Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Study Variables and Measurements
- -
- Probing depth (PD) in millimeters was measured from the peri-implant mucosal margin to the bottom of the peri-implant sulcus,
- -
- Bleeding on probing (BoP) was determined as presence or absence of bleeding 15 s after gentle probing,
- -
- Keratinized tissue (KT) width in millimeters was measured with a periodontal probe at the mid-buccal aspect of the implant from the free gingival margin to the muco-gingival junction. Furthermore, the KT measurements were categorized in two groups, group 1 when KT ≥ 2 mm and group 2 when KT < 2 mm.
- -
- Depth of implant placement: On the day of the surgery, a periapical radiograph was performed to provide the depth of implant placement read on the proximal sides.
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Implant Survival
3.2. Marginal Bone Loss and Implant Success
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The failure rate of C1 implants placed and rehabilitated by inexperienced students at the one- year follow-up was low (3.6%) and comparable to the data obtained by experienced practitioners.
- No contributing factors specific to the inexperience of the students could be identified regarding implant failure and MBL.
- Several factors have been shown to affect MBL such as diabetes, implant depth, PD, and KT. By contrast, thickness of the gingiva and prosthetic abutment height were not found to be contributing factors.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roccuzzo, M.; Bonino, L.; Dalmasso, P.; Aglietta, M. Long-term results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients: 10 year data around sandblasted and acid etched surface. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicilia, A.; Quirynen, M.; Fontolliet, A.; Francisco, H.; Friedman, A.; Linkevicius, T.; Lutz, R.; Meijer, H.J.; Rompen, E.; Rotundo, R.; et al. Long-term stability of peri-implant tissues after bone or soft tissue augmentation. Effect of zirconia or titanium abutments on peri-implant soft tissues. Summary and consensus statements. The 4th EAO consensus conference. Clin. Oral Implants 2015, 26, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; O′Valle, F.; Catena, A. Marginal bone loss as success criterion in implant dentistry: Beyond 2 mm. Clin. Oral 2015, 26, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.; Hertzberg, R.; Har-Nes, S.; Schwartz-Arad, D. Long-term marginal bone loss around single dental implants affected by current and past smoking habits. Implant Dent. 2008, 17, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, L.; Ofec, R.; Grossmann, Y.; Anner, R. Periodontal disease as a risk for dental implant failure over time: A long-term historical cohort study. J. Clin. Peridontol. 2011, 38, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosper, L.; Redaelli, S.; Pasi, M.; Zarone, F.; Radaelli, G.; Gherlone, E.F. A randomized prospective multi-center trial evaluating the platform switching technique for the prevention of post-restorative crestal bone loss. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santiago, J.; Batista, V.; Verri, F.; Honório, H.; De Mello, C.; Almeida, D.; Pellizzer, E.P. Platform switching implants and bone preservation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Lin, G.; Wang, H. Effects of platform-switching on peri-implant soft and hard tissue outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Pico, A.; Caneiro, L.; Nóvoa, L.; Batalla, P.; Martín-Lancharro, P. Effect of abutment height on inter-proximal implant bone level in the early healing: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, A.; Martín-Lancharro, P.; Caneiro, L.; Nóvoa, L.; Batalla, P.; Blanco, J. Influence of abutment height and implant depth position on inter-proximal peri-implant bone in sites with thin mucosa: A 1-year randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Monje, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; O‘Valle, F.; Catena, A. Abutment height influences the effect of platform switching on peri-implant marginal bone loss. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Apse, P.; Grybauskas, S.; Puisys, A. The influence of soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants: A 1-year prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suárez-López, D.A.F.; Lin, G.H.; Monje, A.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Wang, H.L. Influence of soft tissue thickness on peri-implant marginal bone loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavira, L.; Salcido, J.P.; Guda, T.; Ong, J.L. Current trends in dental implants. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 40, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiskel, H.; Tsolka, P. Treatment outcomes in implant therapy: The influence of surgical and prosthodontic experience. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1995, 8, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Sendyk, D.; Chrcanovic, B.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A.; Zindel Deboni, M. Does surgical experience influence implant survival rate? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Kan, J.; Rungcharassaeng, K.; Roe, P.; Lozada, J. Immediate loading of maxillary and mandibular implant-supported fixed complete dentures: A 1 to 10 year retrospective study. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 38, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Weber, H.; Lang, N. Tissue integration of non-submerged implants. 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1990, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Beschnidt, S.; Cacaci, C.; Dedeoglu, K.; Hildebrand, D.; Hulla, H.; Iglhaut, G.; Krennmair, G.; Schlee, M.; Sipos, P.; Stricker, A.; et al. Implant success and survival rates in daily dental practice: 5-year results of a non-interventional study using CAMLOG screw-line implants with or without platform-switching abutments. Int. J. Implants Dent. 2018, 33, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.; Zembic, A.; Pjetursson, B.; Zwahlen, M.; Thoma, D. Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjetursson, B.; Thoma, D.; Jung, R.; Zwahlen, M.; Zembic, A. A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 years. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, J.; Machtei, E.; Frankental, S.; Gabay, E.; Mayer, Y.; Joseph, L.; Cohen, O. Clinical and patient-related outcomes of a tapered implant system with switched platform conical abutments: A private practice field trial. J. Oral Implantol. 2018, 44, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, M.J.; Pellizzer, E.; Gomes, J.; Lemos, C.; Santiago Junior, J.; Vasconcelos, B.; Dantes de Moraes, S.L. Influence of diabetes on the survival rate and marginal bone loss of dental implants: An overview of systematic reviews. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer-Chover, H.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Gomar-Vercher, S.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M. Impact of crestal and subcrestal implant placement in peri-implant bone: A prospective comparative study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, C.; Jammal, G.; Buyers, M.; Tsigarida, A.; Chochlidakis, K.; Feng, C.; Caton, J. Influence of apico-coronal implant placement on post-surgical crestal bone loss in humans. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Chover, H.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Aloy-Prosper, A.; Canullo, L.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D. Does apico-coronal implant position influence peri-implant marginal bone loss? A 36-month follow-up randomized clinical trial. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles, C.; Rodriguez-Ciurana, X.; Muñoz, F.; Permuy, M.; López-Alonso, H.; Nart, J. Influence of implant neck surface and placement depth on crestal bone changes and soft tissue dimensions around platform-switched implants: A histologic study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Tormena, M.; Matarazzo, F.; Araújo, M. The influence of peri-implant keratinized mucosa on brushing discomfort and peri-implant tissue health. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwein, C.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Nelson, K.; Fluegge, T.; Fretwurst, T. Is the presence of keratinized mucosa associated with peri-implant tissue health? A clinical cross-sectional analysis. Int. J. Implants Dent. 2015, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perussolo, J.; Souza, A.B.; Matarazzo, F.; Oliveira, R.; Araújo, M. Influence of the keratinized mucosa on the stability of peri-implant tissues and brushing discomfort: A 4-year follow-up study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Penãrrocha-Oltra, D.; Covani, U.; Botticelli, D.; Serino, G.; Penarrocha, M. Clinical and microbiological findings in patients with peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Becker, J.; Civale, S.; Sahin, D.; Iglhaut, T.; Iglhaut, G. Influence of the width of keratinized tissue on the development and resolution of experimental peri-implant mucositis lesions in humans. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Grasso, G.; Dalmasso, P. Keratinized mucosa around implants in partially edentulous posterior mandible: 10-year results of a prospective comparative study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennström, J.; Derks, J. Is there a need for keratinized mucosa around implants to maintain health and tissue stability? Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Madi, I. Soft-Tissue conditions around dental implants: A literature review. Implants Dent. 2019, 28, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Camacho-Alonso, F.; Tallarico, M.; Meloni, S.; Xhanari, E.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D. Mucosa thickness and peri-implant crestal bone stability: A clinical and histologic prospective cohort trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2017, 32, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, T.; Puisys, A.; Steigmann, M.; Vindasiute, E.; Linkeviciene, L. Influence of Vertical soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants with platform switching: A comparative clinical study. Clin. Implants Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; León-Cano, A.; Ortega-Oller, I.; Monje, A.; Suárez, F.; ÓValle, F.; Spinato, S.; Catena, A. Prosthetic abutment height is a key factor in peri-implant marginal bone loss. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinato, S.; Stacchi, C.; Lombardi, T.; Bernardello, F.; Messina, M.; Zaffe, D. Biological width establishment around dental implants is influenced by abutment height irrespective of vertical mucosal thickness: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, C.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, H. Influence of abutment height on peri-implant marginal bone loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padial-Molina, M.; Gutierrez-Garrido, L.; Lopez-Chaichio, L.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, R.; Guerra-Lorenzo, C.; Lauritano, F.; Monero, P.G. Early loading after 4 weeks of C1 implants with a B+ treated surface-effect on marginal bone level. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragucci, G.M.; Giral-Hernando, M.; Garcia, S.; Hernández–Alfaro, F. Factors affecting implant failure and crestal bone loss. A study of 220 implants placed by students. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2019, 30, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
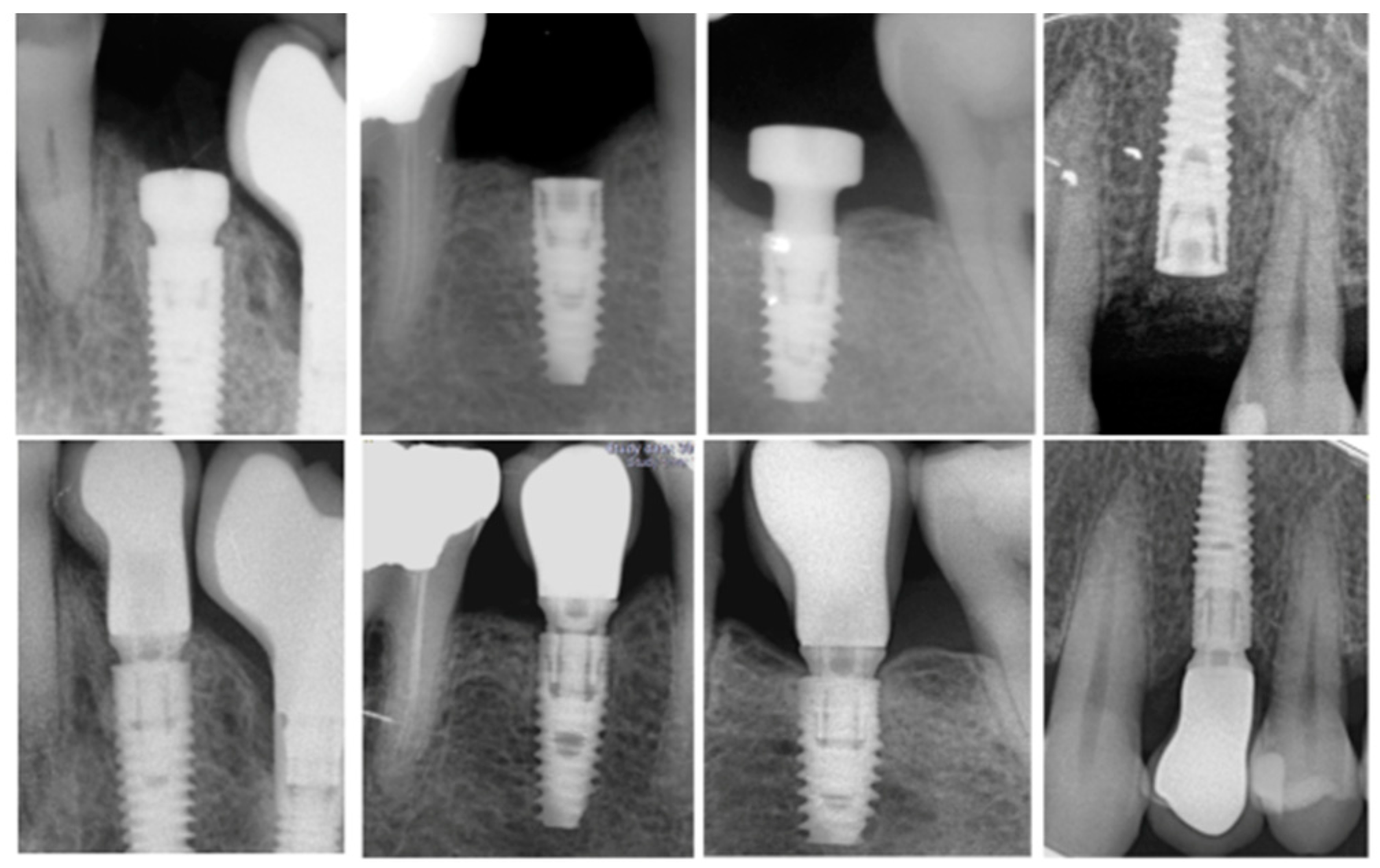




| Patient Variables | Implant Variables | Surgical Variables | Prosthetic Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Diameter | Corono-apical implant placement depth | Screw-retained |
| Gender | Length | Bone/sinus grafting | Cemented |
| Smoking | Local site | Healing protocol | Crown–implant ratio |
| Periodontal disease | Jaw | Insertion torque | - |
| Diabetes | Abutment height | - | - |
| Oral hygiene | Soft tissue thickness | - | - |
| Bone quality | Phenotype | - | - |
| - | Probing depth | - | - |
| - | Keratinized mucosa | - | - |
| - | Bleeding on probing | - | - |
| Implant Failure | Category | OR | IC 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEX | Male (n = 24) | 1 | - | - |
| Female (n = 43) | 0.97 | 0.15–6.39 | 0.972 | |
| SMOKING | No (n = 59) | 1 | - | - |
| Yes (n = 8) | 1.86 | 0.16–21.2 | 0.617 | |
| DIABETES | No (n = 53) | 1 | - | - |
| Yes (n = 4) | 2.64 | 0.23–29.9 | 0.432 | |
| HISTORY OF PERIODONTITIS | No (n = 51) | 1 | - | - |
| Yes (n = 26) | 3.05 | 0.30–31.3 | 0.348 | |
| SEGMENT | Anterior (n = 40) | 1 | - | - |
| Posterior (n = 90) | 0.25 | 0.04–1.60 | 0.143 | |
| ARCH | Maxilla (n = 63) | 1 | - | - |
| Mandible (n = 67) | 1.22 | 0.20–7.47 | 0.832 | |
| DIAMETER (mm) | ≤3.75 (n = 47) | 1 | - | 0.981 |
| 4.00–4.30 (n = 69) | 1.02 | 0.16–6.49 | 0.981 | |
| 5 (n = 14) | - | - | - | |
| LENGTH (mm) | 8,0 (n = 24) | 1 | - | 0.099 |
| 10 (n = 58) | - | - | - | |
| 11.5 (n = 40) | 6.94 | 0.69–69.5 | 0.099 | |
| ≥13 (n = 8) | - | - | - | |
| SURGICAL PROTOCOL | 1 stage (n = 50) | 1 | - | - |
| 2 stage (n = 80) | 1.81 | 0.17–18.8 | 0.62 |
| Independent Variables | Category | Beta | IC 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEX | Male (0.48 ± 0.38) | 0 | ||
| Female (0.54 ± 0.41) | 0.06 | −0.13–0.25 | 0.515 | |
| SMOKING | No (0.52 ± 0.40) | 0 | ||
| Yes (0.50 ± 0.35) | −0.02 | −0.22–0.18 | 0.839 | |
| DIABETES | No (0.55 ± 0.40) | 0 | ||
| Yes (0.32 ± 0.27) | −0.23 | −0.43–−0.02 | 0.035 * | |
| PERIODONTITIS | No (0.51 ± 0.32) | 0 | ||
| Yes (0.54 ± 0.46) | 0.03 | −0.16–0.22 | 0.753 | |
| SEGMENT | Anterior (0.48 ± 0.33) | 0 | ||
| Posterior (0.45 ± 0.42) | 0.06 | −0.08–0.20 | 0.391 | |
| ARCH | Maxilla (0.60 ± 0.46) | 0 | ||
| Mandible (0.46 ± 0.33) | −0.14 | −0.29–0.02 | 0.078 | |
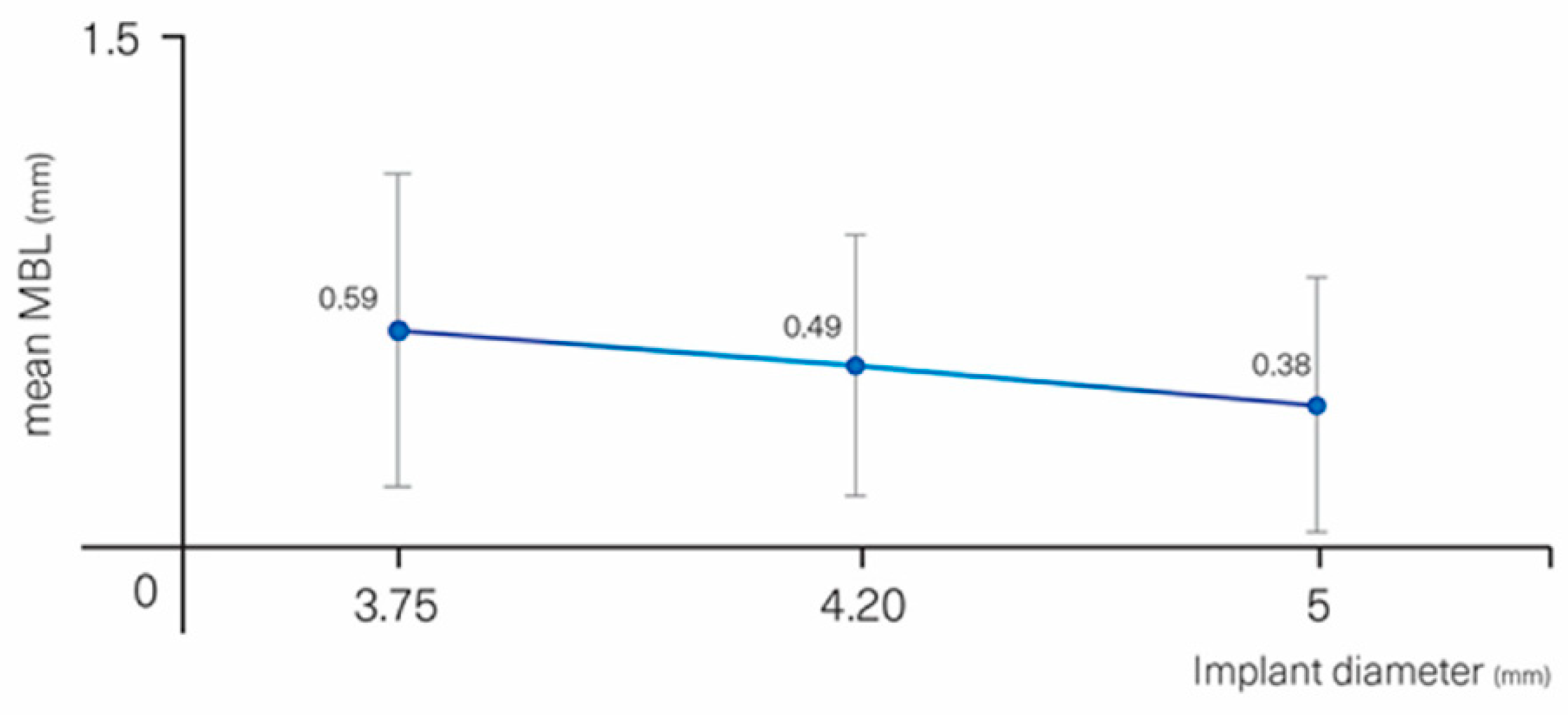
| DIAMETER (mm) | ≤3.75 (0.64 ±0.19) | 0 | 0.221 | |
| 4.00–4.30 (0.69 ± 0.21) | −0.10 | −0.30–0.10 | 0.315 | |
| 5 (0.38 ± 0.36) | −0.22 | −0.47–0.03 | 0.083 | |
| LENGTH (mm) | 8 (0.58 ± 0.43) | 0 | 0.749 | |
| 10 (0.50 ± 0.39) | −0.08 | −0.24–0.08 | 0.338 | |
| 11.5 (0.53 ±0.41) | −0.05 | −0.26–0.17 | 0.662 | |
| ≥13 (0.42 ± 0.27) | −0.12 | −0.37–0.14 | 0.375 | |
| SURGICAL PROTOCOL | 1 STAGE (0.56 ± 0.44) | 0 | ||
| 2 STAGE (0.50 ± 0.37) | −0.06 | −0.27–0.15 | 0.555 | |
| IMPLANT SITE | Healed (0.52 ± 0.40) | 0 | ||
| Post-extraction (0.48 ± 0.34) | −0.04 | −0.29–0.21 | 0.728 | |
| BONE GRAFTING | No (0.51 ± 0.35) | 0 | ||
| Yes (0.58 ± 0.56) | 0.08 | −0.21–0.36 | 0.591 | |
| SINUS GRAFTING | No (0.51 ± 0.37) | 0 | ||
| Yes (0.66 ± 0.61) | 0.15 | −0.27–0.57 | 0.478 | |
| DEPTH OF IMPLANT PLACEMENT (mm) | ≤−1.5 (0.86 ± 0.61) | 0 | 0.002 ** | |
| −1 mm (0.58 ± 0.35 | −0.29 | −0.71–0.14 | 0.189 | |
| −0.5 mm (0.52 ± 0.35) | −0.34 | −0.75–0.07 | 0.102 | |
| ≥0 mm (0.31 ± 0.29) | −0.55 | −0.97–−0.13 | 0.011 * | |
| SOFT-TISSUE PHENOTYPE | Thin (0.57 ± 0.33) | 0 | ||
| Thick (0.51 ± 0.41) | −0.06 | −0.23–0.11 | 0.462 | |
| BONE QUALITY | 1 (0.48 ± 0.54) | 0 | 0.542 | |
| 2 (0.48 ± 0.32) | 0 | −0.34–0.34 | 0.983 | |
| 3 (0.60 ± 0.47) | 0.12 | −0.26–0.51 | 0.532 | |
| 4 (0.40 ± 0.26) | −0.08 | −0.45–0.30 | 0.684 |
| Parameter | Category | Beta | IC 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOP BUCCAL | No (0.48 ± 0.39) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.65 ± 0.40) | 0.17 | 0.00–0.34 | 0.049 * | |
| BOP LINGUAL | No (0.50 ± 0.38) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.63 ± 0.46) | 0.13 | −0.07–0.32 | 0.202 | |
| PD TOTAL | (0.52 ± 0.39) | 0.18 | 0.05–0.31 | 0.008 ** |
| PLAQUE BUCCAL | No (0.54 ± 0.41) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.46 ± 0.32) | −0.08 | −0.20–0.06 | 0.259 | |
| PLAQUE LINGUAL | No (0.52 ± 0.41) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.49 ± 0.32) | −0.04 | −0.22–0.15 | 0.708 | |
| KT | (0.52 ± 0.39) | −0.10 | −0.17–−0.03 | 0.004 ** |
| KT groups | <2 mm (0.78 ± 0.40) | 0 | - | - |
| ≥2 mm (0.45 ± 0.36) | −0.34 | −0.51–−0.16 | <0.001 *** | |
| Ti-BASE | No (0.43 ± 0.43) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.56 ± 0.37) | 0.13 | −0.09–0.35 | 0.235 | |
| MULTI-UNIT | No (0.55 ± 0.37) | 0 | - | - |
| Yes (0.43 ± 0.44) | −0.12 | −0.35–0.11 | 0.304 | |
| SOFT TISSUE PHENOTYPE | Thin (0.57 ± 0.33) | 0 | - | - |
| Thick (0.51 ± 0.41) | −0.06 | −0.23–0.11 | 0.462 | |
| GINGIVAL THICKNESS | - | −0.07 | −0.22–0.08 | 0.384 |
| BONE QUALITY | - | 0.06 | −0.09–0.21 | 0.416 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragucci, G.M.; Giralt-Hernando, M.; Méndez-Manjón, I.; Cantó-Navés, O.; Hernández-Alfaro, F. Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Materials 2020, 13, 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204511
Ragucci GM, Giralt-Hernando M, Méndez-Manjón I, Cantó-Navés O, Hernández-Alfaro F. Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204511
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagucci, Gian Maria, Maria Giralt-Hernando, Irene Méndez-Manjón, Oriol Cantó-Navés, and Federico Hernández-Alfaro. 2020. "Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study" Materials 13, no. 20: 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204511
APA StyleRagucci, G. M., Giralt-Hernando, M., Méndez-Manjón, I., Cantó-Navés, O., & Hernández-Alfaro, F. (2020). Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Materials, 13(20), 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204511






