Simvastatin Induces In Vitro Mineralization Effects of Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. General Function of Statins
1.2. Formation of Dental Hard Tissues
1.3. Pleotropic Effect of Statins
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of the Cytotoxic Concentrations of SV
2.2. Cell Viability (MTT-Assay)
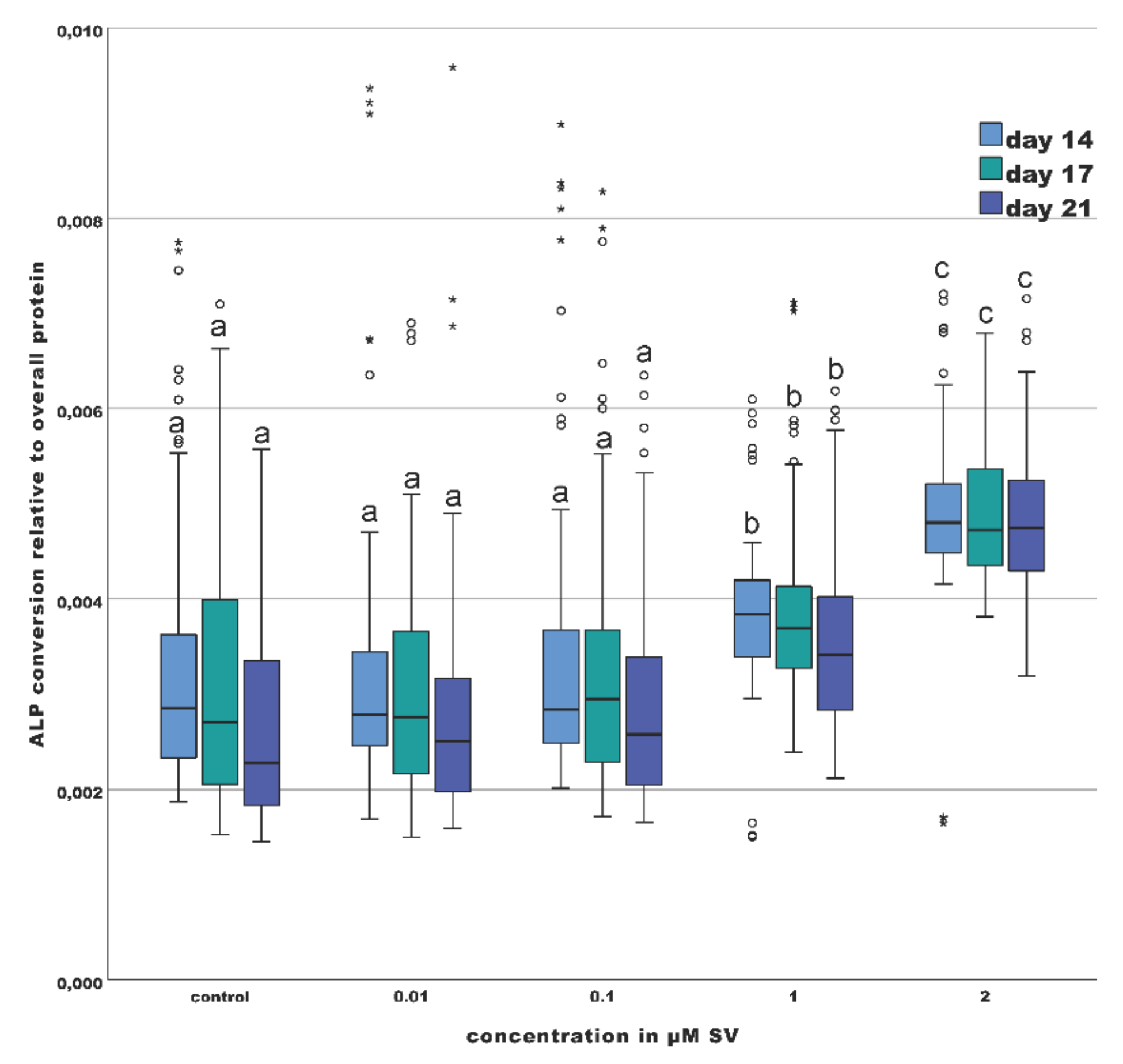
2.3. Osteogenic Marker (ALP-Assay)
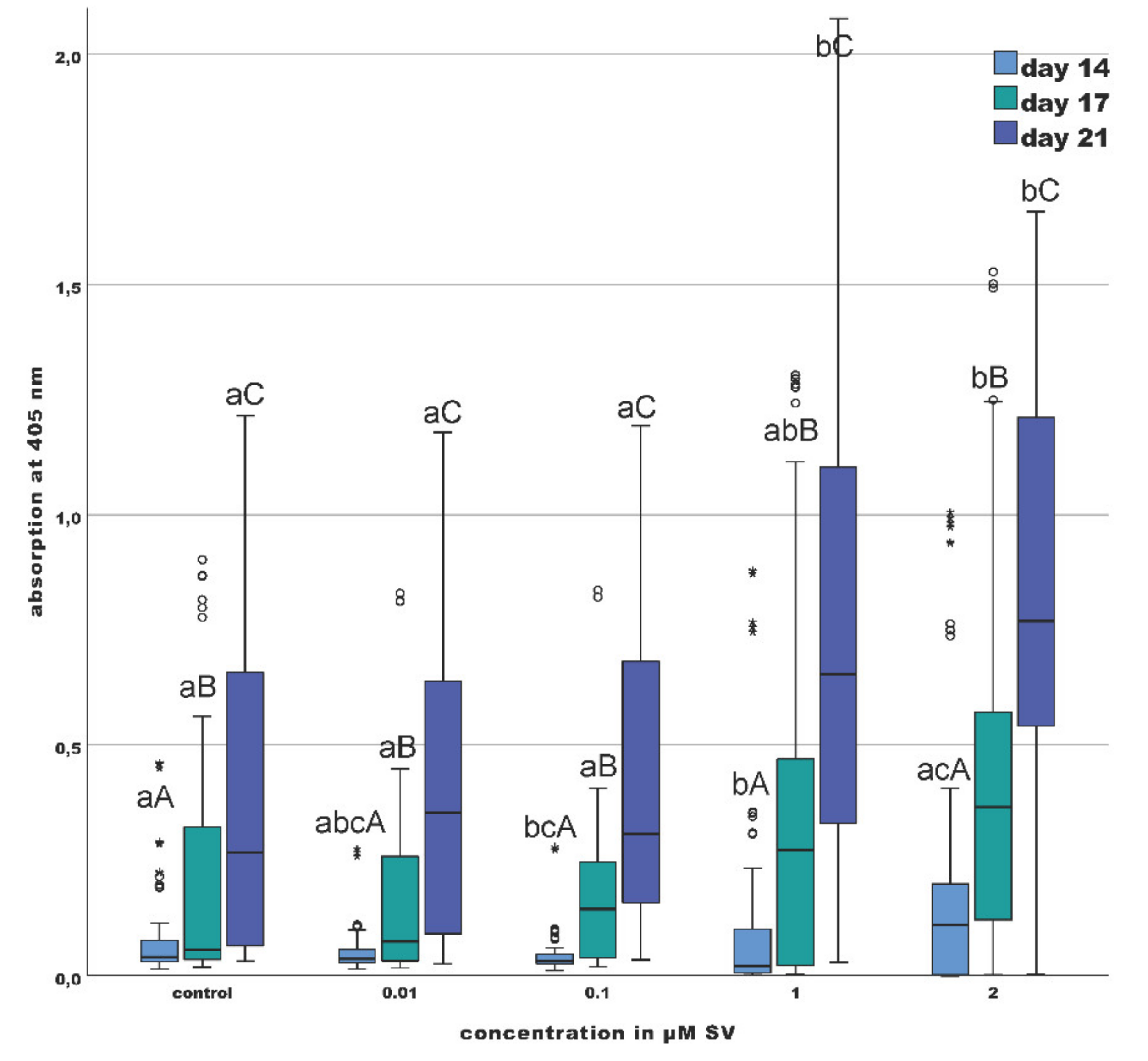
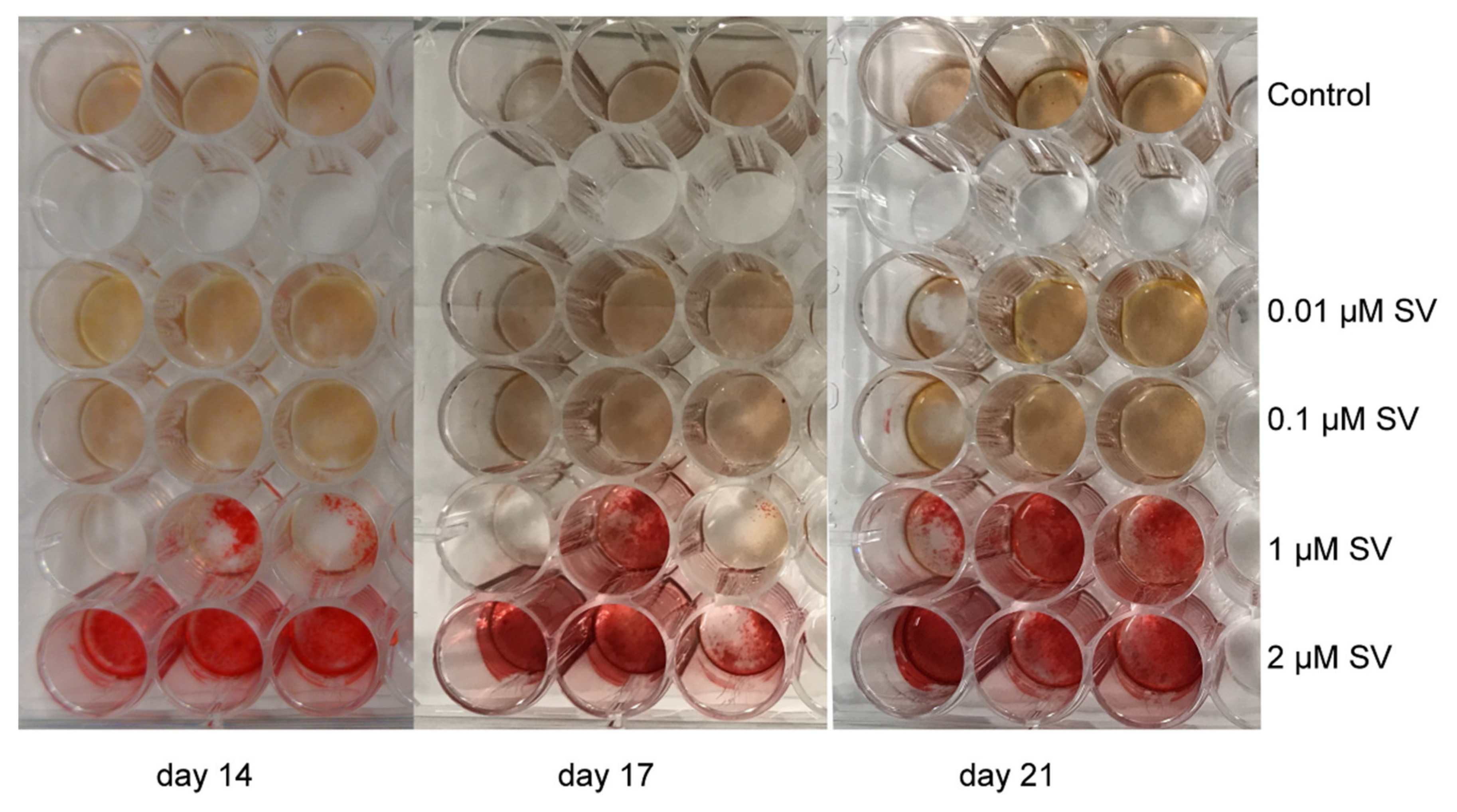
2.4. Mineralization (Alizarin Red S Staining)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approval and Study Design
- tumors in the head and neck area;
- previous systemic administration of statins;
- subjects younger than 18 years;
- possible pregnancy of the subjects.
4.2. Obtaining the Dental Pulp Samples
4.3. Cultivation and Isolation of the Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells
4.4. Characterization of the Primary Odontoblast-Like Cells
4.5. Determination of the Nontoxic Simvastatin Concentration
4.6. Cell Viability (MTT-Assay)
4.7. Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase
4.8. Mineralization Capability
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
References
- Simoons, M.L.; Deckers, J.W. Intensive LDL lowering therapy for prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events: A word of caution: Figure 1. Eur. Hear. J. 2015, 37, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karayan, L.; Qiu, S.; Bétard, C.; Dufour, R.; Roederer, G.; Minnich, A.; Davignon, J.; Genest, J. Response to HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia due to the 10-kb deletion (“French Canadian mutation”) of the LDL receptor gene. Arter. Thromb. A J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirtori, C.R. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najam, O.; Lambert, G.; Ray, K.K. The past, present and future of lipid-lowering therapy. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 10, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Goff, D.C., Jr.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Blum, C.; Schwartz, J.S. 2013 ACC/AHA Cholesterol Guideline Panel: Treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in adults: Synopsis of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2014, 160, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, D.R.; Tobert, J.A. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Adv Protein Chem 2001, 56, 77–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P.J.M.; Aldred, M.; Bloch-Zupan, A. Amelogenesis imperfecta. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, W.T. Dentin Matrix Proteins and Dentinogenesis. Connect. Tissue Res. 1995, 33, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.; Goldberg, M. Dentinogenesis. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1993, 4, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.C.-C.; Chun, Y.-H.P.; Al Hazzazzi, T.; Simmer, J.P. Enamel Formation and Amelogenesis Imperfecta. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 186, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.; Bixler, D.; El-Kafrawy, A. A proposed classification for heritable human dentine defects with a description of a new entity. Arch. Oral Biol. 1973, 18, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabandal, M.M.I.; Schäfer, E. Amelogenesis imperfecta: Review of diagnostic findings and treatment concepts. Odontology 2016, 104, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Simmer, J.P. Hereditary Dentin Defects. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, S.O.; Gaucher, C.; Bardet, C.; Rowe, P.; George, A.; Linglart, A.; Chaussain, C. Tooth dentin defects reflect genetic disorders affecting bone mineralization. Bone 2012, 50, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dechichi, P.; Biffi, J.C.G.; Moura, C.C.G.; De Ameida, A.W. A model of the early mineralization process of mantle dentin. Micron 2007, 38, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevelander, G.; Nakahara, H. The formation and mineralization of dentin. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 1966, 156, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, J.; Gonzales, F.; Sognnaes, R.F. Sclerotic Age Changes in Root Dentin of Human Teeth as Observed by Optical, Electron, and X-Ray Microscopy. J. Dent. Res. 1960, 39, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, B.; Xu, Y.; Ge, W. The role of simvastatin in the osteogenesis of injectable tissue-engineered bone based on human adipose-derived stromal cells and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5325–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Kim, J.E.; Balikov, D.A.; Bae, M.S.; Heo, D.N.; Lee, D.; Rim, H.J.; Lee, D.-W.; Sung, H.-J.; Kwon, I.K. Poly(L-Lactic Acid)/Gelatin Fibrous Scaffold Loaded with Simvastatin/Beta-Cyclodextrin-Modified Hydroxyapatite Inclusion Complex for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2016, 16, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.-C.; Liao, H.-J.; Li, C.-J.; Wang, G.-J.; Chang, J.-K.; Ho, M.-L. Simvastatin enhances human osteoblast proliferation involved in mitochondrial energy generation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 714, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.-X.; Zhou, L. Effects of Simvastatin on osteoblast activity of human periodontal ligament cells. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 27, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Bertl, K.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.-H.; Andrukhov, O.; Rausch-Fan, X. Effect of simvastatin on the osteogenetic behavior of alveolar osteoblasts and periodontal ligament cells. Hum. Cell 2012, 25, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabandal, M.M.I.; Schäfer, E.; Aed, J.; Jung, S.; Kleinheinz, J.; Sielker, S. Simvastatin induces adverse effects on proliferation and mineralization of human primary osteoblasts. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.H.; Lee, W.Y.; Oh, K.W.; Tae, H.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, E.J.; Han, J.H.; Kang, M.-I.; Cha, B.Y.; Lee, K.W.; et al. The Effect of Simvastatin on the Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. J. Korean Med Sci. 2005, 20, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.R.; Werlang, C.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Novel applications of statins for bone regeneration. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 2, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horiuchi, N.; Maeda, T. Statins and bone metabolism. Oral Dis. 2006, 12, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, G.; Garrett, R.; Harris, S.; Chan, J.; Chen, D.; Rossini, G.; Boyce, B.; Zhao, M.; Gutierrez, G. Stimulation of Bone Formation in Vitro and in Rodents by Statins. Science 1999, 286, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, I.; Mundy, G.R. The role of statins as potential targets for bone formation. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanxha, L.; Park, S.-J.; Son, W.-J.; Nör, J.E.; Min, K.-S. Combined Effects of Simvastatin and Enamel Matrix Derivative on Odontoblastic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Min, K.-S.; Choi, G.-W.; Park, J.-H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.-I.; Kim, E.-C. Effects of Simvastain and Enamel Matrix Derivative on Portland Cement with Bismuth Oxide–induced Growth and Odontoblastic Differentiation in Human Dental Pulp Cells. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.-S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Hong, S.-O.; Kim, E.-C. Simvastatin Promotes Odontoblastic Differentiation and Expression of Angiogenic Factors via Heme Oxygenase-1 in Primary Cultured Human Dental Pulp Cells. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Sonoyama, W.; Ono, M.; Akiyama, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Oshima, M.; Tsuchimoto, Y.; Matsuka, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Shi, S.; et al. Simvastatin Induces the Odontogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saewong, S.; Thammasitboon, K.; Wattanaroonwong, N. Simvastatin induces apoptosis and disruption of the actin cytoskeleton in human dental pulp cells and periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Aslaminabadi, N.; Davaran, S.; Shirazi, S.; Ashrafi, F.; Salehi, R. Osteogenic/Odontogenic Bioengineering with co-Administration of Simvastatin and Hydroxyapatite on Poly Caprolactone Based Nanofibrous Scaffold. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, D.G.; Anovazzi, G.; Bordini, E.A.F.; Zuta, U.O.; Leite, M.L.A.S.; Basso, F.G.; Hebling, J.; Costa, C.A.D.S. Biological Analysis of Simvastatin-releasing Chitosan Scaffold as a Cell-free System for Pulp-dentin Regeneration. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varalakshmi, P.R.; Kavitha, M.; Govindan, R.; Narasimhan, S. Effect of Statins with α-Tricalcium Phosphate on Proliferation, Differentiation, and Mineralization of Human Dental Pulp Cells. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijah, V.; Salehi, R.; Aghazadeh, M.; Samiei, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Davaran, S. Towards optimization of odonto/osteogenic bioengineering: In vitro comparison of simvastatin, sodium fluoride, melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2017, 53, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl Aminabadi, N.A.; Maljaei, E.; Erfanparast, L.; Aghbali, A.A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Najafpour, E. Simvastatin versus Calcium Hydroxide Direct Pulp Capping of Human Primary Molars: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2013, 7, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, D.G.; Zhang, Z.; Mohamed, F.; Eyster, T.W.; Costa, C.A.D.S.; Ma, P.X. Simvastatin and nanofibrous poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds to promote the odontogenic potential of dental pulp cells in an inflammatory environment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 68, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magan-Fernandez, A.; Fernández-Barbero, J.E.; O’Valle, F.; Ortiz, R.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Mesa, F. Simvastatin exerts antiproliferative and differentiating effects on MG63 osteoblast-like cells: Morphological and immunocytochemical study. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 53, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Matsunuma, A.; Kurahashi, I.; Yanagawa, T.; Yoshida, H.; Horiuchi, N. Induction of osteoblast differentiation indices by statins in MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granéli, C.; Thorfve, A.; Rüetschi, U.; Brisby, H.; Thomsen, P.; Lindahl, A.; Karlsson, C. Novel markers of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells identified using a quantitative proteomics approach. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 12, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orimo, H. The Mechanism of Mineralization and the Role of Alkaline Phosphatase in Health and Disease. J. Nippon. Med Sch. 2010, 77, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spoto, G.; Fioroni, M.; Rubini, C.; Tripodi, D.; Di Stilio, M.; Piattelli, A. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity in Normal and Inflamed Dental Pulps. J. Endod. 2001, 27, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Sielker, S.; Hanisch, M.R.; Libricht, V.; Schäfer, E.; Dammaschke, T. Cytotoxic effects of four different root canal sealers on human osteoblasts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.-J.; Liu, Y. Simvastatin induces the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 28, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitumori, R.; Fernandes, D.; Jitumori, C.; Favero, G.M. Simvastatin Protects Osteoblasts from the Deleterious Effects of the Liquid Milieu of Multiple Myeloma. West Indian Med J. 2016, 64, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sielker, S.; Jung, S.; Kleinheinz, J. Isolation and cultivation of human mandibular osteoblasts. Available online: https://doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.mtec6je (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- A Gregory, C.; Gunn, W.G.; Peister, A.; Prockop, D.J. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: Comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 329, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primer Forward | Primer Reverse | Product Length | Annealing Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSPP | GTCGCTGTTGTCCAAGAAGA | ATCCTCATCTGCTCCATTCC | 239 bp | 63 °C |
| GAPDH | CTCAGACACCATGGGGAAGG | TCGCTCCTGGAAGATGGTGA | 249 bp | 54 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabandal, M.M.I.; Schäfer, E.; Imper, J.; Jung, S.; Kleinheinz, J.; Sielker, S. Simvastatin Induces In Vitro Mineralization Effects of Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells. Materials 2020, 13, 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204679
Sabandal MMI, Schäfer E, Imper J, Jung S, Kleinheinz J, Sielker S. Simvastatin Induces In Vitro Mineralization Effects of Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204679
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabandal, Martin Mariano Isabelo, Edgar Schäfer, Jessica Imper, Susanne Jung, Johannes Kleinheinz, and Sonja Sielker. 2020. "Simvastatin Induces In Vitro Mineralization Effects of Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells" Materials 13, no. 20: 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204679
APA StyleSabandal, M. M. I., Schäfer, E., Imper, J., Jung, S., Kleinheinz, J., & Sielker, S. (2020). Simvastatin Induces In Vitro Mineralization Effects of Primary Human Odontoblast-Like Cells. Materials, 13(20), 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204679






