The Importance of Ionic Liquids in the Modification of Starch and Processing of Starch-Based Materials
Abstract
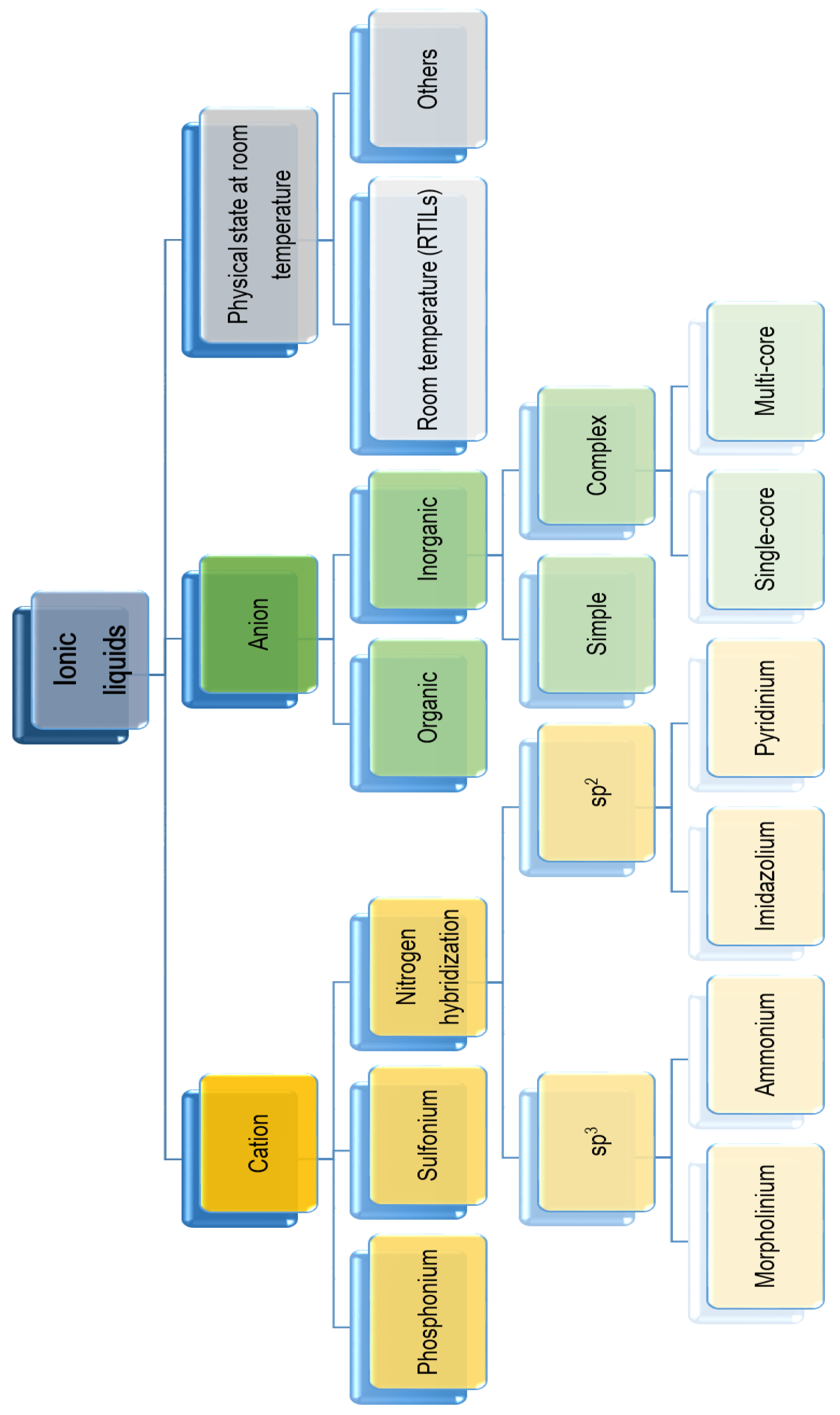
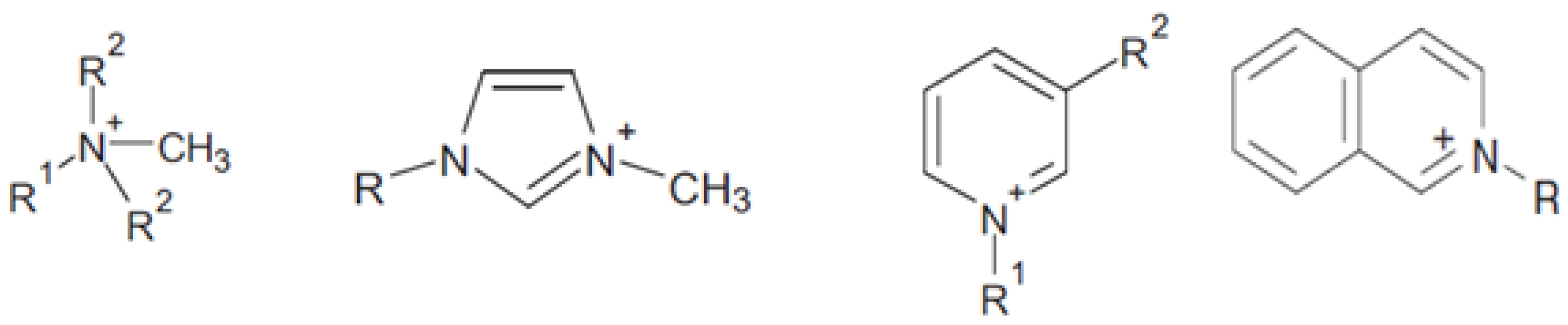
:1. Introduction
2. ILs as “Green” Designing Compounds
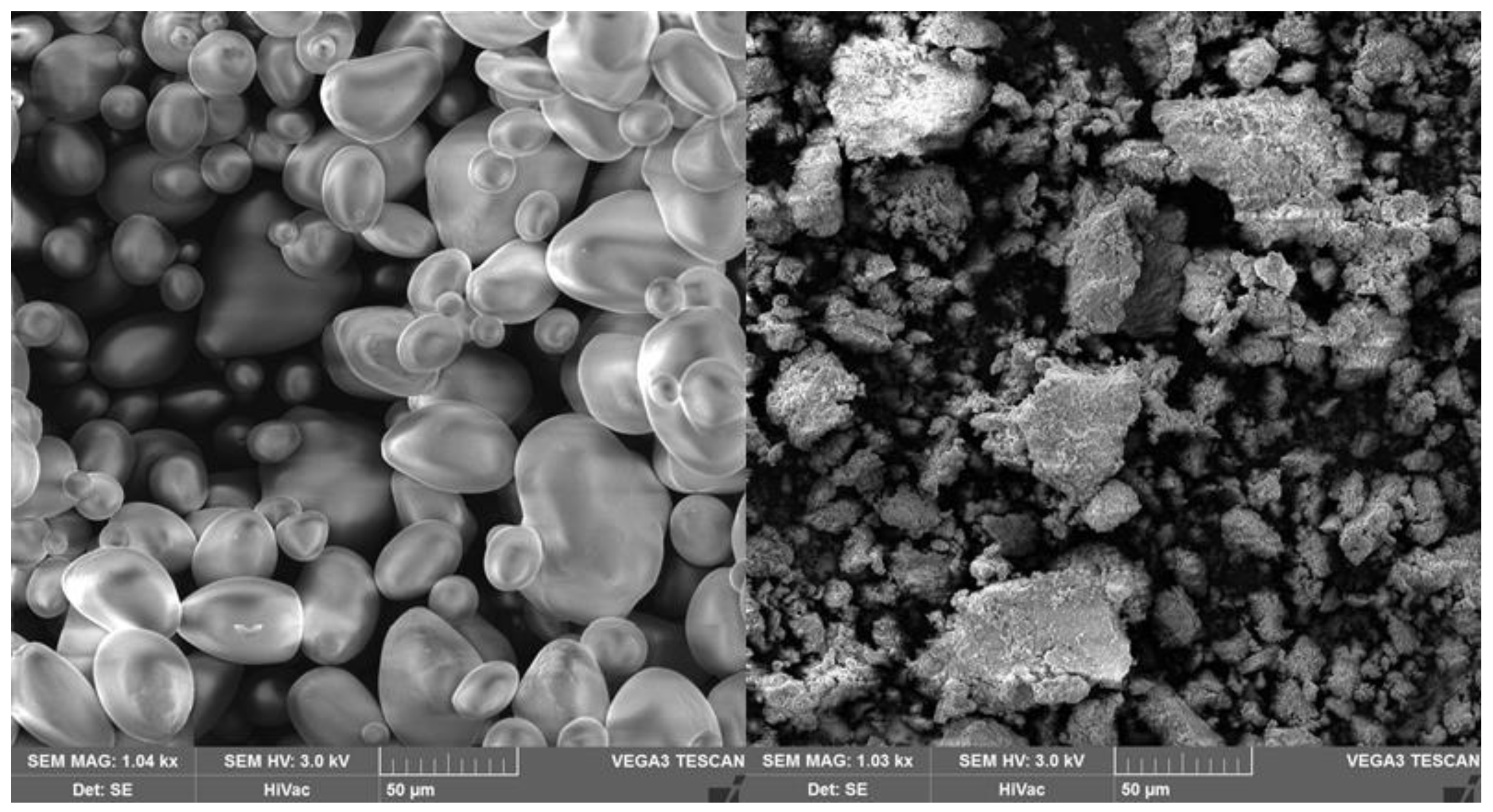
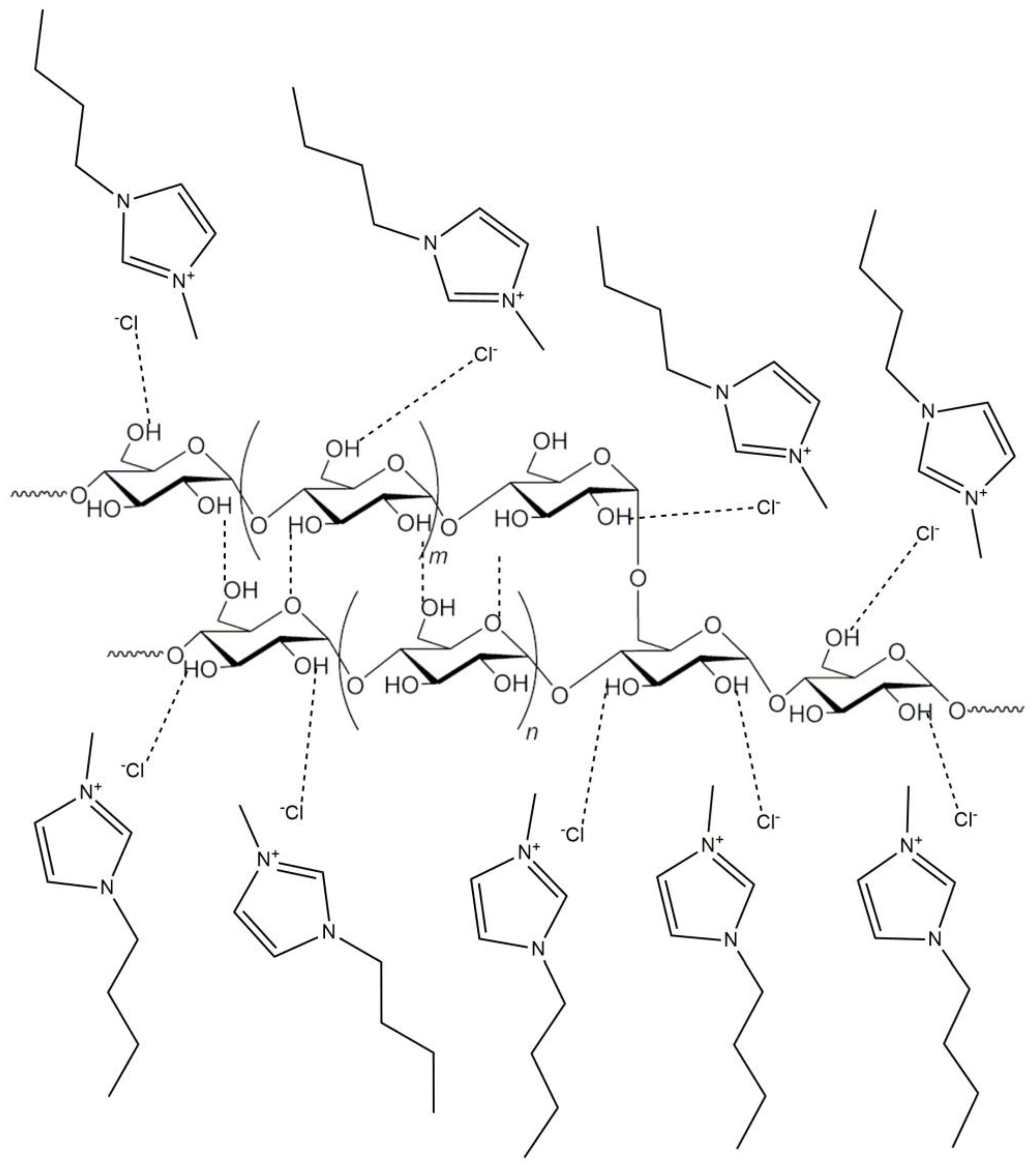
3. ILs Suitable for Starch Dissolution and Gelatinization
4. ILs as Starch Solvents, Compatibilizers, and Plasticizers
5. ILs for Conventional Synthesis of Starch Ethers and Carbonyl Derivatives
6. ILs for Biocatalyzed Synthesis of Starch Esters
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welton, T. Solvents and sustainable chemistry. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindström, U.M. Organic Reactions in Water: Principles, Strategies and Applications; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, M.-O.; Li, C.-J. Green chemistry oriented organic synthesis in water. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Stark, A. Handbook of Green Chemistry, Green Solvents, Ionic Liquids; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyère, C.; Jérôme, C.; Debuigne, A. Input of supercritical carbon dioxide to polymer synthesis: An overview. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, E.J. Supercritical and near-critical CO2 in green chemical synthesis and processing. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2004, 28, 121–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, C.M. The Potential of carbon dioxide in synthetic organic chemistry. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2007, 11, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Spear, S.K.; Huddleston, J.G.; Rogers, R.D. Polyethylene glycol and solutions of polyethylene glycol as green reaction media. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldebrant, D.J.; Witt, H.N.; Walsh, S.M.; Ellis, T.; Rauscher, J.; Jessop, P.G. Liquid polymers as solvents for catalytic reductions. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Giner, B.; Bandrés, I.; Lafuente, C.; Pino, M.R. Physicochemical properties of green solvents derived from biomass. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J. Ciecze jonowe-rozpuszczalniki XXI wieku. Przem. Chem. 2000, 79, 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wilpiszewska, K.; Spychaj, T. Ionic liquids: Media for starch dissolution, plasticization and modification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionic Liquids Market. Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Application (Solvents & Catalysts, Extractions & Separations, Bio-Refineries, Energy Storage), by Region, and Segment Forecasts. 2018–2025. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/ionic-liquids-market (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- El Seoud, O.A.; Koschella, A.; Fidale, L.C.; Dorn, S.; Heinze, T. Applications of ionic liquids in carbohydrate chemistry: A window of opportunities. ChemInform 2007, 38, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilet, A.; Quettier, C.; Wiatz, V.; Bricout, H.; Ferreira, M.; Rousseau, C.; Monflier, E.; Tilloy, S. Unconventional media and technologies for starch etherification and esterification. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1152–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, S.; Roczkowska, M.; Zarski, A.; Kapusniak, J. Esterification of starch with fatty acids. New opportunities and challenges. Przem. Chem. 2014, 93, 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.E. What’s an ionic liquid? Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2007, 16, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.C.; Rakshit, J.N. Nitrites of the alkylammonium bases: Ethylammonium nitrite, dimethylammonium nitrite, and trimethylammonium nitrite. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1911, 99, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, P. Molecular weights and electrical conductivity of several fused salts. Bull. Russian Acad. Sci. 1914, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids-from molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: Wenheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syguda, A. Sole deanolu i jego estrów. Przemysł Chem. 2006, 89, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freemantle, M. An Introduction to Ionic Liquids; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kubisa, P. Perspektywy zastosowań cieczy jonowych w chemii polimerów. Polimery 2006, 51, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domanska, U. Thermophysical properties and thermodynamic phase behavior of ionic liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 448, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, C.L. Room temperature haloaluminate ionic liquids. Novel solvents for transition metal solution chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1988, 60, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Neoteric solvents for clean catalysis. Kinet. Catal. Engl. Transl. 1996, 37, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mohan, R.S.; Scott, J.L. Reactivity of Ionic Liquids. ChemInform 2007, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pernak, J. Ciecze jonowe. Związki na miarę XXI wieku. Przem. Chem. 2003, 82, 521–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Spychaj, T.; Mąka, H. Imidazole-based deep eutectic solvents for starch dissolution and plasticization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R.; Stark, A.; Torres, M.-J. Influence of chloride, water, and organic solvents on the physical properties of ionic liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, J.F.; Maginn, E.J. Ionic liquids: Innovative fluids for chemical processing. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.; Gilea, M.A.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The distillation and volatility of ionic liquids. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, A.; Wasserscheid, P. Ultra purification of ionic liquids by melt crystallisation. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Industrial Crystallization BIWIC, Delft, The Netherlands, 13–15 September 2006; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Margreth, M.; Schlink, R.; Steinbach, A.; Gad, S.C. Water determination by Karl Fischer titration. Pharm. Sci. Encycl. 2010, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Perrin, D.D. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 4th ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids for Clean Technology. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 68, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, K.; Kärkkäinen, J.; Lajunen, M. Dissolution and depolymerization of barley starch in selected ionic liquids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.A.; Ashworth, C.R.; Matthews, R.P. Hydrogen bonding in ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1257–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, K.; Tokuda, H.; Watanabe, M. Ionicity in ionic liquids: Correlation with ionic structure and physicochemical properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; He, J. 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: A New and Powerful Nonderivatizing Solvent for Cellulose. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8272–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaar, J.L.; Jesionowski, A.M.; Berberich, J.A.; Moulton, R.; Russell, A.J. Impact of Ionic Liquid Physical Properties on Lipase Activity and Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4125–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Luo, Z.; Yu, S.; Fu, X. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of starch palmitate in mixed ionic liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9273–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, P.; Muderhwa, J.M.; Graille, J.; Haas, M.J. Customizing lipases for biocatalysis: A survey of chemical, physical and molecular biological approaches. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2000, 9, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L. Ring-opening graft polymerization of L-lactide onto starch granules in an ionic liquid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 2704–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.; Men, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yang, R.; Mahmood, K.; Liu, Z. Corn starch-based graft copolymers prepared via ATRP at the molecular level. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Du, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Preparation of corn starch-g-polystyrene copolymer in ionic liquid: 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, J.; Lappalainen, K.; Joensuu, P.; Lajunen, M. HPLC-ELSD analysis of six starch species heat-dispersed in [BMIM]Cl ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Guo, L.; Cui, B. Comparative study on phase transition and morphology of starch from maize and potato in ionic liquid/water mixtures: Effects of the different ratio. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Homogenous carboxymethylation of starch using 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid medium as a solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Budtova, T. Ionic liquid: A powerful solvent for homogeneous starch–cellulose mixing and making films with tuned morphology. Polymer 2012, 53, 5779–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Iqbal, T.; Yusup, S. Effect of ionic liquids pretreatment on thermal degradation kinetics of agro-industrial waste reinforced thermoplastic starch composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 247, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, W. Synthesis of cationic starch with a high degree of substitution in an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernoux-Villière, A.; Lévêque, J.-M.; Kärkkäinen, J.; Papaiconomou, N.; Lajunen, M.; Lassi, U. Task-specific ionic liquid for the depolymerisation of starch-based industrial waste into high reducing sugars. Catal. Today 2014, 223, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankri, A.; Arhaliass, A.; Dez, I.; Gaumont, A.C.; Grohens, Y.; Lourdin, D.; Pillin, I.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Leroy, E. Thermoplastic starch plasticized by an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Jacquet, P.; Coativy, G.; Reguerre, A.L.; Lourdin, D. Compatibilization of starch-zein melt processed blends by an ionic liquid used as plasticizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Truss, R.W.; Halley, P.J.; Shamshina, J.L.; McNally, T.; Rogers, R.D. Different characteristic effects of ageing on starch-based films plasticised by 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate and by glycerol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Flanagan, B.M.; Li, M.; Sangwan, P.; Truss, R.W.; Halley, P.J.; Strounina, E.V.; Whittaker, A.K.; Gidley, M.J.; Dean, K.M.; et al. Characteristics of starch-based films plasticised by glycerol and by the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate: A comparative study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D.; McNally, T.; Wang, D.K.; Halley, P.J.; Truss, R.W.; Zhao, S.; Chen, L. Facile preparation of starch-based electroconductive films with ionic liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5457–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, L.S.; Das, A.B. Effect of ionic liquid on sol-gel phase transition, kinetics and rheological properties of high amylose starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobregas, M.O.; Camacho, D.H. Gel polymer electrolyte system based on starch grafted with ionic liquid: Synthesis, characterization and its application in dye-sensitized solar cell. Electrochimica Acta 2019, 298, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendaoud, A.; Chalamet, Y. Effects of relative humidity and ionic liquids on the water content and glass transition of plasticized starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Spychaj, T. Ciecze jonowe jako plastyfikatory lub rozpuszczalniki skrobi. Polimery 2011, 11, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakrishna, K.; Manojkumar, K.; Sivaramakrishna, A. Ionic liquids as solvents and/or catalysts in polymerization. In Applications of Ionic Liquids in Polymer Science and Technology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 355–387. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolmaleki, A.; Mohamadi, Z. Acidic ionic liquids catalyst in homo and graft polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Picchioni, F. Modification of starch: A review on the application of “green” solvents and controlled functionalization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y. Synthesis of starch esters in ionic liquids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, Z. Homogeneous synthesis and characterization of starch acetates in ionic liquid without catalysts. Starch 2011, 64, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Volkert, B.; Hassan-Nejad, M.; Greco, T.; Fink, H.-P. Synthesis of thermoplastic starch mixed esters catalyzed by the in situ generation of imidazolium salts. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Volkert, B. Preparing esters from high-amylose starch using ionic liquids as catalysts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shogren, R.; Biswas, A. Acetylation of starch with vinyl acetate in imidazolium ionic liquids and characterization of acetate distribution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shogren, R.L.; Biswas, A.; Willett, J.L. Preparation and physical properties of maltodextrin stearates of low to high degree of substitution. Starch-Stärke 2010, 62, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Luo, Z.-G.; Luo, F.-X. Ionic liquids as solvents for dissolution of corn starch and homogeneous synthesis of fatty-acid starch esters without catalysts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, Y. Synthesis of high fatty acid starch esters with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride as a reaction medium. Starch-Stärke 2011, 63, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalegn, T.; Garcia, I.J.V.; Titman, J.; Licence, P.; Chebude, Y. Synthesis of starch vernolate in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Luo, Z.; Fu, X.; Xiao, Z. Two-step method of enzymatic synthesis of starch laurate in ionic liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9882–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y. Ionic liquids as novel solvents for biosynthesis of octenyl succinic anhydride-modified waxy maize starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desalegn, T.; Villar-Garcia, I.J.; Titman, J.; Licence, P.; Diaz, I.; Chebude, Y. Enzymatic synthesis of epoxy fatty acid starch ester in ionic liquid-organic solvent mixture from vernonia oil. Starch-Stärke 2013, 66, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarski, A.; Ptak, S.; Siemion, P.; Kapusniak, J. Esterification of potato starch by a biocatalysed reaction in an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, S.; Banerjee, R. A green approach for starch modification: Esterification by lipase and novel imidazolium surfactant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarski, A.; Bajer, K.; Zarska, S.; Kapusniak, J. From high oleic vegetable oils to hydrophobic starch derivatives: I. Development and structural studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 214, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarski, A.; Bajer, K.; Raszkowska-Kaczor, A.; Rogacz, D.; Zarska, S.; Kapusniak, J. From high oleic vegetable oils to hydrophobic starch derivatives: II. Physicochemical, processing and environmental properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 243, 116499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

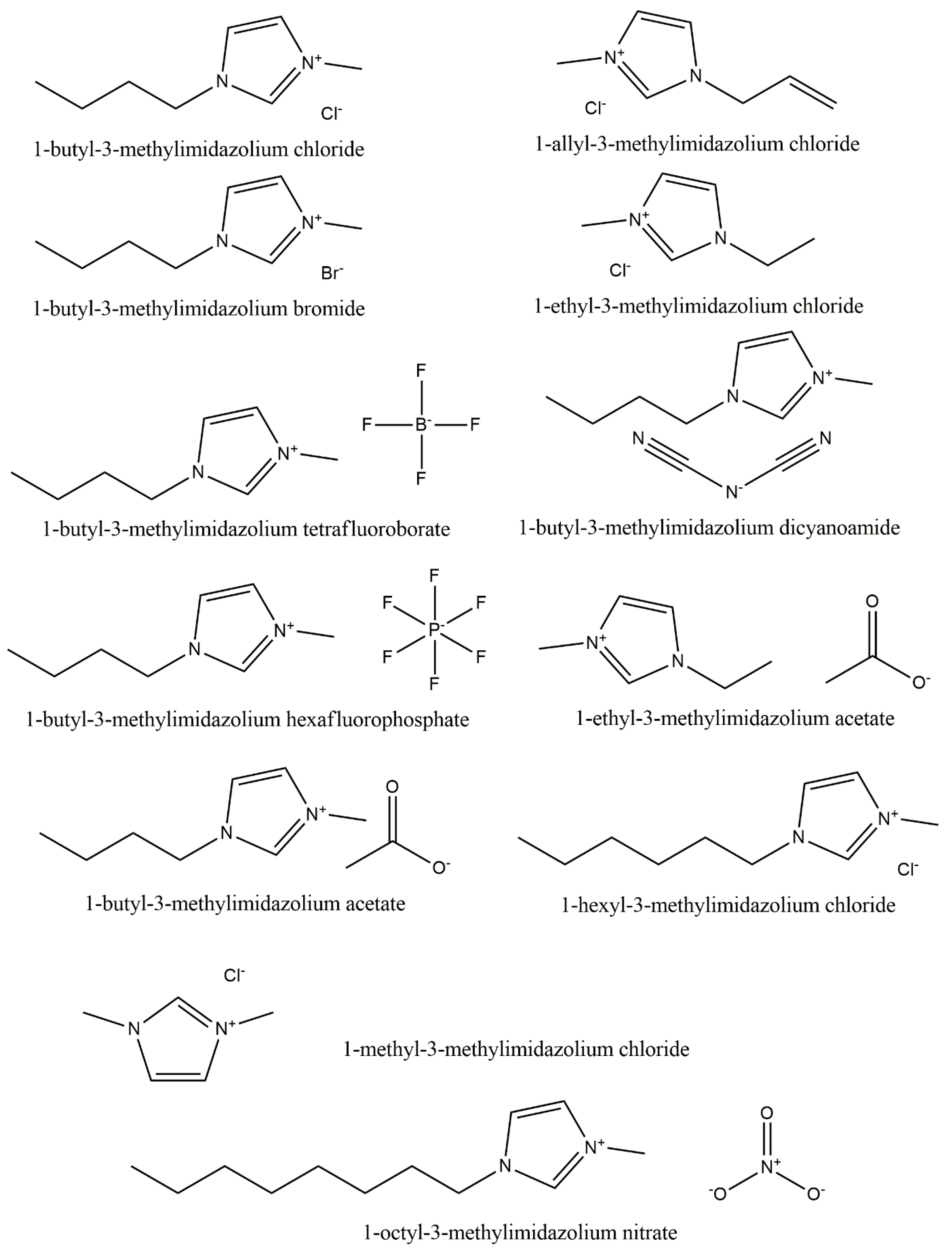
| Properties | Organic Solvent | Ionic Liquids |
|---|---|---|
| Number of compounds | <1000 | >1,000,000 |
| Applicability | single function | multi-function |
| Catalytic properties | rare | common |
| Range of availability | limited | unlimited (“designer solvents”) |
| Vapor pressure | usually high | negligible |
| Flammability | usually flammable | usually non-flammable |
| Polarity | usually high | moderate |
| Cost | normal | expensive |
| Recyclability | rare | frequent |
| Chirality | rare | common, controlled |
| Solvation | usually weak | usually strong |
| Ionic Liquid | Role | Application | Refrence |
|---|---|---|---|
| [AMIM]Cl | solvent | Grafting of corn starch with L-Lactide by ring-opening graft polymerization (ROP) | [49] |
| [AMIM]Cl | solvent | Grafting reaction of polystyrene (PS) and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) via radical polymerization (ATRP) using starch-based macroinitiator | [50] |
| [EMIM]Ac | solvent | Grafting of corn starch with polystyrene by the conventional free radical polymerization | [51] |
| [BMIM]Cl | solvent | Effect of [BMIM]Cl on dissolution and degradation of six different native starches (wheat, barley, potato, rice, corn, and waxy corn) under conventional oil bath and controlled microwave heating | [52] |
| [AMIM]Cl [BMIM]Cl [HexMIM]Cl [BMIM]Br [HexMIM]Br [HMIM]HCOO [HBIM]HCOO [HIM[HCOO [NH3CH2CH2OH]HCOO [EMIM]Me2PO4 | solvent | Effect of ILs with various cations and anions on dissolution process of barley starch | [42] |
| [EMIM]Ac | solvent | Solvent effect on maize starch (MS) and potato starch (PS) | [53] |
| [BMIM]Cl | solvent | Homogenous carboxymethylation of corn starch | [54] |
| [EMIM]Ac | solvent | Preparation of starch-cellulose films | [55] |
| [BMIM]Cl [EMIM]dep | solvent | Pretreatment of oil palm frond fiber with ILs Preparation of biocomposites with TPS as a polymer matrix | [56] |
| [BMIM]Cl | solvent | Preparation of cationic corn starch by reacting corn starch with glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride utilizing 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMIMCl) as a reaction medium | [57] |
| [AMIM]Cl [SBMIM]Cl | solvent | Optimization of the conditions for dissolution and depolymerization of potato starch industrial wastes in ILs. Dual role of SBMIM CL as a solvent and catalyst. | [58] |
| [BMIM]Cl | plasticizer | Plasticizer in the processing of (maize) starch | [59] |
| [BMIM]Cl | compatibilizer | Compatibilizer for the blends of starch and zein | [60] |
| [EMIM]Ac | plasticizer | Plasticizer of starch-based film preparation | [61,62] |
| [EMIM]Ac | plasticizer | Plasticizer in preparation of transparent conductive thermoplastic starch (TPS) at a relatively mild temperature (55 or 65 °C) | [63] |
| [BMIM]Cl | plasticizer | Plasticizer effect on sol–gel phase transition, rheological, and physical properties of high amylose rice starch | [64] |
| GMIC | plasticizer | Grafting 1-glycidyl-3- methylimidazolium chloride (GMIC) ionic liquid onto the polysaccharide chain to afford a cationic starch (CS) | [65] |
| [BMIM]Cl [EMIM]Ac [AMIM]Cl | plasticizer | Preparation of thermoplastic starch (TPS) with different ratios of ionic liquids | [66] |
| Solvent/Medium | Substrate | Reagent | Catalyst | Product | DSMAX | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM]Cl | Corn starch | Acetic or succinic anhydride | Pyridine | Starch acetate or succinate | 2.35 (A) 0.93 (S) | [71] |
| [BMIM]Cl | Corn starch | Acetic anhydride | - | Starch acetate | 2.11 | [72] |
| Anhydride Chloride | Corn starch | Acid anhydride or Acyl chloride | Imidazolium based ILs | Starch mixed esters | ~3 | [73] |
| Anhydride | Corn starch | Acetic or propionic anhydride | [BMIM]Cl | Starch acetate or propionate | 2.89 (A) 2.86 (P) | [74] |
| [BMIM]X; X-halogen | Corn maltodextrin | Vinyl acetate | - | Maltodextrin acetate | 1.8 | [75] |
| [BMIM]DCA | Maltodextrin | Vinyl stearate | - | 2.4 | [76] | |
| IL, DMF or DMSO | Corn starch | Lauric, palmitic, or stearic acid | - | Starch laurate, palmitate, or stearate | 0.105 (L) 0.098 (P) 0.092 (S) | [77] |
| [BMIM]Cl | Corn starch | Methyl laurate or stearate | Pyridine | Starch laurate or stearate | 0.37 (L) 0.28 (S) | [78] |
| [BMIM]Cl | Cassava starch | Vernolic acid methyl ester | Pyridine | Starch vernolate | 1.03 | [79] |
| Solvent/Medium | Substrate | Reagent | Catalyst | Product | DSMAX | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
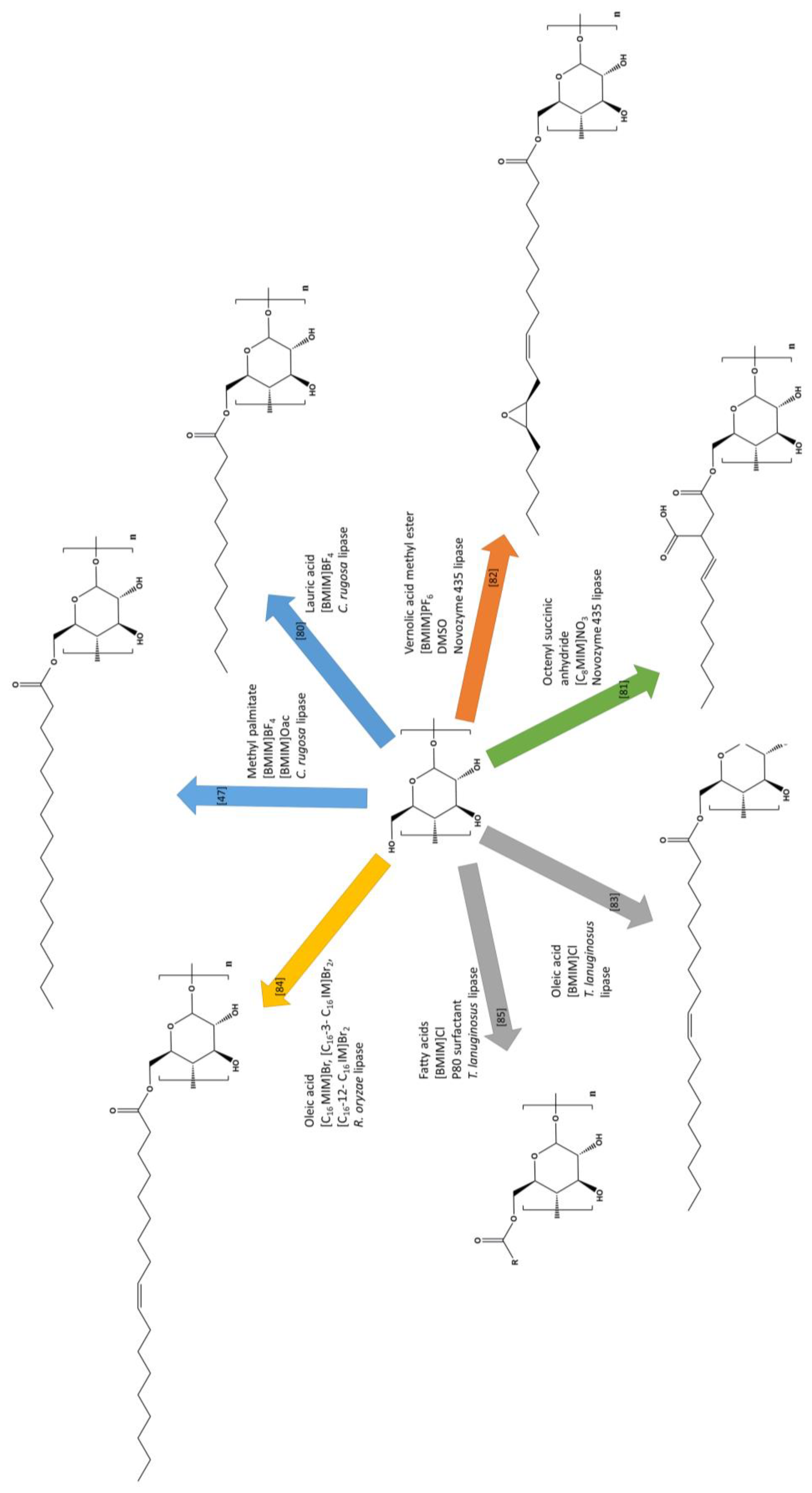
| Mixture of [BMIM]BF4 [BMIM]OAc | High-amylose maize starch | Methyl palmitate | C. rugosa lipase | Starch palmitate | 0.153 | [47] |
| [BMIM]BF4 | High-amylose maize starch | Lauric acid | C. rugosa lipase | Starch laurate | 0.171 | [80] |
| Mixture of [BMIM]PF6 DMSO | Cassava starch | Vernolic acid methyl ester | Novozyme 435 lipase | Starch vernolate | 0.95 | [82] |
| [C8MIM]NO3 | Waxy maize starch | Octenyl succinic anhydride | Novozyme 435 lipase | Starch octenyl succinate | 0.013 | [81] |
| C16 MIMBr, C16-3- C16 IMBr2, C16-12- C16 IMBr2 | Corn starch | Oleic acid | R. oryzae lipase | Starch oleate | 2.75 | [84] |
| [BMIM]Cl | Potato starch | Oleic acid | T.lanuginosus lipase | Starch oleate | 0.22 | [83] |
| [BMIM]Cl P80 surfactant | Potato starch | Fatty acids | T.lanuginosus lipase | Starch esters | 1.36 | [85] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ptak, S.; Zarski, A.; Kapusniak, J. The Importance of Ionic Liquids in the Modification of Starch and Processing of Starch-Based Materials. Materials 2020, 13, 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204479
Ptak S, Zarski A, Kapusniak J. The Importance of Ionic Liquids in the Modification of Starch and Processing of Starch-Based Materials. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204479
Chicago/Turabian StylePtak, Sylwia, Arkadiusz Zarski, and Janusz Kapusniak. 2020. "The Importance of Ionic Liquids in the Modification of Starch and Processing of Starch-Based Materials" Materials 13, no. 20: 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204479
APA StylePtak, S., Zarski, A., & Kapusniak, J. (2020). The Importance of Ionic Liquids in the Modification of Starch and Processing of Starch-Based Materials. Materials, 13(20), 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204479







