A Numerical Wear Simulation Method of Reciprocating Seals with a Textured Rod
Abstract
:1. Introduction
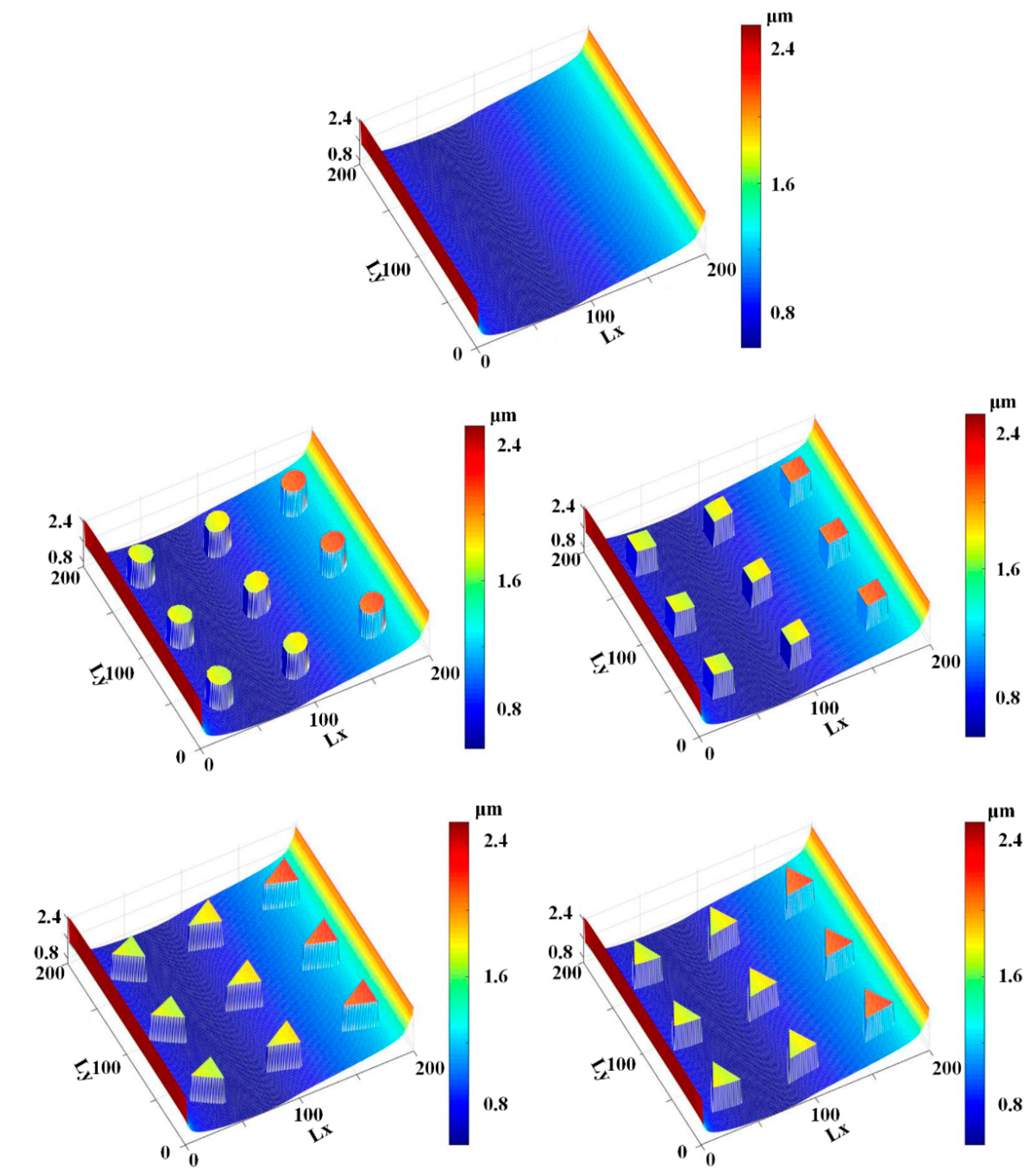
2. Rod Surface Texture
3. Lubrication Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Fluid
3.2. Analysis of Asperity Contact
3.3. Analysis of Deformation
4. Wear Analysis
5. Procedure of the Simulation Method
6. Results and Discussion
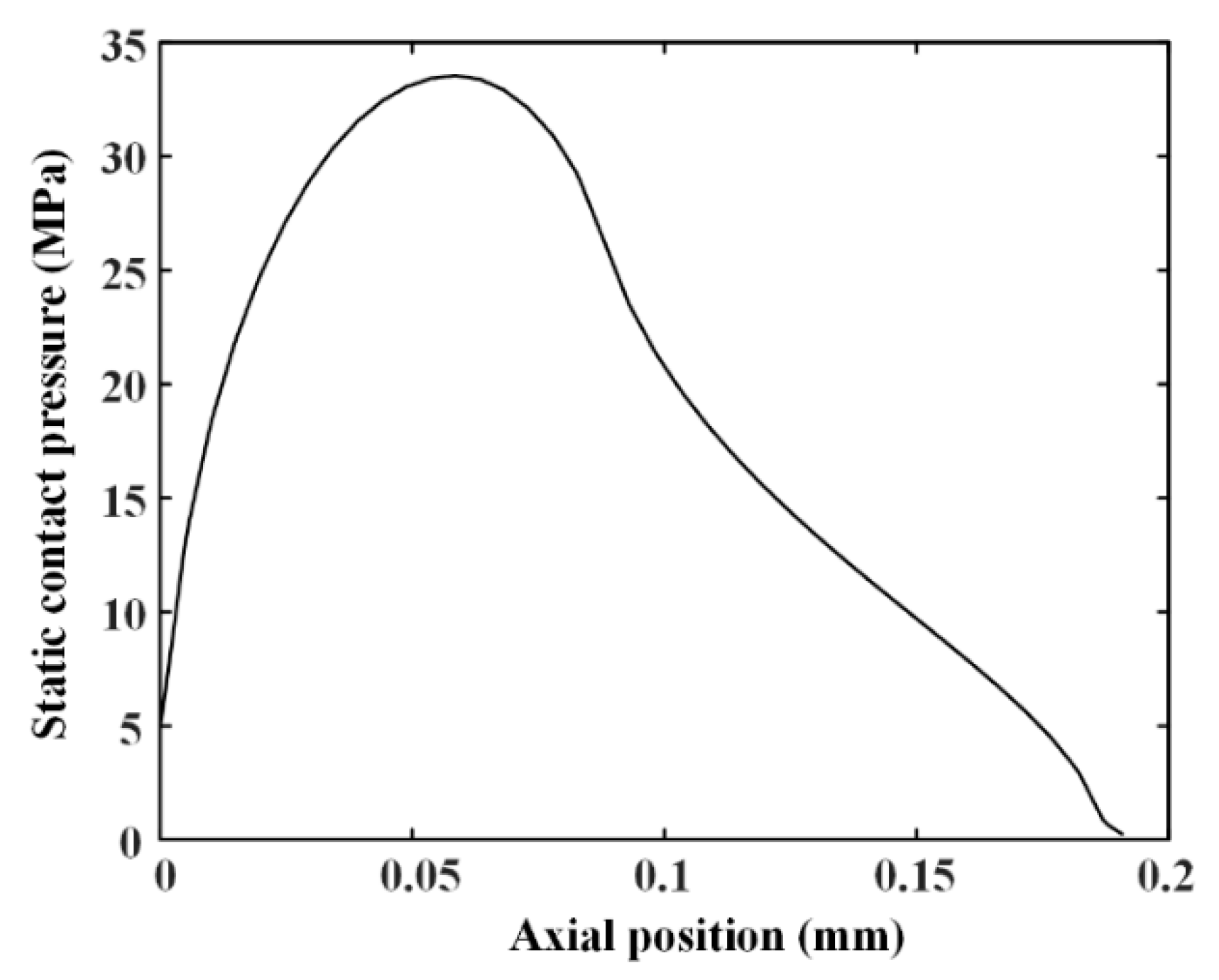
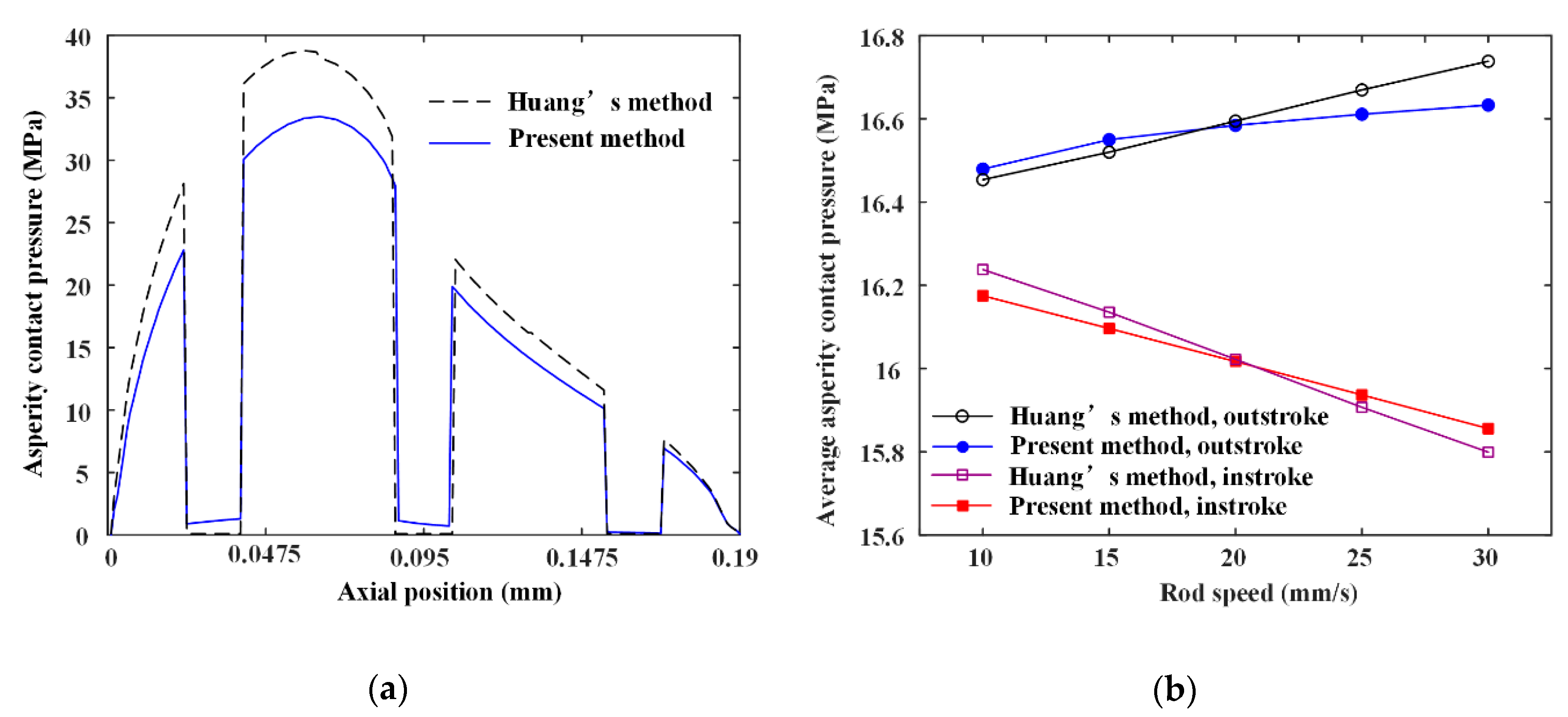
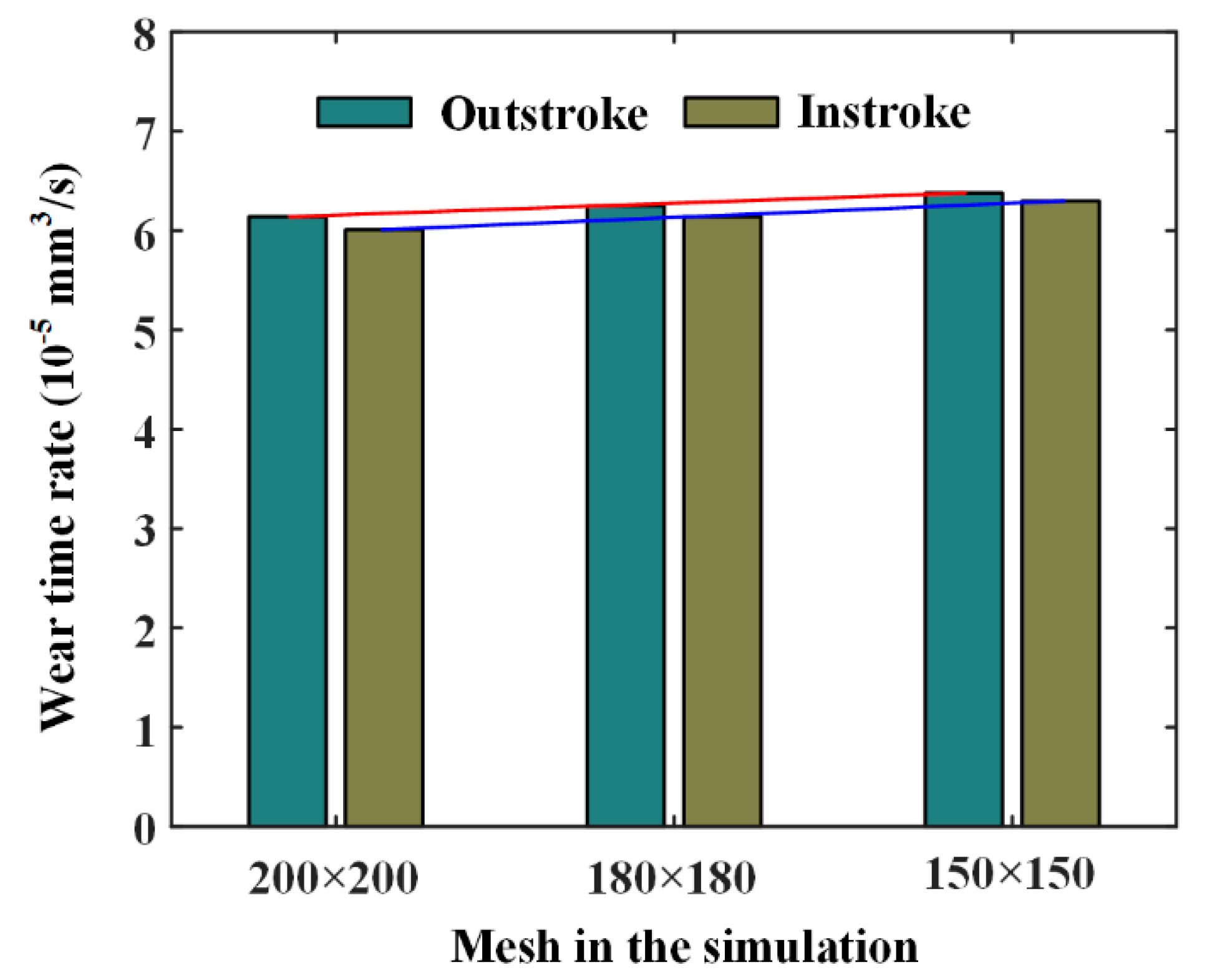
6.1. Validation
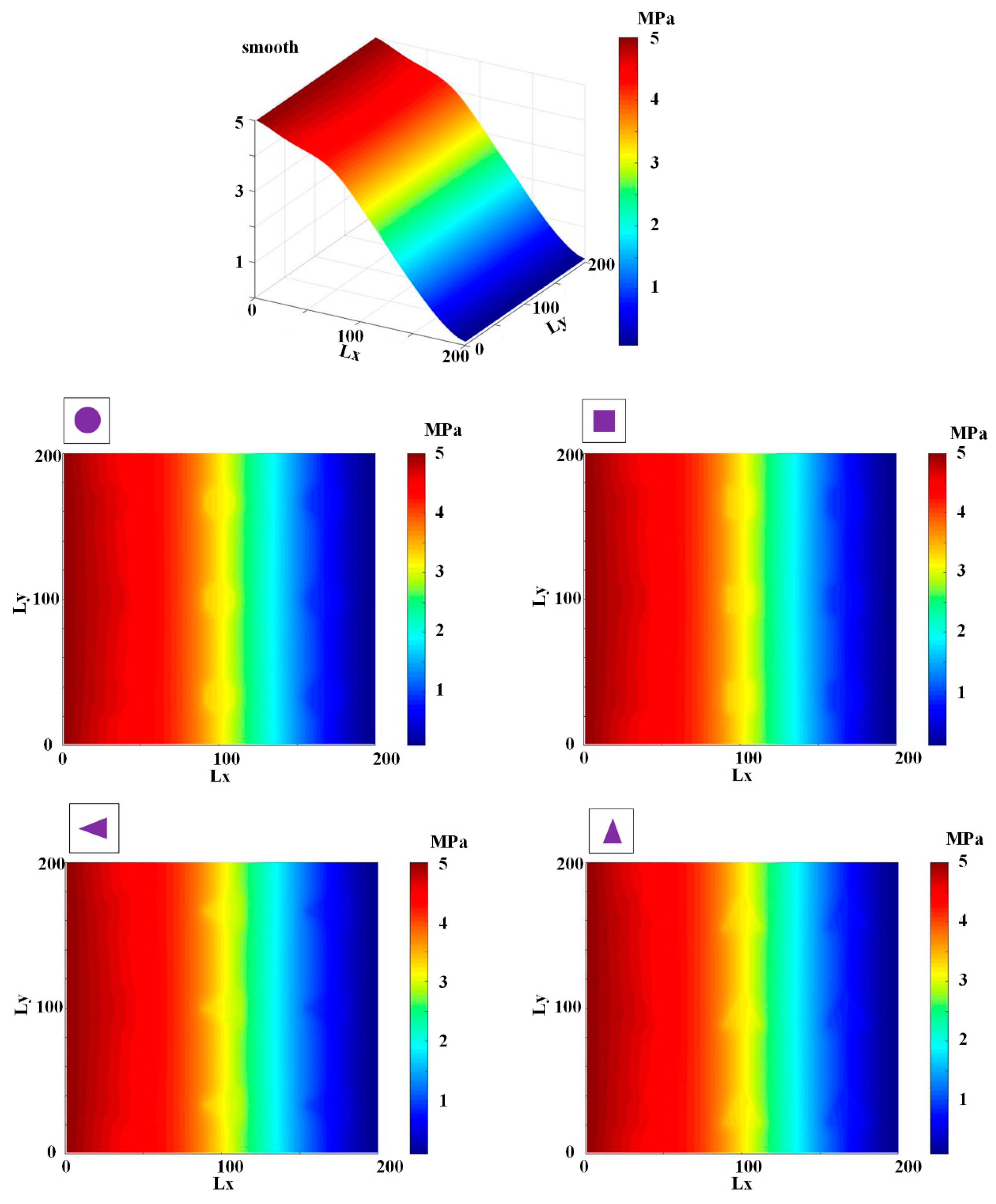
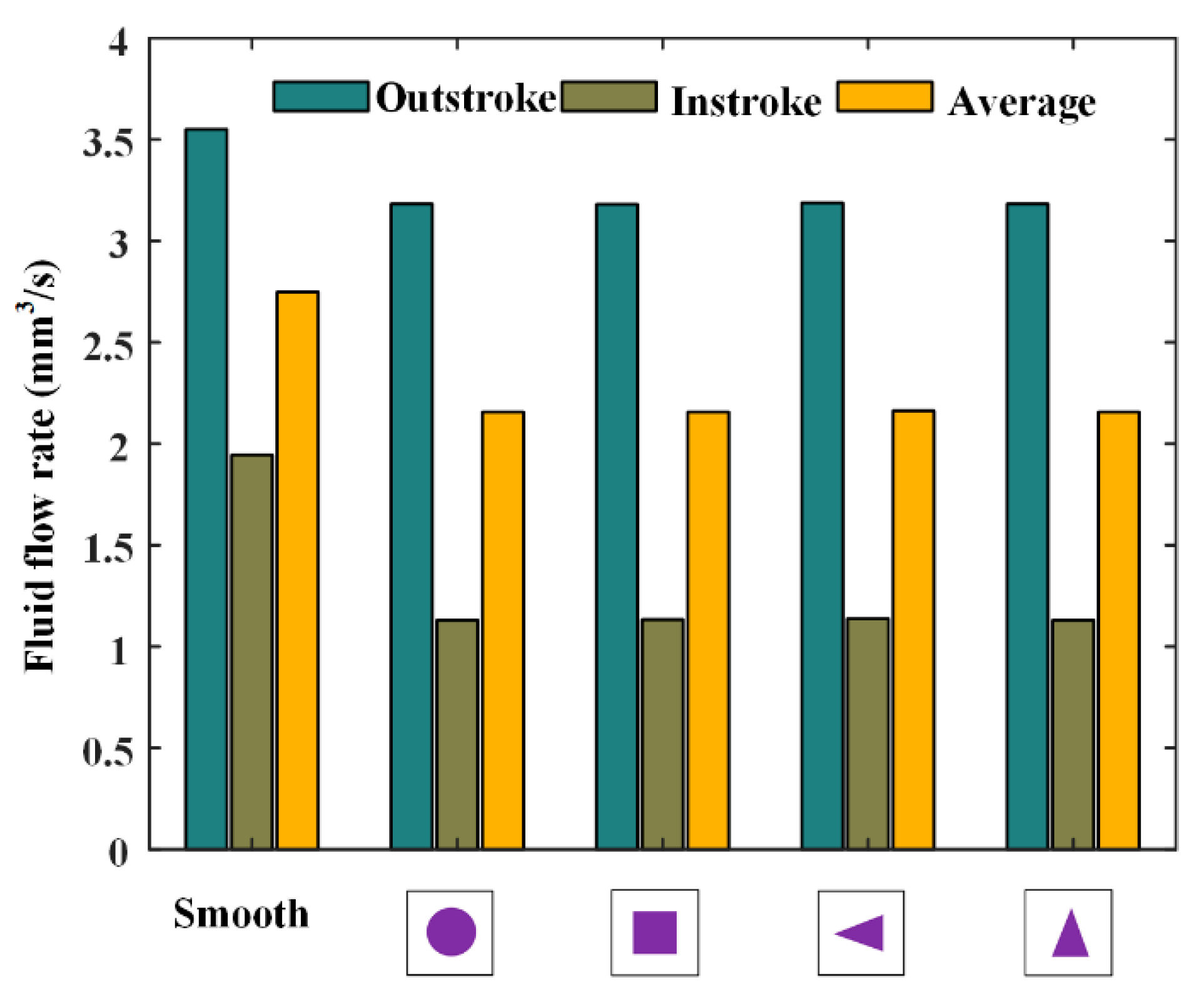
6.2. Effects of Rod Texture on Lubrication
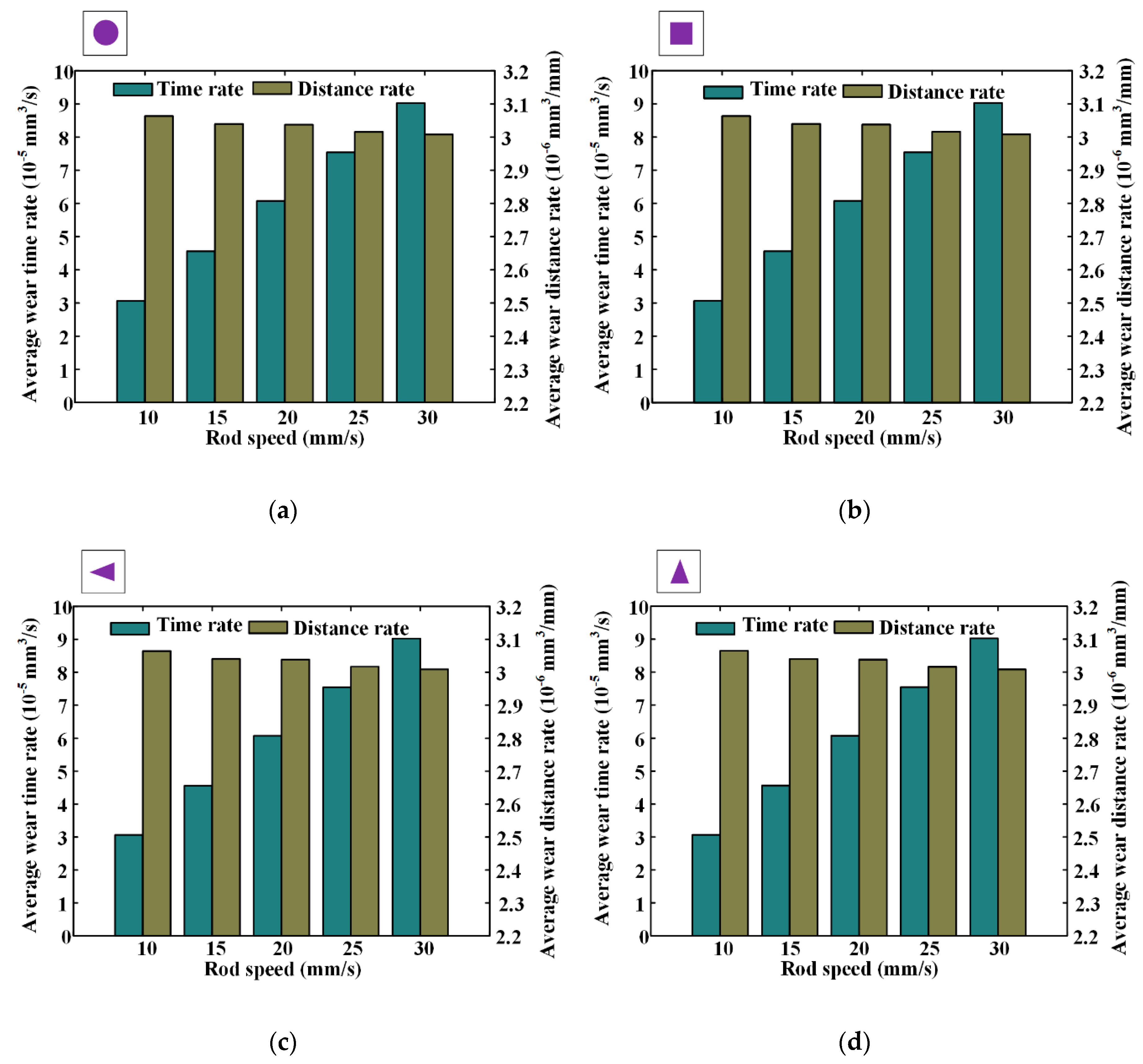
6.3. Effects of Rod Speed
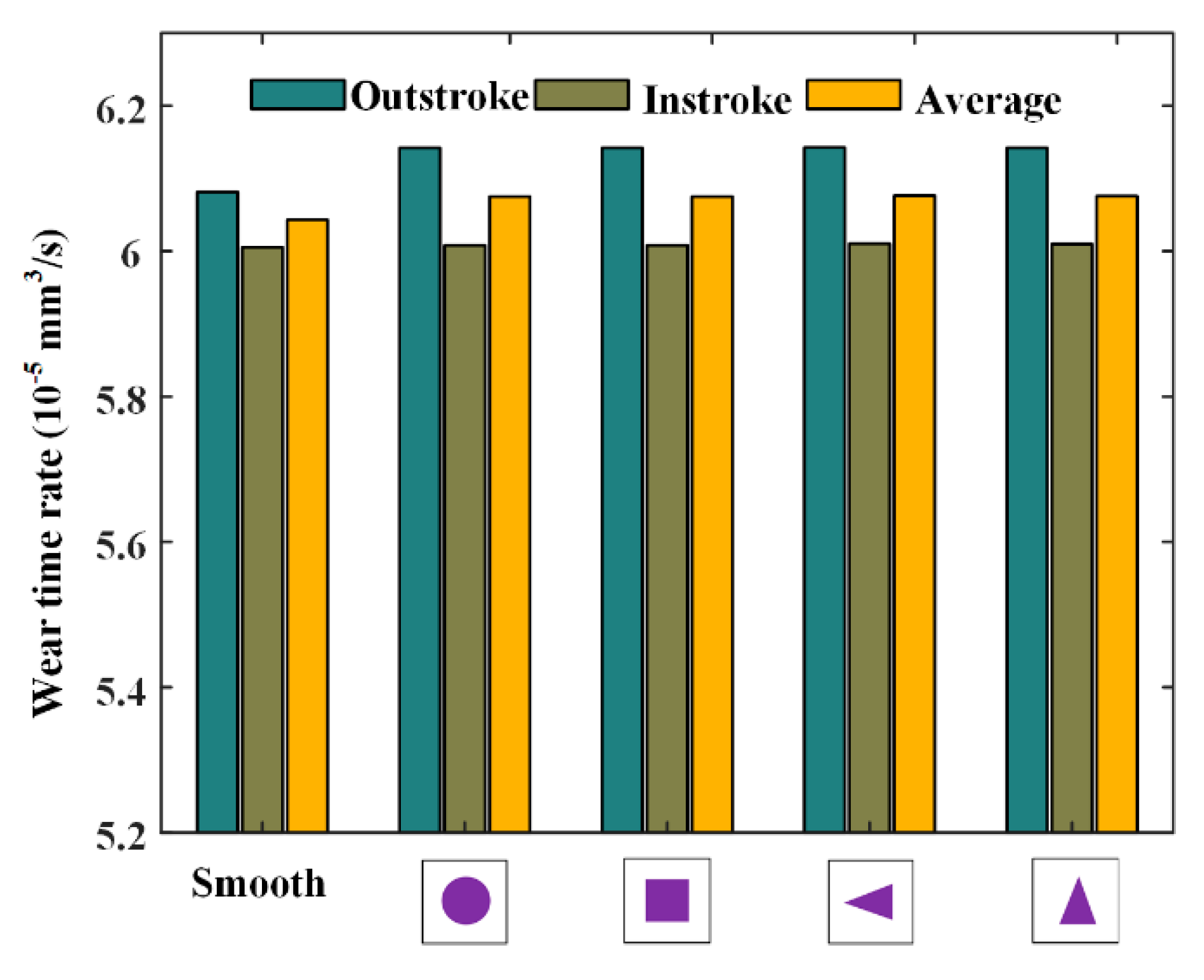
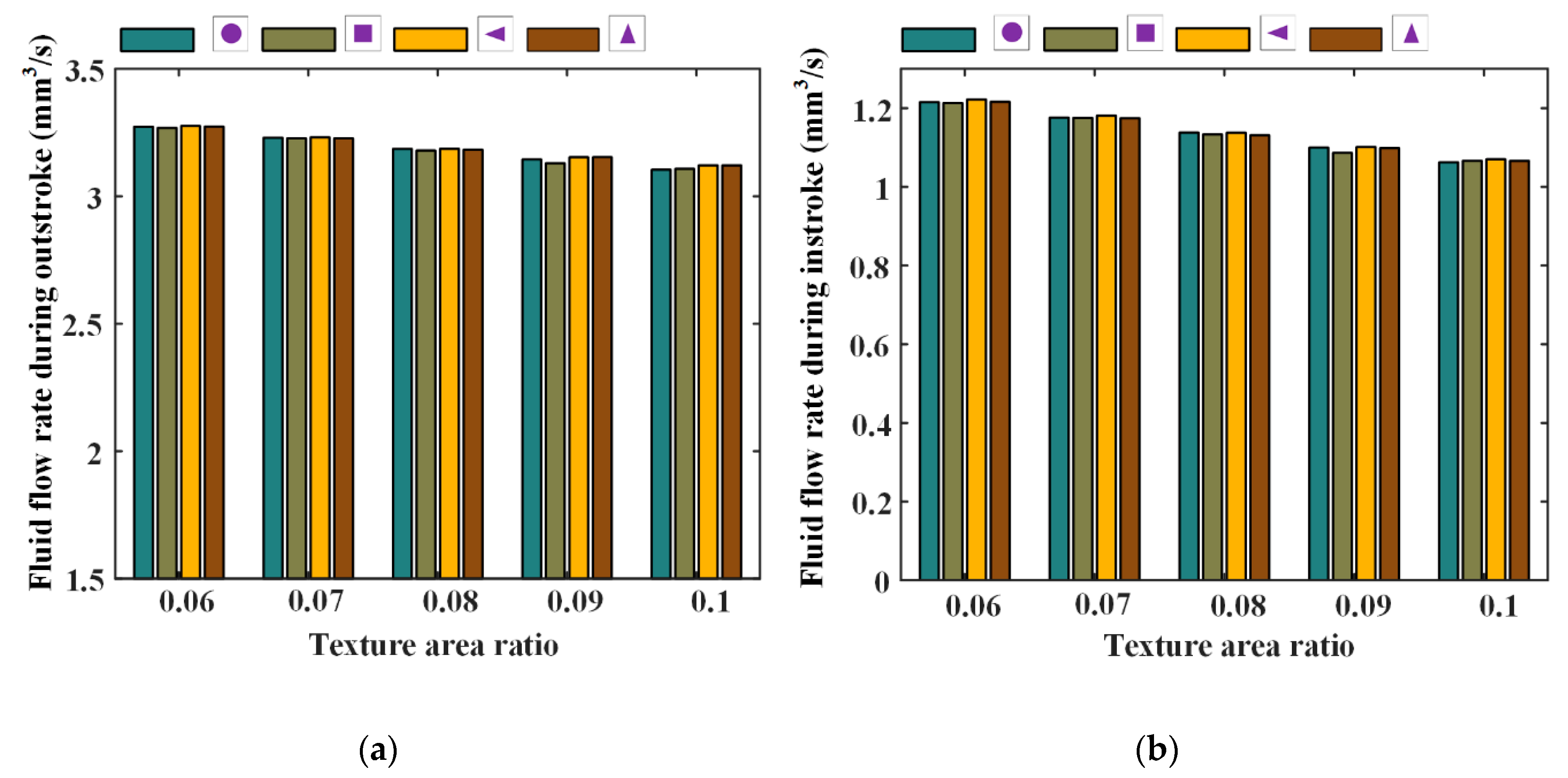
6.4. Effects of Rod Texture
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Symbols
| a length of micro-cavity in axial direction | b length of micro-cavity in circumferential direction |
| C10, C01, d Mooney–Rivlin coefficients | Drod rod diameter |
| E equivalent Young’s modulus | Eseal Young’s modulus of the seal |
| F cavitation factor | Fsum sum of the pressure differences |
| h film thickness | h0 initial film thickness |
| hp depth of the micro-cavity | hr rod surface height |
| hT average truncated film thickness | hw wear depth |
| Δh micro deformation of the sealing lip surface | H hardness |
| I1, I2 deviatoric strain invariants | J parameter relating to the elastic deformation gradient |
| k wear modulus | K wear coefficient |
| L side length of texture | Lx length of the simulation space in axial direction |
| Ly length of the simulation space in circumferential direction | p static contact pressure |
| pa ambient pressure | pc asperity contact pressure |
| pcav cavitation pressure | pf fluid pressure |
| pn normal contact pressure | ps sealed pressure |
| Δp pressure difference | averge asperity contact pressure |
| rc radius of circular micro-cavity | rs wear distance rate |
| rt wear time rate | R asperity radius of the seal |
| S relative sliding distance | u rod speed |
| V material wear volume | W normal load |
| strain energy density | x coordinate in x-axis direction |
| y coordinate in y-axis direction | η asperity density of the seal |
| γ ratio of the axial length of micro-cavity to the circumferential length | μ fluid viscosity |
| μ0 fluid viscosity under the ambient pressure | σ seal surface roughness |
| σs equivalent standard deviation of surface roughness | ϕx, ϕy pressure flow factors |
| ϕs.c.x shear flow factor | Φ fluid pressure or density of the cavitation region |
| υseal Poisson’s ratio of the seal |
References
- Liao, B.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhou, K. Sealing reliability modeling of aviation seal based on interval uncertainty method and multidimensional response surface. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, R.; Bai, G.; Wang, S.; Tomovic, M.M. Reliability estimation of rotary lip seal in aircraft utility system based on time-varying dependence degradation model and its experimental validation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lian, Z. Numerical Investigations on the Sealing Performance of a Reciprocating Seal Based on the Inverse Lubrication Method. J. Tribol. 2019, 141, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Guo, S.; Ouyang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H. An eccentric 3-D fluid-structure interaction model for investigating the effects of rod parallel offset on reciprocating-seal performance. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Peng, X.-D.; Meng, X.-K. A thermo-elastohydrodynamic lubrication model for hydraulic rod O-ring seals under mixed lubrication conditions. Tribol. Int. 2019, 129, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Thermo-elastohydrodynamic mixed-lubrication model for reciprocating rod seals. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Guo, S.; Ouyang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H. Mixed Lubrication Modeling of Reciprocating Seals Based on a Developed Multiple-Grid Method. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Salant, R.F. Numerical analysis of a hydraulic rod seal: Flooded vs. starved conditions. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, S.; Kumaraswamy, A.; Guruprasad, S.; Bhandari, P. Investigation of friction in rectangular Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber (NBR) hydraulic rod seals for defence applications. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 4793–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, M.; Dong, G.-N.; Zhang, D.; Chin, K. A mixed lubrication model for studying tribological behaviors of surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Fan, J. A thermal mixed lubrication model to study the textured ring/liner conjunction. Tribol. Int. 2016, 101, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y. Effects of surface texturing on ring/liner friction under starved lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Salant, R.F. Simulation of the Effects of a Plunge Ground Rod on Hydraulic Rod Seal Behavior. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Salant, R.F. Simulation of a hydraulic rod seal with a textured rod and starvation. Tribol. Int. 2016, 95, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Gadari, M.; Hajjam, M. Effect of the Grooved Rod on the Friction Force of U-Cup Hydraulic Rod Seal with Rough Lip. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 61, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y. The effect of texture on the shaft surface on the sealing performance of radial lip seals. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. The effect of axial position of contact zone on the performance of radial lip seals with a texturing shaft surface. Tribol. Int. 2016, 97, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, P. Research on pressure compensation and friction characteristics of piston rod seals with different degrees of wear. Tribol. Int. 2020, 142, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Longke, W.; Salant, R.F.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Wear on the Performance of a Rotary Lip Seal. J. Tribol. 2014, 136, 041703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Yoo, S.; Kim, D.-E.; Kang, B.; Kim, H. Accelerated wear test of FKM elastomer for life prediction of seals. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, M.; Prakash, B. The Influence of Lubrication on Two-body Abrasive Wear of Sealing Elastomers Under Reciprocating Sliding Conditions. J. Elastomers Plast. 2010, 43, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán-Cabrera, L.I.; Gallardo-Hernández, E.A.; De La Rosa, C.S.; Vite-Torres, M. Micro-scale abrasive wear of some sealing elastomers. Wear 2017, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frölich, D.; Magyar, B.; Sauer, B. A comprehensive model of wear, friction and contact temperature in radial shaft seals. Wear 2014, 311, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhocine, A.-; Ghazaly, N.M. Effects of material properties on generation of brake squeal noise using finite element method. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 12, 1432–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Pohl, H.; Schomburg, U.; Upper, G.; Heine, S. Wear and friction of PTFE seals. Wear 1999, 224, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békési, N.; Varadi, K. Wear simulation of a reciprocating seal by global remeshing. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2010, 54, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békési, N.; Varadi, K.; Felhős, D. Wear Simulation of a Reciprocating Seal. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 031601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Gaoliang, P.; Zhe, L. Prediction of seal wear with thermal–structural coupled finite element method. Finite Elements Anal. Des. 2014, 83, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Peng, G.; Qiang, W.; Yuhui, L. A Numerical Analysis Method of Hydraulic Seals for Downhole Equipments. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 5, 151794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angerhausen, J.; Woyciniuk, M.; Murrenhoff, H.; Schmitz, K. Simulation and experimental validation of translational hydraulic seal wear. Tribol. Int. 2019, 134, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, D. A multiscale wear model for reciprocating rod stepseal under mixed lubricating conditions based on linear elasticity. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C. A multiscale wear simulation method for rotary lip seal under mixed lubricating conditions. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Tyagi, R. Tribological properties of PTFE/laser surface textured stainless steel under starved oil lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Lü, X. Tribological properties of PTFE composites filled with surface-treated carbon fiber. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 8465–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Tomovic, M.M. Numerical study of the effects of textured shaft on the wear of rotary lip seals. Tribol. Int. 2019, 138, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payvar, P.; Salant, R.F. A Computational Method for Cavitation in a Wavy Mechanical Seal. J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, N.; Cheng, H.S. Application of Average Flow Model to Lubrication Between Rough Sliding Surfaces. J. Lubr. Technol. 1979, 101, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The Contact of Two Nominally Flat Rough Surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1970, 185, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jia, X.; Suo, S.; Salant, R.F.; Wang, Y. A mixed lubrication model of a rotary lip seal using flow factors. Tribol. Int. 2013, 57, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; He, G.; Weikai, L.; Guoqiang, H. Storage life of silicone rubber sealing ring used in solid rocket motor. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sujuan, Y.; Xingrong, Z. Tribological Properties of PTFE and PTFE Composites at Different Temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuramiah, A.; Awasthy, K.L.; Prakash, B.; Mahapatra, P.K. Lubricated wear of PTFE and graphited PTFE. Lubr. Sci. 1991, 3, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L. Elastohydrodynamic model of hydraulic rod seals with various rod surfaces. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, December 2014. [Google Scholar]
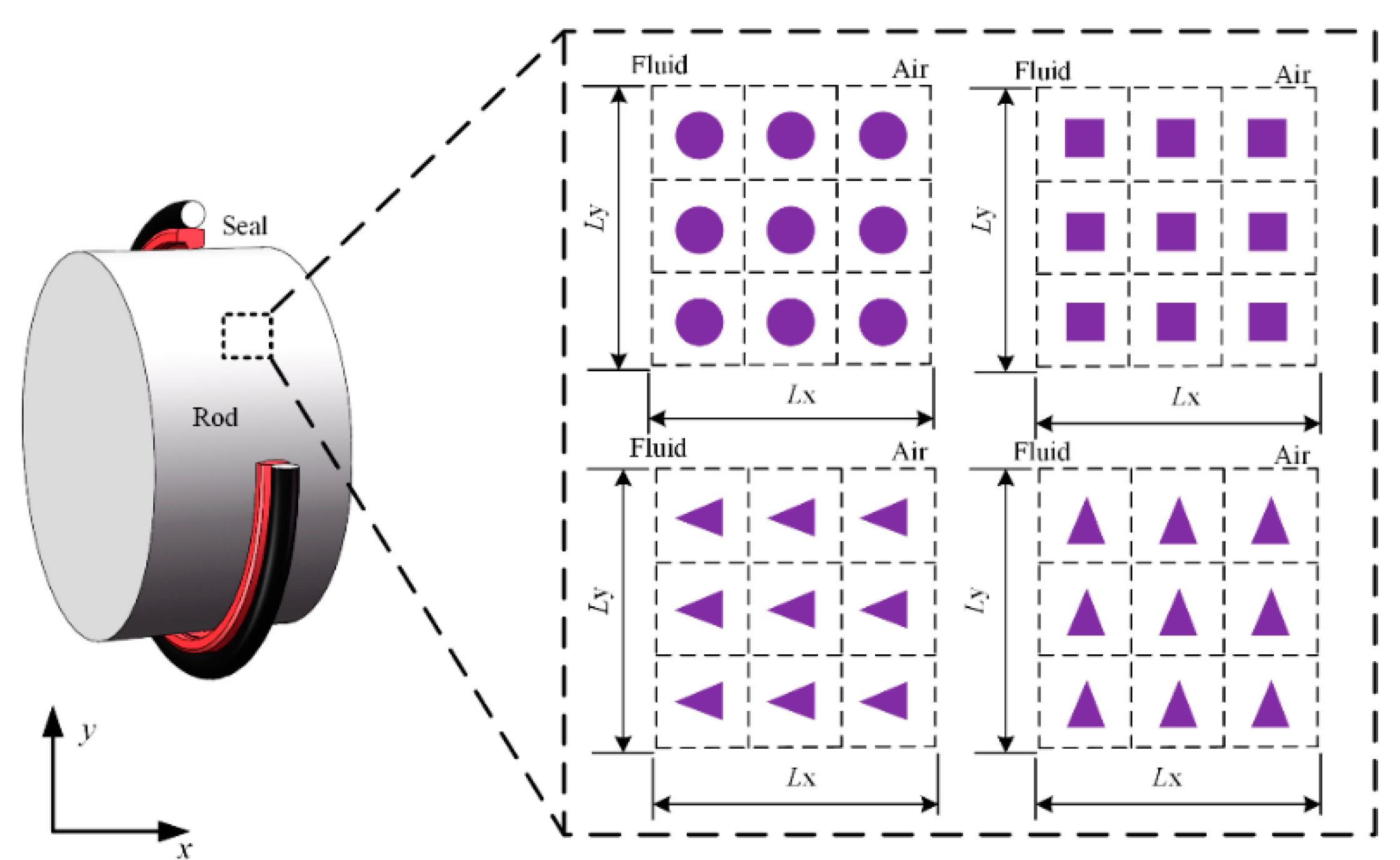
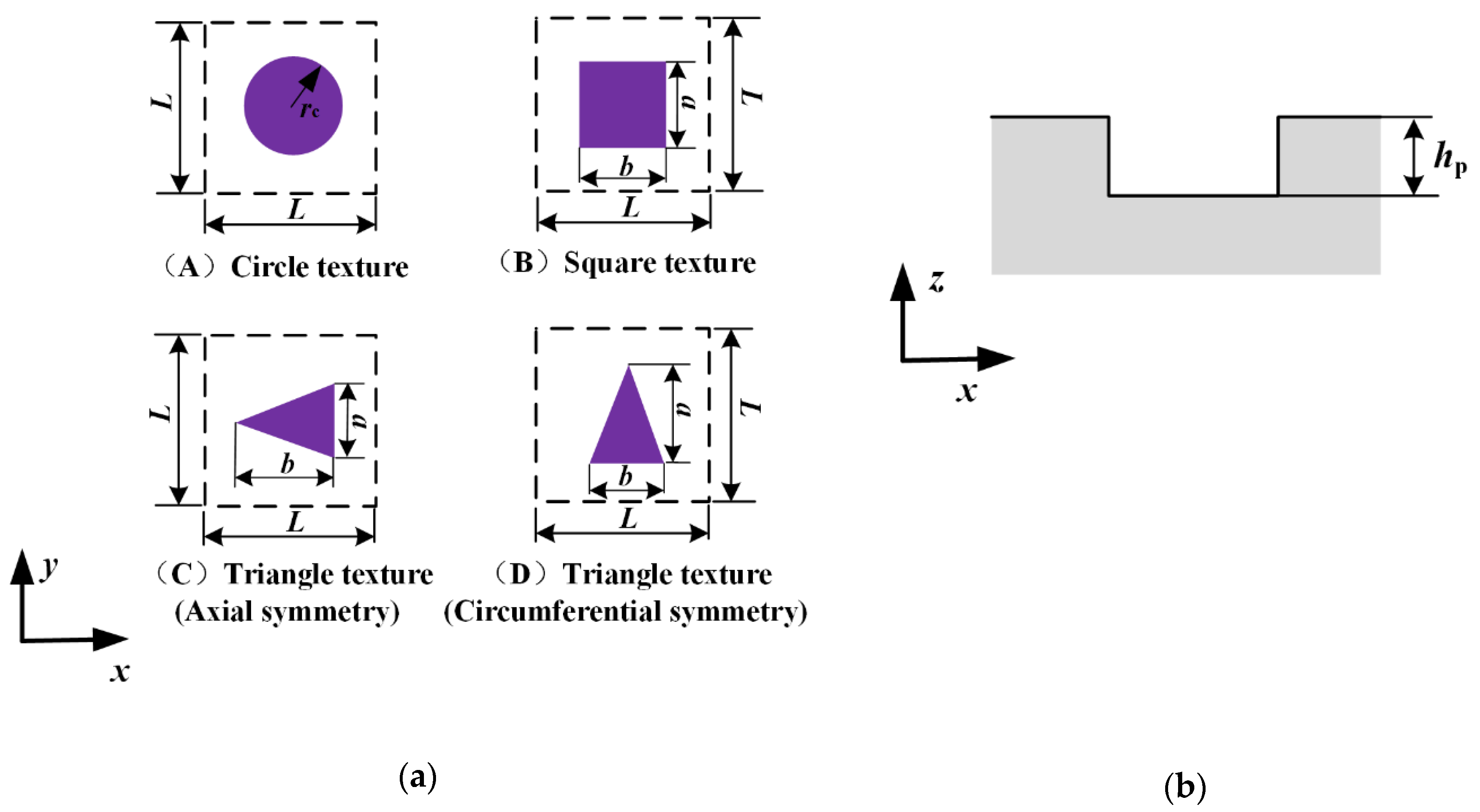
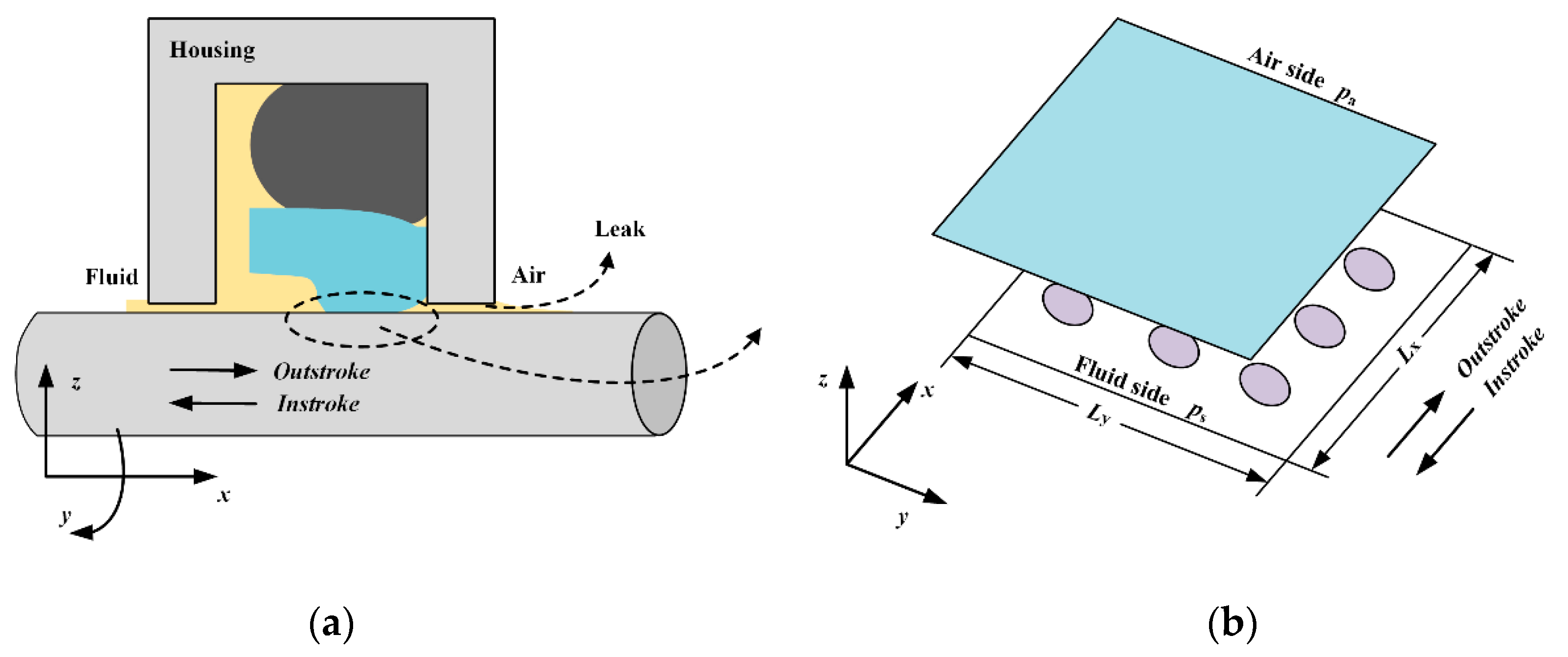


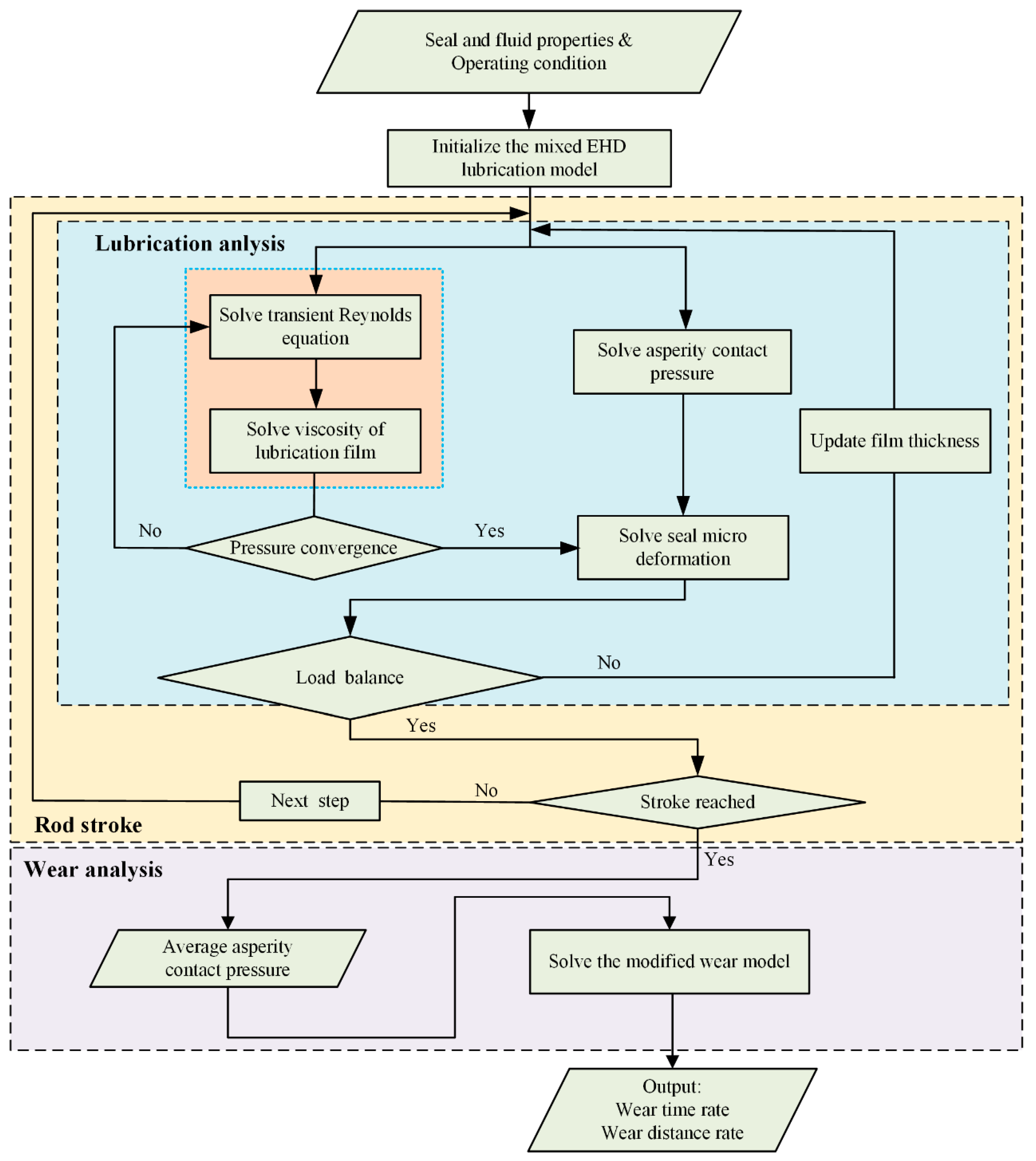

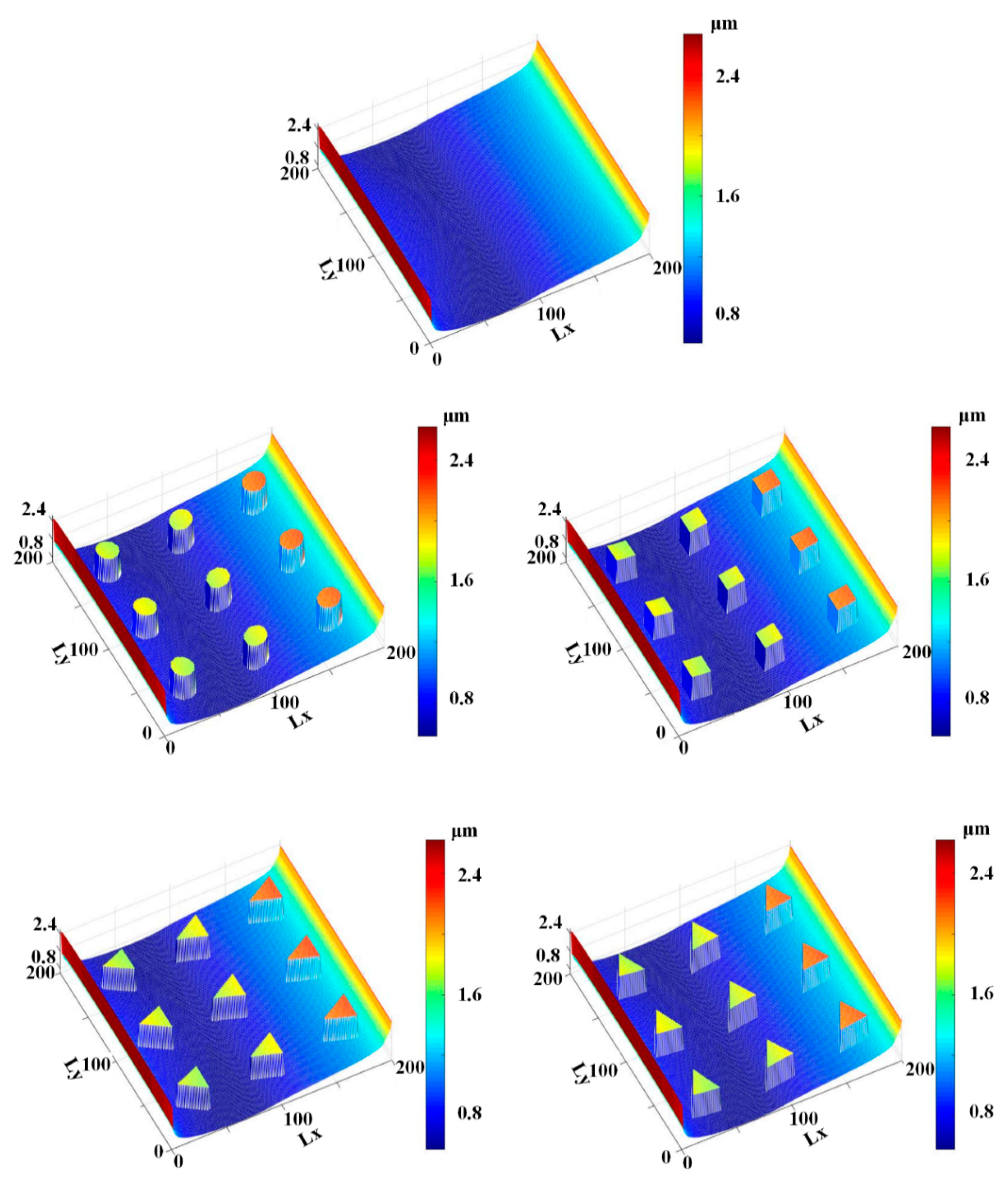
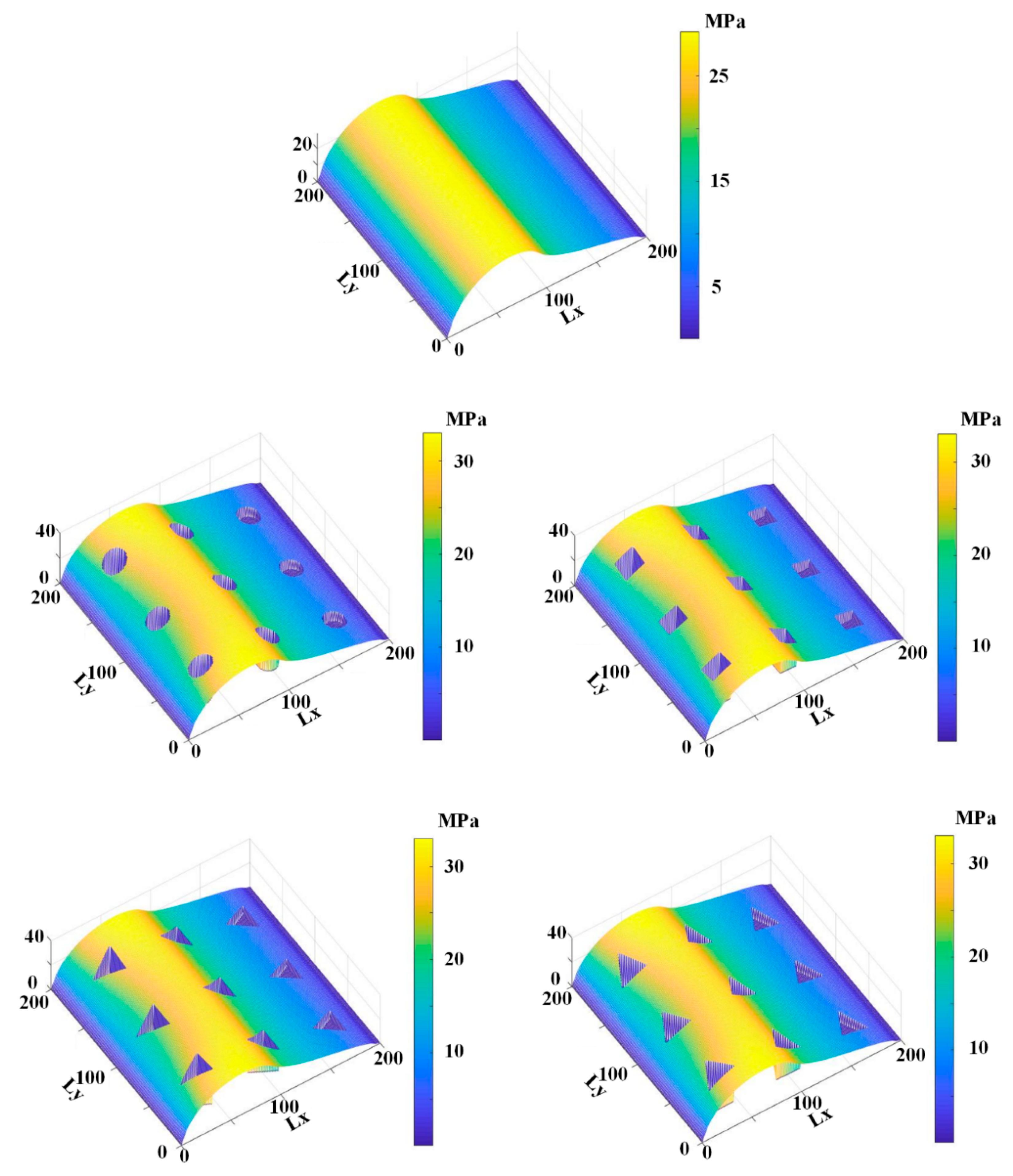
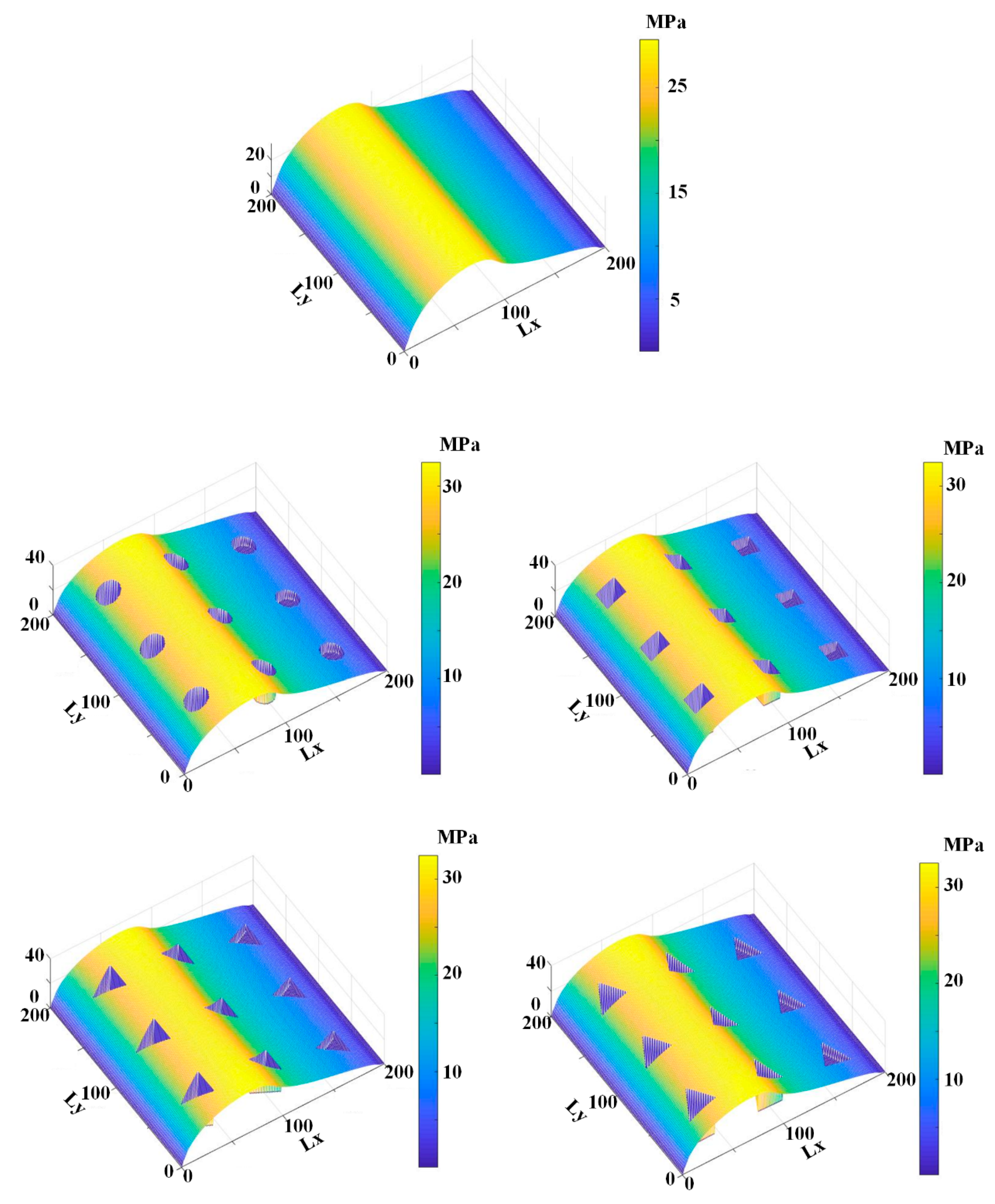






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| C10 | 1.87 MPa |
| C01 | 0.47 MPa |
| d | 0.000113 |
| 250 MPa | |
| 0.4 |
| Parameter | Meaning | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| σ | Root mean square roughness | 0.8 | μm |
| Drod | Diameter of the rod | 25.4 | mm |
| ps | Sealed pressure | 5 | MPa |
| pa | Ambient pressure | 0.1 | MPa |
| R | Asperity radius | 0.8 | μm |
| η | Asperity density | 1 × 105 | mm−2 |
| μ0 | Fluid viscosity | 0.0387 | Pa·s |
| k | Wear modulus | 1.2 × 10−5 | mm3/Nm |
| u | Rod speed | 10–30 | mm/s |
| Number | Texture | Depth | Area Ratio | Shape Feature Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a |  | 1.3 μm | 0.08 | - |
| b |  | 1.3 μm | 0.08 | 1 |
| c |  | 1.3 μm | 0.08 | 1 |
| d |  | 1.3 μm | 0.08 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, S. A Numerical Wear Simulation Method of Reciprocating Seals with a Textured Rod. Materials 2020, 13, 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194458
Ran H, Liu D, Wang S. A Numerical Wear Simulation Method of Reciprocating Seals with a Textured Rod. Materials. 2020; 13(19):4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194458
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Hongliang, Di Liu, and Shaoping Wang. 2020. "A Numerical Wear Simulation Method of Reciprocating Seals with a Textured Rod" Materials 13, no. 19: 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194458
APA StyleRan, H., Liu, D., & Wang, S. (2020). A Numerical Wear Simulation Method of Reciprocating Seals with a Textured Rod. Materials, 13(19), 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13194458







