Use of GRP Pipe Waste Powder as a Filler Replacement in Hot-Mix Asphalt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
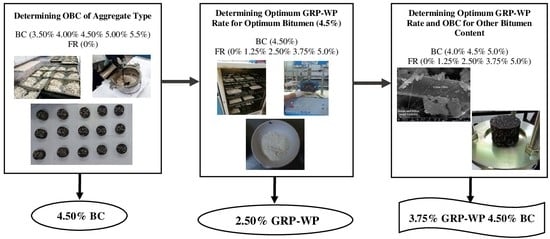
2.2. Methodology
- Binder content corresponding to the maximum stability (found as 4.64 for MS = 1143)
- Binder content corresponding to the maximum bulk specific gravity (found as 4.65 for Gsb = 2409).
- Binder content corresponding to the median value of the specification design limits of air content in the total mix (found as 4.21 for Va = 5%) [50].
- Binder content corresponding to the median value of the specification design limits of VFA in the total mix (found as 4.51 for VFA = 67.5%) [50].
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urban Development USA. A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/30317 (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Hassan, H.F. Recycling of municipal solid waste incinerator ash in hot-mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, A.; Colorado, H.A. Marshall stability and flow tests for asphalt concrete containing electric arc furnace dust waste with high ZnO contents from the steel making process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Application of waste materials as fillers in bituminous mixes. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Rekha, P.; Surya, M. Utilization of Linz–Donawitz slag from steel industry for waste minimization. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Naseri, H.; Nejad, F.M. Sustainable asphalt concrete containing high reclaimed asphalt pavements and recycling agents: Performance assessment, cost analysis, and environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljassar, A.H.; Al-Fadala, K.B.; Ali, M.A. Recycling building demolition waste in hot-mix asphalt concrete: A case study in Kuwait. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2005, 7, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaodan, C.; Wang, H. Life cycle assessment of asphalt pavement recycling for greenhouse gas emission with temporal aspect. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Laboratory evaluation on recycling waste industrial glass powder as mineral filler in hot mix asphalt. In Proceedings of the Civil Engineering Conference—Innovation for Sustainability, Hamirpur, India, 9–10 September 2016; pp. 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chai, J.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Performance evaluation of green-concrete pavement material containing selected C&D waste and FA in cold regions. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Aljassar, A.H.; Metwali, S.; Ali, M.A. Effect of filler types on marshall stability and retained strength of asphalt concrete effect of filler types on marshall stability and retained strength of asphalt concrete. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2016, 5, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkati, A.; Diew, W.; Delai, D. Effects of Fillers on Properties of Asphalt-Concrete Mixture. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 138, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, A.; Cloutier, C.; Bautista, E.G.; Sobolev, K. Impact of Coal Combustion Product Incorporation in Asphalt Mixture Performance. In Proceedings of the 97th Annual Meeting of Transportation Research Board, Washington DC, USA, 8–12 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Al-Qadi, I.; Faheem, A.; Bahia, H.; Yang, S.H.; Reinke, G. Effect of mineral filler characteristics on asphalt mastic and mixture rutting potential. Trans. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2208, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D.; Liao, M.C.; Thom, N.N. Fatigue behaviour of bitumen-filler mastics. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Asphalt Pavements, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 12–17 August 2006; pp. 485–495. [Google Scholar]
- Modarres, A.; Bengar, P.A. Investigating the indirect tensile stiffness, toughness and fatigue life of hot mix asphalt containing copper slag powder. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2017, 20, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasandín, A.R.; Pérez, I. The influence of the mineral filler on the adhesion between aggregates and bitumen. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 58, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.A.; Goetz, W.H. Mechanical behavior and reinforcement of mineral filler-asphalt mixes. Proc. Assoc. Asph. Paving Technol. 1973, 42, 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gubler, R.; Liu, Y.; Anderson, D.A.; Partl, M.N. Investigation of system and asphalt binders by rheological means. J. Asph. Paving Technol. 1999, 68, 284–304. [Google Scholar]
- Recasens, R.M.; Martinez, A.; Jimenez, F.P.; Bianchetto, H. Effect of filler on the aging potential of asphalt mixtures. Trans. Res. Rec. J. Trans. Res. Board 2005, 1901, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Z.; Lin, J.T.; Wu, S.P.; Liu, C.H. Utilization of recycled brick powder as alternative filler in asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, P.; Micaelo, R.; Duarte, C.; Quaresma, L. Influence of bitumen and filler on the selection of appropriate mixing and compaction temperatures. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2014, 7, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.J. Performance evaluation of the use of tire-derived fuel fly ash as mineral filler in hot mix asphalt concrete. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2020, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hdabi, A. Laboratory investigation on the properties of asphalt concrete mixture with rice husk ash as filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 12, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargın, Ş.; Saltan, M.; Morova, N.; Serin, S.; Terzi, S. Evaluation of rice husk ash as filler in hot mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.S.; Mun, P.H.; Keun, R.S. A study on engineering characteristics of asphalt concrete using filler with recycled waste lime. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, İ.; Terzi, S. Evaluation of andesite waste as mineral filler in asphaltic concrete mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woszuk, A.; Bandura, L.; Franus, W. Fly ash as low cost and environmentally friendly filler and its effect on the properties of mix asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 520, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Li, P.; Liang, M.; Yao, Z. Experimental study on rheological properties and moisture susceptibility of asphalt mastic containing red mud waste as a filler substitute. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.C.; Freire, L.; Micaelo, Q.R. Evaluation of waste materials as alternative sources of filler in asphalt mixtures. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Effects of Using Kota Stone as Filler on Mechanical Properties of Asphalt Concrete Mixes. In Recent Developments in Waste Management, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Kalamdhad, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 57, pp. 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, R.; Kumar, A.; Rahman, G. Rheological and mechanical properties of bauxite residue as hot mix asphalt filler. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2019, 12, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, J.; Mareddy, S.S.; Mativenga, P.T. Energy intensity and environmental analysis of mechanical recycling of carbon fibre composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 81, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G. Durability of cementitious products made withblended cements based on GRP industrial waste. In Proceedings of the Atti del VII Congresso Nazionale AIMAT, Associazione Italiana d’Ingegneria dei Materiali, Ancona, Italy, 29 Giugno–2 Luglio 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G. Re-use of GRP industrial waste in cementitious products. In Young Researchers’ Forum, Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Global Construction: Ultimate Concrete Opportunities. Dundee, Scotland, 5–7 July 2005; Dhir, R.K., Halliday, J.E., Csetenyi, E., Eds.; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2005; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G. Effect of GRP industrial waste on durability of cement mortars. In Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Proceedings of the First International Conference. Coventry, UK, 11–13 June 2007; Chun, Y.M., Claisse, P., Naik, T.R., Ganjian, E., Eds.; Taylor & Francis/Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G. Re-use of GRP industrial by-product as filler for SCC. In Proceedings of the SCC2008: Challenges and Barriers to Application, The Third North American Conference on the Design and Use of Self-Consolidating Concrete, Chicago, IL, USA, 10–12 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G. Use of GRP industrial by-products in cement based composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 32, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, F.; Moriconi, G.; Pauri, M.G.; Favoni, O. Re-use of GRP industrial waste in new blended cements. In Proceedings of the Atti del VII Congresso Nazionale AIMAT, Associazione Italiana d’Ingegneria dei Materiali, Ancona, Italy, 29 Giugno–2 Luglio 2004; Volume 43. [Google Scholar]
- Osmani, M.; Pappu, A. Utilisation of Glass Reinforced plastic waste in concrete and cement composites. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Coffey, D.; Sanders, M.; Steuerwald, G. System and Method for Recycling Scrap Fiberglass Products in Concrete and Asphalt Construction. U.S. Patent 2004/0132842 A1, 8 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Asthana, G.; Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Experimental Investigation of Waste Glass Powder as Filler in Asphalt Concrete Mixes. In Recent Developments in Waste Management, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Kalamdhad, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 57, pp. 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Beauson, J.; Bech, J.; Brøndsted, P. Composite recycling: Characterizing end of life wind turbine blade material. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Composite Materials, Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 July–2 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, A. Composites can be recycled. Reinf. Plast. 2011, 55, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Farnsworth, M.; Tiwari, A. A review of optimization techniques used in the composite recycling area: State-of-the-art and steps towards a research agenda. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveux, G.; Bailleul, J.L.; La Salle, E.L.G. Chemical recycling of glass fibre reinforced composites using subcritical water. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoli, A.; Moriconi, G. Particle size, size distribution and morphological evaluation of glass fiber reinforced plastic (GRP) industrial by-product. Micron 2014, 67, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailenko, P.; Kakar, M.R.; Piao, Z.; Bueno, M.; Poulikakos, L. Incorporation of recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) fractions in semi-dense asphalt (SDA) pavements: Volumetrics, durability and mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Directorate of Highways. State Highways Technical Specifications (HTS); General Directorate of Highways: Ankara, Turkey, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, F.; Ağar, E. Pavement Structure; Istanbul Technical University Civil Engineering Faculty Press: Istanbul, Turkey, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Nciri, N.; Shin, T.; Lee, H.; Namjun, C. Potential of Waste Oyster Shells as a Novel Biofiller for Hot-Mix Asphalt. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hislop, W.P.; Coree, B.J. VMA as a design parameter in hot mix asphalt. In Mid-Continent Transportation Symposium; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Xue, J.; Mohammad, L. Effects of in-place volumetric properties on field rutting and cracking performance of asphalt pavement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, A.; Mazzotta, F.; Eskandarsefat, S.; Sangiorgi, C.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Dondi, G. Experimental application of waste glass powder filler in recycled dense-graded asphalt mixtures. Road Mater Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melotti, R.; Santagata, E.; Bassani, M.; Salvo, M.; Rizzo, S. A preliminary investigation into the physical and chemical properties of biomass ashes used as aggregate fillers for bituminous mixtures. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, M.; Woszuk, A.; Franus, W. Laboratory Methods for Assessing the Influence of Improper Asphalt Mix Compaction on Its Performance. Materials 2020, 13, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation and design of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures. Mater. Des. 2008, 30, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morova, N. Investigation of usability of basalt fibers in hot mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sieve Diameter | Limit Values | Gradation of Mixture | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (HTS) % Passing [50] | % Passing | |
| 25 mm | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| 19 mm | 80–100 | 91.0 | 103.0 |
| 12.5 mm | 58–80 | 67.5 | 270.9 |
| 9.5 mm | 48–70 | 59.9 | 86.8 |
| 4.75 mm | 30–52 | 42.1 | 205.5 |
| 2.00 mm | 20–40 | 26.0 | 185.3 |
| 0.425 mm | 8–22 | 11.0 | 172.3 |
| 0.180 mm | 6–14 | 7.4 | 41.4 |
| 0.075 mm | 2–7 | 5.0 | 27.3 |
| Filler | 0 | 0 | 57.5 |
| Total | 100% | 100% | 1150 |
| Properties | Results | Tests Standards | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity (g/cm3) | |||
| Coarse aggregate | Apparent specific gravity | 2.771 | ASTM C 127 |
| Bulk specific gravity | 2.729 | ||
| Fine aggregate | Apparent specific gravity | 2.766 | ASTM C 128 |
| Bulk specific gravity | 2.646 | ||
| Filler | Bulk specific gravity | 2.778 | ASTM C 128 |
| Dry rodded unit weight (g/cm3) | 1.914 | ASTM C 29 | |
| Unit weight (bulk density) (g/cm3) | 1.725 | ASTM C 29 | |
| Abrasion loss (%) (Los Angeles) | 26.12 | ASTM C 131 | |
| Flatness index (%) | 14.65 | ASTM D 4791 | |
| Resistance to disintegration by sulfate (weight loss %) | 4.67 | ASTM C 88 | |
| Properties | Results | Test Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Source of the Binder | Kırıkkale, Turkey | - |
| Penetration Grade (25 °C) | 58 (50/70) | ASTM D 5 |
| Softening Point (°C) | 48.5 | ASTM D 36/D 36 M |
| Specific Gravity (g/cm3) | 1.040 | ASTM D 70–09 e 1 |
| Ductility (25 °C) | >100 cm | ASTM D 113–07 |
| Loss on Heating (%) | 0.43 | ASTM D 6–95 |
| Flash Point (°C) | 280 | ASTM D 92–05 a |
| Viscosity (at 135 °C, cP) | 430.23 | ASTM D 4402–06 |
| Viscosity (at 165 °C, cP) | 120.95 | ASTM D 4402–06 |
| Sample Name | Aggregates % | Limestone in Filler (%) | GRP-WP in Filler (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse | Fine | Filler | |||
| Control Sample | 60 | 35 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| PPAC 1 | 60 | 35 | 5 | 3.75 | 1.25 |
| PPAC 2 | 60 | 35 | 5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| PPAC 3 | 60 | 35 | 5 | 1.25 | 3.75 |
| PPAC 4 | 60 | 35 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beycioğlu, A.; Kaya, O.; Yıldırım, Z.B.; Bağrıaçık, B.; Dobiszewska, M.; Morova, N.; Çetin, S. Use of GRP Pipe Waste Powder as a Filler Replacement in Hot-Mix Asphalt. Materials 2020, 13, 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204630
Beycioğlu A, Kaya O, Yıldırım ZB, Bağrıaçık B, Dobiszewska M, Morova N, Çetin S. Use of GRP Pipe Waste Powder as a Filler Replacement in Hot-Mix Asphalt. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204630
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeycioğlu, Ahmet, Orhan Kaya, Zeynel Baran Yıldırım, Baki Bağrıaçık, Magdalena Dobiszewska, Nihat Morova, and Suna Çetin. 2020. "Use of GRP Pipe Waste Powder as a Filler Replacement in Hot-Mix Asphalt" Materials 13, no. 20: 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204630
APA StyleBeycioğlu, A., Kaya, O., Yıldırım, Z. B., Bağrıaçık, B., Dobiszewska, M., Morova, N., & Çetin, S. (2020). Use of GRP Pipe Waste Powder as a Filler Replacement in Hot-Mix Asphalt. Materials, 13(20), 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204630