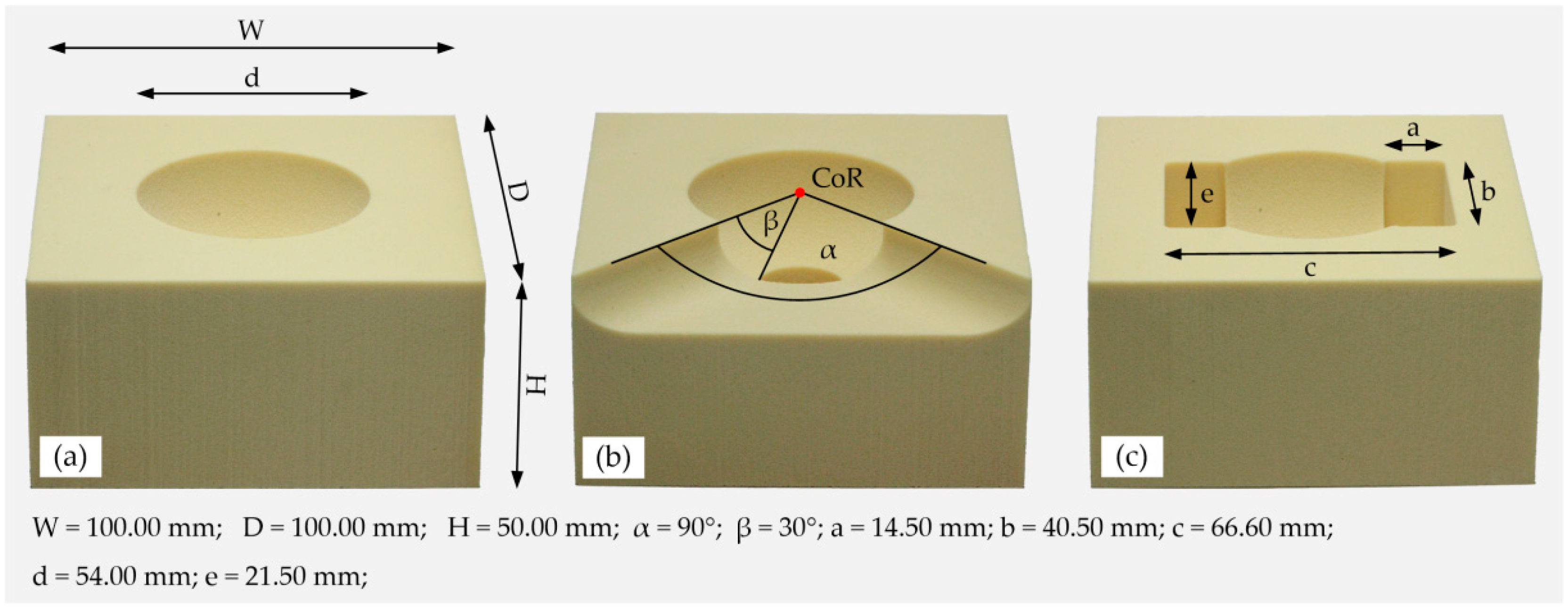
2.1. Preparation of the Specimens
2.2. Experimental Setup
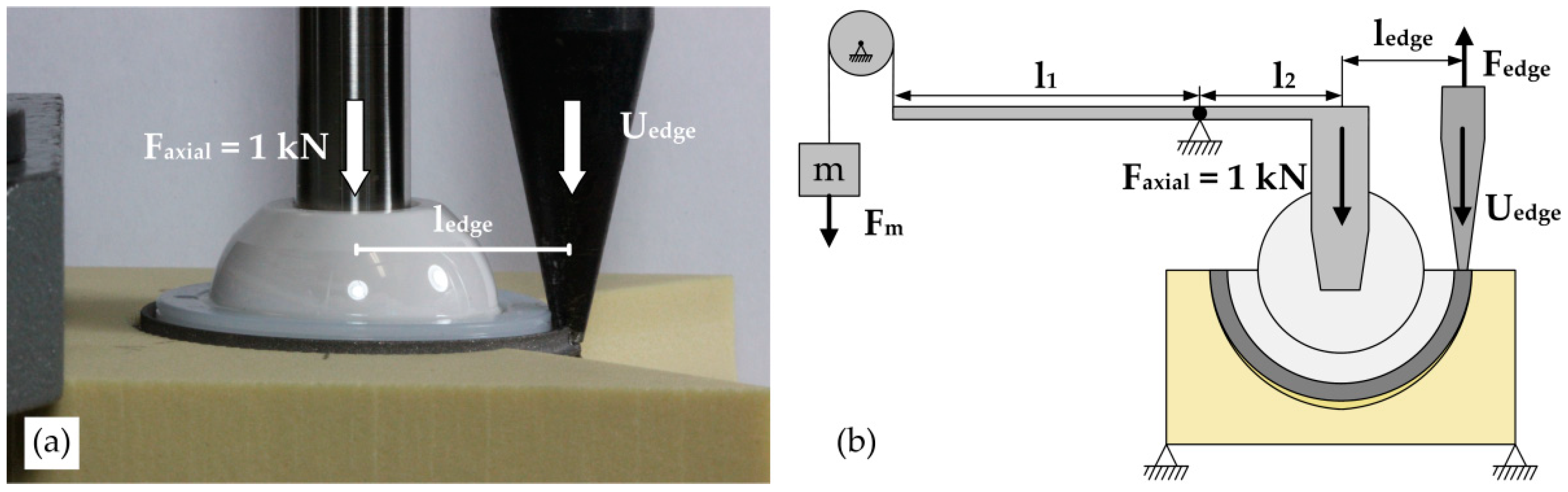
2.2.1. Push-In Procedure
2.2.2. Lever-Out Method
2.2.3. Edge-Load Method
2.2.4. Analyzed Parameters
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
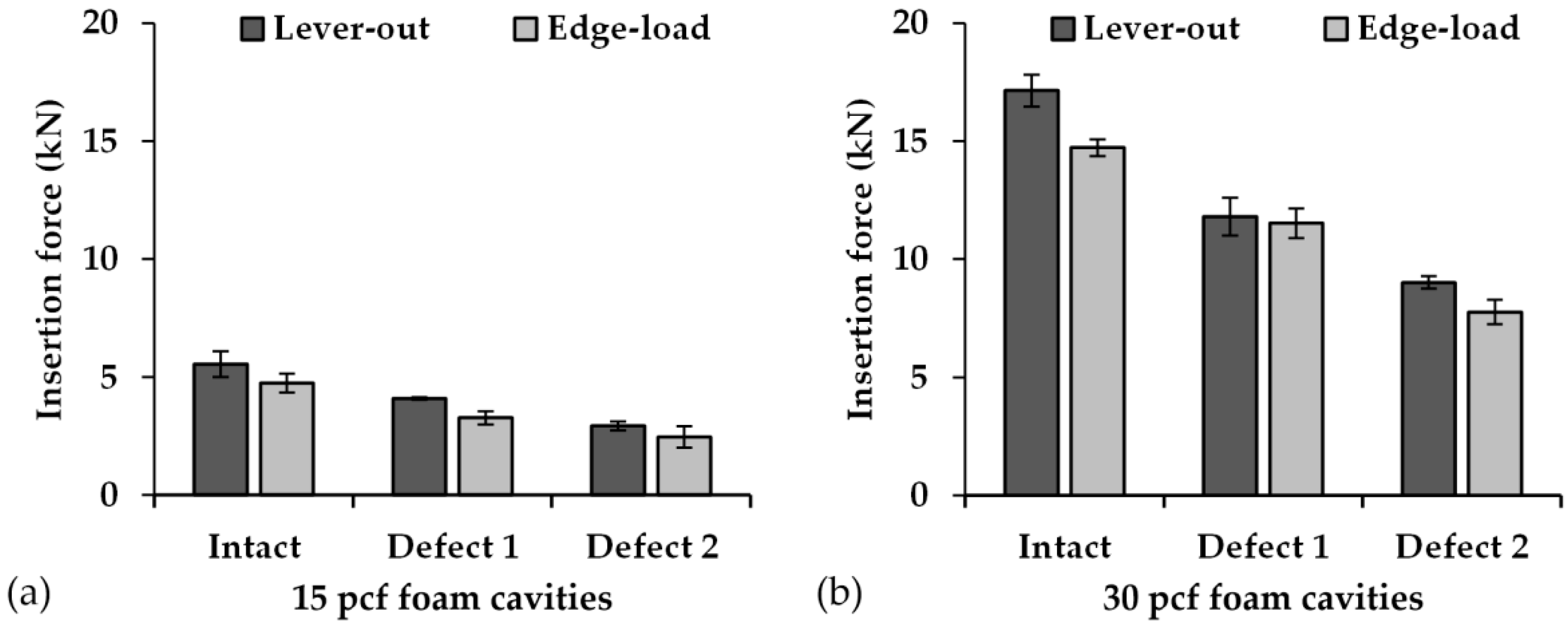
3.1. Insertion Forces
3.2. Lever-Out and Tilting Moments
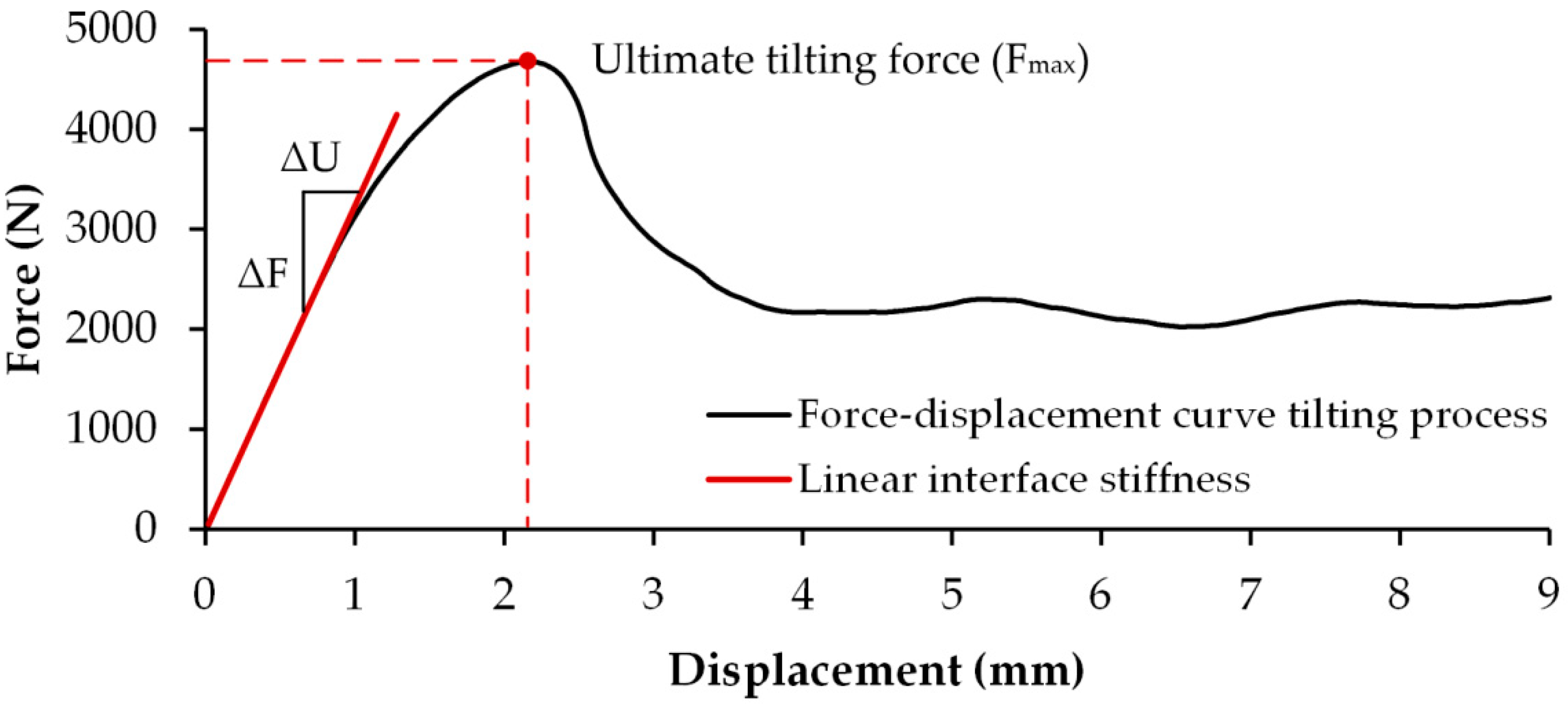
3.3. Interface Stiffness
3.4. Qualitative Characterization of the Two Test Methods
3.5. Force–Displacement Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulze, C.; Morgenroth, R.; Bader, R.; Kluess, D.; Haas, H. Fixation Stability of Uncemented Acetabular Cups with Respect to Different Bone Defect Sizes. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, E.; Stuchin, S.A.; Kummer, F.J. Stability of press-fit acetabular cups. J. Arthroplast. 1992, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.J.; Jinnah, R.H.; Wilson, V.D.; Hungerford, D.S. The initial stability of uncemented acetabular components. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1992, 74, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, J.R.; Callaghan, J.J.; Pedersen, D.R.; Brown, T.D. Areas of contact and extent of gaps with implantation of oversized acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 298, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Brown, T.D.; Pedersen, D.R.; Callaghan, J.J. Reamed surface topography and component seating in press-fit cementless acetabular fixation. J. Arthroplast. 1995, 10, S14–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, W.; Carlsson, L.V.; Charnley, G.J.; Jacobsson, C.; Johansson, C.B. Inaccuracy of acetabular reaming under surgical conditions. J. Arthroplast. 1999, 14, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.; Wilson, D.C.; Jando, V.T.; Masri, B.A.; Duncan, C.P.; Wilson, D.R. Accuracy of cut-off acetabular reamers for minimally invasive THA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 453, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baad-Hansen, T.; Kold, S.; Fledelius, W.; Nielsen, P.T.; Soballe, K. Alteration of the Hip Joint Centre during Acetabular Reaming. HIP Int. 2007, 17, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, M.; Rama, R.K.B.S.; Ganapathi, M.; Nuño, N.; Winzenrieth, R.; Vendittoli, P.-A. Factors affecting acetabular bone loss during primary hip arthroplasty—A quantitative analysis using computer simulation. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, D.; Rathay, A.; Teufel, S.; Ellenrieder, M.; Zietz, C.; Sander, M.; Bader, R. Experimental analysis of insertion torques and forces of threaded and press-fit acetabular cups by means of ex vivo and in vivo measurements. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2017, 19, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Messer-Hannemann, P.; Bätz, J.; Lampe, F.; Klein, A.; Püschel, K.; Campbell, G.M.; Morlock, M. The influence of cavity preparation and press-fit cup implantation on restoring the hip rotation center. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 63, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasty, M.; Anderson, M.J.; Harris, W.H. Total hip replacement for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1995, 311, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.M.; Engh, C.A.; Hopper, R.H.; McAuley, J.P. Acetabular revision with use of a bilobed component inserted without cement in patients who have acetabular bone-stock deficiency. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2000, 82, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporer, S.M.; Paprosky, W.G.; O’Rourke, M.R. Managing bone loss in acetabular revision. Instr. Course Lect. 2006, 55, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fehring, K.A.; Owen, J.R.; Kurdin, A.A.; Wayne, J.S.; Jiranek, W.A. Initial stability of press-fit acetabular components under rotational forces. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißmann, V.; Ramskogler, T.; Schulze, C.; Bader, R.; Hansmann, H. Influence of Synthetic Bone Substitutes on the Anchorage Behavior of Open-Porous Acetabular Cup. Materials 2019, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, W.; Carlsson, L.V.; Charnley, G.J.; Jacobsson, C.M. Press-fit acetabular cup fixation: Principles and testing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 1999, 213, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, A.; Scheller, G.; Schwarz, M. Primärstabilität zementfreier Press-fit-Hüftpfannen. In-vitro-Auskippversuche. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 44, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.; Simnacher, M.; Scheller, G. Primärstabilität von Press-fit Hüftpfannen--eine in-vitro Studie. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 50, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, U.; Simnacher, M.; Scheller, G.; Scharf, H.-P. Der Einfluss von Oberflächenmerkmalen auf die Primärstabilität einer zementfreien Hüftpfanne: Eine mechanische In-vitro-Untersuchung. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 52, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cann, S.; Galland, A.; Rosa, B.; Le Corroller, T.; Pithioux, M.; Argenson, J.-N.; Chabrand, P.; Parratte, S. Does surface roughness influence the primary stability of acetabular cups? A numerical and experimental biomechanical evaluation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosnier, E.A.; Keogh, P.S.; Miles, A.W. A novel method to assess primary stability of press-fit acetabular cups. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2014, 228, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosnier, E.A.; Keogh, P.S.; Miles, A.W. The effect of dynamic hip motion on the micromotion of press-fit acetabular cups in six degrees of freedom. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goossens, Q.; Pastrav, L.C.; Mulier, M.; Desmet, W.; Vander Sloten, J.; Denis, K. Two Different Methods to Measure the Stability of Acetabular Implants: A Comparison Using Artificial Acetabular Models. Sensors 2020, 20, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.M.; Meakins, S.; Morlock, M.M.; Parsons, P.; Hardaker, C.; Flett, M.; Isaac, G. Deformation of press-fitted metallic resurfacing cups. Part 1: Experimental simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, A.; Jin, Z.M.; Donn, A.; Morlock, M.M.; Isaac, G. Deformation of press-fitted metallic resurfacing cups. Part 2: Finite element simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meding, J.B.; Small, S.R.; Jones, M.E.; Berend, M.E.; Ritter, M.A. Acetabular cup design influences deformational response in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antoniades, G.; Smith, E.J.; Deakin, A.H.; Wearing, S.C.; Sarungi, M. Primary stability of two uncementedacetabular components of different geometry: Hemispherical or peripherallyenhanced? Bone Jt. Res. 2013, 2, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.; Bosc, R.; Sailhan, F.; Vayron, R.; Haiat, G. Ex vivo estimation of cementless acetabular cup stability using an impact hammer. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, C.; Vogel, D.; Sander, M.; Bader, R. Calibration of crushable foam plasticity models for synthetic bone material for use in finite element analysis of acetabular cup deformation and primary stability. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 22, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.H.; Armstrong, L.C.; Owen, J.R.; Wayne, J.S.; Jiranek, W.A. Does Increased Coefficient of Friction of Highly Porous Metal Increase Initial Stability at the Acetabular Interface? J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiehl, J.B.; MacMillan, E.; Skrade, D.A. Mechanical stability of porous-coated acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 1991, 6, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, P.G.; Lawrence, J.; Paprosky, W.G.; Patwardhan, A.G.; Sartori, M. Acetabular micromotion as a measure of initial implant stability in primary hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 1992, 7, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, T.A.; Khadem, M.; Wood, T.J.; Dunning, C.E.; Degen, R.; Lanting, B.A. Comparison of trans-cortical and cancellous screws to press fit for acetabular shell fixation in total hip arthroplasty: A cadaveric study. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 69, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißmann, V.; Boss, C.; Bader, R.; Hansmann, H. A novel approach to determine primary stability of acetabular press-fit cups. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weißmann, V.; Boss, C.; Schulze, C.; Hansmann, H.; Bader, R. Experimental Characterization of the Primary Stability of Acetabular Press-Fit Cups with Open-Porous Load-Bearing Structures on the Surface Layer. Metals 2018, 8, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, C.; Fritsche, A.; Kluess, D.; Mittelmeier, W.; Bader, R. Einfluss der Formgebung von künstlichen Hüftpfannen auf die primäre Verankerungsfestigkeit: Eine experimentelle und numerische Analyse. Der Orthop. 2009, 38, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souffrant, R.; Zietz, C.; Fritsche, A.; Kluess, D.; Mittelmeier, W.; Bader, R. Advanced material modelling in numerical simulation of primary acetabular press-fit cup stability. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 15, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, G.; Bender, A.; Dymke, J.; Duda, G.; Damm, P. Standardized Loads Acting in Hip Implants. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockett, C.; Williams, S.; Jin, Z.; Isaac, G.; Fisher, J. Friction of total hip replacements with different bearings and loading conditions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 81, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, P.; Bender, A.; Duda, G.; Bergmann, G. In vivo measured joint friction in hip implants during walking after a short rest. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markel, D.C.; Hora, N.; Grimm, M. Press-fit stability of uncemented hemispheric acetabular components: A comparison of three porous coating systems. Int. Orthop. 2002, 26, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saleh, K.J.; Bear, B.; Bostrom, M.; Wright, T.; Sculco, T.P. Initial stability of press-fit acetabular components: An in vitro biomechanical study. Am. J. Orthop. 2008, 37, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bürkner, A.; Fottner, A.; Lichtinger, T.; Teske, W.; Vogel, T.; Jansson, V.; von Schulze Pellengahr, C. Primary stability of cementless threaded acetabular cups at first implantation and in the case of revision regarding micromotions as indicators. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 57, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa, M.; Tanino, H.; Abo, M.; Kakunai, S.; Banks, S.A. Effect of acetabular component anteversion on dislocation mechanisms in total hip arthroplasty. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1810–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Kluess, D.; Kaehler, M.; Grawe, R.; Rachholz, R.; Souffrant, R.; Zierath, J.; Bader, R.; Woernle, C. A Novel Approach for Dynamic Testing of Total Hip Dislocation under Physiological Conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.; Scholz, R.; Steinhauser, E.; Busch, R.; Mittelmeier, W. Methode zur Evaluierung von Einflussfaktoren auf die Luxationsstabilität von künstlichen Hüftgelenken. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 49, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluess, D.; Martin, H.; Mittelmeier, W.; Schmitz, K.-P.; Bader, R. Influence of femoral head size on impingement, dislocation and stress distribution in total hip replacement. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.D.; Callaghan, J.J. Impingement in Total Hip Replacement: Mechanisms and Consequences. Curr. Orthop. 2008, 22, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, C.; Görgner, A.; Klöhn, C.; Scholz, R.; Voigt, C. Shear stress and von Mises stress distributions in the periphery of an embedded acetabular cup implant during impingement. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 62, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidukewych, G.J.; Jacofsky, D.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Intraoperative fractures of the acetabulum during primary total hip arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2006, 88, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Goriainov, V.; Jones, A.; Briscoe, A.; New, A.; Dunlop, D. Do the cup surface properties influence the initial stability? J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, T.; Kaku, N.; Hara, K.; Tsumura, H. Initial stability of cementless acetabular cups: Press-fit and screw fixation interaction--an in vitro biomechanical study. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustke, K.A.; Levering, M.F.; Miranda, M.A. Use of jumbo cups for revision of acetabulae with large bony defects. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, T.; Faschingbauer, M.; Lutz, B.; Bieger, R.; Reichel, H. Azetabuläre Revision: Rekonstruktion kavitärer und segmentaler Defekte unter besonderer Berücksichtigung modularer hoch poröser Pfannensysteme. Z. Orthop. Unf. 2018, 156, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, K.-H.; Zurfluh, B.; Morscher, E.W. Load transfer and fixation mode of press-fit acetabular sockets. J. Arthroplast. 2002, 17, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olory, B.; Havet, E.; Gabrion, A.; Vernois, J.; Mertl, P. Comparative in vitro assessment of the primary stability of cementless press-fit acetabular cups. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2004, 70, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini, R.M.; Meyer, C.; Buckley, C.A.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Mechanical stability of novel highly porous metal acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.R.; Berend, M.E.; Howard, L.A.; Rogge, R.D.; Buckley, C.A.; Ritter, M.A. High initial stability in porous titanium acetabular cups: A biomechanical study. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleani, M.; Fognani, R.; Toni, A. Initial stability of a cementless acetabular cup design: Experimental investigation on the effect of adding fins to the rim of the cup. Artif. Organs 2001, 25, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.O.; Noble, P.C. Effect of design on the initial stability of press-fit cups in the presence of acetabular rim defects: Experimental evaluation of the effect of adding circumferential fins. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Von Schulze Pellengahr, C.; von Engelhardt, L.V.; Wegener, B.; Müller, P.E.; Fottner, A.; Weber, P.; Ackermann, O.; Lahner, M.; Teske, W. Does osteoporosis reduce the primary tilting stability of cementless acetabular cups? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvert, K.L.; Trumble, K.P.; Webster, T.J.; Kirkpatrick, L.A. Characterization of commercial rigid polyurethane foams used as bone analogs for implant testing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szivek, J.A.; Thomas, M.; Benjamin, J.B. Technical note. Characterization of a synthetic foam as a model for human cancellous bone. J. Appl. Biomater. 1993, 4, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szivek, J.A.; Thompson, J.D.; Benjamin, J.B. Characterization of three formulations of a synthetic foam as models for a range of human cancellous bone types. J. Appl. Biomater. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. 1995, 6, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.S.; McCarthy, I.D.; Lidgren, L.; Ryd, L. Compressive and shear properties of commercially available polyurethane foams. J. Biomech. Eng. 2003, 125, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirouche, F.; Solitro, G.; Broviak, S.; Gonzalez, M.; Goldstein, W.; Barmada, R. Factors influencing initial cup stability in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Denotation | Test Method | Foam Density (pcf) | Cavity Type | Measured Diameter (mm) | Press-Fit (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cup | Cavity | |||||
| M1_15_I | Lever-out (Method 1) | 15 | Intact | 55.30 ± 0.06 | 54.31 ± 0.07 | 0.99± 0.08 |
| M1_15_D1 | Defect 1 | 54.22 ± 0.07 | 1.07 ± 0.06 | |||
| M1_15_D2 | Defect 2 | 54.31 ± 0.05 | 0.98 ± 0.08 | |||
| M1_30_I | 30 | Intact | 54.11 ± 0.02 | 1.18 ± 0.07 | ||
| M1_30_D1 | Defect 1 | 54.07 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.10 | |||
| M1_30_D2 | Defect 2 | 54.02 ± 0.02 | 1.28 ± 0.07 | |||
| M2_15_I | Edge-load (Method 2) | 15 | Intact | 54.32 ± 0.08 | 0.97 ± 0.11 | |
| M2_15_D1 | Defect 1 | 54.22 ± 0.04 | 1.07 ± 0.07 | |||
| M2_15_D2 | Defect 2 | 54.33 ± 0.05 | 0.96 ± 0.10 | |||
| M2_30_I | 30 | Intact | 54.12 ± 0.05 | 1.18 ± 0.06 | ||
| M2_30_D1 | Defect 1 | 54.05 ± 0.03 | 1.24 ± 0.08 | |||
| M2_30_D2 | Defect 2 | 54.02 ± 0.03 | 1.28 ± 0.07 | |||
| Method | Cavity Type | Foam Density | Lever Out | Edge Load | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Defect 1 | Defect 2 | Intact | Defect 1 | Defect 2 | ||||||||
| 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | |||
| Lever Out (Method 1) | Intact | 15 pcf | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 30 pcf | <0.0001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 1 | 15 pcf | 0.0002 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | 0.0052 | 0.0225 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 2 | 15 pcf | 0.0001 | - | 0.2841 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | 0.0004 | - | 0.3287 | 0.0055 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Edge Load (Method 2) | Intact | 15 pcf | 0.0002 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Defect 1 | 15 pcf | - | - | 0.0261 | - | - | - | 0.1812 | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | - | - | 0.0049 | - | - | - | 0.0234 | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 2 | 15 pcf | - | - | - | - | 0.0011 | - | <0.0001 | 0.1327 | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0001 | - | - | 0.0338 | 0.031 | - | ||
| Method | Cavity Type | Foam Density | Lever Out | Edge Load | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Defect 1 | Defect 2 | Intact | Defect 1 | Defect 2 | ||||||||
| 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | 15 pcf | 30 pcf | |||
| Lever Out (Method 1) | Intact | 15 pcf | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 30 pcf | 0.0277 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 1 | 15 pcf | 0.9862 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | 0.0162 | 0.9991 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 2 | 15 pcf | 0.2369 | - | 0.6694 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | 0.0050 | - | 0.3086 | 0.0128 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Edge Load (Method 2) | Intact | 15 pcf | 0.1158 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Defect 1 | 15 pcf | - | - | 0.0207 | - | - | - | 0.8395 | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | - | - | 0.0115 | - | - | - | 0.0135 | - | - | - | ||
| Defect 2 | 15 pcf | - | - | - | - | 0.0132 | - | 0.2703 | 0.0844 | - | - | - | |
| 30 pcf | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0007 | - | - | 0.0362 | 0.0066 | - | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schulze, C.; Vogel, D.; Mallow, S.; Bader, R. Comparison of Test Setups for the Experimental Evaluation of the Primary Fixation Stability of Acetabular Cups. Materials 2020, 13, 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183982
Schulze C, Vogel D, Mallow S, Bader R. Comparison of Test Setups for the Experimental Evaluation of the Primary Fixation Stability of Acetabular Cups. Materials. 2020; 13(18):3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183982
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchulze, Christian, Danny Vogel, Sina Mallow, and Rainer Bader. 2020. "Comparison of Test Setups for the Experimental Evaluation of the Primary Fixation Stability of Acetabular Cups" Materials 13, no. 18: 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183982
APA StyleSchulze, C., Vogel, D., Mallow, S., & Bader, R. (2020). Comparison of Test Setups for the Experimental Evaluation of the Primary Fixation Stability of Acetabular Cups. Materials, 13(18), 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183982





