Effects of Adding Neutralized Red Mud on the Hydration Properties of Cement Paste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Plan
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
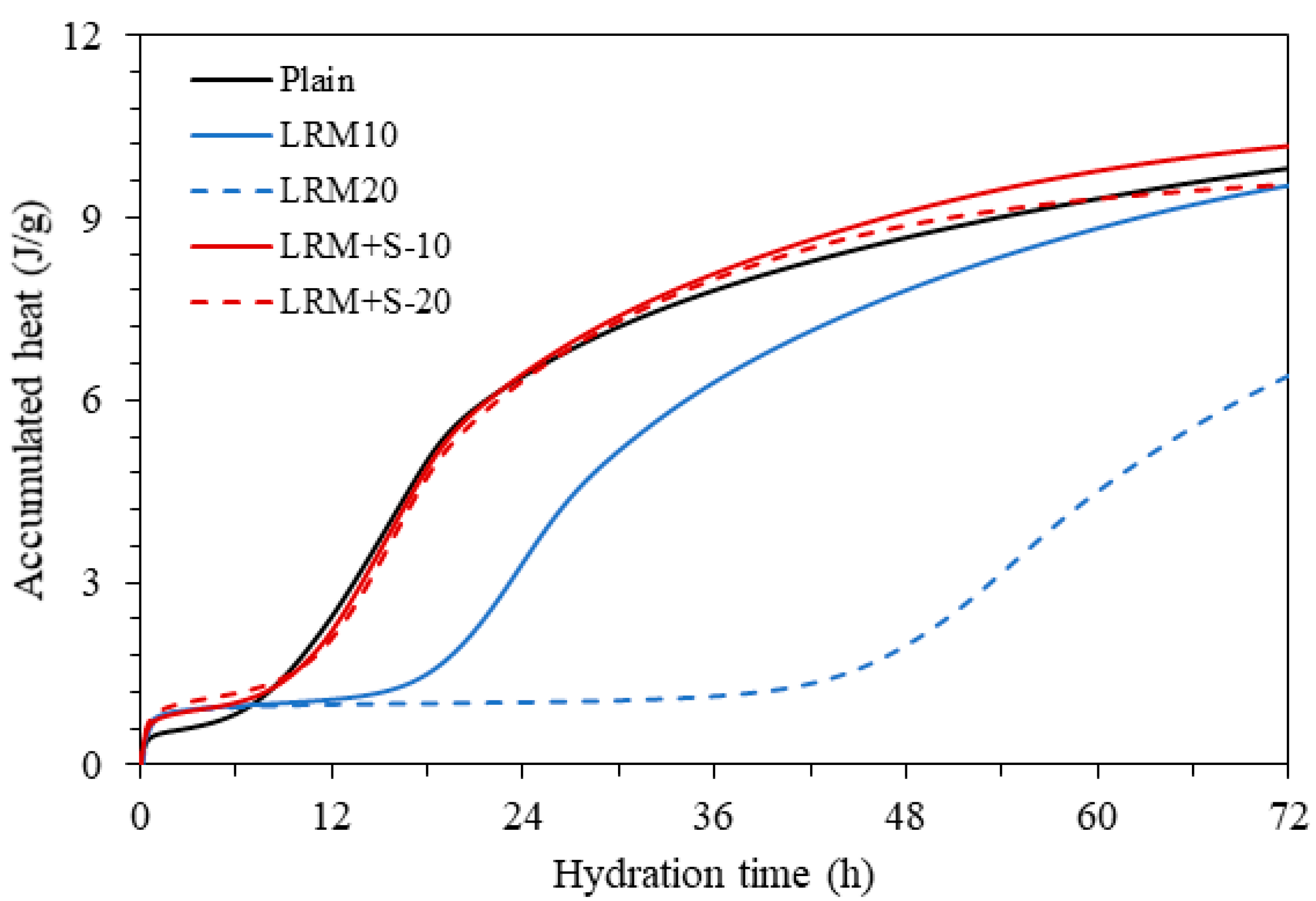
3.1. Heat of Hydration
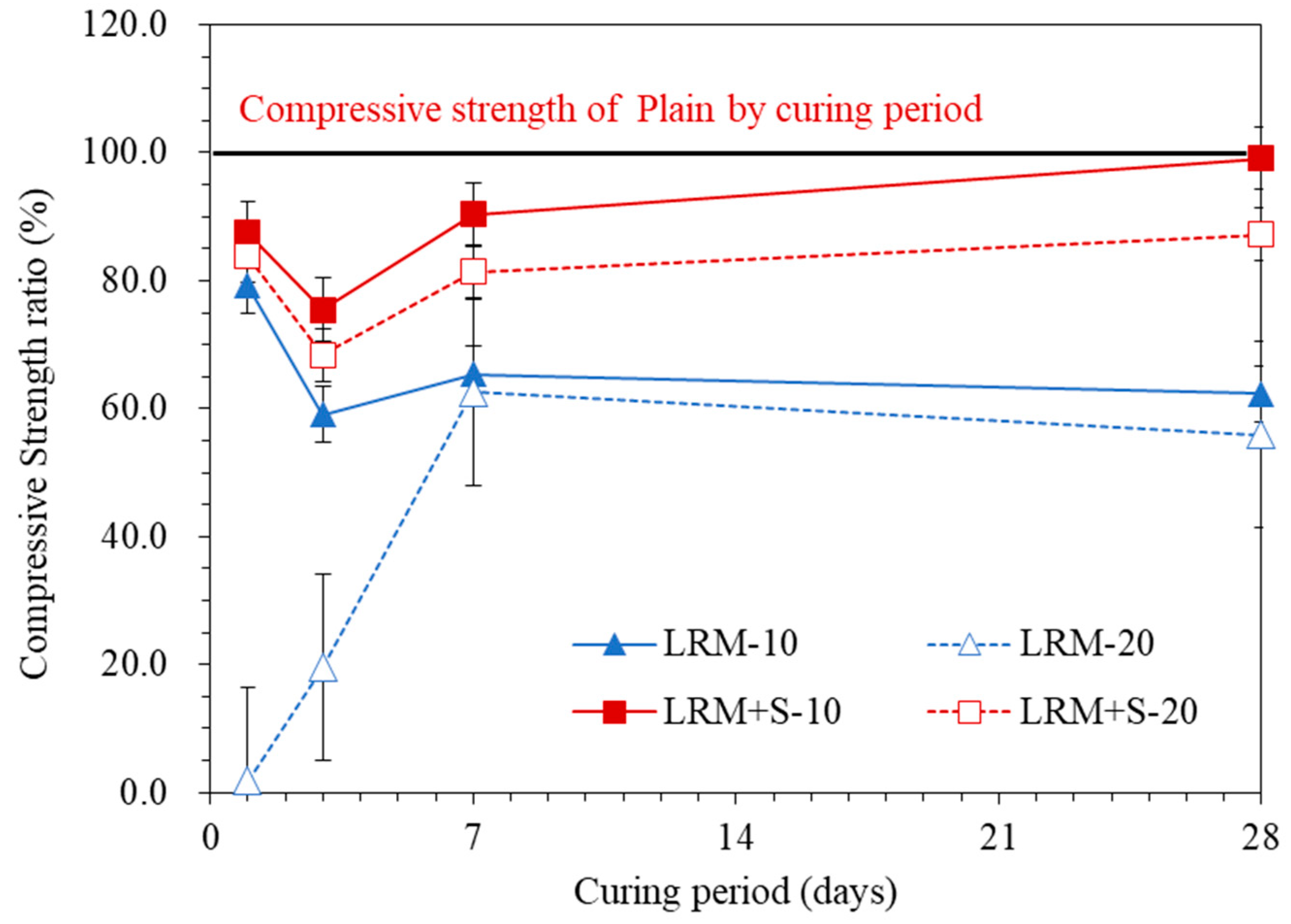
3.2. Compressive Strength
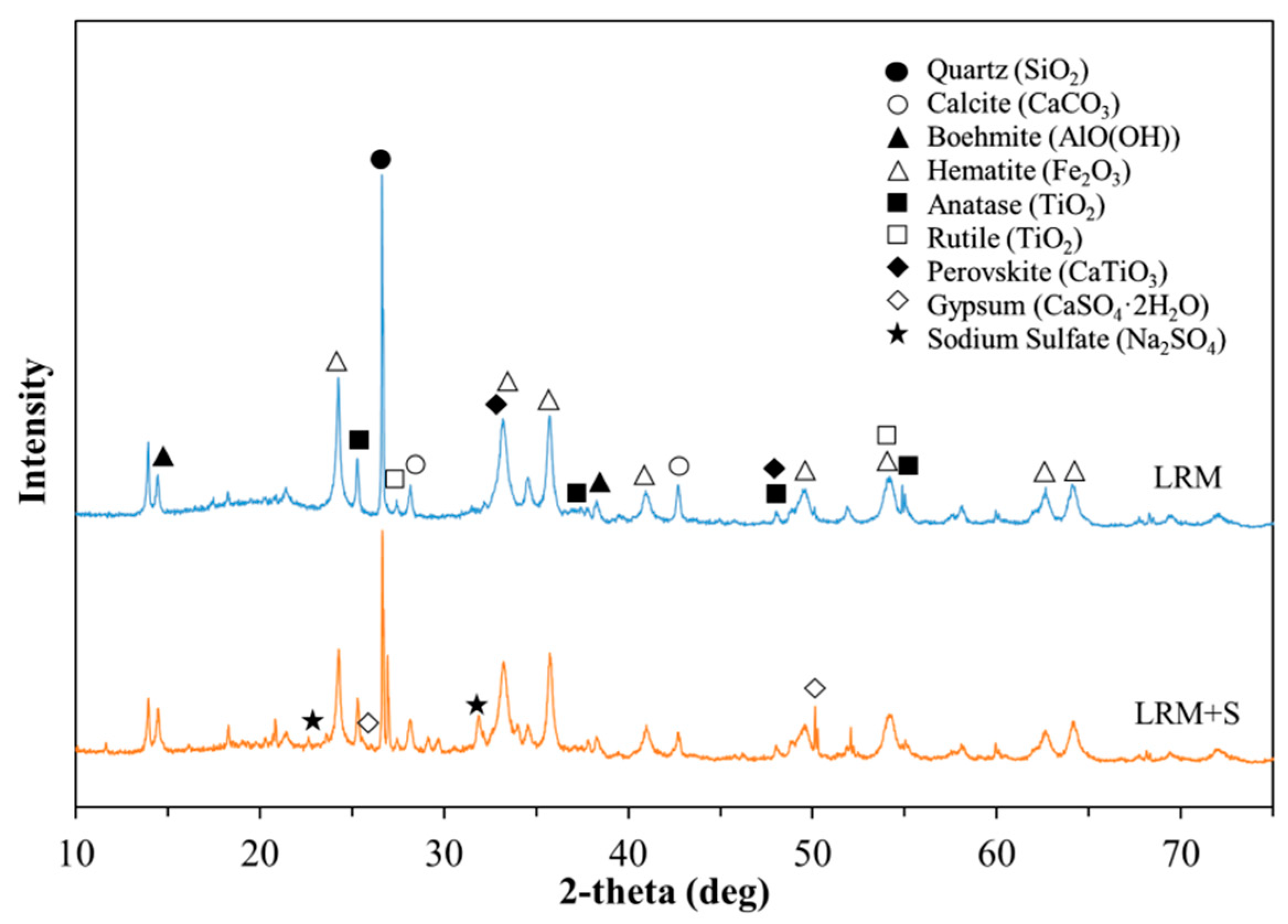
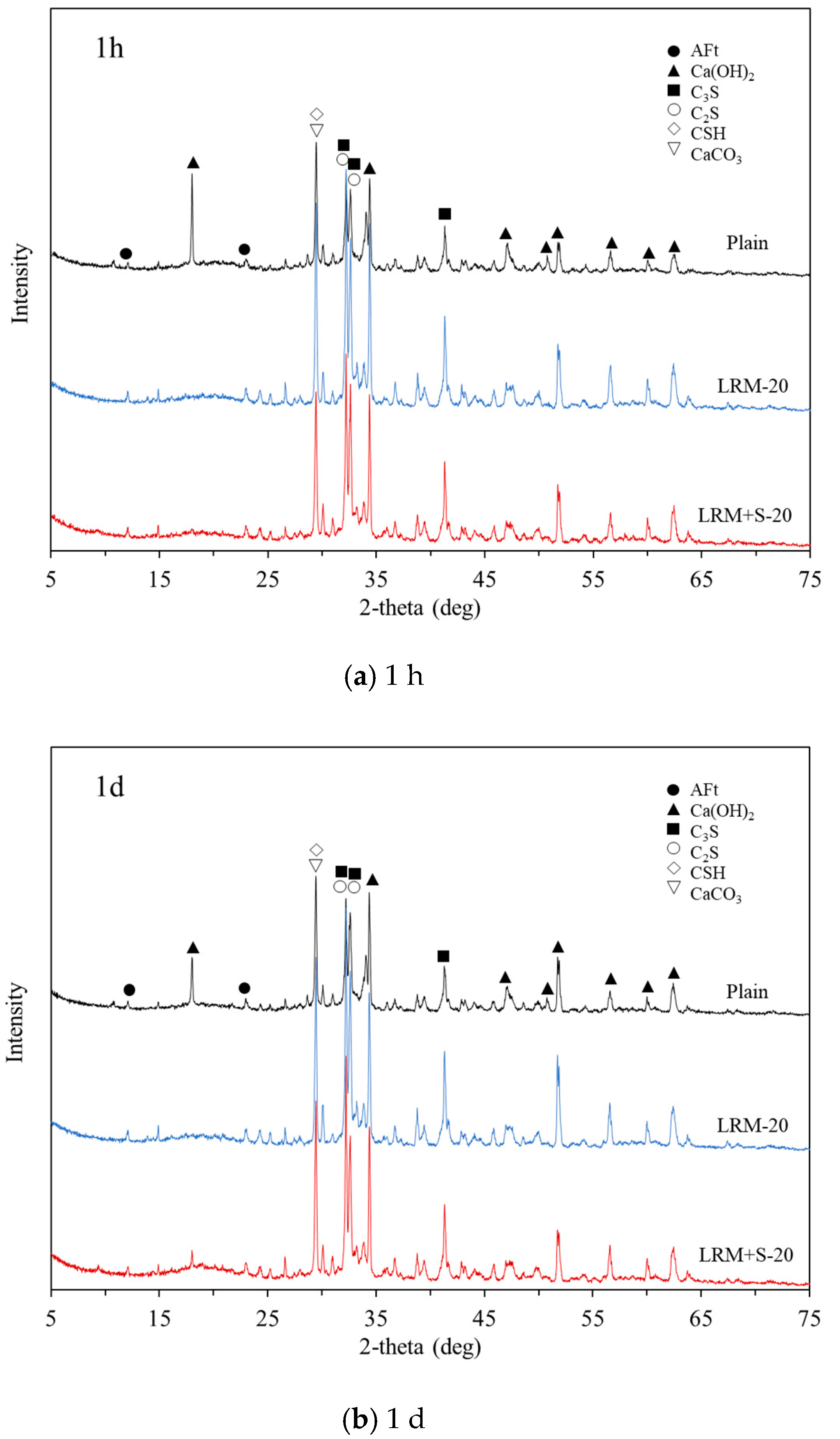
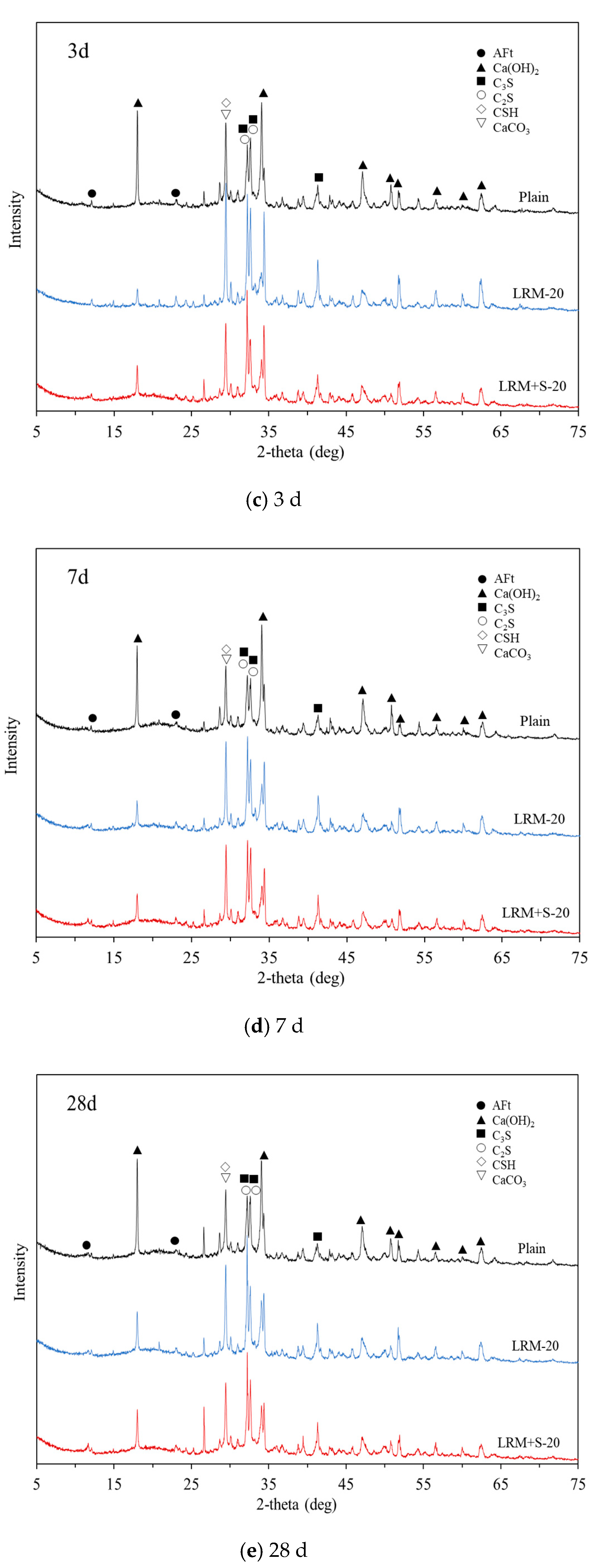
3.3. Microstructure
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The heat of hydration measurement results indicated that the maximum heat of hydration peak exhibited a low calorific value and was delayed for the cement paste with LRM in comparison with Plain. Conversely, the heat of hydration peak of the cement paste containing LRM + S was found to be similar to that of Plain.
- (2)
- The compressive strength at the age of 28 d for the cement paste with LRM was found to be as low as 55% of the compressive strength of Plain, whereas the cement paste with LRM + S showed a strength ratio as high as 99%.
- (3)
- In the XRD analysis, the cement paste with 20% LRM + S, unlike in the case of LRM sample, showed a Ca(OH)2 peak after only 1 h, similar to the case of Plain. In addition, no new products due to the addition of red mud were observed.
- (4)
- As the compressive strength of LRM + S10 at 28 d was similar to that of Plain, it can be assumed that (under the same conditions as in this study) up to 10% neutralized red mud can be added to cement pastes without affecting its strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro, D.V.; Labrincha, J.A.; Morelli, M.R. Potential use of natural red mud as pozzolan for Portland cement. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, P.; Zhai, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhu, W. Novel application of red mud: Facile hydrothermal-thermal conversion synthesis of hierarchical porous AlOOH and Al2O3 microspheres as adsorbents for dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 321, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, B. Development of unsintered construction materials from red mud wastes produced in the sintering alumina process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, H.; Sahoo, A. A study on the characterization of red mud. Int. J. Appl. Bioeng. 2014, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Nuamah, R.A.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Obada, D.O.; Yaya, A. Awaso bauxite red mud-cement based composites: Characterisation for pavement applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2017, 7, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amritphale, S.; Anshul, A.; Chandra, N.; Ramakrishnan, N. A novel process for making radiopaque materials using bauxite—Red mud. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Synthesis and characterization of red mud and rice husk ash-based geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enforcement Regulations of Waste Management Act. Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/%EB%B2%95%EB%A0%B9/%ED%8F%90%EA%B8%B0%EB%AC%BC%EA%B4%80%EB%A6%AC%EB%B2%95%EC%8B%9C%ED%96%89%EA%B7%9C%EC%B9%99 (accessed on 16 September 2020).
- Ribeiro, D.V.; Labrincha, J.A.; Morelli, M.R. Use of red mud as addition for portland cement mortars. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Structural investigation relating to the cementitious activity of bauxite residue—Red mud. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, G.; Kang, S.; Kang, H. Mechanical Properties of Concrete Containing Liquefied Red Mud Subjected to Uniaxial Compression Loads. Materials 2020, 13, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Afshinnia, K.; Rangaraju, P.R. Effect of alkali content of cement on properties of high performance cementitious mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, G.; Kang, S.; Kang, H. Characterization of Slag Cement Mortar Containing Nonthermally Treated Dried Red Mud. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, C.; Shi, Z.; Tong, B.; Wang, D. Early age shrinkage and heat of hydration of cement-fly ash-slag ternary blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, F.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q. Comparison of Effects of Sodium Bicarbonate and Sodium Carbonate on the Hydration and Properties of Portland Cement Paste. Materials 2019, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraya, M.E. Stopping of cement hydration by various methods. HBRC J. 2010, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y. Urea additives for reduction of hydration heat in cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunther, W.; Lothenbach, B.; Scrivener, K. Influence of bicarbonate ions on the deterioration of mortar bars in sulfate solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 44, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerui, Y.; Caiwen, Z.; Zhigang, L. The influence of calcium lignosulphonate–sodium bicarbonate on the status of ettringite crystallization in fly ash cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Cabeza, M.; Tenza-Abril, A.J.; Real, T.; Climent, M.Á.; Sánchez, I. Effects of Red Mud Addition in the Microstructure, Durability and Mechanical Performance of Cement Mortars. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, L.; Modolo, R.; Silva, A.S.; Ferreira, V.; Hotza, D.; Labrincha, J.A. Influence of red mud addition on rheological behavior and hardened properties of mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-X.; Poon, C.-S. Utilization of red mud derived from bauxite in self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Hooton, R.; Ji, T.; Kong, Y. Impacts of sulphates on rheological property and hydration performance of cement paste in the function of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, H.; Murmu, R.; Roy, D.; Mishra, S.C. Effect of Red Mud (RM) Reinforcement on Physio-Chemical Characteristics of Ordinary Portland Slag Cement (OPSC) Mortar. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2016, 6, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, M.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Cao, L. Preparation of alkali-free liquid accelerator based on aluminum sulfate and its accelerating mechanism on the hydration of cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Red Mud | Moisture Content (%) | pH | Density (g/cm3) | Specific Surface Area (cm2/g) | Average Particle Diameter (μm) | Viscosity (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRM * | 49.5 | 11.5 | 1.5 | 2353 | 2.75 | 42,550 |
| LRM + S ** | 49.2 | 6.7 | 1.54 | 2353 | 2.75 | 45,250 |
| Type of Red Mud | SiO2 | A12O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | CaO | TiO2 | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRM | 17.6 | 25.6 | 30.4 | 0.21 | 13.2 | 1.83 | 6.27 | 0.29 |
| LRM + S | 17 | 25.4 | 29.2 | 0.21 | 10.7 | 1.84 | 5.99 | 4.48 |
| Type | Blaine (cm2/g) | Setting Time | Density (g/cm3) | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial (min) | Final (min) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | lg. Loss | |||
| OPC * | 3300 | 200 | 330 | 3.15 | 21.7 | 5.7 | 3.2 | 63.1 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 2.44 |
| Mix ID | Cement (wt%) | Water (wt%) | Extra Discount Red Mud (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRM | LRM + S | |||
| Plain | 100 | 30 | - | - |
| LRM-10 | 10 | - | ||
| LRM-20 | 20 | - | ||
| LRM + S-10 | - | 10 | ||
| LRM + S-20 | - | 20 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Kang, H.; Lee, B. Effects of Adding Neutralized Red Mud on the Hydration Properties of Cement Paste. Materials 2020, 13, 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184107
Kang S, Kang H, Lee B. Effects of Adding Neutralized Red Mud on the Hydration Properties of Cement Paste. Materials. 2020; 13(18):4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184107
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sukpyo, Hyeju Kang, and Byoungky Lee. 2020. "Effects of Adding Neutralized Red Mud on the Hydration Properties of Cement Paste" Materials 13, no. 18: 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184107
APA StyleKang, S., Kang, H., & Lee, B. (2020). Effects of Adding Neutralized Red Mud on the Hydration Properties of Cement Paste. Materials, 13(18), 4107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184107





